利用移动键控和耦合超混沌系统实现异步十六进制数字保密通信系统
阿布都热合曼·卡的尔,木塔力甫·沙塔尔,米热古丽·艾力
(新疆财经大学 计算机科学与工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830012)
0 引言
近年来出现的大量基于混沌同步的保密通信方案,Wang等[1]设计了双信道传输机制,利用信道切换技术增强了通信的安全性。Vaseghi等[2]设计了在不确定噪声环境下,基于鲁棒自适应有限时间混沌同步的无线传感器网络保密通信方案,实现了信号和噪声的分离。Naderi等[3]利用无线性项情况下的混沌指数同步实现了保密通信,并利用指数稳定理论进行了分析。Pano-Azucena等[4]利用多方向多涡卷混沌系统和分段线性函数设计了保密通信方案,基于Arduino的开源环境。Ren等[5]设计了基于时空混沌的同步保密通信系统。以上方案要求接收和发送方之间达到同步。近年来也出现了基于混沌的异步保密通信方案,适用于对信号延迟容忍度高的非实时数据通信,如:Liu等[6]设计了基于超混沌系统动态时滞和状态变量切换的抗噪声异步保密通信系统,Wang等[7]设计了基于超混沌6阶细胞神经网络的异步保密通信系统。
混沌移动键控属经典混沌控制方法,常用于混沌保密通信系统设计[7-8],大多数基于混沌移动键控的方案只能一次发送1~2个比特,而一次发送更多比特则能有效提高通信效率[9-10]。
既然通信系统中信道噪声是不可避免的,如何确保在噪声环境中也能正常通信,是目前的研究热点。Wu等[11]设计了基于超混沌Lü系统被动同步的保密通信方案,数值模拟验证了该方案对信道噪声具有鲁棒性。Zhou等[12]设计一种简单的保密通信方案,利用了存在随机噪声和时滞的不同子网之间自适应组合外同步。
本文设计了一种基于超混沌移动键控的异步十六进制数字保密通信系统。通过动态调整混沌信号增益,即使在噪声条件下系统也具有高的稳定性。通过移动键控的方式把原始信号嵌入到增益后的混沌信号中,可实现一次发送4比特信号。分析了比特误码率(Bit Error Rate, BER)随信噪比(Signal-to-Noise Ratio, SNR)的变化趋势表明,自SNR大于0开始,BER可达到0,数值模拟验证了该方案的有效性。
1 系统描述
超混沌系统[13-14]较其相应的混沌系统具有更复杂的动力学行为。尽管分数阶混沌系统[15-16]及分数阶复混沌系统[17-18]已经实现了混沌同步,并用来设计保密通信方案[19],实验结果表明,求解整数阶微分方程要比分数阶快得多,因此本文利用两个异构整数阶超混沌系统耦合设计保密通信方案。
1.1 超混沌Liu系统
超混沌Liu系统[13]的非线性微分方程如式(1)所示:
(1)
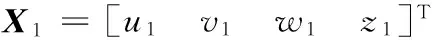
当d=10.6时,4个Lyapunov指数分别为:λ1=1.149 1、λ2=0.126 88、λ3=0和λ4=-13.767。吸引子投影如图1所示,这些由式(1)迭代生成的浮点数状态变量将作为原始信号的载体。
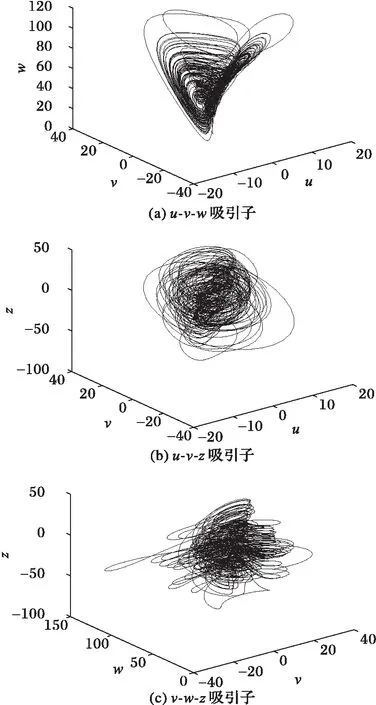
图1 超混沌Liu系统的吸引子投影(d=10.6) Fig. 1 Attractor projections of hyperchaotic Liu system when d=10.6
1.2 超混沌Lorenz系统
超混沌Lorenz系统[14]的非线性微分方程如式(2)所示:
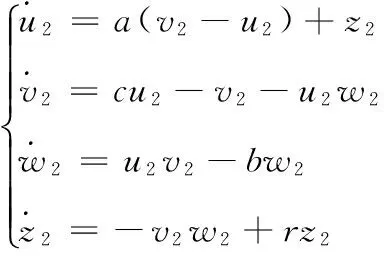
(2)
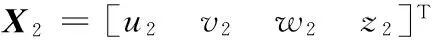
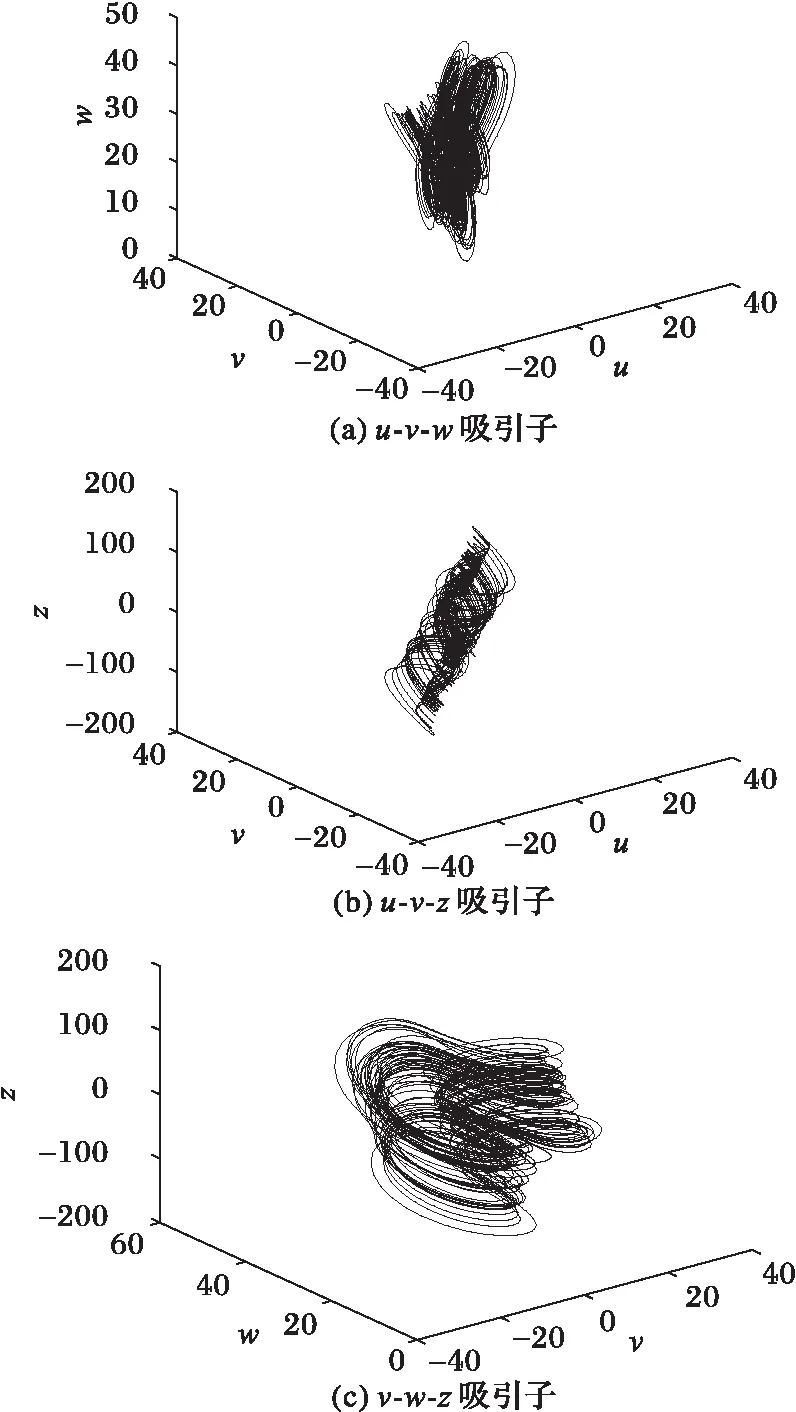
图2 超混沌Lorenz系统的吸引子投影(r=-1) Fig. 2 Attractor projections of hyperchaotic Lorenz system when r=-1
1.3 分段线性混沌映射
分段线性混沌映射(PieceWise Linear Chaotic Map, PWLCM)具有良好的遍历性和伪随机性,常用于设计混沌加密算法,其差分方程如式(3)所示:
(3)
当xi∈[0,1)且控制参数p∈(0,0.5)时,式(3)经迭代后呈混沌状态[20]。PWLCM分布均匀且遍历性好,能够产生良好的伪随机序列,变量x随p的变化分布如图3所示。
PWLCM迭代后由式(4)生成伪随机整数序列D,作为动态时滞的步长。设S(n)为原始二进制信号序列,n=4i(i=1,2,…,n/4)。
D={d1,d2,…,dn/4};di∈{1,2,…,8}
(4)

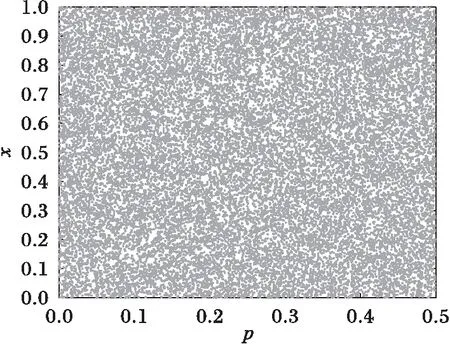
图3 经5 000次迭代后x随p∈(0,0.5)的分布 Fig. 3 Distribution of x with p∈(0,0.5) after 5 000 iterations
2 保密通信方案
2.1 信号调制
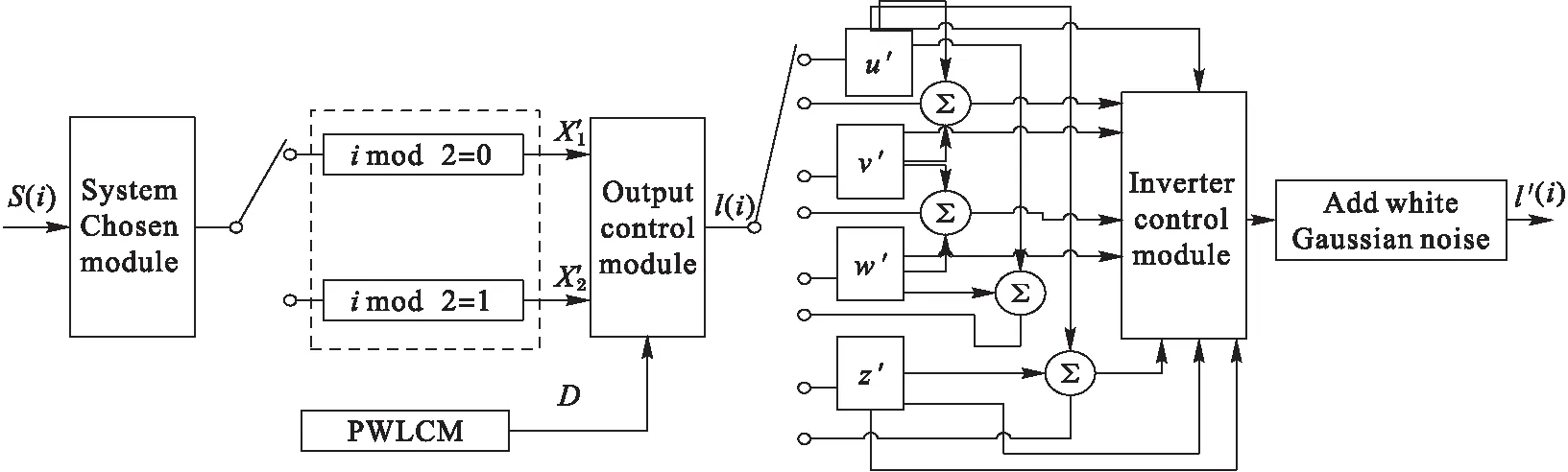
图4 十六进制数字保密通信系统的发送模型 Fig. 4 Transmitter mode of hexadecimal digital communication scheme
第1步 将原始二进制信号S(n)分成4位一组的向量s(i)=(bi1bi2bi3bi4)∈S(n)(i=1,2,…,n/4)。
第2步 由式(4)生成序列D={d1,d2,…,dn/4},di∈{1,2,…,8}。
第3步 迭代式(1)和式(2)有限次以消除暂态过程后,继续迭代n/4次,得到两个状态变量序列X1=[u1(i),v1(i),w1(i),z1(i)]T和X2=[u2(i),v2(i),w2(i),z2(i)]T(i=1,2,…,sum(D)),这些变量有各自的变化区间。
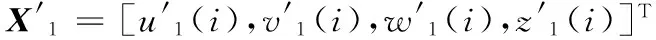
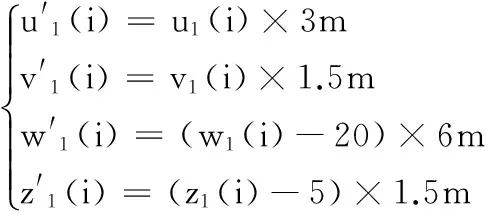
(5)
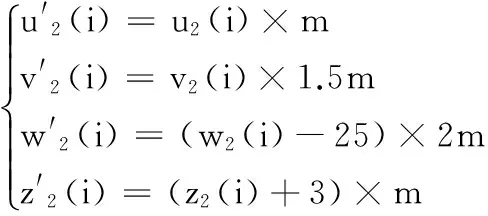
(6)
第5步 由式(7)得到添加高斯白噪声前的混沌信号l(i),作为载体。
(7)
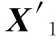
(8)
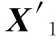
(9)
其中idx(i)是下标,由式(10)计算得到。
idx(i)=sum(1:D(i))
(10)
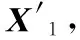
l(idx(i))=
(11)
图4中的转换器控制模块由式(12)定义:
(12)
第8步 由于信道噪声是不可避免的,此处添加高斯白噪声w(i)到l(i)模拟信道噪声, 由式(13)生成最后发送的信号l′(i)。
l′(i)=l(i)+w(i)
(13)
2.2 信号解调
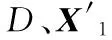

(14)
其中idx(i)是下标,由式(15)计算得到:
idx(i)=sum(1:D(i))
(15)
3 数值模拟和安全性分析
仿真实验电脑硬件环境为Intel Core i7-4700MQ 2.40 GHz,8.00 GB RAM,操作系统分别为Windows 7/8/10,并利用Matlab R2013b进行数值求解和仿真。
3.1 初值和参数
该方案基于异步保密通信,每次通信时发送方可通过安全渠道,如RSA,将初值和参数发送给接收方。
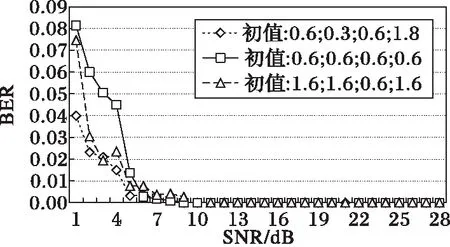
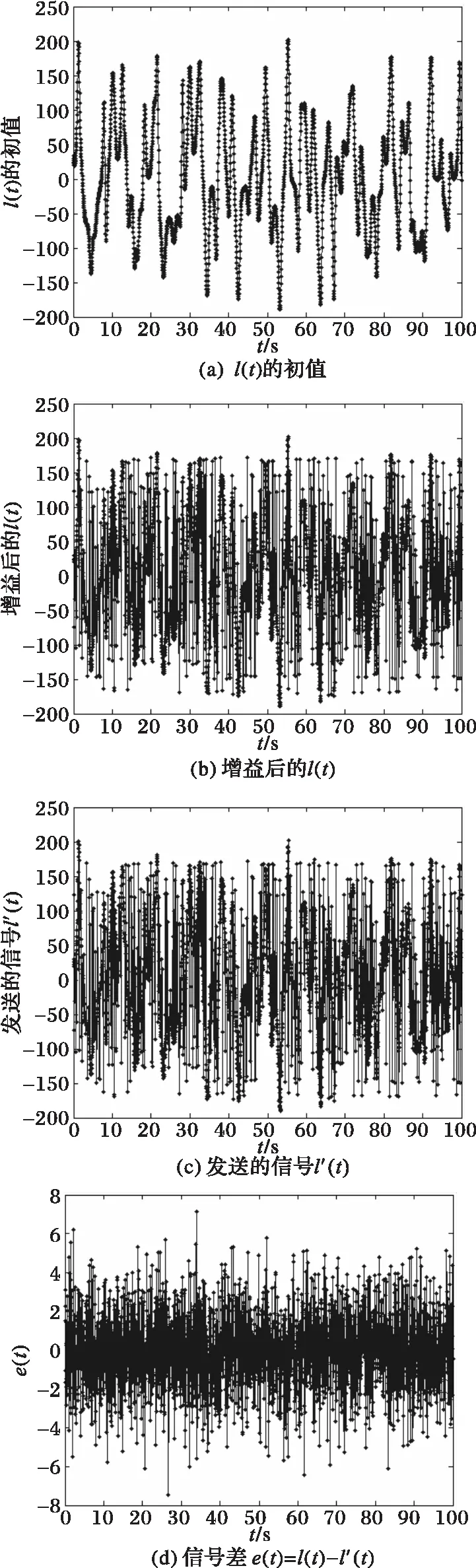
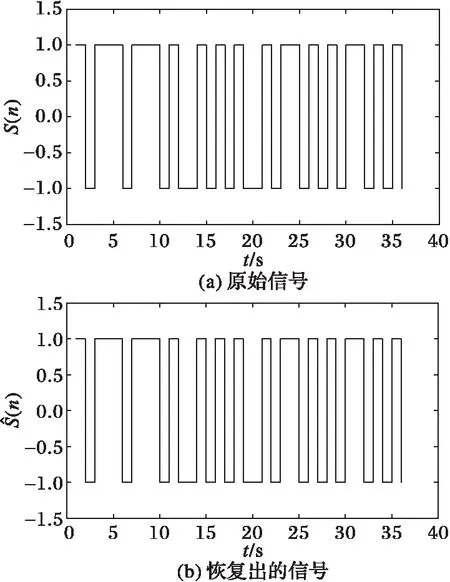
对于超混沌Liu系统,设定参数a=10、b=40、c=2.5、k=1、h=4和0 对于超混沌Lorenz系统,设置参数a=10、b=8/3、c=28和-1.52 (16) 多次模拟测试分析了BER随SNR的变化趋势,结果表明,通过按比例动态调整状态变量的增益以抵御噪声干扰,可确保BER达到零。 此处设置状态变量增益m=2,噪声强度k=8,取Liu系统的3组不同的初值验证通信方案的有效性。BER随SNR的变化趋势如图5所示,可见随着SNR的增加,BER呈平滑降低趋势,自SNR大于0开始,BER达到零,即从接收到的信号中可完整恢复出原始信号。 图5 BER随SNR的变化趋势图 Fig. 5 Diagram of BER versus SNR l(i)和l′(i)的误差e(i)可由式(17)计算: e(i)=l(i)-l′(i) 2.1 热水烫种消毒:先将蔬菜种子装入尼龙网袋中,再用30℃左右的温水浸种30分钟,促使种子上的病菌活化,这样容易杀死病菌。同时应不断搓洗,以洗掉种子上所带的抑制发芽的物质,而且也可使带茸毛(番茄)的种子湿透,以增加烫种效果。 (17) max(|e(i)|)随SNR的变化如图6所示,可见max(|e(i)|)随SNR的增大平稳降低。当SNR为常量时,可设置em为所有最大误差绝对值max(|e(i)|)的最大值。 图6 最大误差的绝对值随SNR的变化趋势图 Fig. 6 Diagram of BER and max(|e(t)|) 图7 增益后的状态变量和 Fig. 7 Modified state variables and 图8 信号l(t), l′(t)和e(t) Fig. 8 Signals l(t), l′(t) and e(t) 图9 原始信号S(n)和恢复出的信号(n) Fig. 9 Original and recovered signals S(n) and (n) 该方案拥有以下密钥以抵御穷举攻击:1) 两个超混沌系统的初值和参数;2) PWLCM的初值和参数。超混沌系统的初值和参数可取到的有效精度为10-14,因此其密钥空间可达10140。对于PWLCM,其初值x0和参数p的有效精度可达10-16[21],因此,总的密钥空间S=10140×1032=10172,在信号被截获的情况下足以抵御穷举攻击。 在信号调制过程中,是将超混沌信号X1和X2转换到传输信号l′(i),l′(i)由四个增益后的耦合状态变量信号、原始信号S(n)及高斯白噪声组成,十六进制信号的嵌入位置由PWLCM生成的伪随机序列决定。 即使攻击者在知道算法的情况下截获了信号l′(i),如果不知道超混沌系统及PWLCM的初值和参数,以及m和k的值,破译仍然是极其困难的。 超混沌系统较低维混沌系统具有更加复杂的非线性动力学行为,因此所设计的保密通信系统会更加安全。即使物理信道中存在噪声,只要噪声强度的变化区间能够检测到,则通过动态调整噪声强度和信号增益可确保BER为零。 本文基于两个超混沌系统的耦合设计了一种异步抗噪声保密通信方案,在发送方利用时变延迟和耦合变量转换嵌入十六进制信号到状态变量中,经添加高斯噪声后发送出去。在接收方,通过随信道噪声强度动态调整检测阈值,成功提取出信号。BER随SNR的变化趋势表明,通过动态调整状态变量的增益和噪声强度,可确保BER达到零。数值模拟验证了该保密通信系统在噪声环境下仍能够自适应稳定通信。 [1] WANG B, ZHONG S M, DONG X C. On the novel chaotic secure communication scheme design [J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2016, 39: 108-117. [2] VASEGHI B, POURMINA M A, MOBAYEN S. Secure communication in wireless sensor networks based on chaos synchronization using adaptive sliding mode control [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 89(3): 1689-1704. [3] NADERI B, KHEIRI H. Exponential synchronization of chaotic system and application in secure communication [J]. Optik—International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(5): 2407-2412. [4] PANO-AZUCENA A D, de JESUS RANGEL-MAGDALENO J, TLELO-CUAUTLE E, et al. Arduino-based chaotic secure communication system using multi-directional multi-scroll chaotic oscillators [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 87(4): 2203-2217. [5] REN H P, BAI C. Secure communication based on spatiotemporal chaos [J]. Chinese Physics B, 2015, 24(8): 233-238. [6] LIU H, WANG X, ZHU Q. Asynchronous anti-noise hyper chaotic secure communication system based on dynamic delay and state variables switching [J]. Physics Letters A, 2011, 375(30/31): 2828-2835. [7] WANG X, XU B, LUO C. An asynchronous communication system based on the hyperchaotic system of 6th-order cellular neural network [J]. Optics Communications, 2012, 285(24): 5401-5405. [8] YANG H, JIANG G P. Simple intra-signal-interference removing detector for HE-DCSK [J]. Journal of China Universities of Posts & Telecommunications, 2013, 20(6): 102-108. [9] KADDOUM G, GAGNON F. Performance analysis of STBC-CSK communication system over slow fading channel [J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(7): 2055-2060. [10] FILALI R L, BENREJEB M, BORNE P. On observer-based secure communication design using discrete-time hyperchaotic systems [J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2014, 19(5): 1424-1432. [11] WU X, ZHU C, KAN H. An improved secure communication scheme based passive synchronization of hyperchaotic complex nonlinear system [J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 252(C): 201-214. [12] ZHOU L, WANG C, HE H, et al. Time-controllable combinatorial inner synchronization and outer synchronization of anti-star networks and its application in secure communication [J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2015, 22(1/2/3): 623-640. [13] WANG F Q, LIU C X. Hyperchaos evolved from the Liu chaotic system [J]. Chinese Physics B, 2006, 15(5): 963-968. [14] ZHOU L, CHEN Z, WANG Z, et al. On the analysis of local bifurcation and topological horseshoe of a new 4D hyper-chaotic system [J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2016, 91: 148-156. [15] WU G C, BALEANU D, XIE H P, et al. Chaos synchronization of fractional chaotic maps based on the stability condition [J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2016, 460: 374-383. [16] RADWAN A G, MOADDY K, SALAMA K N, et al. Control and switching synchronization of fractional order chaotic systems using active control technique [J]. Journal of Advanced Research, 2014, 5(1): 125-132. [17] LUO C, WANG X. Chaos in the fractional-order complex Lorenz system and its synchronization [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 71(1/2): 241-257. [18] LUO C, WANG X. Chaos generated from the fractional-order complex Chen system and its application to digital secure communication [J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2013, 24(4): 1350025. [19] MOHAMMADZADEH A, GHAEMI S. Synchronization of uncertain fractional-order hyperchaotic systems by using a new self-evolving non-singleton type-2 fuzzy neural network and its application to secure communication [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 88(1): 1-19. [20] AHMAD M, RIZVI D R, AHMAD Z. PWLCM-based random search for strong substitution-box design [C]// Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer and Communication Technologies, AISC 379. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 471-478. [21] AHMAD J, KHAN M A, AHMED F, et al. A novel image encryption scheme based on orthogonal matrix, skew tent map, and XOR operation [J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2017, 28(3): 1-11. This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61662073,61363082), the Minority Nationality Technology Talent Cultivation Plan of Xinjiang (201123116), the Key Research Base Project of Humanities and Social Sciences for Regular Institutions of Higher Education in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (050316C02). ABDURAHMANKadir, born in 1975, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include chaos theory, information safety. MUTALLIPSattar, born in 1981, M. S., lecturer. His research interests include chaos theory, cryptographic algorithm. MIREGULIAili, born in 1983, M. S., lecturer. Her research interests include chaos theory, cryptographic algorithm.3.2 BER和SNR变化趋势
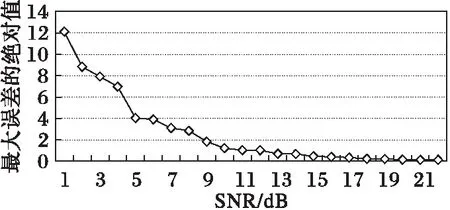
3.3 SNR和最大误差绝对值max(|e(i)|)的最大值
3.4 增益后的状态变量
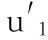

3.5 添加噪声前后的信号l(i)和l′(i)
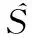
3.6 原始信号、中间信号及恢复出的信号
3.7 密钥空间分析
3.8 安全性分析
4 结语

