2007—2016年SinoMed收录五所中医药大学科技论文的计量学研究
李明利++马路++高书春++刘春宇
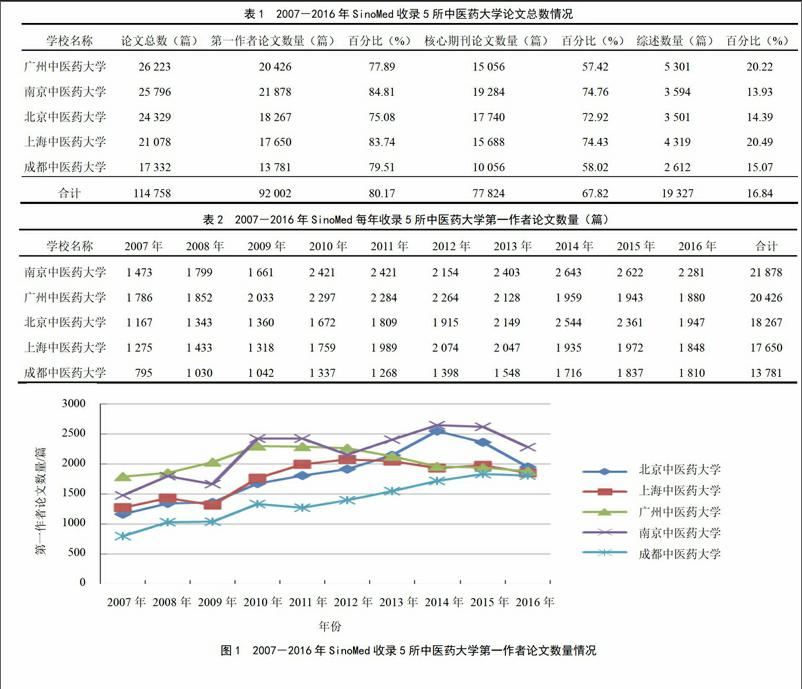


摘要:目的 分析中国生物医学文献服务系统(SinoMed数据库)收录的5所中医药大学发表的科技论文,了解我国中医药院校发展现状、研究趋势和存在问题。方法 以SinoMed数据库为统计源,检索时间范围为2007-2016年,对作者单位为北京中医药大学、上海中医药大学、广州中医药大学、南京中医药大学和成都中医药大学的论文计量分析。通过Python(3.5)软件,去除第一作者不是5所中医药大学的论文,确定纳入分析标准。利用R(3.3.2)软件,对论文数量、期刊分布、受资助情况和关键词进行统计分析。利用Excel 2010对第一作者论文数量、受资助论文占比和受国家级资助占比绘制年度趋势变化折线图,利用R(3.3.2)软件wordcloud,对关键词词频予以可视化,绘制词云图。 结果 5所中医药大学SinoMed收录论文数量逐年增长,发表论文的期刊以本地区和本学校学报为主。论文受资助比例逐年增加,但是受到国家级资助的比例明显低于受资助论文比例。研究领域:中药学以中药化学和中药药理学研究为主,中医学以疾病综述、经典方剂疗效和中医药疗法临床应用总结为主。结论 中医药论文对于我国中医药院校建设发展起到了积极的推动作用,但是论文质量有待加强,国家级课题资助的论文产出有待提高。中医方面需要加强校际国际间合作,中药方面需要在中医理念中发展。
关键词:中医药大学;科技论文;文献计量学;中国生物医学文献服务系统
中图分类号:G353 文献标识码:A 文章编号:2095-5707(2017)06-0010-08
Bibliometric Study on Scientific Papers of Five TCM Colleges and Universities in SinoMed Database during 2007 - 2016
LI Ming-li1,2, MA Lu1,3*, GAO Shu-chun1, LIU Chun-yu1
(1. School of Health Management and Education, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China; 2. Capital Medical University Division of Marxism, Beijing 100069, China; 3. Office of International Cooperation, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China)
Abstract: Objective To analyze scientific papers of five TCM colleges and universities in SinoMed-China Biomedical Literature Service System (SinoMed database); To understand the current status of the development, research trends and existing problems of TCM colleges and universities. Methods SinoMed database was set as statistical sources, and the retrieval time range was from 2007 to 2016. Papers of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine and Chengdu University of Chinese Medicine were under bibliometric study. Python software was used to exclude papers whose first author does not belong to the above five
第一作者:李明利,2016級硕士研究生。E-mail: 995299429@qq.com
*通讯作者:马路,教授,研究方向为医学信息管理。E-mail: malulib@ccmu.edu.cn
universities. Analysis standard of inclusion was confirmed. Paper quantity, periodical distribution, funded situation and key words were analyzed by R (3.3.2). Excel 2010 was used to draw the annual trend change line chart about paper quantity with the first author belonging to the five universities, the percentage of funded papers and percentage of papers funded by national projects. R (3.3.2) software wordcloud was used to visualize frequency of key words and draw wordcloud map. Results The number of papers of the five universities in SinoMed database accelerated year by year. The periodicals published these papers were mainly journals in the regions or schools where the five universities are located. The percentage of funded papers increased year by year. However, the percentage of papers funded by national projects was significantly lower than that of funded papers. The research fields: TCM pharmacy was mainly TCM chemistry and TCM pharmacology; TCM science was mainly review of diseases, efficacy of classical prescriptions and clinical application of TCM therapy. Conclusion TCM papers have played a positive role in promoting the construction and development of TCM colleges and universities in China, but the quality of papers is not high, as well as the quality of national funded papers. In terms of TCM, it needs to strengthen inter-school international cooperation, and in terms of Chinese materia medica, it should be developed within TCM concepts.endprint

