马尔可夫跳变时滞系统的无源性分析
李 敏,黄勤珍
(西南民族大学电气信息工程学院,四川 成都 610041)
马尔可夫跳变系统是一类特殊的随机混杂系统.马尔可夫跳变往往来源于系统在运行过程中所受到的环境突变、内部子系统连接方式突然改变、系统部件损坏等随机因素干扰[1-2].因此,研究马尔可夫跳变系统为解决工程控制问题提供了理论基础[3-4].众所周知,时滞广泛存在于各种实际系统中,然而,它的存在会使系统不稳定或性能遭到破坏[5].因此,研究马尔可夫时滞跳变系统具有实际的意义.
许多实际系统通过考虑无源性问题可以有效地抑制外界噪声干扰[6-7].近年来,系统无源性研究成为了一个重要的热点问题[8-9],吸引了众多学者的关注[10-12].文献[1]给出时滞马尔可夫跳变系统的随机无源性定义.文献[13]分析了线性时滞系统的时滞相关无源控制问题.文献[14]讨论了时变时滞的神经网络无源性问题.
本文研究了具有不确定性矩阵的马尔可夫跳变时滞系统的无源性问题.文章其余部分结构如下:第1节介绍本文研究的马尔可夫跳变时滞系统和推导所需的定义与引理.第2节得到满足系统无源性约束的充分判据.第3节给出一个数值例子验证所得理论结果的有效性与可行性.第4节总结全文.
1 预备知识

2 主要定理
本节主要推导保证系统(2)具有随机无源性的充分条件.
定理1若存在对称正定矩阵使得如下线性矩阵不等式成立:
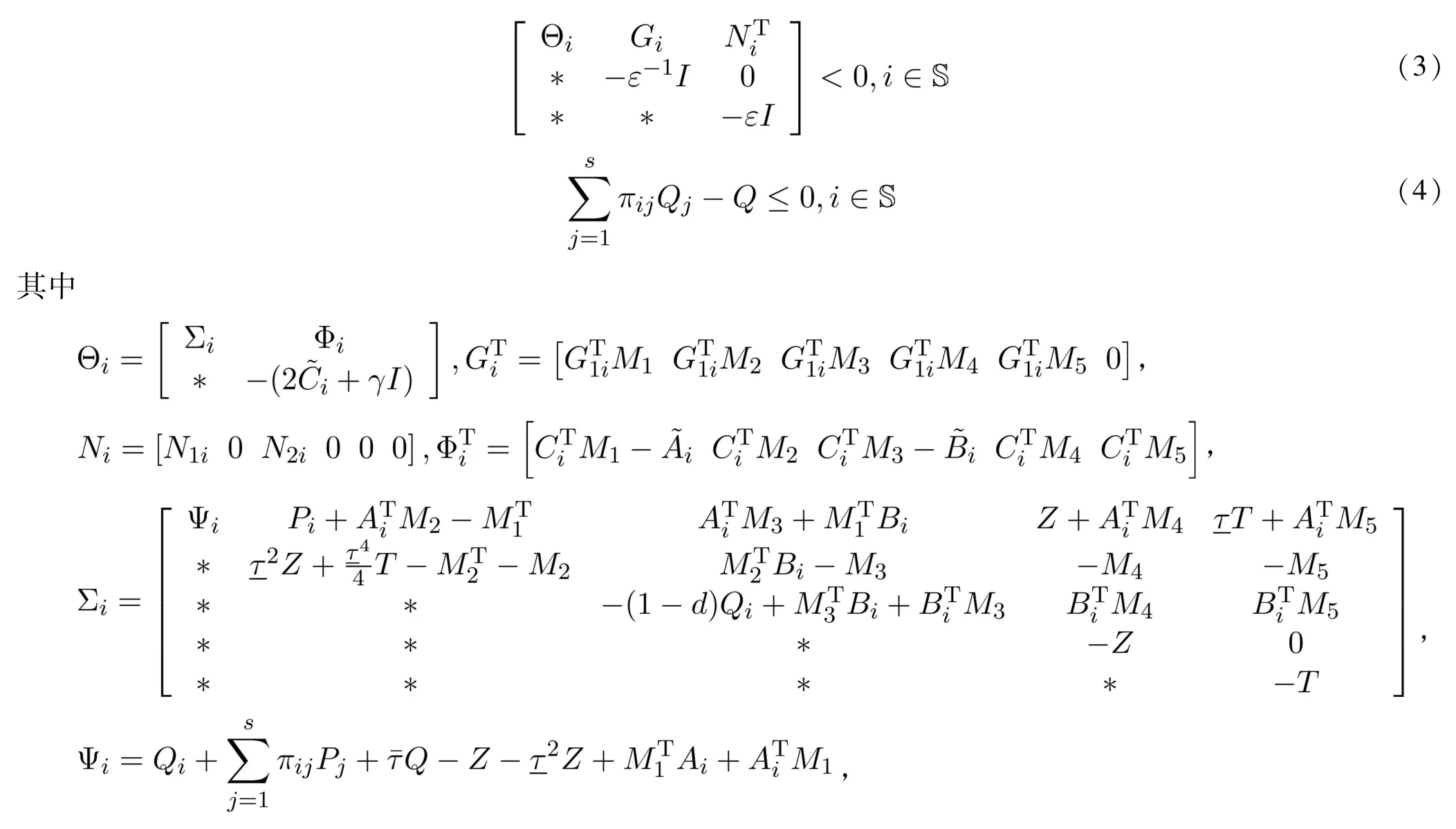
则系统(2)是随机无源的.



3 数值例子
这部分用一个例子来验证所提出的主要结果.
例1给定一个完备概率空间,考虑一个两模态的马尔可夫跳变系统(2),具体参数设置如下:


表1 最大时滞上界TTable 1 Upper bounds of T for different values of d
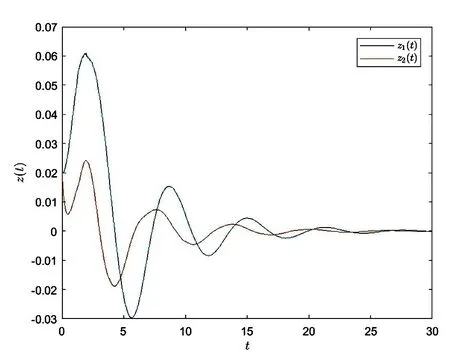
图1 输出信号图Fig.1 Output signal of system

图2 切换信号图Fig.2 The switching signals
4 结论
本文研究了马尔可夫跳变系统的无源性问题,其中,转移概率是已知的.通过构建Lyapunov泛函,得到马尔可夫跳变时滞系统的随机无源性充分判据.在实际系统中,转移概率是变化或未知的,研究不确定马尔可夫跳变系统具有一定的挑战性.因此,在未来的工作中将进一步对不确定马尔可夫时滞系统展开研究.
[1]WU Y Q,SU H,LU R,et al.Passivity-based non-fragile control for Markovian jump systems with aperiodic sampling[J].Systems& Control Letters,2015,84:35-43.
[2]SONG J,NIU Y,ZOU Y.Asynchronous output feedback control of time-varying Markovian jump systems within a finite-time interval[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2017,354(15):6747-6765,.
[3]RAKKIYAPPAN R,SASIREKHA R,LAKSHMANAN S,et al.Synchronization of discrete-time Markovian jump complex dynamical networks with random delays via non-fragile control[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2016,353(16):4300-4329.
[4]FEI Z,GAO H,SHI P.New results on stabilization of Markovian jump systems with time delay[J].Automatica,2009,45(10):2300-2306.
[5]LIU X,ZHONG S,ZHAO Q.Dynamics of delayed switched nonlinear systems with applications to cascade systems[J].Automatica,2018,87:251-257.
[6]YUE D,LAM J.Non-fragile guaranteed cost control for uncertain descriptor systems with time-varying state and input delays[J].Optimal Control Applications & Methods,2005,26(2):85-105,.
[7]YANG G H,WANG J L.Non-fragile H∞ control for linear systems with multiplicative controller gain variations[J].Automatica,2001,37(5):727-737.
[8]SHEN H,XU S,LU J,et al.Passivity-based control for uncertain stochastic jumping systems with mode-dependent round-trip time delays[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2012,349(5):1665-1680.
[9]HE S,LIU F.Optimal finite-time passive controller design for uncertain nonlinear Markovian jumping systems[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2014,351(7):3782-3796.
[10]WANG B,ZHU Q.Stability analysis of Markov switched stochastic differential equations with both stable and unstable subsystems[J].Systems& Control Letters,2017,105:55-61.
[11]CHEN G,XIA J,ZHUANG G.Delay-dependent stability and dissipativity analysis of generalized neural networks with Markovian jump parameters and two delay components[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2016,353(9):2137-2158.
[12]MA C.Non-fragile mixed H∞and passive synchronization of Markov jump neural networks with mixed time-varying delays and randomly occurring controller gain fluctuation[J].PLoS One,2017,12(4):e0175676.
[13]XIA Z,LI J,LI J.Passivity-based resilient adaptive control for fuzzy stochastic delay systems with Markovian switching[J].Journal of the Franklin Institute,2014,351(7):3818-3836.
[14]ZHANG Z,MOU S,LAM J,et al.New passivity criteria for neural networks with time-varying delay[J].Neural Networks,2009,22(7):864-868.
[15]HAN Q L.A new delay-dependent stability criterion for linear neutral systems with norm-bounded uncertainties in all system matrices[J].International Journal of Systems Science,2005,36(8):469-475.
[16]XIE L.Output feedback H∞ control of systems with parameter uncertainty[J].International Journal of Control,1996,63(4):741-750.

