Ultrasound-guided supine lumbar plexus block versus iliac fascia block for analgesia in older adult patients undergoing hip replacement:a randomized controlled trial
Xiao-Long Lu ,Xue-Feng YuSi-Mao HuXue-Lei ZhengQiong LiYong LiuPan-Ru WangJian-Min PengBin Mei
1 Department of Anesthesiology,Lu’an Civily Hospital,Lu’an,Anhui Province,China
2 Department of Anesthesiology,First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University,Hefei,Anhui Province,China
Abstract
Key words:ultrasound guidance; lumbar plexus block; iliac fascia block; hip replacement; anesthesia; Visual Analog Scale score; sufentanil;perdipine; ephedrine; adverse reaction; randomized controlled trial
INTRODUCTION
Background
Hip fracture is a common and traumatic event that occurs particularly in older adults,and hip replacement is the common surgical treatment.1-4Improper anesthesia and perioperative management in older adult patients with hip fracture greatly increase postoperative complications and mortality.5-8Proper anesthesia can improve prognosis and reduce postoperative complications.9-10With the development of ultrasound techniques in anesthesia,ultrasound-guided nerve block has been increasingly used when replacing hips in older adult patients.There are a variety of nerve block methods.11-12There are few reports in China regarding lumbar plexus block versus iliac fascia block for hip replacement.This study is designed to compare the anesthetic effects of lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block during hip replacement surgery in older adult patients,as well as the effect on perioperative hemodynamic change.
The lumbar plexus is primarily composed of the femoral nerve,obturator nerve,and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.It dominates the lateral,anterior,and medial thigh sensations,but its position is deep.The effect of the conventional method is not clear.Ultrasound can visualize nerve position,local anesthetic diffusion,and the condition of surrounding organs.13Thus,ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block makes most of the nerves innervating the hips unable to send pain-related signals to the brain,which greatly reduces the intraoperative sensation of pain and avoids complications such as piercing the blood vessels and puncturing the peritoneum.14
Lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block,as means of inducing analgesia or in assisting general anesthesia are common nerve block methods.The preferred methods(i.e.,better efficacy)of nerve block for postoperative analgesia include iliac fascia block,femoral nerve block,lumber plexus block,and combinations of these techniques.The purpose of lumbar plexus and iliac fascia blocks is to block the femoral nerve,obturator nerve,and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.The iliac fascia block is a fascia block.Ultrasound cannot display clear neuroacoustic shadows,which often leads to an imperfect iliac fascia-block effect.Iliac fascia block often fails to block the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve and the obturator.Multi-angle multi-point iliac fascia block has been shown to have a more rapid onset and a higher success rate than single-point iliac fascia block.15While most previous studies have compared multi-point block and single-point block from different perspectives,few have compared lumbar plexus and iliac fascia block techniques.This is a novelty of the current study; to compare multi-point iliac fascia block and supine lumbar plexus block from different perspectives.
The first author(XLL)performed an online search of PubMed database for papers published from January 2014 through August 2018 using the search terms “anesthesia”,“hip replacement”,and “ultrasound”.The three most recent studies16-18regarding the analgesic effect of different nerve block methods in older adult patients undergoing hip replacement were screened(Table 1).
Study objective
Based on a previous small-sample-size pilot study,this trial will compare the local analgesic effect of ultrasound-guided supine lumbar plexus block with that of iliac fascia block in older adult patients undergoing hip replacement.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Study population and recruitment
This prospective,single-center,randomized,controlled trial will include older adult patients scheduled to undergo hip replacement in Lu'an Civily Hospital of China.Recruitment will beviaadvertising lea flets providing details of the trial that will be distributed among patients in the hospital wards.Patients interested in participating will contact the principal investigatorviatelephone.They will be included according to eligibility criteria and after providing written informed consent.

Table 1:Three representative studies regarding the anesthetic effect of ultrasound-guided nerve block methods in older adult patients undergoing hip replacement
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria
-Patients with hip fracture scheduled to undergo hip replacement
-Patients with traumatic hip diseases such as Garden type-IV femoral neck fracture
-Age between 65 and 85 years; either sex
-An American Society of Anesthesiologists(ASA)class I-III hip fracture
-Unilateral lesion
-Provision of written informed consent
Exclusion criteria
-Allergic to ropivacaine
-Redness and swelling of the block site
-Abnormal blood coagulation
-Severe liver and kidney dysfunction
-Those who have no self-care ability or have language communication difficulties
Withdrawal criteria
-Poor intraoperative nerve block(i.e.,pain during surgery)
-Presence of uncontrollable intraoperative hemorrhage
-Severe intraoperative and postoperative adverse reactions
Grouping and blinding
A random digital table containing numbers 1-208 will be generated using SAS 9.2 software(SAS Institute Inc.,Cary,NC,USA).A Ranuni function will be used to generate a random number between 0 and 1 for each patient.Then the random numbers will be sequenced using proc sort and grouped at a 1:1 ratio.Thus,208 patients will be randomly divided into two groups(random digital 0 and random digital 1),with 104 patients in each group.Blind grouping and allocation concealment will not be used.
Methods of inducing analgesia
Lumbar plexus block group:Patients will be placed in the supine position and the skin will be disinfected with iodophor.Ultrasound examination(SonoSite Edge Portable Ultrasound System,Sono Site,USA)will be performed following the methods in a previous report.19A low-frequency convex array ultrasound probe(2-5 MHz)will be wrapped in a sterile glove.The probe will be placed parallel to the posterior axillary line between the anterior superior iliac spine and the lower edge of the rib arch on the affected side.Longitudinal axis scanning in the sagittal plane will be performed.In the ultrasound view,there will be a high-density echo shadow on the caudal side and an acoustic shadow toward the bottom.This is the anterior superior iliac spine.On the cranial side,there will be a high-density echo shadow of the spine and an acoustic shadow toward the bottom.Using the ultrasound system,the superficial lumbar muscle and the lower psoas muscle will be clearly visualized.The longitudinal high-density echo shadow seen in the lateral vertebral body and posterior 1/3 region of the psoas muscle will be in the image of the lumbar plexus long axis.Using an in-plane technique,a peripheral nerve plexus stimulation needle(D-type,22G,0.71 mm × 120.00 mm)will be inserted from the cranial side to the caudal side,passing through the lumbar quadrate muscle and reaching the region surrounding the lumbar plexus.If no blood or cerebrospinal fluid is re-extracted,30 mL of 0.5% ropivacaine hydrochloride(Nexus,AstraZeneca,UK)will be administered.
Iliac fascia block group:Patients will be placed in the supine position and their affected limbs will be laterally abducted as described previously.20A high-frequency linear array ultrasound probe(10-12 MHz)will be horizontally placed 2 cm below the inguinal ligament.A cross-sectional ultrasound image of the iliac fascia interspace will be visible using an in-plane technique,and a peripheral nerve plexus stimulation needle(D-type,22G,0.71 mm × 80.00 mm)will be oriented at a 60° angle to the skin and inserted at 30°,90°,and 150°angles to the probe planes,respectively,until it reaches the iliac fascia interspace.If no blood is re-extracted,10 mL of 0.5% ropivacaine hydrochloride will be injected at each angle.
General anesthesia and intraoperative management
After confirming the effect of the nerve block,general anesthesia will be performed using a laryngeal mask airway.Intravenous propofol(2 mg/kg; China Jiangsu Enhua Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,State Drug Approval No.H20123138)and sufentanil(0.05-0.10 μg/kg; Yichang Humanwell Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,State Drug Approval No.H20054256)will be administered.Two to three percent Sevo flurane will be inhaled using a laryngeal mask(oxygen flow rate 1.0-1.5 L/min; Shanghai Hengrui Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,State Drug Approval No.H20070172)for maintaining anesthesia at BIS 45-60.During surgery,the patients will be kept breathing spontaneously.Sufentanil and vasoactive drugs will be added according to the conditions indicated through monitoring.
Postoperative management
Patients in both groups will undergo patient-controlled analgesia.Analgesics include sufentanil(2.5 μg/kg; Yichang Renfu Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Yichang,Hubei Province,China;State Drug Approval No.H20054256)and flurbiprofen ester(100 mg; Tide Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,Beijing,China; State Drug Approval No.H20041508),which will be dissolved in 100 mL of normal saline.Background doses will be 2 mL/h.A single dose of 3 mL will be added using an electronic analgesia pump(Tuoren Medical Device Co.Ltd.,Henan Province,China).The compression lock time of the electronic analgesia pump will be designated to be 15 minutes.
Study flow chart
The flow diagram of this study is shown in Figure 1.
Outcome measures
Primary outcome measure
A Visual Analog Scale(VAS)score obtained 24 hours postsurgery,which will be used to evaluate the postoperative analgesic effect.VAS score = 0,no pain; ≤ 4,mild pain; =5-6,moderate pain; ≥ 7,severe pain,= 10,excruciating pain.21
Secondary outcome measures
-VAS score at 2,6,and 12 hours post-surgery,which will be used to evaluate the analgesic effect post-surgery:evaluation criteria will be the same as above.
-Heart rate at various time points during the surgery(laryn geal mask placement,T0; surgical incision,T1; surgical reaming,T2; prosthesis implantation,T3; incision suture,T4; and resuscitation,T5).
-Mean arterial pressure at T0,T1,T2,T3,T4,and T5.Mean arterial pressure is the mean value of arterial blood pressure during a cardiac cycle.Mean arterial pressure in normal adults is 70-105 mm Hg(1 mm Hg = 0.133 kPa).
-Blood oxygen saturation at T0,T1,T2,T3,T4,and T5:Blood oxygen saturation refers to the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is bound to oxygen(i.e.,the concentration of oxygen in the blood),which is used to evaluate the extent of hypoxia.
-Intraoperative sufentanil dosage:Sufentanil is mainly used as a μ-opioid receptor for general anesthesia.It exhibits high-intensity long-lasting analgesic effects.Intraoperative sufentanil dosage will be recorded.
-Intraoperative perdipine dosage:When blood pressure increases too much during surgery,perdipine will be administered to lower it to safe levels.Perdipine dosage will be recorded.
-Intraoperative ephedrine dosage:When blood pressure decreases too much during surgery,ephedrine will administered to raise it to safe levels.Ephedrine dosage will be recorded.
-Total amount of intravenous patient-controlled analgesics at 2,6,12,and 24 hours post-surgery:The amount of intravenous analgesics(drug preparation as described above)used for patient-controlled analgesia after surgery will be recorded.Low amounts of intravenous analgesics indicate that the nerve block had a stronger analgesic effect.
-Incidence of adverse reactions at 2,6,12,and 24 hours post-surgery:The incidence of adverse reactions including nausea/vomiting and sore throat will be recorded.
Schedule for primary and secondary outcome measures is shown in Table 2.

Figure 1:Flow diagram of this study.
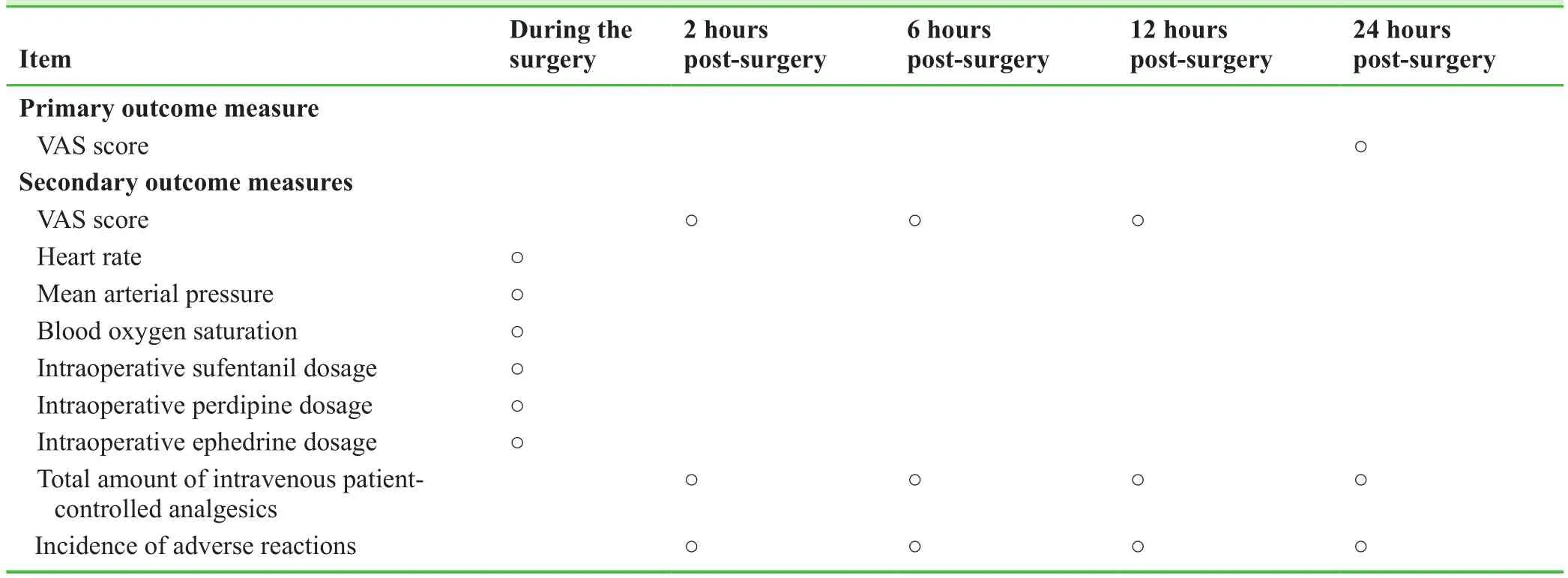
Table 2:Timing of primary and secondary outcome measures
Adverse events
Investigators should make a record of adverse events during the trial.The records include at least,but not limited to,description of the adverse event,date of onset and termination,severity and attack frequency,whether treatment is needed,if necessary,recording the treatment given.The adverse events will be treated by clinical investigators according to patient's condition,and the precaution to prevent and treat the subjects and emergencies in medical treatment is initiated if necessary.
Sample size
A pilot study involving 60 older adult patients undergoing hip replacement was performed between March 2018 and September 2018.The pilot study results showed that a VAS score at 24 hours post-surgery was 2.3 ± 0.5 and 3.4 ± 0.7 in the lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups,respectively.According to these data and our clinical experience,we hypothesized that VAS score was 2.5 ± 1.0 in the lumbar plexus block group at the end of the trial,and a score of 0.5 was increased in the iliac fascia block group compared with the lumbar plexus block group.Assumingβ= 0.05,power =90%,andα= 0.05(two-sided),afinal effective sample size ofn= 86 per group was calculated using the PASS 11.0 software(PASS,Kaysville,UT,USA).Assuming a patient loss rate of 20%,we would require 104 patients per group.
Statistical analysis
Data description
All data will be statistically processed using the SPSS 22.0 software(IBM,Armonk,NY,USA).Measurement data will be expressed means,standard deviation,median,minimum and maximum values,upper and lower quartiles.Count data will be expressed as numbers and percentages.
Statistical methods
The two-samplet-test(normally distributed data)or Mann-WhitneyUtest(non-normally distributed data)will be used to compare VAS score,heart rate,mean arterial pressure,blood oxygen saturation,intraoperative sufentanil dosage,intraoperative perdipine dosage,intraoperative ephedrine dosage,and total amount of intravenous patient-controlled analgesics at each time point between the lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups.Repeated measures analysis of variance and the least significant difference test will be used to compare the abovementioned indices in each group among different time points.Pearson chi-square test will be used to compare the incidence of adverse reactions between the lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups.An inspection level ofα= 0.05(unilateral)will be considered.
Data sets
Included patients will consist of populations assigned to perprotocol set.The situations of violating protocol that obviously affect the efficacy arefinally determined at the time of data review may include but not limited to,subjects who do not meet the inclusion criteria,treatment interference,poor compliance,and follow up beyond the window period.
Data collection
Patients' clinical records will be used as the original data of the clinical trial and well preserved.All datafilled in case report forms will be checked for its accuracy and completeness as well as consistency with original records.All corrected or commented mistakes will be signed and dated by the investigators.
Data management
Epi-Data 3.0 software will be used to establish the corresponding entry procedure based on the items in the case report form.The local review qualification conditions will be designated at the time of entry and an attempt will be made to run the database to establish the database system dedicated to this trial.Data will be input by data manager using the double entry method.Data will be checked for accuracy.
Audits
Independent Data Monitoring Committee composition
The Independent Data Monitoring Committee is composed of experts from the disciplines including medicine(having related medical experience),epidemiology,clinical imaging,clinical trial management,statistics,and ethics.
Investigator qualification
All anesthesiologists participating in this study have more than 10 years of anesthesia experience.The surgery will be performed by associated chief surgeons or those with higher professional titles.
Auditing
The clinical monitor will visit the trial site on a regular basis or according to the actual situation to conduct clinical audit work.The Independent Data Monitoring Committee will report the progression of the Medical Ethics Committee every other 2 months.Trial registration will be updated simultaneously.
Compensation to study population
Patients included in this trial will receive complimentary study protocol-related laboratory and imaging examinations during the follow-up period.
Ethics and dissemination
Ethical approval
The study design was approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Lu'an Civily Hospital of China(approval No.PJ2018-001)in March 2018(Additionalfile 1).This study will be performed in strict accordance with the with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.The study protocol version is 1.0.This manuscript was prepared according to CONsolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials(CONSORT)2010 statement(Additionalfile 2).
Informed consent
Patients will volunteer to participate in this study.Patients will provide written informed consent after fully understanding the study protocol(Additionalfile 3).
Dissemination
Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be published at www.figshare.com.
RESULTS
Small-sample-size pilot study results
A pilot study involving 60 older adult patients undergoing hip replacement during March 2018-September 2018 was performed.There were 30 patients in either lumbar plexus block or iliac fascia block groups.
Comparison of baseline data between lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups
Two groups of patients received local anesthesia that meet surgical requirements.There were no significant differences in database between lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups(P> 0.05; Table 3).
Comparison of hemodynamic parameters
Heart rate at T2,T3,T4,and T5 in the iliac fascia block group was significantly higher than that in the lumbar plexus block group(P< 0.05).In the iliac fascia block group,heart rate at T1,T2,T3 and T5 was significantly higher than that at T0(P< 0.05).Mean arterial pressure at T1,T2,T3,T4 and T5 was significantly higher in the iliac fascia block group than that in the lumbar plexus block group(P< 0.05).In the iliac fascia block group,mean arterial pressure at T1,T2,T3 and T4 was significantly higher than that at T0(P< 0.05).In the lumbar plexus block group,mean arterial pressure at T3 and T4 was significantly higher than that at T0(P< 0.05).There was no significant difference in blood oxygen saturation between the iliac fascia block and lumbar plexus block groups(P> 0.05;Table 4).
Comparisons of analgesic and vasoactive drug dosages between iliac fascia block and lumbar plexus block groups
Intraoperative sufentanil and perdipine dosages in the lumbar plexus block group were significantly lower than those in the Iliac fascia block group(P< 0.05).Total amount of intravenous patient controlled analgesics at 24 hours post-surgery in the lumbar plexus block group was significantly lower than that in the Iliac fascia block group(P< 0.05).There was no significant difference in intraoperative ephedrine dosage between lumbar plexus block and Iliac fascia block groups(Table 5).
Comparison of postoperative pain between iliac fascia block and lumbar plexus block groups
VAS score at 6,12,and 24 hours post-surgery was significantly lower in the lumbar plexus block group than in the iliac fascia block group(P< 0.05; Table 6).
Comparison of the incidence of adverse reactions post-surgeryIn the lumbar plexus block group,the incidence of post-operative nausea/vomiting and sore throat was 16.7%(5/30)and 10%(3/30)respectively,and which was 23.3%(7/30)and 13.3%(4/30)respectively in the iliac fascia block group.There were no significant differences between lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups(P> 0.05).

Table 3:Comparison of baseline data between lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block groups

Table 4:Comparison of hemodynamic parameters between iliac fascia block and lumbar plexus block groups

Table 5:Comparisons of analgesics and vasoactive drug dosages between iliac fascia block and lumbar plexus block groups

Table 6:Comparison of postoperative pain between groups
DISCUSSION
Results from the pilot study
Compared with iliac fascia block,lumbar plexus block exhibited a stronger block effect.Lumbar plexus block in combination with general anesthesia using a laryngeal mask airway could maintain relatively stable hemodynamics and effectively avoided perioperative cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accidents in older adult patients with hip fracture,thus reducing postoperative complications.22However,ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus nerve blockviaa typical approach requires patients in the lateral position.23-24Because of the hip lesion,the lateral position is quite painful.Moreover,long-duration lumbar plexus block increases patient discomfort.Ultrasoundguided lumbar plexus nerve block in the supine position is more suitable for patients who are unable to cooperate with the lateral position due to pain,and using it increases patient satisfaction.Iliac fascia block only requires patients to be in the prostration position,takes a short time,and is therefore more comfortable.Multi-angle multi-point iliac fascia block has a more rapid onset and exhibits a higher success rate than single-point iliac fascia block.
Lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block primarily involve the femoral nerve,obturator nerve,and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.Lumbar plexus block also involves the iliohypogastric nerve,iliac inguinal nerve,and genitofemoral nerve.Lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block exhibit different intraoperative and postoperative analgesic effects and affect different nerve branches.In the lumbar plexus block group,under ultrasound assistance,analgesics can be injected to the area surrounding the nerve.However,in the iliac fascia group,analgesics are injected into iliac fascial space and then disperse toward the nerve.This requires high drug doses and the distribution and neuroanatomical variation among patients cannot be avoided.25Because older adult patients have poor tolerance,safe dosages of local anesthetics are lower for them than they are for other adults.Therefore,a more precise method for nerve block is needed.
Novelty of this study
In this study,a novel lumbar plexus block method will be used that differs in body position and puncture paths from conventional puncture.22The lumbar plexus primarily includes the femoral nerve,obturator nerve,and lateral femoral cutaneous nerve,and it dominates lateral,anterior,and medial sensation of the thigh.But its location is deep.Conventional block methods do not provide adequate blocking effects.Ultrasound localization can visualize nerve position,dispersion of local anesthetics,and surrounding organs.Thus,most nerves that dominate the hip can be blocked,greatly reducing intraoperative pain and avoiding complications such as pricking blood vessels and breaking the peritoneum.
Conventional lumbar plexus block methods require patients to lie in the lateral position.Patients with hip fractures are unable to cooperate with position requirements due to pain.The novel lumbar plexus block method allows patients to remain in the supine position,changes the body position required for anesthesia and the puncture path,which can theoretically solve the problems mentioned above.This nerve block method has been reported before,but little information has been reported about its clinical efficacy.This study will compare the analgesic effects of lumbar plexus block and iliac fascia block.The novelty will be comparing the clinical efficacy between lumbar plexus block and multi-angle multi-point iliac fascia block in the supine position.
Limitations to this study
This study only investigates perioperative analgesic effects,does not examine long-term outcomes or mortality,and lacks long-term follow up and blind evaluation.All these factors will be considered in future studies.
Clinical significance of this study
Results from this study will provide evidence indicating the ultrasound-guided block method that provides the best analgesic effect.The hypothesis is that supine lumbar plexus block in combination with general anesthesia can more effectively maintain stable hemodynamic index during hip replacement and exhibit more encouraging postoperative analgesic effects that reduce perioperative adverse reactions in older adult patients than multi-angle multi-point iliac fascia block.
Additionalfiles
Additionalfile 1:Hospital ethics approval(Chinese).
Additionalfile 2:CONSORT checklist.
Additionalfile 3:Informed consent form(Chinese).
Author contributions
Study design and authorization:XLL; patient recruitment:XFY,SMH and QL; data collection:XLZ,YL,PRW,and JMP; data analysis:BM.All authors approved thefinal version of this manuscript..
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no con flicts of interest to declare.
Financial support
This study was supported by a grant from Youth Fund Development Program of Lu'an Civily Hospital of China(to XLL).
Institutional review board statement
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee,Lu'an Civily Hospital of China(approval No.PJ2018-001)in March 2018.This study will be performed in strict accordance with the with theDeclaration of Helsinkiformulated by the World Medical Association.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate pa-tient consent forms.In the form,the patients have given their consent for patients' images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal.The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity,but anonymity will not be guaranteed.
Reporting statement
This manuscript was prepared according to the CONsolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials(CONSORT)2010 statement.
Biostatistics statement
The statistical methods of this study were reviewed by the biostatistician of Lu'an Civily Hospital of China.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Data sharing statement
Individual participant data that underlie the results reported in this article,after deidentification(text,tables,figures,and appendices).Data will be available immediately following publication,with no end date.Results will be disseminated through presentations at scientific meetings and/or by publication in a peer-reviewed journal.Anonymized trial data will be available indefinitely at www.figshare.com.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement
This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
 Clinical Trials in Orthopedic Disorder2018年4期
Clinical Trials in Orthopedic Disorder2018年4期
- Clinical Trials in Orthopedic Disorder的其它文章
- Efficacy of silver needle acupuncture combined with muscle relaxation in the treatment of capulohumeral periarthritis:study protocol for a prospective,single-center,randomized,parallel-controlled trial
- Hemostasis following local versus intravenous tranexamic acid in patients undergoing posterior open reduction and internalfixation of thoracolumbar fractures:study protocol for a parallel-group,randomized controlled trial
- Efficiency of tight monitoring by nurse practitioners in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission after treatment with rituximab:study protocol for a randomized,open-label,controlled trial
- Clinicopathological characterization of long bone non-union:a prospective cross-sectional study
- Local anesthetic infiltration before open reduction and internalfixation for ankle fracture:a single-blind randomized controlled study
- Efficacy of arthroscopic surgery for discoid lateral meniscus injury in knee joint:a self-control study
