SD大鼠与FH/Wjd大鼠神经行为学差异比较
熊庭旺,贺 希,魏胜焦,刘 波,吴 芹,石京山
(遵义医学院 基础药理教育部重点实验室暨特色民族药教育部国际合作联合实验室,贵州 遵义 563099)
Depression,a common mental disorder,seriously affects the life and work of the patient and imposes a great burden on the patient's family and society.Depressed people frequently feel sad,anxious,hopeless,worthless,and so on.Furthermore,they may lose interest in physical activities,have a loss of appetite or overeating,insomnia or excessive sleeping,loss of energy,digestive problems and have problems of concentrating,and may contemplate or attempt suicide.Population affected by depression is gradually expanding,and depressive symptoms become a growing public health concern.According to the World Health Organization,depression is the second contributor to the global burden of disease by 2020.However,the symptoms of depression are hard to be produced in laboratory animals.Ideal animal models of depression are needed for identifying novel therapies for depression,and are of great significance.At present,animal models of depression can be divided into four categories:physical factor depression model,drug-induced stress model,olfactory bulbectomy model and transgenic model.Physical factor-induced depression models include chronic unpredictable mild stress model,learned helplessness model,early life stress model,and social contact defeat model.Drug-induced stress model including glucocorticoid repeated injection induced depression model,reserpine reversal model,and apomorphine induced model[1].However,no single model can adequately simulate all the pathological characteristics and show all symptoms of depression.Therefore,this study was designed to investigate whether FH/Wjd rats meet some of the criteria for animal models of depression.
Fawn-Hooded (FH/Wjd) rats were obtained from Wistar rats inbreeding for 19 generations through selective breeding technology.Moreover,FH/Wjd rats have the characteristics of high alcohol preference and obvious alcohol deprivation symptoms,which can be considered as an innate animal model of alcoholism[2].The abnormal of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) function is one of the pathogenesis of alcohol abuse,and the 5-HT system is also hypo-functional in FH/Wjd rats.The immobility of the FH/Wjd rats is more obvious in the forced swimming test,and this behavioral despair can be reversed by chronic treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors[2-3].In addition,FH/Wjd rats have elevated cortisol levels and exhibited blunted hormonal responses to serotonergic challenges the same as the depression individuals.Recent studies have found that the levels of 5-HT,glutamic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in serum and urine of FH/Wjd rats are significantly different from those of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats.Meanwhile,FH/Wjd rats have a feature of chronic visceral hypersensitivity,and some inherent depression characteristics[4-5].All of these studies suggested FH/Wjd rats meet some criteria for animal model of depression,so it maybe an inherent depression rat model,which can be used for depression studies[6-9].However,depression is a very complex disorder disease and is associated with a variety of behavioral and physiological abnormalities.FH/Wjd rats did not meet other important criteria for animal models of depression such as anhedonia,appetite/weight decrease and psychomotor retardation[6].Therefore,whether FH/Wjd rats can be regard as a genetic animal model of depression-like behavior is still controversial.
SD rats and FH/Wjd rats are both bred from Wistar rats[2,10],they have the same ancestral source.The nervous system of SD rats is similar to that of human beings,so SD rats are widely used in the research of higher nervous activity such as reward and punishment experiments,maze experiments,neurosis and neurodevelopmental arrest field[11].Our previous research has confirmed that the alcoholism difference between SD rats and FH/Wjd rats,and verified the alcohol drinking characteristics of FH/Wjd rats[12].However,whether FH/Wjd rats meet the performance of depression,such as cognitive disorder and sleep disorder have not been reported as yet[4].Therefore,this study used the age and sex-matched SD rats as controls to illustrate whether FH/Wjd rats meet some criteria of depression model in neurobehavioral experiments.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Animals Two-month old,male specific pathogen free grade (SPF) SD rats were purchased from the animal experimental center of Daping Hospital of Third Military Medical University (Chongqing,China).The certificate number is SCXK 2017-0005.FH/Wjd rats were presented by Professor Jianhui Liang of Peking University.They were bred in the SPF grade animal laboratory of the Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology of Ministry of Education,Zunyi Medical University.Animal experiment procedures follow the Animal Care and Use Guidelines in China and were approved by Animal Use and Care Committee of Zunyi Medical University.
1.2 Instruments Morris water maze,Y-maze and TopScan 3.0 behavior analysis system (Beijing Ji-An Dell Science and Technology Company),ZH-300 rat fatigue type rotarod instrument (Anhui ZhengHua biological instrument and equipment Technology company).
1.3 Morris water maze test Morris water maze experiments were carried out when SD rats and FH/Wjd rats aged 3,6 and 9 months,respectively.The experiment consists of two parts:directional navigation and space exploration experiments.The directional navigation experiment is to fix the platform in one quadrant.Rats were put into the pool from other quadrants except the platform with the head up and facing the basin wall,trained 3 times a day for 4 consecutive days.The time when the rats found the platform was recorded as the escape latency.If they can’t find it in 120s,the escape latency was record as 120s,then,letting the rats stay on the platform for 30s.The space exploration experiment was carried out on the 5th day.The platform was removed,and rats were put into pool at any quadrant except the quadrant of the original platform,the number,distance and duration time the rats in the original platform quadrant within 120s were recorded.
1.4 Y-maze test The Y-maze test was carried out when the FH/Wjd rats and SD rats were 3,6 and 9 months old.The Y-maze is composed of a central area and three similar closed arms with an angle of 120 degrees.Rats were put into the maze from the end of either arm keeping their heads up,freely exploring and moving for 10 min.Recording the moving speed,the total number of entering in closed arms (N).The rat successively entering three different arms was regard as one correct alternating reaction.Spontaneous alternation rate (%) =[correct number of alternate reactions / (N-2)]× 100.
1.5 Rotarod Male SD rats and FH/Wjd rats at different ages of 3,6 and 9 month-old were used for fatigue rotary rod test.At the beginning of the experiment,the rats were put on the rotary rod for climbing training daily for 2 days,and the formal tests were carried out on the 3rd day.The system started rotating at the speed of 10 rpm/min,and followed by an increase of 5 rpm/min.The time at which the rats fall off the rod is recorded.

2 Results
2.1 The learning and memory ability of SD and FH/Wjd rats At 3 months old,there was no obvious difference in escape latency between SD rats and FH/Wjd rats.With the increase of training,the escape latency of SD rats and FH/Wjd rats gradually shortened (Fig 1A).The percentage of target quadrant duration time,entries,distance of FH/Wjd rats was lower than that of SD rats (Figure 1B,C,D).At 6 month old,the escape latency of FH/Wjd rats was significantly longer than that of SD rats,and the difference was significant (P<0.05) on the second day in directional navigation experiment.The percentages of target quadrant duration time,entries and moving distance (P<0.05) were significantly lower than those of the SD rats.At 9 months old,the escape latency of FH/Wjd rats was longer than that of SD rats.The percentage of target quadrant time,entries and moving distance were both lower than those of SD rats,without statistical significance.The results suggest that the spatial learning and memory ability of FH/Wjd rats were lower than those age-and sex-matched SD rats.Besides,with the age increasing,the FH/Wjd rat’s learning and memory ability presented more obvious downtrend than SD rats.
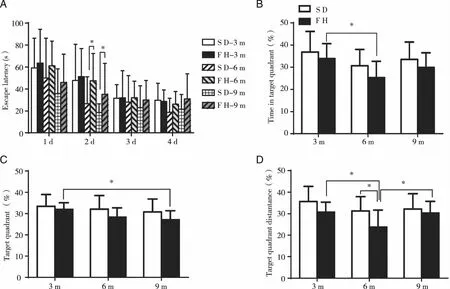
A:Directional navigation experiment; B,C,D:Space exploration 0.05; d:day; m:month.Fig 1 The results of SD rats and FH/Wjd rats in Morris water maze test at the age of 3,6 and 9 months
2.2 The spatial working memory and self-activity ability of SD and FH/Wjd rats The spatial working memory of FH/Wjd rats at 3 and 9 months old was lower than that of SD rats (Fig 2A).At the ages of 3,6,and 9 months,the total arm entries of FH/Wjd rats were more than that of SD rats (42.07%,52.26%,143.37%,Fig 2B),and the moving speed of FH/Wjd rats both were significantly faster than that of the same month old SD rats (28.86%,68.89%,108.65%,Fig 2C).However,the movement speed of SD rats in the Y-maze gradually decreased with the increase of the age (P<0.05).
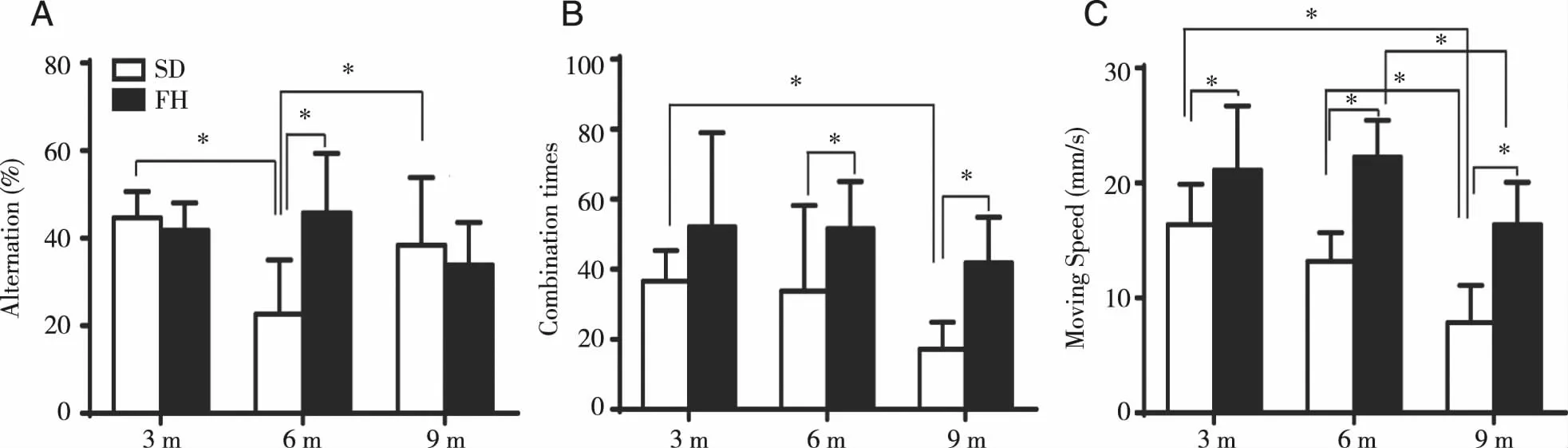
Fig 2 The results of SD rats and FH/Wjd rats in Y-maze test at the age of 3,6 and 9 months
2.3 The fatigue endurance ability of SD and FH/Wjd rats Respectively compared with 3,6 and 9 month old SD rats,the duration times of FH/Wjd rats on the rotary rod were shorter than that of the age-matched SD rats (29.10%,40.42%,20.03%,P<0.05,Fig 3),indicating that FH/Wjd rats had lower fatigue endurance and motor coordination ability than that of SD rats.Moreover,the fatigue endurance ability of SD rats and FH/Wjd rats gradually decreased with the increase of age.
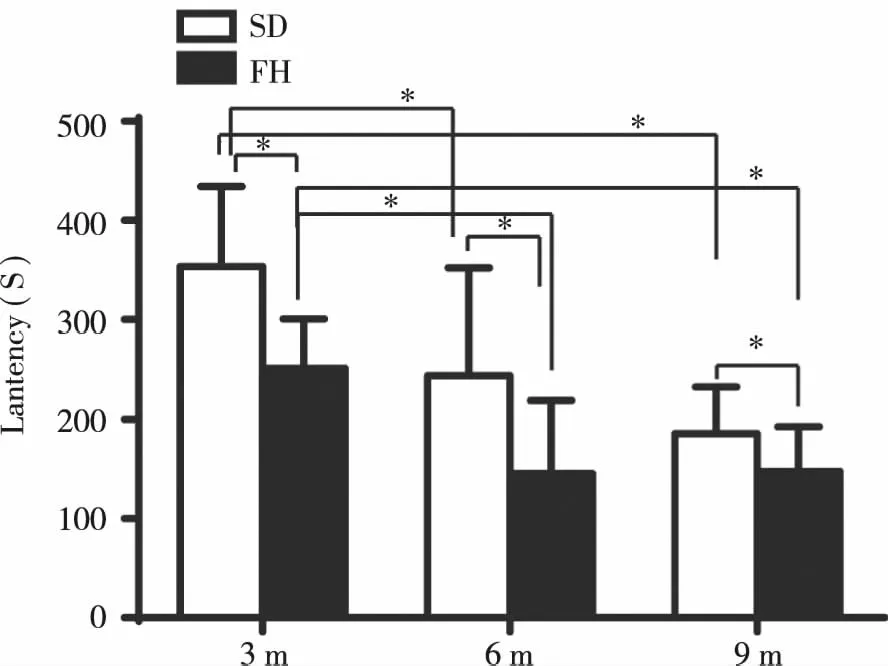
Fig 3 The result of SD rats and FH/Wjd rats in rotarod test at the age of 3,6 and 9 months
3 Discussion
Depression and alcoholism often co-occur in human beings,both are related to abnormal release of central neurotransmitters such as γ-aminobutyric acid,glutamic acid,dopamine,in which abnormal 5-HT is the common pathogenesis of alcoholism and depression[13].Therefore,alcoholism is closely related to depression.FH/Wjd rats are an ideal animal model of inherent alcoholism[10].The drinking behavior differences between SD rats and FH/Wjd rats have been studied in the early stage by our group[12].Therefore,the purpose of this study is to further investigate the behavioral neurological differences between FH/Wjd rats and SD rats from the aspects of cognitive impairment,spontaneous activity and fatigue endurance,and to further explore whether FH/Wjd rats meet some criteria of depression model.
The core symptom of depression is the persistent depression,and it is also accompanied with many common mental symptoms,such as learning and memory deficit that is one of the main mental symptoms associated with depression[14].In this study,Morris water maze and Y-maze were used to evaluate the learning and memory ability of FH/Wjd rats at different months of age.Due to repeated entry into the same maze environment for many times,the escape latency of the 6-and 9-month-old rats was shorter than that of 3 month-old rats[15].Kong Lin-lin and others reported that swimming training and climbing on the rod could improve synaptic plasticity,the expression of related mRNA in hippocampus,and improve the learning and memory ability[14].Even so,the learning and memory ability of FH/Wjd rats are not as good as the age- and sex-matched SD rats.Therefore,FH/Wjd rats meet some criteria for animal models of depression.
The Y-maze can evaluate the spatial learning and memory ability through spontaneous activities and the ability to choose independently without specific training[16],and the numbers of entering in all arms reflect the rats’ spontaneous activities[17].It was reported that the movement distance,probe and standing times of FH/Wjd rats are significantly higher than those of SD rats in the hole-board test[8].The open arms entries,time in open arms and spontaneous activities in the elevated plus-maze are higher than those of SD rats[18-19].FH/Wjd rats performed hyperactive in novel maze environment and had the same results with this study.Spontaneous activities reflect the animal's voluntary movement ability and the degree of central excitability.When the central nervous system is excited,spontaneous activities increase,and vice versa[20].Therefore,it is suggested that FH/Wjd rats have higher activity than SD rats when entering a new environment,and suggested FH/Wjd rats could meet the criteria of depression for central nervous excitability.
Depression and fatigue exist at the same time.Depressive patients often have symptoms of fatigue[21].In this study,the fatigue endurance and coordination ability of 3,6 and 9 month-old SD rats and FH/Wjd rats were detected by the rotary rod instrument.During the experiment,it was observed that the FH/Wjd rats had lower climb movement coordination ability and tolerance ability than SD rats,and the latency on rotary rod was shorter than that of SD rats.Therefore,FH/Wjd rats may have fatigue disorder and movement coordination disorder compared with SD rats.In short,this study reported that innate alcoholism FH/Wjd rats have lower spatial learning ability and fatigue endurance than age- and sex-matched SD rats,which conforms to a few manifestations of depressive animal models.Furthermore,it was shown that FH/Wjd rats have significantly higher self-activity and exploration ability than SD rats at different ages.It provides some basic experimental evidence for the application of FH/Wjd rats in the field of neuroscience research.

