Effects of electroacupuncture of different frequencies on free radicals in hippocampus of mice with vascular dementia
Wu Ze-hui (武泽惠), Xu Xiao-kang (许晓康), Liang Yu-lei (梁玉磊), Zhang Chuang (张闯), Zhang Xiao-qi (张晓琪),Zhang Xin (张莘), Zhang Xuan-ping (张选平), Zhang Hui-zhen (张会珍), Guo Fei (郭菲)
Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Frequency; Dementia, Vascular; Hippocampus; Free Radical;Reperfusion Injury; Mice
Vascular dementia (VD) refers to a syndrome of intelligent and cognitive dysfunction caused by cerebrovascular factors[1].With the aging of the population, changes in working and living environment,as well as the dietary components, the incidence of VD is increasing, and its morbidity and mortality are also increasing.This not only seriously affects the patients’quality of life (QOL), but also imposes a heavy burden on families and society[2-3].Studies have shown that cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced cerebral ischemia, hypoxia and free radical damage are the direct causes of VD[4].After cerebral ischemia, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) level is decreased, cerebral vasospasm appears, and microcirculatory disorder aggravates Ca2+overload, thus nitric oxide synthase(NOS) is overactivated, and a large amount of nitric oxide (NO) is produced, which mediates excitatory damage of hippocampal neurons[5-6].The destruction of free fatty acids on cell membrane and the peroxidation toxic effects of free radicals are the main factors leading to VD intelligent damage.Superoxide dismutase (SOD)is an important oxygen radical scavenger in the body.Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a decomposition product of lipid peroxidation.The changes of these two factors can reflect the situation of lipid peroxidation damage[7].The cholinergic system disorder is the main material basis for the occurrence of VD[8], and acetylcholine (ACh)plays an important role in the maintenance of advanced neurological functions such as cognitive function and intelligent state[9].
In recent years, experimental research on the prevention, control and improvement of VD by acupuncture has made great progress[1,10], among which,electroacupuncture (EA) shows obvious advantages[11-14].Frequency is one important parameter of EA stimulation, but the frequency of EA used in clinical and experimental studies of VD is not unified.This experiment was designed to further explore the effects and mechanisms of different EA stimulation parameters in VD treatment, and to provide objective basis for clinical application of EA in VD treatment with scientific stimulation parameters, thus to improve the clinical efficacy.The effects of EA with a sparse wave (2 Hz), a dense wave (80 Hz), and a sparse-dense wave(2 Hz/80 Hz) on the levels of free radicals, CGRP, NOS,MDA, SOD and true choline esterase (TChE), in hippocampus of VD mice were detected.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animal
A total of 100 male Kunming mice, weighing 25-28 g,were purchased from Hebei Experimental Animal Center (certificate number: 706175).The mice were free access to water, and were adaptively fed for 1 week in a clean animal room at room temperature (18-22 ℃)with 12 h in light and 12 h in dark.The whole animal experiment was in line with the requirements of theGuiding Opinions on the Treatment of Experimental Animalsissued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China in 2006.A total of 100 mice were randomly divided into a sham operation group, a model group, a 2 Hz EA group(sparse wave), an 80 Hz EA group (dense wave), and a 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group (sparse-dense wave), with 20 mice in each group.
1.2 Main instruments and reagents
WQ-1002 Han's EA instrument (Beijing Anlong Photoelectric Co., Ltd., China); DP-200 mouse jumping stand instrument (Chengdu Taimeng Testing Instrument Equipment Co., Ltd., China); DY89-1 electric glass homogenizer (Ningbo Xinzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd.,China); 1-15K high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Sigma,USA); 722 visible spectrophotometer (Shanghai Third Analytical Instrument Factory, China); 600 mode electric heating constant temperature water tank (Tianjin Taisite Instrument Co., Ltd., China); CGRP radioimmunoassay kit (Beijing Puer Weiye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); CGRP radioimmunoassay kit (Beijing Puer Weiye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); NOS, SOD, MDA and TChE assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China).
1.3 Model preparation method
Except for the sham operation group, mice in the other groups were subjected to model preparation according to the related literature[15]: the mice were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate by intraperitoneal injection at 0.35 g/(kg·bw), and the incision was performed in the middle of the neck after routine disinfection.The bilateral common carotid arteries were isolated and blood flow was blocked for 20 min by tightening the silk thread (No.4) buckle, meanwhile,0.3 mL blood was released by cutting at 1 cm away from the tip of the tail followed by thermal hemostasis.The silk thread buckle was loosened to infuse blood for 10 min; the blood flow was blocked again for 20 min;the skin was then sutured after 30 min observation following the reperfusion.In the sham operation group,the common carotid arteries were isolated, the thread was braided but not ligated; tail tip bleeding was not performed; the observation time was the same as that in the other groups.Intramuscular injection of penicillin was given 2 000 U daily for 3 continuous days.In this experiment, the mouse's anal temperature was maintained at (36.0±0.5) ℃ to prevent the protective effect of hypothermia on ischemic brain damage.
1.4 Treatment methods
Treatment began on the 4th day after modeling.The mice were placed in a prone position on a self-made mousetrap.
Acupoints: Baihui (GV 20), Dazhui (GV 14), bilateral Zusanli (ST 36) and Geshu (BL 17).
Methods: According to the related literature[16], an acupuncture needle of 0.3 mm in diameter and 15 mm in length was inserted into the above mentioned acupoints, and connected to Han's EA instrument.The 2 Hz EA group used sparse wave with a frequency of 2 Hz.The 80 Hz EA group used dense wave with a frequency of 80 Hz.The 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group used sparse-dense wave with a frequency of 2 Hz/80 Hz.The stimulation intensity of each group was scaled by gently twitched limbs without struggle or squeaking (current intensity was 2.0 mA), 10 min each time.The mice in the sham operation group and the model group did not receive EA intervention, but received the same position fixation for 10 min each time.Each group was intervened once a day for 15 d.
1.5 Observation indicators and detection methods
1.5.1 Learning and memory performance test
After 15 d of treatment, the jumping stand test was performed to test the learning performance, and the memory performance was tested on the next day[17-18].
The experimental device was a mouse jumping stand reaction box (10 cm × 10 cm × 60 cm), which was divided into 6 chambers.The bottom of the box has copper grids that can achieve continuous electric stimulation of 36 V.A rubber pad (4.5 cm in diameter and height) was placed in the right rear corner of each chamber to serve as a safe area for the mouse to avoid electric shock.During the experiment, the mice were placed on a jumping stand instrument and allowed to adapt to the environment for 3 min.Then the bottom copper grids were connected to a 36 V alternating current, and the reaction time for the mouse to jump on the rubber pad after electric stimulation and the electric shock times(error numbers) within 5 min were recorded, which were used as the result of learning performance.On the next day, the mouse was placed on the jumping stand for 3 min followed by connection to a 36 V alternating current, and then placed on the rubber pad to record the latency period of the first time to jump away from the rubber pad and the numbers of electric shocks(error numbers) within 5 min, which were used as the result of memory performence.
1.5.2 Detection of free radical levels in hippocampus
Mice in each group received behavioral tests after 15 d of treatment.After the tests, the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation; the brain was quickly isolated on a ice tray; hippocampus in the right hemisphere was separated, and homogenized with the electric homogenizer in pre-cooled saline; then 10% of the brain tissue homogenate was centrifuged at 4 ℃and 4 000 r/min for 20 min when microscopic examination showed no intact cells; the supernatant was collected and stored in a refrigerator at –20 ℃ for testing.
CGRP level in hippocampus was determined by radioimmunoassay.MDA level was determined by thiobarbituric acid colorimetric assay.The activities of NOS and TChE in hippocampus was determined by spectrophotometry.The activity of SOD was determined by xanthine oxidase method.
1.6 Statistical processing
The SPSS 22.0 statistical software was used for data processing.Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation ().One-way analysis of variance was used to compare among groups.Least significant difference (LSD)t-test was used to compare among groups for the data with homogeneity of variance, and Tamhane’s T2 test was used for the data with heterogeneity of variance.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2 Results
At the end of the intervention, the number of surviving mice was 19 in the sham operation group, 17 in the model group, 15 in the 2 Hz EA group, 11 in the 80 Hz EA group, and 12 in the 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group.Ten experimental animals were randomly selected from each group for data collection and statistical analysis.
2.1 Comparison of learning and memory performances
The learning and memory performances in each group are shown in Table 1.
Mouse’s learning performance: Mice in the model group showed longer reaction time and increased error numbers, which were significantly different from those in the sham operation group (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the mice’s reaction time in each EA group was shortened and the error number was reduced (P<0.01).The 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group was superior to the 2 Hz EA group and the 80 Hz EA group (P<0.01).
Mouse’s memory performance: The latency of mice in the model group was shortened, and the error number was increased, which were significantly different from those in the sham operation group(P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the latency of mice in each EA group was prolonged, and the error number was decreased (P<0.05 orP<0.01).The 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group was superior to the 2 Hz EA group and the 80 Hz EA group (P<0.05).
2.2 Comparison of the free radical levels in mouse’s hippocampus
Compared with the sham operation group, in the model group, the CGRP level in mouse’s hippocampus was decreased; the MDA level was increased, the activities of NOS and TChE were increased, and the activity of SOD was decreased.The differences were statistically significant (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the CGRP level was increased, the MDA level was decreased, the NOS and TChE activities were decreased, the SOD activity was increased in each EA group, and the differences between groups were statistically significant (P<0.05 orP<0.01).The 2 Hz/80 Hz EA group was superior to the 2 Hz EA group and the 80 Hz EA group (P<0.05 orP<0.01).Details are in Table 2.
Table 1.Comparing the learning and memory performances of mice ()
Note: Compared with the sham operation group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05, 3) P<0.01; compared with the 2 Hz EA group, 4) P<0.05, 5) P<0.01; compared with the 80 Hz EA group, 6) P<0.05, 7) P<0.01
Group n Learning performance Memory performance Reaction time (s) Number of errors (Time) Latency time (s) Number of errors (Time)Sham operation 10 28.05±13.99 2.40±1.17 198.65±60.29 2.20±1.03 Model 10 100.94±22.841) 10.20±2.411) 38.90±12.311) 9.90±2.601)2 Hz EA 10 52.17±18.833) 5.40±1.963) 105.86±47.542) 5.10±1.793)80 Hz EA 10 60.57±16.27 3) 7.20±2.253) 97.02±43.002) 5.20±2.103)2 Hz/80 Hz EA 10 32.30±10.573)5)7) 2.90±1.373)5)7) 192.74±59.733)4)6) 2.30±0.953)4)6)
Table 2.Comparing the free radical levels in mouse hippocampus ()
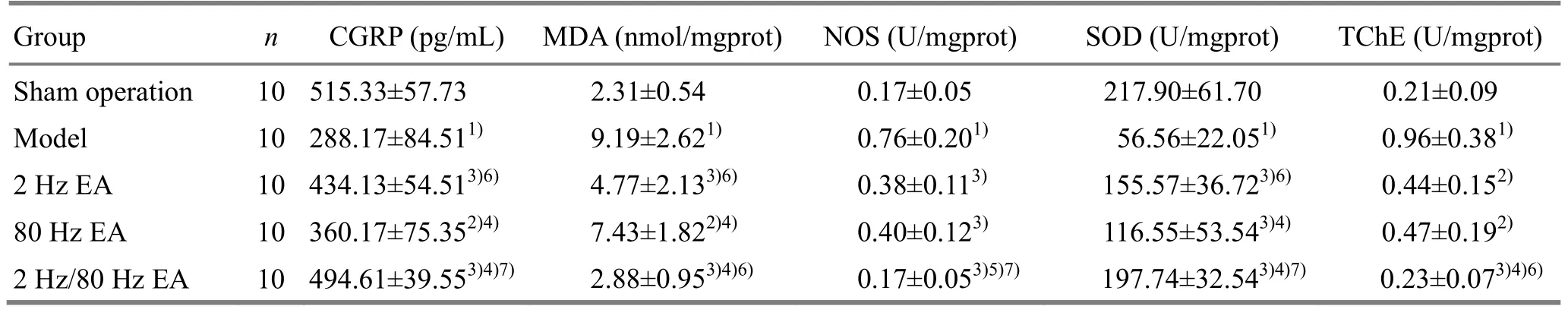
Table 2.Comparing the free radical levels in mouse hippocampus ()
Note: Compared with the sham operation group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.05, 3) P<0.01; compared with the 2 Hz EA group, 4) P<0.05, 5) P<0.01; compared with the 80 Hz EA group, 6) P<0.05, 7) P<0.01
Group n CGRP (pg/mL) MDA (nmol/mgprot) NOS (U/mgprot) SOD (U/mgprot) TChE (U/mgprot)Sham operation 10 515.33±57.73 2.31±0.54 0.17±0.05 217.90±61.70 0.21±0.09 Model 10 288.17±84.511) 9.19±2.621) 0.76±0.201) 56.56±22.051) 0.96±0.381)2 Hz EA 10 434.13±54.513)6) 4.77±2.133)6) 0.38±0.113) 155.57±36.723)6) 0.44±0.152)80 Hz EA 10 360.17±75.352)4) 7.43±1.822)4) 0.40±0.123) 116.55±53.543)4) 0.47±0.192)2 Hz/80 Hz EA 10 494.61±39.553)4)7) 2.88±0.953)4)6) 0.17±0.053)5)7) 197.74±32.543)4)7) 0.23±0.073)4)6)
3 Discussion
VD is a chronic progressive disease, and its symptoms are mainly the manifestations of dementia and cerebrovascular diseases[19].Cognitive impairment is the core symptom of VD[20].Studies have shown that hippocampus is an important brain area related to cognitive function, and a high-level center of learning and memory.It directly participates in the storage and processing of information[21].Ischemia and hypoxia usually cause dysfunction of cerebral vasomotor function, which will further aggravate ischemia and hypoxia, and that is the main cause of chronic damage in hippocampal tissue cells, and also the basic pathological factor inducing VD[3,22].
The toxic effect of free radicals is an important pathological factor of cerebral ischemia and hypoxia damage, and also the main factor of intelligent damage caused by nerve cell damage after VD cerebral ischemia.Free radicals may damage learning and memory abilities, and the damage to intelligence is mainly caused by the destruction and peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids on the cell membrane[23].Under physiological conditions, there is a corresponding free radical scavenging enzyme in the human body, and a dynamic balance is maintained between the generation and elimination of free radicals in the body.Under pathological conditions, such as cerebral ischemia,intracellular calcium overload can cause excessive free radical production.Decrease in free radical scavenging enzyme after decompensation initiates free radical chain reaction, destroys the structure and function of nerve cells, and leads to neuronal death.The related intelligence will be impaired[24].
CGRP is the main product of calcitonin gene, widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous system.It is the most known vasodilator substance.CGRP can inhibit Ca2+influx, reduce cell damage, and promote brain cell growth and development, thus protect the brain cells from damage[25].MDA is the main degradation product of free radical damage to cell membrane.It can reflect the level of free radicals and the degree of cell damage.SOD is an antioxidant enzyme that protects body against oxygen free radical damage and destruction.It can promote the oxidation of superoxide anion to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen ions, and can directly scavenge free radicals.Its activity basically represents the ability of tissues to scavenge oxygen free radicals[26].NO acts with superoxide radicals to form substances with strong oxidative effects,causing fatal oxidative damage in cells.
ACh is an important neurotransmitter in the central cholinergic nervous system.It exerts a biological effect through the ACh receptor and plays an important role in maintaining learning, memory and cognition.The dysfunction of the cholinergic system in hippocampus is one of the pathological mechanisms of VD[27].After cerebral ischemia and reperfusion, the activity of TChE is increased to over-produce the decomposed ACh in the brain, which may further lead to the decline of learning and memory abilities and the occurrence of intelligent disorders[9].Acetylcholine can effectively increase central nervous cell excitability, increase brain tissue oxygen consumption, and increase the production of MDA[28].
Studies have shown that the release of CGRP can play a nutritional role in the target tissues, dilate the surrounding blood vessels, promote the synthesis of anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR), and inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species and reduce the oxidative stress of tissues, therefore, to produce an endogenous protection of the tissues[29].
In this study, VD mice were prepared by repeated ischemia-reperfusion method.After modeling, the learning and memory abilities were decreased,suggesting successful modeling.Moreover, the detection of free radical levels in hippocampus showed that the CGRP level was decreased, the MDA level was increased, the NOS and TChE activities were increased,and the SOD activity was decreased.After treatment with EA at 2 Hz, 80 Hz or 2 Hz/80 Hz, the cognitive impairment of VD mice was reduced by different degrees; the CGRP level in hippocampus was increased;the MDA level, and the activities of NOS, TChE and SOD were decreased.These results suggested that EA can improve brain blood circulation, block neurotoxic cascade, restore cholinergic system function, fight against lipid peroxidation damage, and promote nerve cell repair, thus to improve cognitive obstacle caused by ischemia-reperfusion.This study found that EA with different frequencies had different therapeutic effects on VD mice, and the stimulation effect of 2 Hz/80 Hz sparse-dense wave was the best.
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年5期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2018年5期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effect of liver-soothing and mind-regulating acupuncture on resting-state electroencephalographic signals in rats with post-traumatic stress disorder
- Experimental study on the influence of pressing force and time on thermal effect of An-pressing manipulation
- Clinical experience of Xiangxi Liu’s infantile tuina for exogenous fever in children
- Therapeutic observation of acupuncture plus tuina for cervical vertigo
- Clinical observation of sinew-regulating and bone-setting manipulation combined with functional exercise to treat rotator cuff injury
- Effect of modified Qing Long Bai Wei needling on the levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and INF-α in synovial fluid of knee osteoarthritis patients
