DMS算法在Map/Reduce任务调度中的应用
裴树军 孔德凯 苗辉


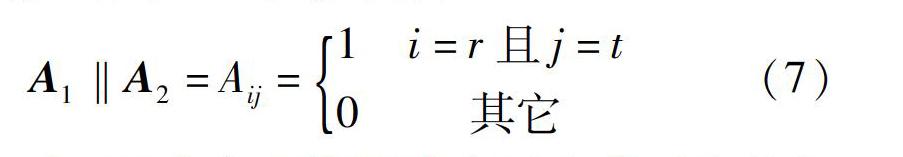
摘要:云环境下传统的任务调度算法整体效率较低,为了提高任务调度的整体效率,在Map/Reduce基础上提出了一种基于处理时间的DMS任务调度算法。首先,对复杂任务进行预处理,将复杂任务转化为DAG图,依据任务依赖关系大小产生最佳拓扑排序,并依据排序结果将复杂任务交给work节点进行处理;其次,通过将节点处理任务的预测时间与节点处理能力的比值作为子任务在每个节点的处理“时间”进行量化建模,建立任务和处理时间的度量矩阵,依据DMS算法进行处理,从而获得任务分配最佳方案;最后,从任务调度效率与资源使用率的角度将DMS算法与公平调度算法、遗传算法行对比验证。实验结果表明,DMS算法能明显提高任务调度整体效率,充分利用各节点的计算能力提高了Map/Reduce的调度效率。
关键词:
云计算;Map/Reduce;任务调度;差值矩阵
DOI:10 15938/j jhust 2019 01 012
中图分类号: TP319
文献标志码: A
文章编号: 1007-2683(2019)01-0071-07
DMS Algorithm in the Application of the Map/Reduce Tasks Schedule
PEI Shu jun,KONG De kai,MIAO Hui
(School of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin 150080, China)
Abstract:The whole efficiency of traditional task scheduling algorithms is low under the cloud environment, In order to improve the whole efficiency of the task scheduling, this article based on Map/Reduce presents a Difference Matrix Scheduling tasks schedule algorithm based on processing time Firstly, pretreatment of complex tasks, the complex tasks is converted to Directed Acyclic Graph figure, the tasks are topological sorted in an optimal manner according to the size of the task dependencies, and the work node is accordance with the sort to processing the complex tasks; Secondly, using the ratio of predictive time that node process tasks to node process capacity as a subtask in each node time quantitative modeling, then establish the task and the metric matrix of process time, according the Difference Matrix Scheduling to processing the matrix, and obtain the optimal scheme of task assignment. Finally, the experiment evaluates the Difference Matrix Scheduling ,fair scheduling algorithm, genetic algorithm in the task scheduling and resource utilization efficiency angles The results show that the algorithm can significantly improve the overall efficiency of complex task scheduling and make full use of the capacity of the compute nodes to improve the Map / Reduce scheduling efficiency
Keywords:cloud computing; map/reduce; tasks assign; difference matrix
0引言
隨着物联网、移动互联网、社会化网络的快速发展,数据来源的渠道逐渐增多,半结构化及非结构化数据呈几何倍增长,从而加速了大数据[1-2]处理技术的快速发展与变革。云计算作为一种新兴的商业计算模式,采用并行的处理方式提高了大数据的处理效率。任务调度[3-5]问题一直是云计算系统关注的核心问题,而影响任务调度效率的因素很多,其中任务调度模型与算法的好坏能够直接影响云计算系统的整体性能。现在很多学者都提出了很多有效的方法:国内的Hadoop[6]技术论坛的总编易剑等学者提出了Map Balance Reduce模型,即在Map节点处理完任务形成中间任务后,使用一个balance的循环过程进行均衡Reduce的输入,这样可以用来解决输入不均衡问题;Abhishek Verma提出了一种LATE调度算法,该算法主要是通过计算待执行和正在执行任务的剩余时间,将执行最慢的任务进行备份从而缩短Map/Reduce作业执行时间;Tang Zhou等提出了MTSD算法,该算法主要考虑数据的本地行与集群异构特点,并且以任务执行截止期限作为依据。依据节点计算能力大小决定数据存储的大小,提高了任务数据本地性。

