钉齿式残膜捡拾机构运动仿真分析及性能试验
史增录,唐学鹏,甄 军,鄢金山,张学军,靳 伟
钉齿式残膜捡拾机构运动仿真分析及性能试验
史增录1,唐学鹏1,甄 军2,鄢金山1,张学军1※,靳 伟1
(1. 新疆农业大学机电工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830052; 2. 新疆农业大学交通与物流工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830052)
由于钉齿式残膜捡拾机构是被动式的动力驱动,且钉齿的运动受滚筒等多个动参考系的影响,造成钉齿运动过程的理论计算难度大、分析依据不足等问题。通过开展钉齿式残膜捡拾机构工作原理和动力学的分析,应用ADAMS完成运动学分析,获得钉齿相对地面的运动轨迹、齿尖的位移、速度变化曲线,完成样机的试制和田间试验。通过分析,钉齿式残膜捡拾机以5km/h的速度作业时,滚筒转速为50.04 r/min,大于滚筒的临界转速44.61 r/min,且钉齿相对地面的轨迹为余摆线;钉齿入土时合速度的方向与垂直方向夹角为18.1°,出土时合速度的方向和垂直方向基本重合,有利于钉齿的扎入土壤及顺利挑膜,满足设计要求;相邻钉齿齿尖上的标记点MARKER_76和MARKER_77在入土、出土时捡拾区长分别为51.44和50.08 mm,同水平位置相邻余摆线间的距离为59.4 mm,大于最大捡拾区长51.44 mm。田间试验表明,钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的拾净率达71.7%,缠膜率为1.52%,满足耕层残膜捡拾作业的性能要求。该研究可为优化作业参数、研发相关装备提供参考。
机械化;计算机仿真;优化;钉齿;耕层残膜;动力学
0 引 言
地膜覆盖种植技术因其显著的土壤增温、保湿、维持土壤结构、防止害虫侵袭的作用,已在蔬菜、瓜果、棉花、花生、玉米等作物种植上广泛应用[1-2]。中国使用的地膜是聚乙烯烃类有机高分子化合物,在自然条件下极难降解,在土壤中可存在200~400 a。地膜使用后由于日照风化而容易破碎,耕整地作业后,大量残膜和作物根茬、土壤混合在一起被埋在耕层中,加大了残膜回收的难度。经过多年的耕作,积累在耕层的残膜不断增加,可造成土壤品质下降、作物减产[3-6],也给农业生态环境造成严重的“白色污染”。因此,治理农田残膜污染已成为亟待解决的难题,治理耕层残膜污染问题更是迫在眉睫。
按工作原理分类,残膜回收机械可分为弹齿式、钉齿式、夹持式、链齿式、伸缩杆齿式等[6-9]。但能够回收耕层内残膜的机具较少,目前研究耕层残膜回收机械的主要有张学军团队研发的链齿式耕层残膜回收机,可回收150~200 mm深的耕层残膜[10-11],该机具的作业阻力和动力消耗较大;张攀峰等研究的旋耕钉齿式的耕层残膜回收机,可回收耕层150 mm深度的残膜[12-13],但钉齿上易堆积残膜,卸膜效果不理想;靳伟等研究了自动卸膜式残膜回收机,其作业深度为80 mm[14],未达到耕层残膜回收的作业深度。
钉齿式残膜捡拾机构是为解决新疆南疆地区使用的扎膜辊捡拾和卸膜切换操作不方便的问题而研发的,适用于春播前、耕整后土壤松软、土块较小的农田条件。通过凸轮机构实现边扎膜、边卸膜的作业过程,能够捡拾耕层深度为100 mm的残膜。钉齿是残膜捡拾机的重要作业部件,其性能优劣决定了捡拾机的作业可靠性、捡拾率等关键指标。钉齿式残膜捡拾机的动力驱动是拖拉机的牵引力,依靠钉齿扎入土壤的反作用力驱动滚筒转动,钉齿的运动不仅受滚筒的约束,还要受推杆、卸膜板等动参考物的影响,增加了理论分析的难度。
以理论研究的方法进行钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的钉齿运动轨迹、速度等的理论计算难度大、实际测量的可操作性差,限制了钉齿捡拾残膜过程的理论分析及结构参数优化[15-17]。为此,利用虚拟仿真技术进行钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的仿真,在滚子和凸轮之间添加接触约束,模拟真实的运动过程,开展钉齿式捡拾机构的运动过程分析,是研究被动驱动式残膜捡拾机构的有效方法。
1 钉齿式残膜捡拾机的工作原理及结构
1.1 主要结构
为提高钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的捡拾率,增加钉齿的数量,以增加钉齿扎膜的次数是关键。研制的钉齿式残膜捡拾机构滚筒直径为530 mm,钉齿轴向排布距离为75 mm,圆周间的排布距离为120 mm。钉齿式残膜捡拾机的结构如图1所示。

1.悬挂机构 2.钉齿 3.卸膜板 4.推杆 5.滚筒 6.端盖 7.凸轮 8.刷膜辊 9.机架 10.集膜箱
1.2 工作原理
钉齿式残膜捡拾机的机构简图如图2所示。滚筒和端盖固定。钉齿一端与滚筒铰接,钉齿穿在卸膜板上,卸膜板可绕钉齿转动,作业时滚筒在土壤对钉齿的反作用下逆时针转动。卸膜板两端和推杆铰接,推杆的一端和端盖上的铰接杆连接,推杆的中间孔和卸膜板铰接,另一端安装滚子轴承,滚子轴承安装在凸轮滑槽内转动,凸轮与机架固定。滚子轴承沿着凸轮轨迹带动推杆运动,运动到最低点时,推杆拉回卸膜板,钉齿伸出卸膜板的长度最长。滚子轴承运动至最高点时,推杆向上推动卸膜板,卸膜板相对钉齿向外运动,同时在液压马达的作用下,刷膜辊顺时针反向转动将残膜梳刷到集膜箱中,完成边扎膜边卸膜的作业过程。

1.滚筒 2.卸膜板 3.钉齿 4.端盖 5.铰接杆 6.推杆 7.滚子轴承 8.凸轮
1.Roller 2.Unloaded plate 3.Nail tooth 4.End cap 5.Hinge bar 6.Handspike 7. Roller bearing 8.Cam
注:为滚筒的转动角速度,rad·s-1;为机具的前进速度,m·s-1。
Note:is angular velocity of roller, rad·s-1;is forward speed of machinery, m·s-1.
图2 钉齿式残膜捡拾机的机构简图
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue
2 残膜捡拾机构分析
2.1 凸轮的设计分析
凸轮是驱动捡拾机构的钉齿伸出、缩回的关键部件。凸轮轮廓线设计如图3所示,建立坐标系,在反转运动中,当推杆相对于凸轮转过时,推杆处于111位置,则1点的坐标如式(1)所示,式(1)是凸轮的理论轮廓线坐标。

注:δ为反转运动时凸轮的转角,rad;α为推杆在A1C1位置时的角位移,rad;β为推杆的位置角,rad;a为推杆距回转中心的长度,mm;L为推杆A1C1的长度,mm;θ为理论轮廓线法线和水平线的夹角,rad;r0为理论轮廓线的最小半径,mm;rr为滚子的半径,mm。

凸轮的理论轮廓线和工作轮廓线在法向方向的距离应等于滚子半径r,因此在理论轮廓线上任意一点上,只要沿理论轮廓线在该点的法线方向取长度为r,即可得工作轮廓线上的相应点,由此可得1的工作轮廓线方程,如式(2)所示。

为确保安装在推杆上的滚子轴承和凸轮保持接触,设计了沟槽式凸轮结构,如图4所示。

图4 凸轮结构示意图
2.2 卸膜过程的分析
残膜捡拾机构作业过程中,在凸轮作用下钉齿相对卸膜板伸出时钉齿入土捡拾扎膜,等钉齿运动到刷膜辊位置时,在凸轮作业下钉齿相对卸膜板缩回,在卸膜板和刷膜辊共同作用下,残膜被卸入集膜箱,实现残膜捡拾机构在入土时捡拾残膜,在卸膜位置时自动卸膜。卸膜过程如图5所示。

注:ω1为刷膜辊的转动角速度,rad·s-1。
刷膜辊能顺利将残膜从钉齿上卸下的条件为,刷膜辊叶片的速度大于钉齿齿尖的速度,如式(3)所示。

式中为滚筒中心到钉齿齿尖的长度,mm;为刷膜辊直径,mm。
刷膜辊的转动角速度1为

经计算,刷膜辊的转速应不低于225 r/min。考虑刷膜过程中卸膜的阻力较小,选用BM1-160的液压马达,其连续运转时的转速达370 r/min。
2.3 捡拾机构的运动分析
钉齿式残膜捡拾机构作业时,钉齿的运动是由机具的前进运动、滚筒的转动、推杆限制钉齿摆动和卸膜板相对钉齿的移动,形成的合成运动。残膜捡拾机构的运动简图如图6所示。进行钉齿运动的理论计算时,需建立以滚筒为中心的坐标系为定参考系,同时建立钉齿绕滚筒摆动的动参考系、推杆相对滚筒摆动的动参考系以及卸膜板相对滚筒的动参考系。若计算钉齿上某一动点的运动,需利用坐标变换的原理建立绝对、相对和牵连运动之间的关系,不仅分析过程复杂,且计算难度也大[18-23]。

图6 残膜捡拾机构的运动简图
2.4 捡拾机构的动力学分析
钉齿式残膜捡拾机构作业时,残膜被钉齿挑起时受力情况如图7所示。
捡拾机构的实际受力不仅包括残膜的重力、钉齿对残膜的摩擦力以及运动时离心惯性力,还有土壤、根茬对残膜的粘压力和风的阻力等。但钉齿式残膜捡拾机构是回收100 mm耕层内的陈年旧膜,残膜的强度很低,决定钉齿是否能克服土壤、根茬对残膜粘压力的关键,是残膜的强度能否承受钉齿对残膜的作用力,且土壤、根茬对残膜的粘压力和风的阻力是随机力,力的大小、方向无法确定。因此,在捡拾机构的动力学分析中未将土壤、根茬对残膜的粘压力和风的阻力考虑到受力分析中。
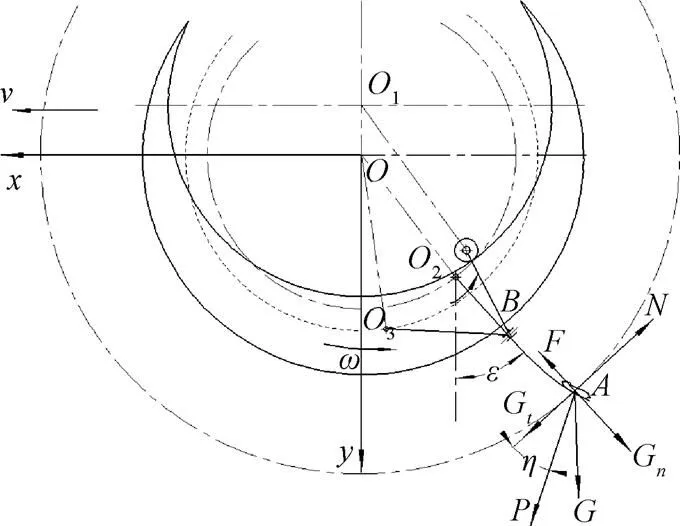
注:ε为钉齿与垂直线的夹角,rad;η为离心惯性力和法向力方向的夹角,rad;P为离心惯性力,N;N为残膜法向力,N;G为残膜的重力,N;F为摩擦力,N;Gt为残膜重力的切向力,N;Gn为残膜重力的法向力,N。
根据图4可知,钉齿对残膜作用的法向力为




式中为残膜的质量,g;为被捡残膜重心的瞬时半径,m;为重力加速度,m/s2。
为使残膜能够被钉齿挑起的必要条件为

式中为钉齿和残膜的摩擦系数。
式(9)简化可得

经计算,得≥4.67 rad/s,对应的滚筒转速为44.61 rad/s,该值是钉齿能够顺利挑起残膜的临界角速度。当小于4.67 rad/s时,钉齿捡拾的残膜可能会沿钉齿滑落,降低捡拾残膜的作用。由于钉齿式残膜捡拾机构是被动驱动的方式,依靠钉齿扎入土壤所受的作用力和卸膜板所受土壤的摩擦力带动滚筒转动。因此,作业速度的大小影响滚筒转动的角速度的大小,也决定着捡拾机构的残膜捡拾性能。为保证捡拾机构的捡拾性能,将残膜捡拾机构被动驱动的方式变为主动驱动的方式,可提高钉齿捡拾残膜的可靠性。
3 仿真分析
3.1 建模、添加约束和驱动
用Solidworks软件建立钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的三维参数化模型,并完成装配。将三维模型另存为Parasolid(.X_T)格式。将Parasolid(.X_T)格式文件导入到ADAMS软件中,生成ADAMS环境下的模型[24-25]。
利用ADAMS中的工具箱操作,在大地、机架、钉齿、推杆、凸轮、拐臂、滚筒之间添加适当的约束。为准确的模拟残膜捡拾机构在工作中的实际运动情况,对其各部件均按实际情况添加部件的材料属性。为提高仿真计算的速度,只保留了相邻的2个钉齿,删掉其他的钉齿、摆杆、刷膜辊、集膜箱等部件。
钉齿式残膜捡拾机构以5 km/h的速度作业时,滚筒转速为50.04 r/min。经计算,添加在机架上的平移驱动速度为1 388.89 mm/s,作用在滚筒上的旋转驱动的角速度值为300.45 °/s。
3.2 求解计算
进行ADAMS的求解计算时,设置仿真的时间为1.8 s、步长为300步。
3.3 仿真研究
为方便分析钉齿齿尖运动,在相邻钉齿的齿尖上分别创建了MARKER_76和MARKER_77 2个标记点。仿真结束后,从后处理器输出一系列仿真结果。图8是相邻钉齿齿尖的运动变化曲线,其中图8a是钉齿齿尖相对地面的运动轨迹曲线,图8b是钉齿齿尖在垂直方向的位移变化曲线,图8c是钉齿齿尖在水平方向的位移变化曲线,图9是相邻钉齿齿尖的速度的变化曲线。
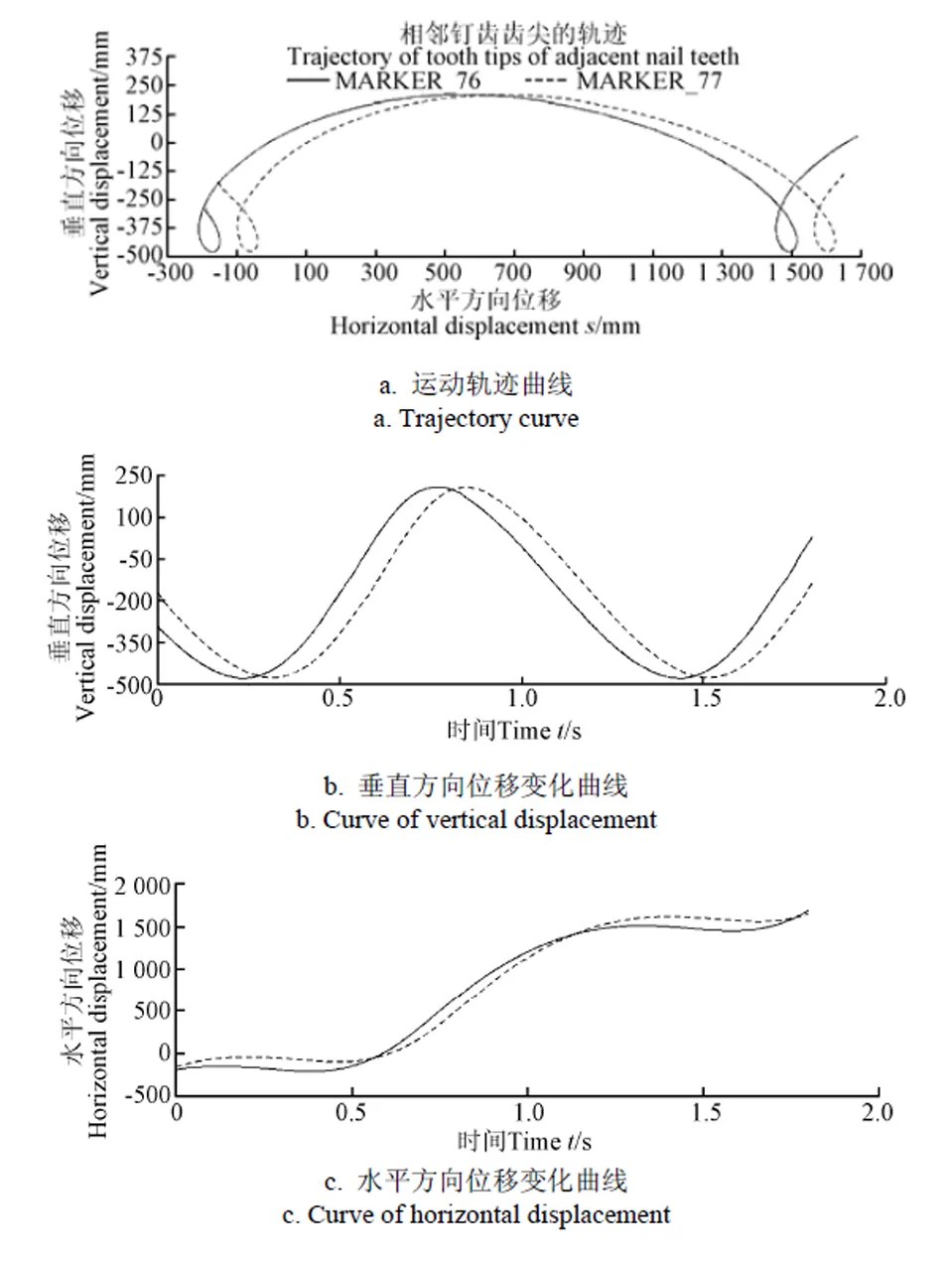
图8 相邻钉齿齿尖的位移变化曲线

图9 相邻钉齿齿尖的速度变化曲线
根据图8a所示钉齿齿尖的运动轨迹线,结合残膜捡拾机构的作业深度,确定从钉齿齿尖最低点的位移向上100 mm为捡拾区,当捡拾滚筒运动1.8 s时,钉齿齿尖的标记点MARKER_76和MARKER_77分别2次入土和出土。为确保钉齿入土、出土的数据准确性,去掉第一次入土、出土的数据,以MARKER_76和MARKER_77第二次入土、出土的数据为依据,进行分析。
图9所示的MARKER_76和MARKER_77的速度变化曲线存在一定幅度的波动。通过对残膜捡拾机构的运动原理和施加约束等的分析,主要原因是推杆一端和滚筒端盖铰接,推杆另一端和凸轮用接触命令进行约束,推杆在凸轮的轨道内运动时,在上、下轨道面的切换过程中存在一定的冲击力,造成了钉齿速度变化的波动。
在ADAMS/Postprocessor中利用轨迹点跟踪功能,完成图8a所示曲线数据的采集[24]。通过对钉齿齿尖的运动轨迹分析,以钉齿入土100 mm为理论耕层深度,确定MARKER_76和MARKER_77分别在入土、出土时的垂直方向位移。结合图8b所示的曲线变化,确定MARKER_76和MARKER_77分别在入土、出土时对应的时间。根据图9所示,获得MARKER_76和MARKER_77在入土、出土时的水平方向速度和垂直方向速度;根据图8c所示的钉齿齿尖水平方向位移的变化曲线,取得入土和出土时的水平位移,通过计算可获得单个钉齿的作业捡拾区长度,具体数据如表1所示。
3.4 结果分析
通过仿真分析,钉齿运动时齿尖相对地面的轨迹是余摆线,依靠余摆线从最低点向上100 mm的区域为残膜捡拾区域。图8a所示的钉齿轨迹线满足设计的预期要求,可完成设计的捡拾动作。
根据钉齿相对地面的轨迹线,利用图解法完成钉齿入土和出土时的速度分析图,如图10所示。MARKER_76的入土合速度为1 103.69 mm/s,出土合速度为1 254.10 mm/s;MARKER_77入土合速度为1 081.03 mm/s,出土合速度为1 249.89 mm/s。钉齿入土合速度方向和垂直方向的夹角为18.1°,出土的合速度和垂直方向基本重合。
根据图8c所示的钉齿在水平方向位移变化曲线,钉齿在100 mm深的耕层作业时,MARKER_76在入土、出土的捡拾区长为51.44 mm;MARKER_77入土、出土的捡拾区长为50.08 mm;结合图8a所示,在MARKER_76 和MARKER_77的余摆线从下往上100 mm深耕层位置,相邻两余摆线间的距离为59.4 mm,大于钉齿的最大捡拾区长51.44 mm。

表1 相邻钉齿齿尖的运动参数 Table 1 Motion parameter of tooth tips of adjacent nail teeth

图10 相邻钉齿齿尖入土、出土速度分析
4 田间性能试验
为了验证所设计样机的作业性能指标,试制了整机物理样机。2017年4月,在新疆阿克苏6团试验田进行了田间耕层残膜捡拾机构的作业性能试验[26-31],如图11所示。试验田选择耕后(播前)较平坦的棉花地,配套铁牛754型拖拉机为动力,作业速度为5 km/h,捡拾滚筒的转度为50 r/min。

图11 钉齿式残膜捡拾机的田间试验
残膜捡拾机构作业性能试验时,作业前在测区内进行作业前的测点采样,测点采样采用五点法,每个测点面积为1 m2,按耕层深度为100 mm取样。去除尘土和水分后,称取样残膜的质量,求其平均值获得作业前耕层残膜质量;作业后在同一测区不同的测点位置进行作业后的测点采样,按照同样的方法获得作业后耕层残膜质量。按式(11)计算耕层的拾净率。

式中为拾净率,%;为作业后的耕层残膜质量,g;0为作业前耕层残膜质量,g。
残膜捡拾机构的缠膜率计算根据式(12)计算。

式中为缠膜率,%;1为测区内缠绕在残膜机上的残膜质量,g;2为测区内收集在集膜箱内的残膜质量,g。
按照标准GB/T 25412-2010《残地膜回收机》的试验要求,进行残膜捡拾作业试验指标的测定,田间测试结果如表2所示。

表2 残膜捡拾机构作业性能 Table 2 Performance of mechanism for collecting plastic residue
5 结 论
1)通过对捡拾机构的分析,钉齿可挑起残膜的滚筒临界转速为44.61 r/min。为保证钉齿能将残膜顺利挑起,则滚筒的转速不能低于44.61 r/min。
2)通过ADAMS软件对残膜捡拾机构作业过程的仿真,相邻钉齿入土合速度分别为1 103.69和1 081.03 mm/s,合速度的方向与垂直方向的夹角为18.1º,作业时钉齿入土的阻力较小;相邻钉齿的出土合速度分别为1 254.10和1 249.89 mm/s,合速度方向基本和垂直方向平行,钉齿可顺利将残膜挑起。由此可见,采用凸轮机构实现钉齿式残膜捡拾机构边扎膜、边卸膜的原理是可行的。
3)仿真结果表明,钉齿在100 mm深的耕层作业时,相邻钉齿齿尖上的标记点MARKER_76和MARKER_77在入土、出土时的捡拾区长分别为51.44和50.08 mm,以余摆线最低点向上100 mm的位置,MARKER_76和MARKER_77的余摆线间的距离为59.4 mm,大于钉齿的最大捡拾区长51.44 mm。通过增大钉齿式残膜捡拾机构的钉齿捡拾区长度,减少相邻两余摆线间的距离,可提高耕层拾净率。
4)通过分析、仿真和田间试验研究发现,钉齿式残膜捡拾机构通过改变被动驱动方式为主动驱动方式及优化相邻钉齿余摆线间的距离,可进一步提高该机构的残膜拾净率。
[1] 陈勤平,吴昌湛,陈国泽,等. 不同覆盖物对春花生生长及产量的影响[J]. 广西农学报,2013,28(2):28-30.
Chen Qinping, Wu Changzhan, Chen Guoze, et al. The effect of the different overlay on growth and yield of spring peanut[J]. Journal of Guangxi Agriculture, 2013, 28(2): 28-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 谢建华,陈学庚,孙超伟. 杆齿式残膜回收机卸膜过程分析及高速摄像试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(10):17-24.
Xie Jianhua, Chen Xuegeng, Sun Chaowei. Unloading film process analysis and high-speed photography experiment of pole-tooth residual plastic film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(10): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 严昌荣,梅旭荣,何文清,等. 农用地膜残留污染的现状与防治[J]. 农业工程学报,2006,22(11):269-272.
Yan Changrong, Mei Xurong, He Wenqing, et al. Present situation of residue pollution of mulching plastic film and controlling measures[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2006, 22(11): 269-272. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 何文清,严昌荣,刘爽,等. 典型棉区地膜应用及污染现状的研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2009,28(8):1618-1622.
He Wenqing, Yan Changrong, Liu Shuang, et al. The use of plastic mulch film in typical cotton planting regions and the associated environmental pollution[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 2009, 28(8): 1618-1622. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王海敏. 全降解聚乙烯地膜的制备与性能研究[D]. 青岛:山东科技大学,2011.
Wang Haimin. Preparation and Performance Study of the Full-degradable Polythene Films[D]. Qingdao:Shangdong University of Science and Technology, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 严伟,胡志超,吴努,等. 铲筛式残膜回收机输膜机构参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(1):17-24.
Yan Wei, Hu Zhichao, Wu Nu, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment for plastic film transport mechanism of shovel screen type plastic film residue collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(1): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 周新星,胡志超,严伟,等. 国内残膜回收机脱膜装置的研究现状[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(11):263-268.
Zhou Xinxing,Hu Zhichao,Yan Wei,et al. Research status of domestic residual film recovery machine to take off the film device[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(11): 263-268. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 徐弘博,胡志超,吴峰,等.网链式花生地残膜回收机设计与试验[J] .农业工程学报,2017,33(17):1-9.
Xu Hongbo, Hu Zhichao, Wu Feng, et al. Design and experiment of network chain type residual plastic film collector for peanut field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(17): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 段文献,王吉奎,李阳,等. 夹指链式残膜回收装置的设计及试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(19):35-42.
Duan Wenxian, Wang Jikui, Li Yang, et al. Design and test of clamping finger-chain type device for recycling agricultural plastic film[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(19): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 赵攸乐,张学军,靳伟,等. 链齿耙式耕层残膜回收机捡拾机构的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2019,41(2):119-123.
Zhao Youle, Zhang Xuejun, Jin Wei, et al. Design of Pick-up mechanism for the chain-teeth-rake topsoil incomplete plastic film recycling machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(2): 119-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李辰,白圣贺,靳伟. 链齿式耕层残膜回收机捡拾机构设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2019,41(4):107-111.
Li Chen, Bai Shenghe, Jin Wei. Design and experiment on picking mechanism of chain tooth type plough residue film reclaiming machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(4): 107-111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张攀峰,胡灿,王旭峰,等. 旋耕钉齿式耕层残膜回收机起膜部件动力学分析[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(4):14-19.
Zhang Panfeng, Hu Can, Wang Xufeng, et al. Kinetic analysis of rotary tillage nail Tooth plastic film recycling machine hook film unit[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(4): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 张攀峰. 旋耕钉齿式耕层残膜回收机的设计与试验研究[D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学,2018.
Zhang Panfeng. Design and Test Research of Rotary Tillage Nail Tooth Plastic Film Recycling Machine[D]. Alar: Tarim University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 靳伟,张学军,张朝书,等. 自动卸膜式残膜回收机捡拾齿和滚筒的优化[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2016,18(3):96-103.
Jin Wei, Zhagn Xuejun, Zhang Chaoshu, et al. Optimization of pick-up teeth and roller for automatic unloading film recycling machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2016, 18(3): 96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李斌,王吉奎,胡凯,等. 残膜回收机顺向脱膜机理分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(21):23-28.
Li Bin, Wang Jikui, Hu Kai, et al. Analysis and test offorward film removing mechanism for polythene film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(21): 23-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陈发,史建新,王学农,等. 弧型齿残膜捡拾滚筒捡膜的机理[J]. 农业机械学报,2006,37(6):36-41.
Chen Fa, Shi Jianxin, Wang Xuenong, et al. Study on collecting principle of arc-type tooth roller for collecting plastic residue[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(6): 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈发,史建新,赵海军,等. 固定凸轮残膜捡拾机构的优化设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(12):43-46.
Chen Fa, Shi Jianxin, Zhao Haijun, et al. Optimum design of fixing cam combination mechanism for collecting plastic residue[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(12): 43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Han, C J, Yuan P P, Zhang X J, et al. Design and test of combined operation machine for collecting nail-tooth plastic film. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 2017, 26(1): 87-94.
[19] 王春耀,陈发,王学农,等. 弧形挑膜齿残膜清理滚筒主要部件的强度分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2007,38(2):76-78.
Wang Chunyao, Cheng Fa, Wang Xuenong, et al. Analytical research on intensity of the arc spring-finger type plastic film residue pickup cylinder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(2): 76-78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 那明君,董欣,侯书林,等. 残膜回收机主要工作部件的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1999,15(2):112-115.
Na Mingjun, Dong Xin, Hou Shulin, et al. Research on main components of the machine for retrieving the used plastic film after harvesting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1999, 15(2): 112-115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 娄秀华,张东兴,耿端阳,等. 残膜回收机起膜器的设计与试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2002,18(6):88-90.
Lou Xiuhua, Zhang Dongxing, Gen Duanyang, et al. Research and design on loosening shovel of polythene film collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2002, 18(6): 88-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 严伟,胡志超,吴努,等. 铲筛式残膜回收机输膜机构参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(1):17-24.
Yan Wei, Hu Zhichao, Wu Nu, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment for plastic film transport mechanism of shovel screen type plastic film residue collector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(1): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 李宝筏. 农业机械学[M]. 北京:农业出版社,2003.
[24] 赵武云,史增录,戴飞,等. ADAMS2013基础与应用实例教程[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2015:251-265.
[25] 史增录,张学军,赵武云,等. 4UX-550型马铃薯挖掘机振动筛运动特性分析及仿真研究[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2013,48(3):156-160.
Shi Zenglu, Zhang Xuejun, Zhao Wuyun,et al. Analysis of kinetic characteristics and simulation of vibrating sieve of 4UX-550 potato harvester[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2013, 48(3): 156-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 25412—2010残地膜回收[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2010.
[27] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 1227-2006残地膜回收机作业质量[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2016.
[28] 靳伟,张学军,李超新,等. 钉刺式残膜回收机的设计及试验研究[J]. 中国农机化学报,2014,35(4):52-54.
Jin Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Li Chaoxin, et al. Design and experiment of stud type residual film recycling machine[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2014, 35(4): 52-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 戴飞,赵武云,张锋伟,等. 玉米全膜双垄沟残膜回收机作业性能优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(18):50-60.
Dai Fei, Zhao Wuyun, Zhang Fengwei, et al. Optimization and experiment of operating performance of collector for corn whole plastic film mulching on double ridges[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(18): 50-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 靳伟,张学军,张朝书,等. 钉刺式残膜回收机凸轮机构的设计与分析[J]. 农机化研究,2014,36(12):140-143.
Jin Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Zhang Chaoshu, et al. Analysis and design of CAM mechanism in stud type residual film recycling machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(12): 140-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 王海新. 钉齿式残膜捡拾机的优化及试验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2016.
Wang Haixin. Optimization and Experimental Study of Nail Tooth Plastic Film Residue Collector[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Performance test and motion simulation analysis of nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue
Shi Zenglu1, Tang Xuepeng1, Zhen Jun2, Yan Jinshan1, Zhang Xuejun1※, Jin Wei1
(1.,,830052,; 2.,,830052,)
The problem of residual film pollution is serious in the fields of Xinjiang,and the mechanical recycling of residual film is the main recycling method.However, few mechanism can be used to recover the plastic residue of the plough layer. The nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue can recover the plastic residue from the plough layer. Nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue is composed of roller, unloaded plate, nail tooth, end cap, handspike and cam, etc. When the mechanism for collecting plastic residue is operated, the nail tooth pick-up and tie the plastic residue when the nail tooth reach the position of film-brushing roller relative to the film-removing plate, the nail tooth retract relative to the film-removing plate under the cam operation, and the film-removing plate when the nail tooth reach the position of film-removing roller under the cam operation. Under the joint action of the plastic residue brushing roller, the plastic residue is unloaded into the film collecting box, to realize the function of side pick up and unloading. Through the virtual simulation technology, the trajectory of the nail tooth and the speed of the nail tooth are obtained. The nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue is a passive driving method, in which the cam, handspike, unloading plate and the nail tooth interact and the nail tooth is driven by the force of the nail tooth penetrating into the soil. The constraint between roller bearing and cam cannot simply be given a point-line constraint pair, but according to the actual situation, the contact constraint between roller and cam is added, which can better simulate the real motion. For nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue is passive power drive, and nail tooth movement is influenced by roller, and other moving reference frame, the nail tooth movement process of the theoretical calculation is difficult, lack of theoretical basis to carry out the nail tooth type mechanism collecting plastic residue working principle and dynamics analysis. By use of ADAMS, we completed kinematics analysis, and obtained the nail tooth relative to the movement of the ground, and the tooth curves of displacement and velocity. We also completed the prototype trial-manufacture and field experiment. Through analysis, When the nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue operates at a speed of 5 km/h, the rotational speed of the drum is 50.04 r/min, greater than the critical speed of roller 44.61 r/min, and nail tooth relative to the ground track for trochoid, nail tooth into the soil when the resultant velocity direction and vertical direction Angle was 18.1°. The out-earth combined speed paralleled the vertical direction, which is advantageous to the nail tooth into the soil and the smoothly picked plastic residue, meeting the design requirements. Marking points MARKER_76 and MARKER_77 on the tips of adjacent nail teeth were respectively 51.44 and 50.08 mm in length of collecting area when they were put into soil and excavated. The distance between adjacent cycloid lines at the same horizontal position was 59.4 mm, greater than the maximum picking area of 51.44 mm. Field experiments showed that the net collected rat of the deep layer of nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue was 71.7% and the wrapping rate was 1.52%, which can meet the performance requirements of the tillage residual film scavenging operation. The analysis results provide references for optimizing operation parameters and developing related equipment.
mechanization; computer simulation; optimization; nail tooth; plastic residue of plough layer; dynamics
史增录,唐学鹏,甄 军,鄢金山,张学军,靳 伟. 钉齿式残膜捡拾机构运动仿真分析及性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(4):64-71. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.04.008 http://www.tcsae.org
Shi Zenglu, Tang Xuepeng, Zhen Jun, Yan Jinshan, Zhang Xuejun, Jin Wei. Performance test and motion simulation analysis of nail tooth type mechanism for collecting plastic residue[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(4): 64-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.04.008 http://www.tcsae.org
2018-08-07
2019-01-27
获国家重点研发计划课题(2017YFD0701102);国家自然基金项目(51665057);新疆维吾尔自治区高校科研计划(XJEDU2017T005)
史增录,实验师,主要从事农业工程技术与装备研究。 Email:shizlfd@qq.com
张学军,教授,博士,主要从事农业工程技术与装备研究。Email:zhaxjau@sina.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.04.008
S224.9
A
1002-6819(2019)-04-0064-08

