Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Texture Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors
Botao Wang, Wenping Fan, Huan Xu, Lihui Li,Xiaohuan Zhang, Kun Wang, Mengqi Liu, ,Junhao You*, Zhiye Chen, *
1Department of Radiology, 2Department of Oncology, Hainan Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Sanya, Hainan 572013, China 3Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China
Key words: breast tumor; texture analysis; magnetic resonance imaging; differential diagnosis
B REAST cancer is a common malignant tumor and the main cause of death for the females. It accounted for up to 7%-10%of the malignant tumors occurred over the whole body of women and presented an increasing tendency in China.[1]Early diagnosis and therapy of breast cancer could improve survival of the patients.Currently imaging methods including mammography,ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)are frequently used to diagnose breast cancer.[2]Although MRI examination could increase detection rate of breast cancer, it had a relatively poor specificity. In this study we expected to improve diagnostic accuracy of breast cancer by using quantitative texture analysis of MRI diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) images.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Patients
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients admitted to the Hainan Hospital of Chinese pLA General Hospital between July 2012 and July 2018,and enrolled 56 patients pathologically diagnosed with massive breast cancer, 16 with fibroadenoma of breast and 4 with intraductal papillary neoplasm of breast after surgery in this study. The exclusion criteria included: (1) The images of DWI had evident artefacts;(2) The MR data were not acquired from the same MR 1.5T scanner. All the patients were females with a mean age of 49.8±9.0 years. The subjects were classified into the benign group (20 patients with a mean age of 43.7±11.3 years ) and the malignant group (56 patients with a mean age of 49.8±9.0 years) based on pathological results. The onset age of the two groups showed comparable (t=2.448, P=0.017).
The Ethics Committee of Chinese pLA General Hospital gave us permission to carry out this study,and this study did not require the informed consents from the enrolled subjects because DWI scans were routinely performed in clinical practice at our institute.
MR imaging
Bilateral breast MRI was performed for all patients in prone position with the breast hanging naturally by using a 1.5T Tesla (T) whole-body MR imaging system (Signa Hdxt, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI,USA). Axial DWI parameters are listed as follows:repetition time (TR) 8750 ms, time echo (TE) 86 ms,matrix 128×128, slice thickness 4 mm, field of view 30 cm×30 cm, and b value=0 and 1000 s/mm2.
Image analysis
Axial images of breast tumor were exported as bmp format from picture Archiving and Communication Systems (pACS), which was imported to ImagJ(1.41v, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/) to calculate Angular Second Moment (ASM), Contrast, Correlation,Inverse Difference Moment (IDM) and Entropy using Gray-level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) method with its plugin. Texture parameters were evaluated with the size of the step in pixels 1 and the direction of the step 0 degree.
Regions of interest (ROIs) were defined as large as possible on the solid part of tumors, avoiding the area with necrosis and cystic changes. To improve accuracy of the measurement, ROI was placed for 3 times on the same image by the same neuroradiologist, and the mean value of three replicates for the indicated texture parameter was regarded as the final value.
Statistical analysis
The texture feature data following normal distribution were presented as mean ± SD and analyzed with independent t test for intergroup comparison. Data with non-normal distribution were expressed as median(quantile range) and intergroup comparison was performed with Mann-Whitney U test. If the texture parameters showing significant differences between the malignant group and the benign group, Logistic regression analysis was applied to establish Regression model using backwards method. The variables that would be enrolled in the logistic regression equation were determined by Wald χ2value, and diagnostic point was computed based on false positive rate obtained according to the preoperative MRI diagnosis and pathological diagnosis.[3-4]Receiver operating characteristic (ROC)curve was drawn with 1-specificity as horizontal coordinate and sensitivity as vertical coordinate, and the point with maximal sum of specificity plus sensitivity was regarded as the optimal diagnostic point. The area under ROC curve (AUC) was calculated to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency.
Statistically significant difference was set at a P value less than 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using the SpSS Statistics Software Version 22.0 (SpSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
Comparisons of texture features between the benign and malignant groups
As illustrated in Table 1, the texture parameters ASM (P=0.014, U=352.500), Contrast (P=0.019,t=2.405), Correlation (P=0.010, U=275.000) and Entropy (P=0.007, t=2.761) between the benign and malignant groups showed significant differences,however IDM showed no significant difference between the two groups (P=0.305, U=473.000). ROC analysis demonstrated that the AUC was 0.685,0.681, 0.754 and 0.683, and the optimal diagnostic point was 0.0075, 908.7935, 0.0004 and 4.9345 for ASM, Contrast, Correlation and Entropy, respectively(Table 2).
Results of Lo gistic regression analysis of texture features
Binary Logistic regression analysis was performed with texture parameters ASM, Contrast, Correlation and Entropy which were regarded as independent variables,and then a regression equation was obtained as following: P=1/1+e-(-12.137+58.453×ASM+0.003×Contrast+1.980×Entropy).The diagnostic point was 0.819 according to the false positive rate (21.4%) based on the current clinical data with sensitivity 0.607 and specificity 0.800, which could be explained as follows: (1) If P>0.819, the case should be diagnosed with malignant breast tumor; (2)If P<0.819, the case should be diagnosed with benign breast tumor. The equation was applied to the present group data, and the predictive accuracy for differentiation of benign and malignant breast tumors was 79.5%. Further ROC analysis demonstrated that AUC was 0.802 for the combined variables enrolled in the regression equation (Table 3, Figure 1).
DISCUSSION
DWI has been a commonly used MR sequence to differentiate benign from malignant breast tumors based on visual assessment and post-processed apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value. Compared with DWI, texture analysis is time-saving, because ADCsare calculated based on signal intensity of pixels using 2 b-value images (b=0 s/mm2and 1000 s/mm2), however texture parameters of DWI are measured on the images acquired with a b value of 1000 s/mm2. Up to now, reports on texture analysis of DWI that enables differential diagnosis of breast tumors were rare. In this study we performed GLCM texture analysis on raw DWI images, aiming to verify whether texture analysis could differentiate benign from malignant breast tumors.
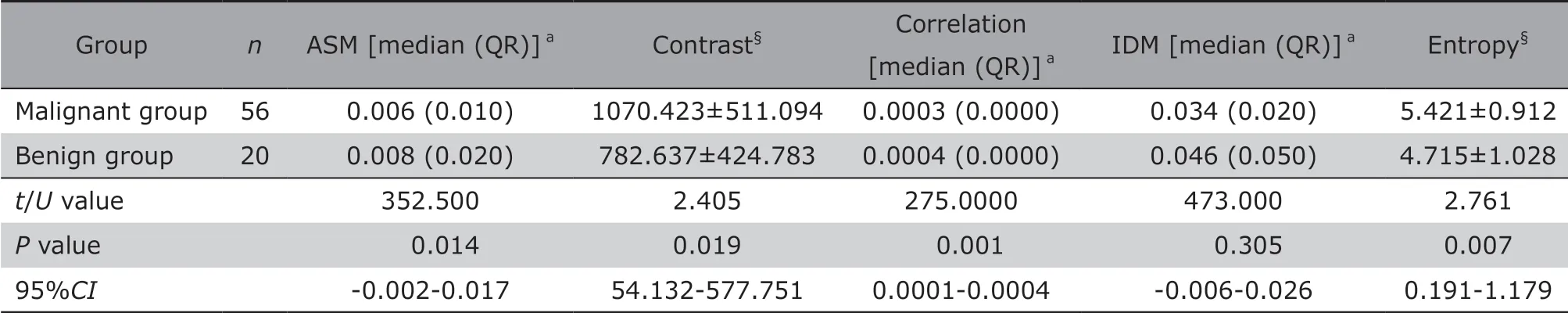
Table 1. Comparisons of texture parameters of DWI between the two groups
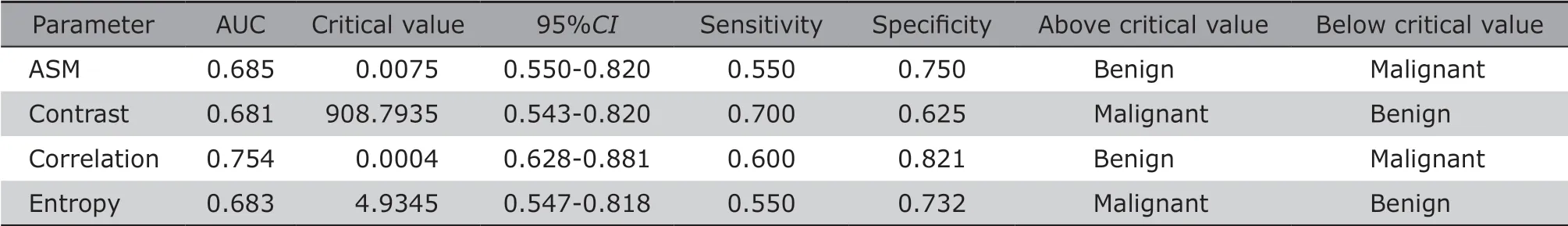
Table 2. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for the positive texture variables in the Logistic regression model between the breast benign and malignant tumor groups
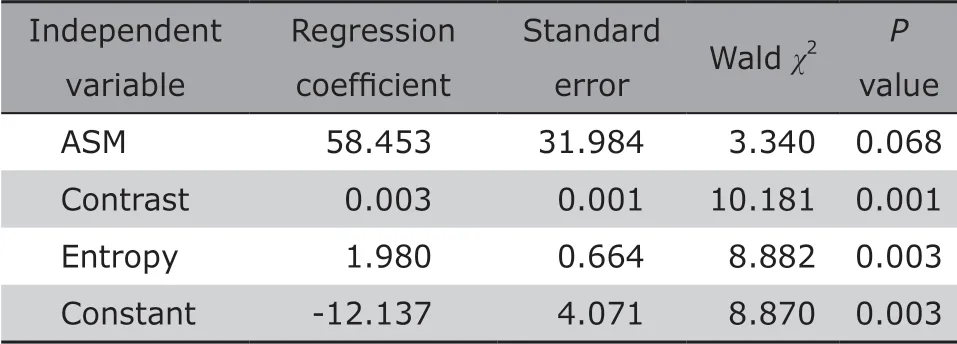
Table 3. Binary Logistic regression coefficients, standard error and P value of texture parameters
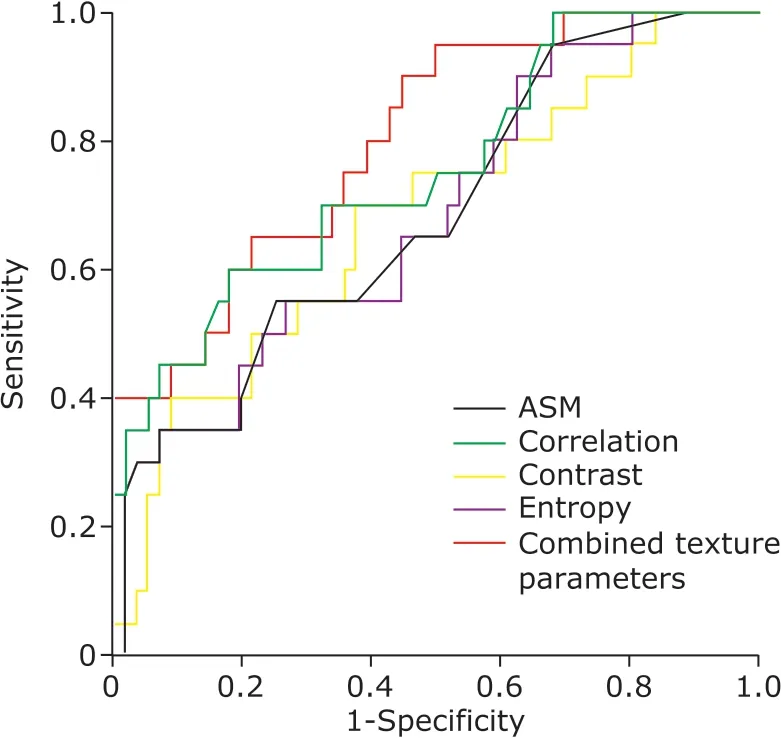
Figure 1. ROC curve of texture parameters of logistic regression model for breast benign and malignant tumors.
In this study, we extracted 5 frequently used texture features to differentiate benign from malignant breast tumors. When extracting GLCM texture features, we used the default settings (size=1 pixel and direction=0 degree) because texture values measured with GLCM method are insensitive to moving window size and direction.[5]
The results revealed that texture parameters ASM,Contrast, Correlation and Entropy of DWI images presented significant differences between the benign and malignant breast tumors. ASM and Correlation showed significant decrease of the malignant breast tumors compared with the benign breast tumors. ASM reflects homogeneity, the value of which is quite high when the image has perfect homogeneity or when pixel intensity is very similar.[6]In the present study, the malignant group presented a lower ASM value compared with the benign group, which indicated that malignant breast tumors might have heterogeneous tumor parenchyma.[7]
Texture Correlation reflects linear dependency of grey levels of neighboring pixels,[6]and higher values can be obtained for similar gray-level regions.[8]Texture Correlation have been used to differentiate benign from malignant breast tumors for ultrasound images. In the present study[8-11]texture Correlation of DWI image was used to distinguish benign from malignant breast tumors. The result indicated that malignant breast tumor lacked similar gray-level regions,which might be consistent with lower ASM value.Therefore, the decreased texture ASM and Correlation showed optimal performance in distinguishing malignant breast tumors from benign breast ones.
The texture Contrast reflects amount of gray-level variation of an image, and a high Contrast value indicates the presence of noise or wrinkled texture in an image.[12]The increased texture Contrast of malignant breast tumors suggested that the higher noises or winkled textures were identified in the malignant breast tumor lesions, which may be associated with the local heterogeneous intensity.
The texture Entropy represents amount of information needed for image compression. The higher texture Entropy represents the more loss of image information or message.[13]In this study, the malignant breast tumors had higher texture Entropy value compared with the benign breast ones, which suggested that the malignant breast tumors lost more image information or message, thereby indicating increased complexity presented in the malignant breast tumors.
Although texture ASM, Contrast, Correlation and Entropy had a relative classifying efficacy for the breast tumors, single texture parameter showed the lower diagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, we wondered if multiple texture parameters analysis would improve diagnostic accuracy and obtain the best differential efficacy. Binary logistic regression analysis revealed that ASM combined with Contrast and Entropy which were enrolled in the regression equation attained the better diagnostic sensitivity and specificity(0.607 and 0.800 respectively) at the diagnostic point.
Furthermore, ROC analysis was used to evaluate diagnostic efficacy of single texture parameter and the combined texture parameters enrolled in the regression equation in differentiating the benign from malignant breast tumors. AUC of the combined texture parameters was 0.802, which was larger than that of signal texture parameter (0.681-0.754). Therefore,logistic regression model achieved the best diagnostic efficacy in classifying the benign and malignant tumors than signal texture parameter analysis did.
The regression equation was applied to differentiate the benign from malignant breast tumors, and the results showed the final predictive accuracy rate was 79.5% for 76 cases, which demonstrated the relatively higher accuracy of the logistic regression equation. Although the texture analysis had a relatively lower accuracy rate for diagnosis, its AUC of the three combined texture features was relative larger (0.802)and reached the good level of diagnostic efficiency,[14]therefore which could be used to differentiate the benign from malignant breast tumors.
The limitations of this study are: (1) The study only included three types of massive breast tumors; (2) The sample size was relatively small for benign breast tumors; (3) Only DWI images were used for texture analysis and other MR images should be enrolled in the future.
In summary, this study demonstrated that texture ASM, Contrast and Entropy derived from DWI images enrolled in the logistic regression equation could differ benign from malignant breast tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年1期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2019年1期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Value of Texture Analysis of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Parameters in Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Differential Diagnostic Value of Texture Feature Analysis of Magnetic Resonance T2 Weighted Imaging between Glioblastoma and Primary Central Neural System Lymphoma
- MRI Histogram Texture Feature Analysis of the Optic Nerve in the Patients with Optic Neuritis
- Value of Texture Analysis on Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR for Detecting Liver Fibrosis in a Rat Model
- Prediction of Hidden Blood Loss During Posterior Spinal Surgery
- Bilateral Peripheral Facial Paralysis Combined with HIV Meningitis During Acute HIV-1 Infection: A Case Report
