大棚蔬菜土壤重金属污染及其控制的研究进展与展望
陈玉鹏 ,梁东丽 ,刘中华 ,王春玲 ,甄志磊 ,闫昭如
(1.山西农业大学城乡建设学院,山西 太谷 030801;2.西北农林科技大学资源环境学院,陕西 杨凌 712100;3.农业部西北植物营养与农业环境重点实验室,陕西 杨凌 712100)
随着温室大棚蔬菜栽培年限的延长,土壤重金属不断积累[1],不仅严重影响作物生长发育,也会带来严重的蔬菜食品安全问题,威胁人的健康。近年来,我国设施蔬菜栽培迅速发展,2010年我国的设施蔬菜面积已经达到466.7万hm2,并以每年10%的速度不断增长[2]。设施蔬菜用24%的土地面积提供了50%的蔬菜产量和60%的产值[3],在蔬菜生产中起到至关重要的作用。大棚种植通过人为地控制棚内的小气候,能延长蔬菜生产时间,增加淡季蔬菜的品种和产量,丰富市场供应,提高土地利用率[4]。蔬菜大棚种植多采用高投入、高产出、集约化的栽培措施,生产者为追求高产,往往过量施用化肥、农药及畜禽粪便,这会造成温室土壤中重金属的积累[5-6],导致大棚土壤受到不同程度的污染,对农业生产和人身健康造成威胁。另外,由于日光温室栽培下土壤长期处于封闭的环境,一方面,蔬菜在生长过程中需要频繁灌溉来满足水分要求,随着水分的下渗,会有部分重金属离子向下层土体移动;另一方面,由于温室内部的高温、高湿和高蒸发量,一部分重金属离子还会随水分的蒸发上升到地表。所以,日光温室特殊的水热条件及栽培管理措施将会对重金属在土壤中的迁移累积及形态分布产生一定的影响[7]。
有研究表明,土壤中重金属含量会随棚龄增长呈大幅持续升高的趋势[8],尤其是5年以上大棚,土壤重金属含量显著高于露天菜地[1],土壤重金属在作物体内积累,不仅影响作物自身的生长发育和品质安全,还会威胁人和动物的健康[9],这成为大棚蔬菜持续发展的制约因素,因此,如何在保证大棚正常的生产功能的同时,控制大棚蔬菜的重金属含量成为一项尤为艰巨的任务。本文结合大棚重金属的来源,从植物对重金属吸收和累积的角度,探讨控制土壤污染及减少蔬菜中重金属累积的方法,以期为设施农产品安全生产和土壤污染防治等提供参考。
1 大棚土壤重金属研究现状
1.1 我国大棚土壤重金属污染现状
目前,国内多个省市地区设施蔬菜集散地出现土壤重金属超标现象,各地因种植条件而不同,就污染的普遍性和程度而言,Cd污染最严重,其次为Pb和Cu(表 1)。
1.2 大棚土壤重金属来源
土壤重金属污染主要源于大气沉降、污水灌溉、农业投入品携带(化肥、畜禽粪便及农药等)等,温室土壤污染不存在大气沉降和污水灌溉这两种形式,其主要与施入化肥、畜禽粪便及农药等密切相关(表2)。对不同重金属元素而言,Cd、Cu、Zn污染主要源于过度施肥,而Hg和Pb主要是由农药如杀虫剂和除草剂残留所致[3]。
1.3 土壤重金属含量与大棚种植年限的关系
设施菜地处于封闭或半封闭的特殊环境,雨水淋洗等流失作用小,土地利用频度高,导致重金属长年在棚内积累,其含量也与大棚种植年限有较强相关,具体见表3。
2 大棚土壤重金属污染的控制措施
土壤重金属修复的方法主要有物理修复、化学修复、生物修复和农业生态修复,鉴于设施环境土壤的封闭性和低污染性,最适用的控制措施应属农业生态修复技术,即在原有的耕作方式和管理方法上做出调整,或种植一些特殊植物(不进入食物链的植物)来改善重金属污染的土壤[35]。其主要包括两种方法:①农艺措施,通过合理使用农药、化肥和有机肥,调整耕作管理制度以及作物品种,种植不进入食物链的植物,或利用某些植物对重金属的超累积性进行植物提取,来降低重金属污染的潜在风险;②生态措施,通过控制土壤中生态因子(水分、养分、湿度等)和调节土壤氧化还原电位,来降低重金属的危害。

表1 我国设施蔬菜土壤污染现状Table 1 The present situation of heavy metal pollution in vegetable greenhouses soils in China

表2 我国设施蔬菜大棚土壤重金属来源Table 2 The sources of heavy metal pollution in vegetable greenhouses soils in China
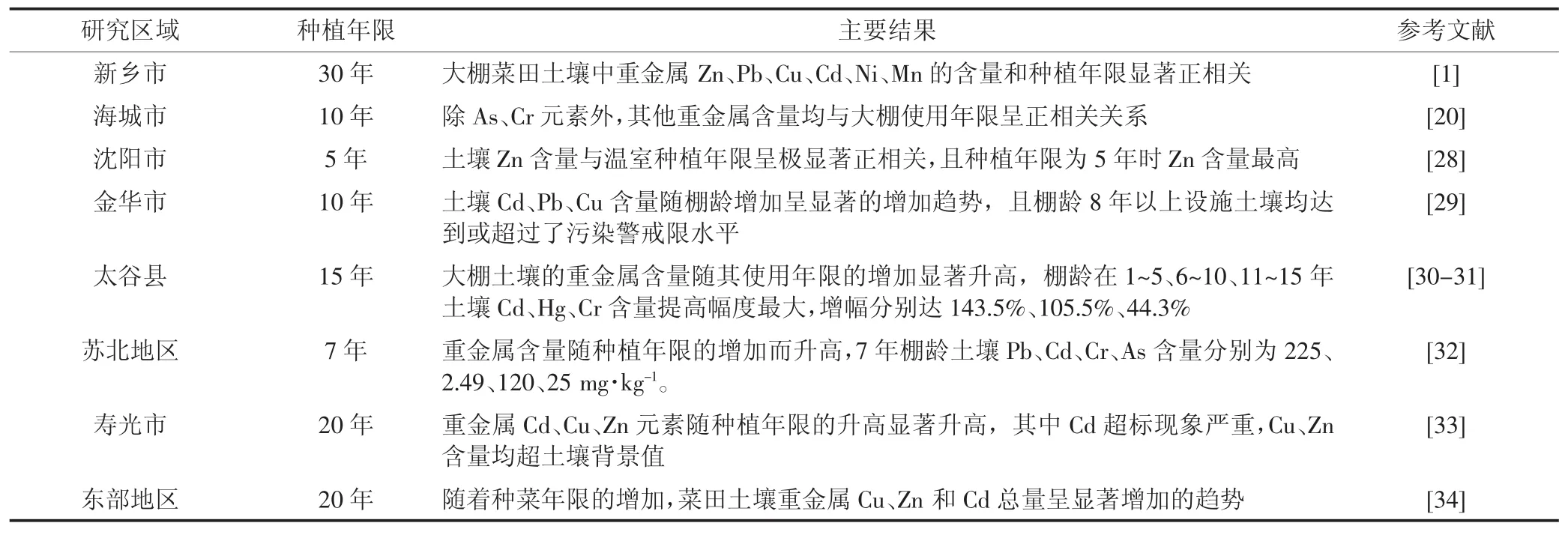
表3 土壤重金属含量与大棚种植年限的关系Table 3 Relationships between soil heavy metal content and planting years of greenhouses
2.1 调控肥力条件
施肥对植物根区环境及污染物迁移能力有较强影响,从而改变土壤-作物系统中重金属的迁移和累积。一方面,化肥中的K+、SO2-4、Cl-等离子能活化土壤中的重金属离子,增加其可交换态含量,提高重金属的生物有效性[36-38]。如土壤铵氮可降低向日葵根际土壤pH值,促进根际碳酸镉的溶解,且施氮肥量越大,土壤中有效态镉含量越高,从而为超富集植物提取更多的镉创造有利条件[39]。另一方面,化肥还能与土壤中重金属离子形成络合物,如磷肥能通过磷酸根与土壤中多种重金属生成磷酸盐化合物,将重金属稳定和固化[40-42],降低重金属的生物可利用性,明显降低蔬菜体内的重金属含量,并较好地修复被污染的旱地土壤[43]。此外,施肥可提高植物对污染物的抗逆性,最大限度减轻重金属对植物生长造成的不利影响。综上所述,施肥能从不同角度改变重金属的生物有效性,故可以通过调控肥力条件来缓解重金属对作物的不利影响。
2.2 添加土壤改良剂
改良剂是通过与重金属离子发生经氧化还原、沉淀、吸附、络合和螯合等化学反应钝化土壤中的重金属,降低其活性,或是以改变土壤的pH、Eh值等理化性质,影响土壤中重金属有效态含量[44],达到治理和修复重金属污染的目的(表4)。
土壤改良剂多为生活中常见的物质,因其经济廉价、来源广泛,适用于治理重金属轻中度污染的土壤。
2.3 作物品种及耕作制度
2.3.1 不同植物对重金属累积的影响
重金属元素在土壤-作物系统中的迁移转化规律不仅受土壤理化性质等因素影响,还与作物的种类、部位、生长期、基因型等有关。不同作物对重金属的积累效应差异较大,富集能力表现为叶菜类>花菜类>根茎类>茄果类>禾谷类,叶菜类如菠菜、芹菜等对重金属有较强的富集能力[54],且对不同重金属的富集有明显的选择性,对Cr的富集能力最强,其次为Zn、Cu、Ni,Pb 最弱[55];作物的不同器官对同一重金属的富集能力也有差异,表现为根>叶、茎>果实[56]。

表4 土壤改良剂对土壤重金属含量的影响Table 4 The influences of soil amendments on soil heavy metal content
鉴于不同作物之间富集能力的差异,在蔬菜生产时,应充分考虑土壤污染程度,根据不同蔬菜品种的富集能力,来生产安全无公害蔬菜[57]。李博文等[58]根据蔬菜可食部分对重金属Cd、Pb、Zn吸收累积的特点,将蔬菜分为4种累积类型:①低度累积型,在土壤受污染程度轻时进行生产可优先种植,如胡萝卜、茄子、番茄、辣椒等;②中度累积型,可在重金属污染情况不严重的土壤中适当种植,如菜花、莴苣、大葱、韭菜等;③重度累积型,种植时应避免重金属污染的土壤,如芹菜、茴香、圆白菜等;④极重度累积型有白菜、油菜等,种植时最好选用清洁土壤,此类植物能将土壤中的重金属提取固定到植物体内,减少或去除土壤和淋溶水中重金属,可利用其特性,控制或修复重金属污染土壤[59]。
2.3.2 不同耕作制度对土壤重金属吸收的影响
通过种植制度来控制土壤重金属含量的方法可以分为两种:一种是间套作,另一种是轮作。这两种方法均能种植重金属富集植物或筛选低富集植物来降低作物中的重金属含量,前者是通过植物提取土壤中的重金属来降低其含量,从而控制污染,而后者则是用低富集植物或可食部位低累积性的作物来降低和规避重金属对人或动物的风险。
(1)间套作模式:间作套种是我国传统农业的耕作方式,谭建波等[60]发现,续断菊与蚕豆间作较单作处理可降低土壤pH值,增加土壤有机质和碱解氮含量,使可交换态Cd含量降低,最终增强了续断菊对Cd的吸收,降低了蚕豆对Cd的吸收。间作鸡眼草显著降低了Pb、Cd在番茄、白菜等可食部位中的含量,却能提高其在油冬菜、花椰菜中的积累[56]。因此,不同作物间作对重金属的累积存在差异。另外,间作重金属富集植物,能保护与之间套作的部分植物,如锌超富集植物天蓝遏蓝菜与同属的非超富集植物遏蓝菜互作在Zn污染的土壤上,遏蓝菜的吸Zn量明显降低,生物量显著增加,这是由于天蓝遏蓝菜有很强的吸Zn能力,能优先吸收土壤中的Zn,从而减少了Zn对遏蓝菜的毒害[61]。然而,菜心、白菜等叶菜类蔬菜,与富集植物油菜间作是不可行的,种植在污染土壤上的叶菜会带来健康风险,如Cd富集植物油菜与白菜间作,油菜可以减轻Cd对小白菜的毒性,小白菜有较高的地上部生物量和较低的Cd累积量,但白菜中Cd浓度依然不低[62-63]。因此,利用适当的植物形成间套作复合体系,实现对污染土壤的边修复边生产,不失为一条土壤修复的新途径。
(2)轮作模式:大棚作物多采用不同蔬菜轮作方式。吸收土壤营养不同、根系深浅不同的作物相互轮作,如根菜类、茄果类、瓜果与浅根性的叶菜类、葱蒜类轮作,能增加土壤有机质含量,改良团粒结构,充分调节土壤养分的有效性,大幅提高土壤养分利用率[64-65],并能通过改变土壤水分、有机质、pH值和氧化还原环境等理化性质,降低重金属进入植物体内的可能性,影响植物对土壤重金属的吸收累积和利用[66-67]。
首先,不同的作物轮作模式下,重金属不同活性形态的累积效应不同。土壤中重金属的毒性及其生物有效性不仅与总量有关,更取决于其存在形态,而影响重金属赋存形态的因素较多,其中土壤pH值通过影响重金属在土壤中的化学形态和吸附能力,对土壤中重金属的移动性和生物有效性产生最大程度的影响[68-69]。
其次,轮作一些超富集植物,进行重金属的植物提取,能安全有效地去除轻度污染土壤中的重金属。郭晓静等[70]在Cd污染地区开展轮作模式试验,发现该地区产量和经济效益位居首位的白萝卜-番茄-青萝卜的种植模式,Cd元素在蔬菜可食部位的积累最少,较其他轮作模式更具优势。选择轮作蔬菜种类时应充分考虑重金属的累积和分布特性,如Cd容易在土壤表层累积,导致土壤表面含量最高[71],而叶菜类根系较浅,因此叶菜类蔬菜的种植需谨慎。
此外,作物轮作可以减少重金属元素在土壤耕作层的积聚,使其往下层土壤迁移,从而减轻设施农产品对土壤耕作层中重金属污染物的吸收[72]。且不同的轮作模式对防治重金属污染的效果不一。黄瓜、花椰菜、甘蓝、豇豆和菱白等果、花、叶、茎类蔬菜作物是低富集轮作优先选择的对象,与普通轮作相比,低富集轮作不仅能提高蔬菜产量和产值,还可使污染田块的蔬菜Sn含量降低50%~80%,并显著减少Cd进入食物链的量[73]。菜稻菜轮作能使耕作层可氧化态As含量显著降低,残渣态显著升高,导致土壤中As的生物有效性明显降低[74]。麦季间作伴矿景天能有效降低后茬茄子对Cd的吸收,并使土壤Cd浓度比对照降低24.3%[75],达到较好的修复效果。
单独种植超积累植物修复污染土壤所需周期长、问题多,而采用吸收重金属少或运移到食用部位少的低积累作物与超积累植物联合种植,有可能在修复污染土壤的同时收获符合安全标准的农产品,成为一种不需要间断生产、较经济合理地控制设施农业土壤重金属污染的方法[76]。
3 展望
对土壤重金属污染的修复已有大量研究,并取得了良好的效果,但针对温室大棚土壤重金属污染问题的研究涉及很少,为了达到更好经济效益和生态效益的种植模式,在充分考虑农产品收获的经济效益及农作物种植模式的可持续性,保证大棚正常生产功能的同时,控制修复大棚污染土壤,从而确保设施农产品生产环境安全。笔者认为,大棚土壤重金属污染的控制还需从以下方面加强研究:
(1)加大对大棚土壤重金属污染现状的研究力度。目前设施大棚土壤污染的研究多集中于对人体健康风险的评价,也有部分关于污染与种植年限之间关系的研究,但还需进行长期定位试验,拓宽污染涉及的种植模式,明确大棚土壤重金属污染的途径、种类和程度,从而提出相应的控制措施。
(2)改进已存在污染土壤的物理化学改良措施。现有改良剂大多针对田间条件,农家肥、绿肥、草炭和作物秸秆等有机物料中累积的重金属容易产生二次污染等问题,尤其是在大棚封闭和半封闭环境,因此应加强可以长期连续施用的改良剂的研发,并深化其修复机理的研究,构建适用于大棚环境的联合修复体系。
(3)深入研究水肥条件对土壤重金属形态之间的关系,深入探究施肥对重金属含量及其形态影响的机理,通过调控水肥条件控制重金属污染。
(4)加强不同耕作制度中重金属在土壤-植物系统的累积特征。作物轮作研究多集中于其对土壤肥力、土壤酶活性和微生物菌群的影响,以及在减少后作病虫害、防治连作次生盐渍化、增加经济收益等方面的作用,可加强大棚轮作方式下土壤重金属含量与其在土壤-作物体系中的迁移和累积特征的研究。
(5)重点寻找当前设施蔬菜重金属低累积或超富集植物种间的生态组合。筛选重金属低积累蔬菜品种的研究进展较缓慢,而能够在蔬菜地很好应用的超富集蔬菜品种对土壤的修复工作大多尚在试验阶段。以不同种植模式来减少蔬菜可食用部位的重金属残留,同时通过非可食用部位对重金属的超富集作用以修复污染土壤等研究成为当前的热点,但相关研究较少且部分结果缺乏一致性。因此,优化大棚种植模式,选择适当的蔬菜种类,降低重金属污染的风险,是植物修复和控制土壤重金属污染的新思路。
[1]陈碧华,杨和连,周俊国,等.大棚菜田种植年限对土壤重金属含量及酶活性的影响[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(1):213-218.CHEN Bi-hua,YANG He-lian,ZHOU Jun-guo,et al.Effect of cultivating years of vegetable field on soil heavy metal content and enzyme activity in plastic shed[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2012,28(1):213-218.
[2]Li C G,Li X M,Kong W D,et al.Effect of monoculture soybean on soil microbial community in the Northeast China[J].Plant and Soil,2010,330(1/2):423-433.
[3]Yang L Q,Huang B,Hu W Y,et al.Assessment and source identification of trace metals in the soils of greenhouse vegetable production in Eastern China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2013,97:204-209.
[4]焦 坤,李德成.蔬菜大棚条件下土壤性质及环境条件的变化[J].土壤,2003,2(2):94-97.JIAO Kun,LI De-cheng.Changes in soil properties and environment in vegetable greenhouses[J].Soils,2003,2(2):94-97.
[5]王 美,李书田,马义兵,等.长期不同施肥措施对土壤和作物重金属累积的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2014,33(1):63-74.WANG Mei,LI Shu-tian,MA Yi-bing,et al.Effect of long-term fertilization on heavy metal accumulation in soils and crops[J].Journal of A-gro-Environment Science,2014,33(1):63-74.
[6]姜 萍,金盛杨,郝秀珍,等.重金属在猪饲料-粪便-土壤-蔬菜中的分布特征研究[J].农业环境科学学报,2010,29(5):942-947.JIANG Ping,JIN Sheng-yang,HAO Xiu-zhen,et al.Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in feeds,pig manures,soils and vegetables[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2010,29(5):942-947.
[7]陈召亚,刘会玲,张新星,等.不同种植年限温室土壤中铜、铅垂直分布特征[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(1):321-325.CHEN Zhao-ya,LIU Hui-ling,ZHANG Xin-xing,et al.Vertical distribution of Cu and Pd in greenhouse soils with different growing years[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2016,30(1):321-325.
[8]Eriksson J.Critical load set to“no further increase in Cd content of agricultural soils”-consequences[R].Proceedings from Ad hoc international expert group on effect-based critical limits for heavy metals,11th-13th October,2000:54-58.
[9]Sharma R K,Agrawal M,Marshall F M.Heavy metals in vegetables collected from production and market sites of a tropical urban area of India[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2009,47(3):583-591.
[10]Fan Y,Li H,Xue Z J,et al.Accumulation characteristics and potential risk of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system under greenhouse cultivation condition in Northern China[J].Ecological Engineering,2017,102:367-373.
[11]Yang L Q,Huang B,Hu W Y,et al.The impact of greenhouse vegetable farming duration and soil types on phytoavailability of heavy metals and their health risk in Eastern China[J].Chemosphere,2014,103:121-130.
[12]Hu W Y,Huang B,Tian K,et al.Heavy metals in intensive greenhouse vegetable production systems along Yellow Sea of China:Levels,transfer and health risk[J].Chemosphere,2017,167:82-90.
[13]唐希望,同延安,吉普辉,等.关中地区日光温室重金属污染及其田块尺度下的特征[J].干旱地区农业研究,2016,34(1):272-278,287.TANG Xi-wang,TONG Yan-an,JI Pu-hui,et al.Assessment of greenhouse heavy metal pollution in Guanzhong area and analysis of its spatial distribution on field scale using Geo-statistical software[J].Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2016,34(1):272-278,287.
[14]Xu L,Lu A X,Wang J H,et al.Accumulation status,sources and phytoavailability of metals in greenhouse vegetable production systems in Beijing,China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2015,122:214-220.
[15]刘 苹,杨 力,于淑芳,等.寿光市蔬菜大棚土壤重金属含量的环境质量评价[J].环境科学研究,2008,21(5):66-71.LIU Ping,YANG Li,YU Shu-fang,et al.Evaluation on environmental quality of heavy metal contents in soils of vegetable greenhouses in Shouguang City[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2008,21(5):66-71.
[16]Li F L,Shi W,Jin Z F,et al.Excessive uptake of heavy metals by greenhouse vegetables[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2017,173:76-84.
[17]陈碧华,杨和连,李新峥,等.新乡市大棚菜田土壤重金属积累特征及污染评价[J].土壤通报,2012,43(4):967-971.CHEN Bi-hua,YANG He-lian,LI Xin-zheng,et al.Heavy metal accumulation characteristics and pollution assessment of vegetable soils in plastic shed in Xinxiang[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2012,43(4):967-971.
[18]贺小琴,张永清.离石区蔬菜大棚土壤重金属污染现状评价[J].北方园艺,2014(4):155-159.HE Xiao-qin,ZHANG Yong-qing.Assessment of heavy metal pollution in vegetable greenhouse in Lishi district[J].Northern Horticulture,2014(4):155-159.
[19]刘子姣,李廷亮,田 源.太谷县蔬菜大棚土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J].山西农业科学,2015,43(1):58-60.LIU Zi-jiao,LI Ting-liang,TIAN Yuan.Ecological risk assessment and heavy metal pollution of vegetable greenhouse soils in Taigu County[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2015,43(1):58-60.
[20]陈晓云,张亚文,詹德江,等.辽宁海城设施蔬菜土壤重金属污染评价研究[J].北方园艺,2014(1):165-169.CHEN Xiao-yun,ZHANG Ya-wen,ZHAN De-jiang,et al.Study on evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution of greenhouse vegetable in North China[J].Northern Horticulture,2014(1):165-169.
[21]张 琳,谭雾凇,杜 蒙,等.瓦房店市设施大棚用地土壤重金属累积评价[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,38(3):13-19.ZHANG Lin,TAN Wu-song,DU Meng,et al.Soil heavy metal accumulation assessment of greenhouse in Wafangdian City[J].Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition),2017,38(3):13-19.
[22]赵 明,蔡 葵,王文娇,等.施肥对大棚土壤有效态重金属含量及生物效应的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2010,29(增刊):26-31.ZHAO Ming,CAI Kui,WANG Wen-jiao,et al.Effects of fertilization on soil available heavy metal content and biological effects in greenhouse[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2010,29(Suppl):26-31.
[23]周 焱,陆若辉,董越勇,等.浙江省复混肥料、有机-无机复混肥料和有机肥料品质的研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2007,13(1):148-154.ZHOU Yan,LU Ruo-hui,DONG Yue-yong,et al.Quality investigation of organic fertilizers,inorganic-organic compound fertilizers and compound fertilizers in Zhejiang Province[J].Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,2007,13(1):148-154.
[24]何飞飞,任 涛,杨 君.三元复混肥和鸡粪肥中重金属含量特征分析与评价[J].湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版,2011,37(6):665-668.HE Fei-fei,REN Tao,YANG Jun.Investigation of heavy metal characteristics of NPK compound fertilizer and chicken manure in Shouguang[J].Journal of Hunan Agricultural University(Natural Sciences),2011,37(6):665-668.
[25]何梦媛,董同喜,茹淑华,等.畜禽粪便有机肥中重金属在土壤剖面中积累迁移特征及生物有效性差异[J].环境科学,2017,38(4):1576-1586.HE Meng-yuan,DONG Tong-xi,RU Shu-hua,et al.Accumulation and migration characteristics in soil profiles and bioavailability of heavy metals from livestock manure[J].Environmental Science,2017,38(4):1576-1586.
[26]黄治平,徐 斌,张克强,等.连续四年施用规模化猪场猪粪温室土壤重金属积累研究[J].农业工程学报,2007,23(11):239-244.HUANG Zhi-ping,XU Bin,ZHANG Ke-qiang,et al.Accumulation of heavy metals in the four years′continual swine manure-applied greenhouse soils[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2007,23(11):239-244.
[27]许 浩,韩丽媛,茹淑华,等.不同有机肥中Cu、Zn在农田土壤中的有效性与形态归趋[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2016,22(4):998-1009.XU Hao,HAN Li-yuan,RU Shu-hua,et al.Bioavailability and form tendency of Cu and Zn in farmland soils after application of different organic fertilizers[J].Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,2016,22(4):998-1009.
[28]王 俊,郭 颖,吴 蕊,等.不同种植年限和施肥量对日光温室土壤锌累积的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2009,28(1):89-94.WANG Jun,GUO Ying,WU Rui,et al.Effects of different planting years and organic manure fertilization on Zn accumulation in greenhouse soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2009,28(1):89-94.
[29]方 勇.不同棚龄土壤重金属含量变化及污染评价[J].湖南农业科学,2012,1:58-61.FANG Yong.Content changes and pollution evaluation of heavy-metals in different cultivation ages of greenhouse soils[J].Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2012,1:58-61.
[30]李 曈,吴 荣,李 杰,等.不同使用年限大棚土壤重金属污染评价[J].河南农业科学,2016,45(12):62-66.LI Tong,WU Rong,LI Jie,et al.Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution in greenhouses with different planting years[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2016,45(12):62-66.
[31]杜慧玲,冯两蕊,郭平毅,等.土壤重金属元素含量与大棚使用年限的相关性研究[J].山西农业科学,2006,34(3):56-59.DU Hui-ling,FENG Liang-rui,GUO Ping-yi,et al.Correlationship between the heavy metal contents in soil and cultural time at greenhouse[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2006,34(3):56-59.
[32]薛延丰,石志琦.不同种植年限设施地土壤养分和重金属含量的变化特征[J].水土保持学报,2011,25(4):125-130.XUE Yan-feng,SHI Zhi-qi.Characteristics of soil nutrient and heavy metal content with the different years of cultivation[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2011,25(4):125-130.
[33]井永苹,李 彦,薄录吉,等.不同种植年限设施菜地土壤养分、重金属含量变化及主导污染因子解析[J].山东农业科学,2016,48(4):66-71.JING Yong-ping,LI Yan,BO Lu-ji,et al.Variation of soil nutrient and heavy metal accumulation in greenhouse soil with cultivation years and analysis on main pollution factors[J].Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2016,48(4):66-71.
[34]黄绍文,唐继伟,李春花.不同栽培方式菜田耕层土壤重金属状况[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2016,22(3):707-718.HUANG Shao-wen,TANG Ji-wei,LI Chun-hua.Status of heavy metals in vegetable soils under different patterns of land use[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,2016,22(3):707-718.
[35]邵 云,郝真真,王文斐,等.土壤重金属污染现状及修复技术研究进展[J].北方园艺,2016(17):193-196.SHAO Yun,HAO Zhen-zhen,WANG Wen-fei,et al.Research progress on heavy metal contaminated soils and research advances in remediation technology[J].Northern Horticulture,2016(17):193-196.
[36]杨永杰.氮肥形态与用量对水稻镉积累和毒害的影响及调控机制研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2016.YANG Yong-jie.Effects of nitrogen fertilizer form and dosage on cadmium accumulation and toxicity and its regulatory mechanism in rice[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Dissertation,2016.
[37]郑志斌.长期施肥对紫色土-作物体系铅镉铬富集的影响[D].重庆:西南大学,2016.ZHENG Zhi-bin.Effect of long-term fertilization on lead,cadmium,chromium accumulation of purple soil-crop system[D].Chongqing:Southwest University,2016.
[38]王腾飞,谭长银,曹雪莹,等.长期施肥对土壤重金属积累和有效性的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2017,36(2):257-263.WANG Teng-fei,TAN Chang-yin,CAO Xue-ying,et al.Effects of long-term fertilization on the accumulation and availability of heavy metals in soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2017,36(2):257-263.
[39]Zaccheo P,Crippa L,Pasta V D M.Ammonium nutrition as a strategy for cadmium mobilisation in the rhizosphere of sunflower[J].Plant and Soil,2006,283(1):43-56.
[40]Dermatas D,Shen G,Chrysochoou M,et al.Pb speciation versus TCLP release in army firing range soils[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2006,136(1):34-46.
[41]雷 鸣,曾 敏,胡立琼,等.不同含磷物质对重金属污染土壤-水稻系统中重金属迁移的影响[J].环境科学学报,2014,34(6):1527-1533.LEI Ming,ZENG Min,HU Li-qiong,et al.Effects of different phosphorus-containing substances on heavy metals migration in soil-rice system[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2014,34(6):1527-1532.
[42]Cao X D,Wahbi A,Ma L N,et al.Immobilization of Zn,Cu,and Pb in contaminated soils using phosphate rock and phosphoric acid[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,164(2):555-564.
[43]刘昭兵,纪雄辉,彭 华,等.磷肥对土壤中镉的植物有效性影响及其机理[J].应用生态学报,2012,23(6):1585-1590.LIU Zhao-bing,JI Xiong-hui,PENG Hua,et al.Effects of phosphorous fertilizers on phytoavailability of cadmium in its contaminated soil and related mechanisms[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2012,23(6):1585-1590.
[44]刘维涛,周启星.不同土壤改良剂及其组合对降低大白菜镉和铅含量的作用[J].环境科学学报,2010,30(9):1846-1853.LIU Wei-tao,ZHOU Qi-xing.Effectiveness of different soil ameliorants in reducing concentrations of Cd and Pb in Chinese cabbage[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2010,30(9):1846-1853.
[45]Singh B R,Oste L.In situ immobilization of metals in contaminated or naturally metal-rich soils[J].Environmental Reviews,2001,9(2):81-97.
[46]Caporale A G,Sarkar D,Datta R,et al.Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi(Glomus spp.) on growth and arsenic uptake of vetiver grass(Chrysopogon zizanioides L.)from contaminated soil and water systems[J].Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition,2014,14(4):955-972.
[47]周贵宇,姜慧敏,杨俊诚,等.几种有机物料对设施菜田土壤Cd、Pb生物有效性的影响[J].环境科学,2016,37(10):4011-4019.ZHOU Gui-yu,JIANG Hui-min,YANG Jun-cheng,et al.Effects of different organic materials on bio-availability of Cd,Pb in a contaminated greenhouse soil[J].Environmental Science,2016,37(10):4011-4019.
[48]Waqas M,Khan S,Qing H,et al.The effects of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar on PAHs and potentially toxic element bioaccumulation in Cucumis sativa L.[J].Chemosphere,2014,105:53-61.
[49]代允超,吕家珑,刁 展,等.改良剂对不同性质镉污染土壤中有效镉和小白菜镉吸收的影响[J].农业环境科学学报,2015,34(1):80-86.DAI Yun-chao,L譈 Jia-long,DIAO Zhan,et al.Effects of soil amendments on Cd bioavailability to and uptake by Brassia chinensis in different Cd-contaminated soils[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2015,34(1):80-86.
[50]高瑞丽,朱 俊,汤 帆,等.水稻秸秆生物炭对镉、铅复合污染土壤中重金属形态转化的短期影响[J].环境科学学报,2016,36(1):251-256.GAO Rui-li,ZHU Jun,TANG Fan,et al.Fractions transformation of Cd,Pb in contaminated soil after short-term application of rice straw biochar[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstontiae,2016,36(1):251-256.
[51]Lombi E,Hamon R E,McGrath S P,et al.Lability of Cd,Cu,and Zn in polluted soils treated with lime,beringite,and red mud and identification of a non-labile colloidal fraction of metals using isotopic techniques[J].Environmental Science&Technology,2003,37(5):979-984.
[52]Naidu R,Kookana R S,Sumner M E,et al.Cadmium sorption and transport in variable charge soils:A review[J].Journal of Environmental Quality,1997,26(3):602-617.
[53]陈远其,张 煜,陈国梁.石灰对土壤重金属污染修复研究进展[J].生态环境学报,2016,25(8):1419-1424.CHEN Yuan-qi,ZHANG Yu,CHEN Guo-liang.Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by lime:A review[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2016,25(8):1419-1424.
[54]Jinadasa K,Milham P J,Hawkins C A,et al.Survey of cadmium levels in vegetables and soils of greater Sydney,Australia[J].Journal of Environmental Quality,1997,26(4):924-933.
[55]窦 磊,马 瑾,周永章,等.广东东莞地区土壤-蔬菜系统重金属分布与富集特性分析[J].中山大学学报(自然科学版),2008,47(1):98-102.DOU Lei,MA Jin,ZHOU Yong-zhang,et al.Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system of Dongguan area,GuangdongProvince[J].ActaScientiarumNaturaliumUniversitatisSunyatseni,2008,47(1):98-102.
[56]杨 晖,梁巧玲,赵 鹂,等.7种蔬菜型作物重金属积累效应及间作鸡眼草对其重金属吸收的影响[J].水土保持学报,2012,26(6):209-214.YANG Hui,LIANG Qiao-ling,ZHAO Li,et al.The cumulative effect on heavy metal of seven kinds of vegetable crops and effects on heavy metal absorption of intercropping Kummerowia striata[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2012,26(6):209-214.
[57]徐明飞,郑纪慈,阮美颖,等.不同类型蔬菜重金属(Pb,As,Cd,Hg)积累量的比较[J].浙江农业学报,2008,20(1):29-34.XU Ming-fei,ZHENG Ji-ci,RUAN Mei-ying,et al.Comparison of the amounts of heavy metals accumulated by different groups of vegetables[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2008,20(1):29-34.
[58]李博文,谢建治,郝晋珉.不同蔬菜对潮褐土镉铅锌复合污染的吸收效应研究[J].农业环境科学学报,2003,22(3):286-288.LI Bo-wen,XIE Jian-zhi,HAO Jin-min.Effects of complex contamination of cadmium,lead and zinc on vegetables grown in meadow cinnamon soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2003,22(3):286-288.
[59]仇荣亮,仇 浩,雷 梅,等.矿山及周边地区多金属污染土壤修复研究进展[J].农业环境科学学报,2009,28(6):1085-1091.QIU Rong-liang,QIU Hao,LEI Mei,et al.Advances in research on remediation of multi-metal contaminated soil in mine and surrounding area[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2009,28(6):1085-1091.
[60]谭建波,湛方栋,刘宁宁,等.续断菊与蚕豆间作下土壤部分化学特征与Cd形态分布状况研究[J].农业环境科学学报,2016,35(1):53-60.TAN Jian-bo,ZHAN Fang-dong,LIU Ning-ning,et al.Soil chemical properties and Cd form distribution in Vicia faba and Sonchus asper intercropping system[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2016,35(1):53-60.
[61]Whiting S N,de Souza M P,Terry N.Rhizosphere bacteria mobilize Zn for hyperaccumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens[J].Environmental Science&Technology,2001,35(15):3144-3150.
[62]Liu Y G,Fei Y,Zeng G,et al.Effects of added Cd on Cd uptake by oilseed rape and pai-tsai co-cropping[J].Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2007,17(4):846-852.
[63]Su D C,Lu X X,Wong J W C.Could cocropping or successive cropping with Cd accumulator oilseed rape reduce Cd uptake of sensitive Chinese Cabbage?[J].Practice Periodical of Hazardous,Toxic,and Radioactive Waste Management,2008,12(3):224-228.
[64]刘永亮.水旱轮作对设施连作番茄土壤特性的影响研究[D].银川:宁夏大学,2015.LIU Yong-liang.Effect of paddy-upland crop rotation on soil properties under continuous tomato cropping in greenhouse[D].Yinchuan:Ningxia University,2015.
[65]张 皓,何腾兵,林昌虎,等.不同轮作方式黔产半夏土壤物理性状分析[J].水土保持研究,2015,22(3):127-131.ZHANG Hao,HE Teng-bing,LIN Chang-hu,et al.Analysis on soil physical properties in pinellia fields under different rotation systems in Guizhou Province[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2015,22(3):127-131.
[66]Datta A,Sanyal S K,Saha S.A study on natural and synthetic humic acids and their complexing ability towards cadmium[J].Plant and Soil,2001,235(1):115-125.
[67]刘 凯,张 健,杨万勤,等.不同农业种植模式土壤-作物系统中Zn的分配与迁移[J].四川农业大学学报,2012,30(1):30-36.LIU Kai,ZHANG Jian,YANG Wan-qin,et al.Distribution and translocation of zinc in soil-crop systems under different cropping modes[J].Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University,2012,30(1):30-36.
[68]Singh B R,Myhr K.Cadmium uptake by barley as affected by Cd sources and pH levels[J].Geoderma,1998,84(1):185-194.
[69]常同举,崔孝强,阮 震,等.长期不同耕作方式对紫色水稻土重金属含量及有效性的影响[J].环境科学,2014,35(6):2381-2391.CHANG Tong-ju,CUI Xiao-qiang,RUAN Zhen,et al.Long-term effects of tillage methods on heavy metal accumulation and availability in purple paddy soil[J].Environmental Science,2014,35(6):2381-2391.
[70]郭晓静,胡承孝,赵小虎,等.不同种植模式下蔬菜吸收积累镉的差异[J].浙江农业学报,2015,27(8):1387-1393.GUO Xiao-jing,HU Cheng-xiao,ZHAO Xiao-hu,et al.Difference of cadmium uptake and accumulation in vegetables under different planting patterns[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2015,27(8):1387-1393.
[71]黄宝同,徐永刚,宇万太,等.不同轮作模式下设施菜地土壤和蔬菜中砷汞镉铬铅的分布特征[J].中国科学院大学学报,2012,29(2):212-219.HUANG Bao-tong,XU Yong-gang,YU Wan-tai,et al.Distribution characteristics of As,Hg,Cd,Cr,and Pb in soil and vegetable in protectedvegetablefieldunderdifferentrotationmodes[J].Journal of Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,2012,29(2):212-219.
[72]孙凯宁,王克安,杨 宁,等.轮作模式下设施菜地主要重金属元素空间分布特征[J].山东农业科学,2016,48(11):81-84.SUN Kai-ning,WANG Ke-an,YANG Ning,et al.Spatial distribution features of main heavy metal elements in greenhouse soil under rotation mode[J].Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2016,48(11):81-84.
[73]汪雅各,章国强.蔬菜区土壤镉污染及蔬菜种类选择[J].农业环境保护,1985,4(4):7-10.WANG Ya-ge,ZHANG Guo-qiang.Cadmium pollution and vegetable species selection in vegetable[J].Agro-Environmental Protection,1985,4(4):7-10.
[74]杨 凯.东莞菜稻菜轮作对土壤Cd、Pb、As形态分布及其生物有效性的影响[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2013.YANG Kai.The effects of vegetable-rice-vegetable rotation system on the form distribution and bioavailability of soil Cd,Pb and As in Dongguan[D].Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University,2013.
[75]居述云,汪 洁,宓彦彦,等.重金属污染土壤的伴矿景天/小麦-茄子间作和轮作修复[J].生态学杂志,2015,34(8):2181-2186.JU Shu-yun,WANG Jie,MI Yan-yan,et al.Phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by intercropping with Sedum plumbizincicola and Triticum aestivum and rotation with Solanum melongena[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology,2015,34(8):2181-2186.
[76]卫泽斌,吴启堂,龙新宪.利用套种和混合添加剂修复重金属污染土壤[J].农业环境科学学报,2005,24(6):1262.WEI Ze-bin,WU Qi-tang,LONG Xin-xian.Phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil with mixed chelators in co-crop system[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2005,24(6):1262.

