Validity and Reliability of Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale Thai Version (ASRS-V1.1 TH)
Komsan KIATRUNGRIT, Suwannee PUTTHISRI*, Sirichai HONGSANGUANSRI, Pattaraporn WISAJAN,Sudawan JULLAGATE
•ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE•
Validity and Reliability of Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale Thai Version (ASRS-V1.1 TH)
Komsan KIATRUNGRIT, Suwannee PUTTHISRI*, Sirichai HONGSANGUANSRI, Pattaraporn WISAJAN,Sudawan JULLAGATE
adult ADHD, screening, Thailand, validity and reliability, ASRS-V1.1
1. Introduction
ADHD is one of the most common developmental psychiatric disorders among children and of ten persists into adulthood.[1,2]The prevalence of the ADHD persistence strongly depends on how it is defined. If‘ADHD remission’ is defined as no longer meeting the full diagnostic criteria than the remission rate has been shown to be quite high (about 60% of subjects), despite the fact that 30% of those in ‘remission’ still met criteria for some ADHD symptoms and also reported a low level of functioning.[3,4]Over the past twenty years, many studies about the prevalence of adult ADHD reported 2.9%-3.2% for full criteria diagnosis based on DSM-IV and 6.6%-16.4% for partial diagnosis.[5,6,7]
According to the WHO Disability Assessment,[1,3,6,7,11]many adults with ADHD not only had psychiatric comorbidities (mood disorders, anxiety disorders,substance use disorders, intermittent explosive disorder)but also significant loss of basic functioning (self-care,mobility, cognition), occupational functioning (days of fwork, loss of productivity, loss of social functioning ),and relational functioning (marital relationship, parentchild relationship, co-worker relationships).
Despite the fact that ADHD often persists into adulthood and has significant impact on the relationships, career, and even the personal safety of the individual,[1,12,13]only 10.1% of population who are suspected to have ADHD were diagnosed and received treatment. This means that most of adults with ADHD have gone overlooked and untreated.
In Thailand, there are very few studies about adult ADHD. Only one study, focused on the prevalence of ADHD in parents of ADHD children, reported 16%of parents had a diagnosis of adult ADHD.[15]The first reason for so few studies in this area is because the previous DSM diagnosis criteria for ADHD were developed only for children and need modification to address the disorder in adults. Secondly, no practical screening instruments for diagnosing adult ADHD were available in Thai especially self-report questionnaires which can screen potential adult ADHD from the general population. The preliminary objective of this study was to develop a Thai version instrument for screening adult ADHD.
WHO developed the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale version 1.1 (ASRS-V1.1) in conjunction with revision of the WHO Composite International Diagnostic Interview(CIDI) for the WHO World Mental Health initial surveys in 2004. It is a standardized and well validated tool for assessing current ADHD symptoms in individuals aged 18 years or older,[8,9,10]it has been translated into many languages and used in many countries. This tool has two forms which are in a 6-question and an 18 question form. The 6-question outperformed the 18-question in terms of sensitivity (68.7% v. 56.3%), specificity(99.5% v. 98.3%), total classification accuracy (97.9% v.96.2%), and cohen’s kappa κ (0.76 v. 0.58).[8]Although the 6-question form has been translated into Thai, it is still in the process of validation and many aspects of the 18-question form would provide more details about adult ADHD. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the reliability and validity of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 - Thai version to assess symptoms and to use it as a screening instrument for adult ADHD.
2. Methods
2.1 Study design
This study was conducted in the kindergarten and the elementary schools which joined the school mental health network of the psychiatric department at Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok.The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the faculty of medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University on January 8, 2013. All subjects provided their verbal and written informed consent prior to study participation.
2.2 Participants
Participants consisted of parents of the students in the classes which were randomly selected from each level of included schools. To be included in this study the participants had to be more than 18 years old and agree to participate in this study. There were no exclusion criteria. 1500 questionnaires were distributed to parents, 816 of them were returned (54.4%). There were 52 and 764 participants who had positive and negative screening results, respectively. 50 participants of each group were randomly selected for telephone interview (Figure 1).
2.3 Measurements
The 18-question ASRS-V1.1 is a symptom checklist instrument which consisted of 18 ADHD symptoms from the DSM-IV-TR criteria[16]for children which have been adjusted for adult ADHD. The questionnaire included the 6-question ASRS-V1.1 as the first six items of the questionnaire. The 18-question version was divided into two groups of symptoms:
1) Inattentive group: questions number 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8,9, 10, 11.
2) Hyperactive/impulsivity group: question numbers 5, 6, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18.
Each item has a 5-point scale in which 0 = never, 1= seldom, 2 = sometimes, 3 = often, 4 = very often. This instrument was translated into Thai according to WHO World Mental Health initiative interview translation guidelines after obtaining permission from the copyright holder. The process of translation included forward translation from the original English to Thai, reaching consensus among the language experts on the forward translation, back translation into English, international harmonization by the authors, and completing and giving feedback by 10 parents. The last modification and adjustment were made for the final version. The WHO CIDI advisory committee provided permission to test the validity and reliability of the final version.
2.4 Procedure
The 18-question ASRS-V1.1 Thai version (ASRS-V1.1 TH)was administrated by 1,500 randomly selected parents between October and November 2014. The results from the questionnaires were divided into two groups: the positive result group and negative result group. The positive result group was the group of participants who responded with 4 or more checkmarks in the darkly shaded area of the first six questions (appendix 1). This method was chosen because in previous studies it had been found to have higher reliability and validity than using the sum score of the full 18-question version of the original ASRS-V1.1.[8]Afterwards, from January to March 2015 fifty randomly selected parents from each group were interviewed by 3 psychiatrists who had experience in diagnosing adult ADHD and were blinded to the groupings.(figure 1). The clinical interview had four parts. First, interviewers used a semi-structured interview according to the symptoms from the ADHD criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth edition (DSM-5, 2013), which were matched with current ADHD symptoms in the adults. Concurrent with DSM-5 criteria a clinical diagnosis of adult ADHD required at least five symptoms of either inattention or hyperactivity/impulsivity during the 6 months before the interview. Secondly,participants were assessed about childhood symptoms of ADHD by asking “Were these symptoms present prior to 12 years of age?”. Thirdly, information about the setting where these symptoms were present was assessed by asking “Have these symptoms occurred in more than two settings such as your home, workplace or other setting?” Finally, the impairment criteria were assessed by asking “Do these symptoms impact your daily life in areas such as working, parenting, or relationships with others?”
Participants who had five symptoms or more in the first part with symptoms occurring prior to age 12, in more than two settings and having an impact on their daily life were grouped into the adult ADHD positive group, the remaining were grouped into the adult ADHD negative group.

Figure 1. Flowchart of the study
2.5 Data analysis
The collected data were analyzed using SPSS version 22.0. Descriptive statistics were used to report frequencies, percent, means, and standard deviations of demographic data. For reliability of the questionnaire,the internal consistency was analyzed with Cronbach’s alpha coefficient.
For validity of the questionnaire, the construct validity and criteria validity were assessed by performing exploratory factor analysis (axis rotation by promax method) and the indices of sensitivity and specificity respectively. The strength of association between the first six questions score and the full 18 questions with a clinical diagnosis was assessed by calculating the area under curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and to determine the proper sensitivity and specificity of the questionnaire for the best cut-off score. Following a study by Swets and colleagues[17], the predictive utility of ASRS-V1.1TH was analyzed by comparing the positive result of the first 6 questions and the total score from the 18 questions.
3. Results
3.1 Descriptive statistics
A total of 816 parents completed the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH from the 1,500 questionnaires which were sent out (54.4% completion rate). Respondents ages ranged from 18 to 72, mean (sd) age was 37.7 (8.36)years, and 454 (56.1%) of the respondents were female.Other demographic data are reported in table 1.
The mean (sd) score of the 18-question version was 21.20 (9.06). The mean (sd) number of items offirst six ques ti ons which were marked in the darkly shaded area was 1.36(1.28) (mean score and SD for each item were reported in table 2). There were 53 par ti cipants (6.8%)which had positive screening results according to the first six items on the ques ti onnaire.

Table 1. Demographic data of study participants (total and those contacted for follow-up)
3.2 Reliability and item analysis
The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of the total 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH was 0.86. It was 0.79 for the inattention subscale and 0.76 for the hyperactive/impulsive subscale.
Table 2 shows the correlation between each item and the ASRS-V1.1 TH total score. Each item had a correlation with the total score of more than 0.3, which means that each item was acceptable and didn’t need to be revised or dropped. The mean scores for all items and the α values (if item deleted) were also shown.
3.3 Validity analysis
3.3.1 Exploratory factor analysis
The sample was adequate for factor analysis (Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin [KMO] measure = 0.920; and χ² of Bartlet t’s test of sphericity = 2989.35 [p < 0.0001]), the loading factor value of every question was > 0.4 and the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH was divided into 4 groups(table 3)
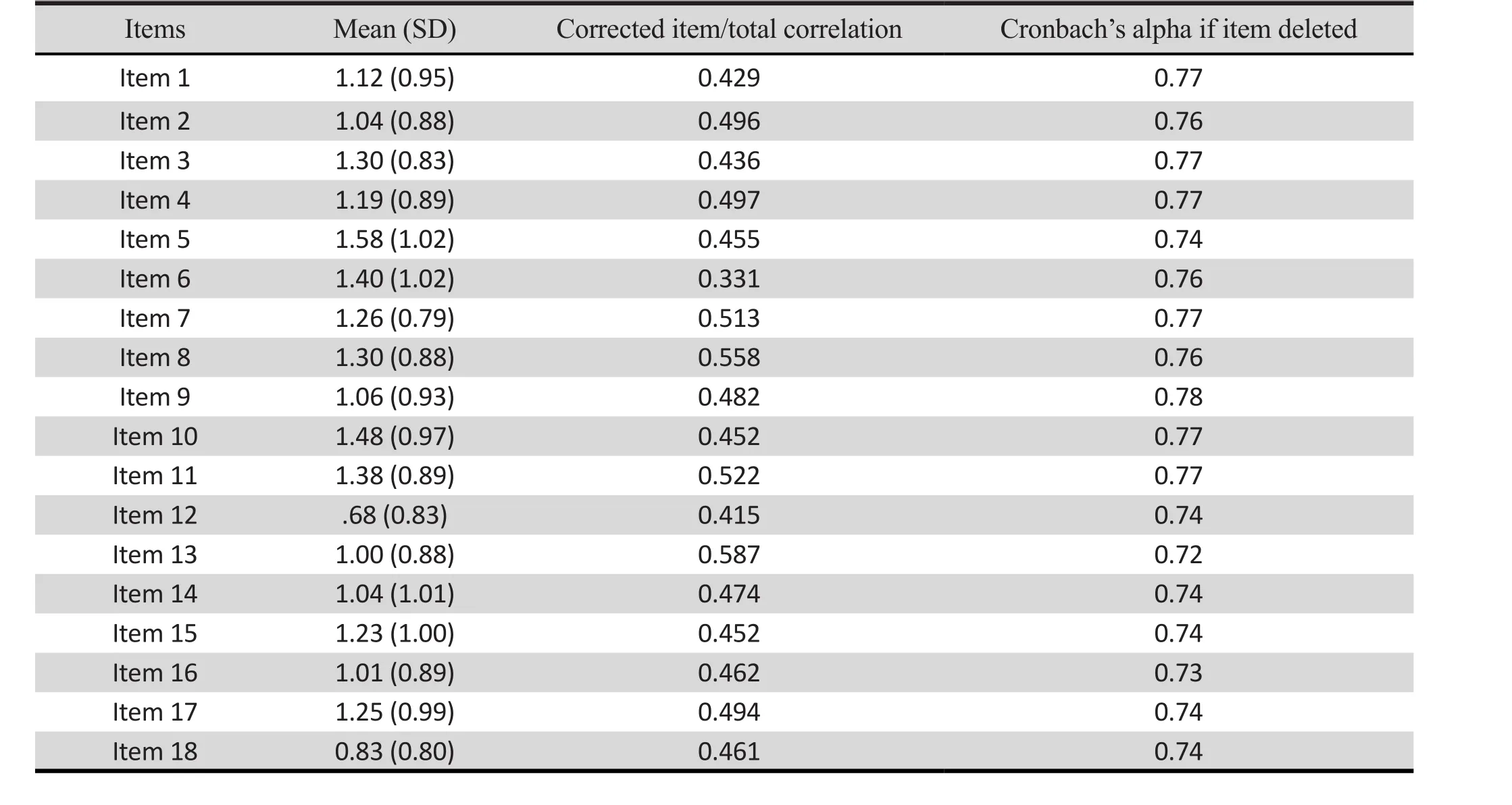
Table 2. Mean and SD scores for each item, correlation between each item and the ASRS-V1.1 TH total score,and Cronbach’s alpha if item deleted
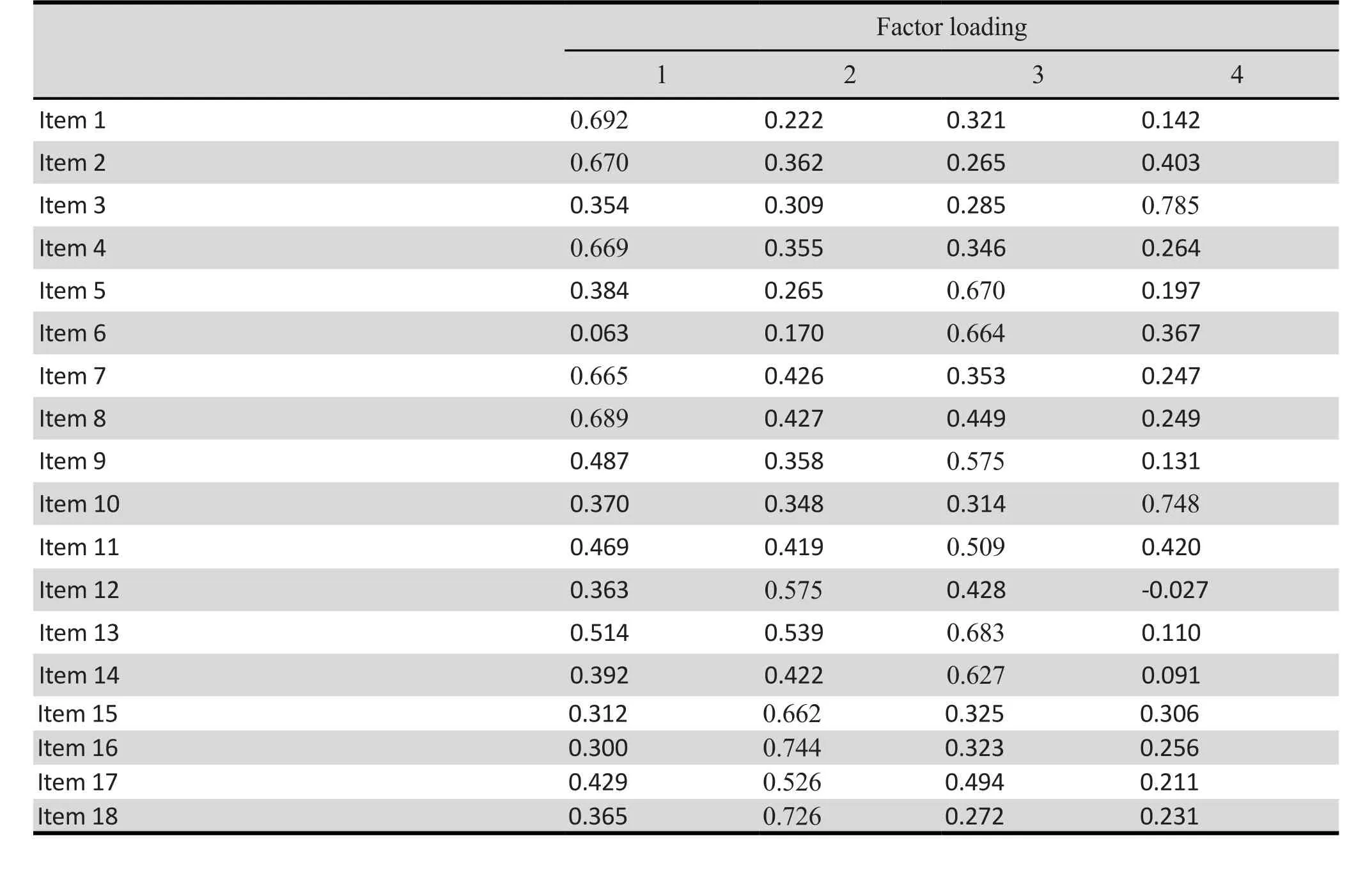
Table 3. Test of construct validity using factor loading for each item of ASRSv1.1-TH
The 1stfactor consisted of questions number 1, 2, 4, 7, 8 The 2ndfactor consisted of questions number 12, 15, 16,17, 18
The 3rdfactor consisted of questions number 5, 6, 9, 11,13, 14
The 4thfactor consisted of questions number 3, 10
3.3.2 Criteria validity
The criteria validity was assessed by calculating the sensitivity and specificity from the results of the psychiatric interview, comparing the positive and negative groups results. The possible cut-off point was estimated by plotting the receiving operation characteristic (ROC) curve. The area under curve (AUC)of ROC curve from the first 6 questions was 0.80 (95%CI:0.68-0.92) (figure 2a). AUC from the full 18 questions was 0.71 (95%CI: 0.55-0.86) (figure 2b).
Sensitivity and specificity for the best cut-offpoint of the first six questions of ASRS-V1.1 TH were 90.91%and 62.50%, respectively. While the sensitivity for the best cut-off of the full 18 questions for an ADHD diagnosis was equal to the first six questions (90.91%),specificity was lower (45.00%). Positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), and negative likelihood ratio(NLR) for the best cut-off of the first six items of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH were 40%, 96.15%, 2.42,and 0.15, respectively. While the PPV, NPV, PLR, NLR of the full 18 questions of the ASRS-V1.1 TH were 31.25,94.74, 1.65 and 0.20 respectively. Sensitivity, specificity,PPV, NPV, PLR, NLR for the other cut-offpoint offirst six questions and total 18 questions are shown in table 4.
AUC of ROC curve of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH in the inattentive area for ADHD-I or ADHD-C diagnosis was 0.62 (95%CI: 0.46-0.79) and AUC of ROC curve in the hyperactive/impulsive area for ADHD-H or ADHD-C was 0.72 (95%CI: 0.55-0.89). Sensitivity and specificity of both the inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive areas are shown in table 5.
4. Discussion
4.1 Main findings
The objective of this study was to test the validity and reliability of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH for screening adult ADHD. The internal consistency using Cronbach’s coefficient was 0.86 which shows good internal consistency for this questionnaire. The internal consistency of the subscales are acceptable for both the inattentive section (α = 0.79) and hyperactive/impulsive section (α = 0.76). These results were higher than the original 6-question ASRS-V1.1TH (α = 0.63-0.72). These results are understandable given that the more items there are on the questionnaire the higher Cronbach’s alpha will be. However these results represented not only good internal consistency for the whole questionnaire but also acceptable internal consistencyin both inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive subscale.Cronbach’s alpha did not increase after removing any of the items, meaning that each item was necessary.

Figure 2. Comparing area under curve (AUC) from plotting receiving operation characteristics (ROC) curve between the 6-question (2a) and 18-question (2b) version of ASRS-V1.1 TH
Using factor analysis to test the construct validity,the loading factor value of every question was high(>0.4) which indicated high constructive validity of this questionnaire. The 18 questions of ASRS-V1.1TH were divided into 4 groups. The 1stFactor consisted of the inattentive subscale items. The 2ndFactor consisted of the hyperactive/impulsive subscale items. The 3rdFactor consisted of the hyperactive/impulsive subscale items except for items 9 and 11 which were in the inattentive subscale. Although items 9 and 11 have the highest loading on the 3rdfactor, we found that they also havea high loading on the 1st factor as well. The reason may come from the fact that these items imply both impulsive and inattentive characters. Concordant with Barkley’s contention, inhibition problems can contribute to problems with inattention, distractibility, and working memory.[18]For the last factor, all items were in the hyperactive/impulsive subscale. By using factor analysis of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH, the questionnaire was divided into 4 factors instead of 2 factors according to inattentive and hyperactive/impulsive symptoms. The reason may be due to all items in 1stfactor reflecting symptoms related to task difficulty, but items in 4thfactor represented forget f ulness symptoms. Items in 3rdfactor reflected symptoms characteristic of restlessness and agitation, while 2ndfactor represented both verbal and behavioral impulsive symptoms. These patterns of behavior may represent a semi-independent dimension of ADHD symptoms in adults, which might different from children. Also this factor analysis result was in concordance with other studies, which examine factor structure in adults. However, they found three factor structures (inattentive symptoms, verbal impulsivity and behavioral impulsivity with other hyperactive symptoms).[19,20]When the factor analysis of the ASRS-V1.1 TH was analyzed with only inattentive items,we also found the same results.
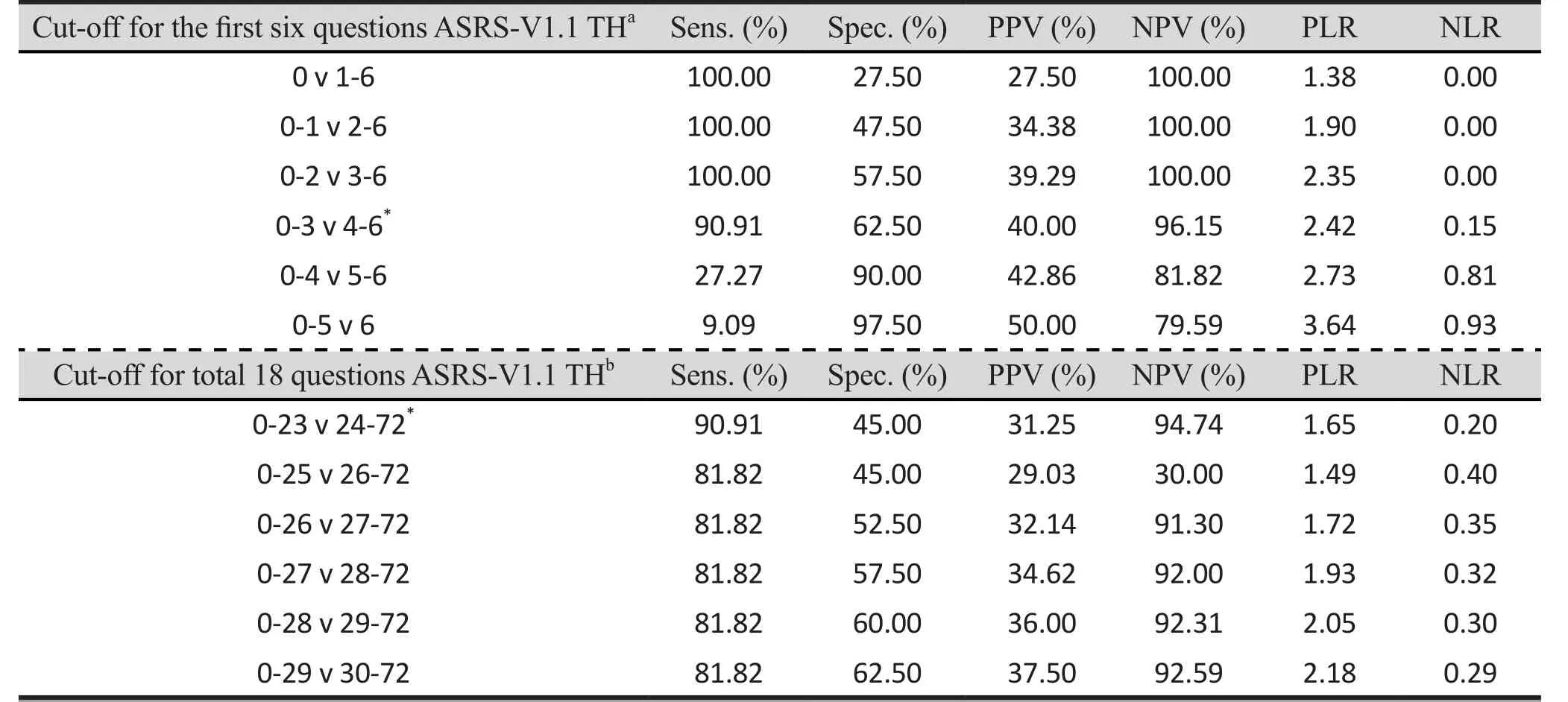
Table 4. Comparing sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, PLR, and NLR of the 6-question and 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH

Table 5. Sensitivity and Specificity of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH for inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive domain
From studying the AUC, the AUC value of the ASRS-V1.1 TH of the first six questions shows good concordance (0.80) while the AUC of the total 18 questions shows fair concordance (0.71). The results indicate better screening potential using only the first six questions compared to the total 18 questions, which is consistent with the results of the original ASRS-V1.1 study.[8]However these AUC results were lower than results testing the original version.[10]
Testing of the criterion validity for the 18 question version of ASRS-V1.1TH showed that sensitivity was 90.91% and specificity was 45.0%. While sensitivity for the best cut-offof the first six questions ASRS-V1.1 TH was equal to the full 18 questions version (90.91%),specificity was higher (62.5%). These results indicate that using the 6-question version of the ASRS-V1.1 TH could be a better screening tool than the 18-question version. This result is in concordance with the results of Kessler and colleagues study using the original version.[8]However the sensitivity and specificity of the 6-question version were different from this original version where the sensitivity was 68.7% and the specificity was 99.5%.[10]However, when we changed the definition of the positive result group to be a group of participants who responded with 5 or more checkmarks in the darkly shade area of the first 6 questions, the sensitivity and the specificity turned out to be 27.27% and 90.00%respectively. This change can reduce false positive results and should be appropriate for use when the sample size is large or when clinical interview is not available but false negative results are a concern.The first strength of this study is the large number of respondents (816 parents). Even though the percentage of overall respondents was 54.4%, the sample is still quite large. Secondly, the reliability and validity of the original ASRS-V1.1 had already been tested and testing of the ASRS-V1.1 TH followed the WHO WMH Initiative Interview Translation Guidelines. Thirdly, adjusted DSM-5 criteria for adult ADHD was matched to criteria for adult ADHD that were used during the clinical interview process. Finally, all interviewers were blinded to the ASRS-V1.1 TH results.
4.2 Limitations
This study has several limitations. Firstly, there were 44 parents who did not attend the clinical interview due to missing data on the questionnaire (e.g. no contact details recorded), and the amount of time it took to complete the questionnaire created difficulty in collecting participants full data. However the demographic data and sum of all ASRSv1.1 TH questions score between the 2 groups were not different, except for gender with the number of male participants being significantly more than female participants (p = 0.004)(table1). Secondly, inter-rater and intra-rater reliability were not tested. However all 3 interviewers worked together in the process of questionnaire translation and had a consensus regarding the details of the semistructured interview for adult ADHD questions. Thirdly,we did not have other informants (as were commonly used in other studies). Results from other studies have shown that self reporting is less accurate than including other’s reports along with self-reporting.[20,21,22]Finally,comorbidity and other medical conditions were not assessed. These conditions may have interfered with our ADHD diagnosis results.[7,23,24,25]
4.3 Implications
The 18-question ASRS-V1.1TH is a psychometrically reliable and valid measure for screening ADHD in adults.Although ASRS-V1.1 TH can be used as a screening tool,the clinical interview with patients and other informants such as parents, spouse, colleagues are still important for diagnosis. Further studies should look at the other benefits from the 18-question ASRS-V1.1TH as a tool for the assessment of ADHD severity.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants for their kind assistance in data collection, and cooperation in answering the research questions. We thank Assoc. Prof. Rattana Saipanich and Assoc. Prof. Dr. Teeradej Chaiaroon for their suggestions regarding data analysis and manuscript revisions.
Funding statements
The authors have no funding source relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflicts of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Ethical approval
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all parents and students in this study.
Authors’ contributions
KK and SP contributed to the design of this study,developed the questionnaire, and prepared the manuscript. KK, SJ, and PW collected and analyzed the data. SH participated and assisted in data collection.All authors have revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
背景:18项成人ADHD自评量表(ASRS-V1.1)是一份针对成人ADHD的筛查量表。
目标:旨在测试泰国版18项成人ADHD筛查量表(ASRS-V1.1)的信度和效度。
方法:将原版18项成人ADHD筛查量表翻译为泰语。经翻译、回译、对比,并通过国内的文化调适、现场测试和最终确认等一系列步骤完成。对1500名来自曼谷幼儿园、小学的家长采用泰国版18项成人ADHD自评量表进行阳性结果和阴性结果筛查,并从中随机选取各50例进行诊断性访谈。最终由3名精神科医生进行临床访谈,根据DSM-5注意缺陷多动障碍诊断标准明确诊断为成人ADHD患者。
结果:泰国版18项成人ADHD筛查量表有较好的内部一致性(Cronbach alpha = 0.86: 其中注意缺陷型Cronbach alpha = 0.78,多动/冲动型Cronbach alpha =0.76)。泰国版18项成人ADHD自评量表效度检验显示问卷有较好敏感性 (90.9%)和特异性 (62.5%)。前6项的AUC为0.80 (95% CI: 0.68 - 0.92), 18项的AUC为0.71(95% CI: 0.55 - 0.86)。
结论:18项ASRS-V1.1泰国版对成人ADHD筛查量表具有较好的信度和效度,特别是量表前6项。
1. Mannuzza S, Klein RG, Bessler A, Malloy P, LaPadula M. Adult outcome of hyperactive boys. Educational achievement, occupation rank, and psychiatric status. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993; 50(7): 565-576. doi: https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820190067007
2. Shekim WO, Kashni J, Beck N. The prevalence of attention deficit disorder in rural Midwestern community sample of nine-year-old children. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 1985;24(6): 765-770
3. Biederman J, Petty CR, Evans M, Small J, Faraone SV. How persistent is ADHD? A controlled 10-year follow-up study of boys with ADHD. Psychiatry Res. 2010; 177(3): 299-304. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2009.12.010
4. Faraone SV, Biederman J, Mick E. The age-dependent decline of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis of follow-up studies. Psycho Med. 2006; 36(2): 159-165. doi:https://doi.org/10.1017/S003329170500471X
5. Faraone SV, Sergeant J, Gillerg C, Biederman J. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: Is it an American condition?World Psychiatry. 2003; 2(2): 104-113
6. Faraone SV, Biederman J. What is the prevalence of adult ADHD? Results of a population screen of 966 adults.J Atten Disord. 2005; 9(2): 384-391. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054705281478
7. Kessler RC, Adler L, Barkley RA, Biederman J, Conner CK,Demler O, et al. The prevalence and correlates of adult ADHD in United States: Results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Am J Psychiatry. 2006; 163(4): 716-723.doi: https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.2006.163.4.716
8. Kessler RC, Adler L, Ames M, Demler O, Faraone SV, Hiripi E,et al. The World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS): A short screening scale for use in the general population. Psycho Med. 2005; 35(2): 245-256. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13956
9. Kessler RC, Adler L, Berkley R, Biederman J, Conner CK,Faraone SV, et al. Patterns and predictors of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder persistence into adulthood:results from national comorbidity survey replication. Biol Psychiatry. 2005; 57(11): 1442-1451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.04.001
10. Kessler RC, Adler L, Gruber MJ, Serawate CA, Spencer T, Van Brunt DL. Validity of the World Health Organization Adult ADHD Self –Report Scale (ASRS) Screener in a representative sample of health plan members. Int J Methods in Psychiatr Res. 2007; 16(2): 52-65. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/mpr.208
11. Klein RG, Mannuzza S, Olasagasti MA, Roizen E, Hutchison JA, Lashua EC, et al. Clinical and functional outcome of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivivity disorder 33 years later. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012; 69(12): 1295-1303. doi:https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.271
12. Schweitzer JB, Cummins TK, Kant CA. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Med Clin North Am. 2001; 85(3):757-777
13. Berkley RA. ADHD in Adult. In: Berkley RA, editor. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment, 3rd ed. New York: The Guilford Press; 2006. p.248-296
14. Biederman J, Faraone SV, Spender T, Wilens T, Norman D,Lapey KA, et al. Pattern of psychiatry comorbidity, cognition,and psychosocial functioning in adult with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1993; 150(12):1792-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.150.12.1792
15. Hongsanguansri S, Sukanich P. Adult ADHD in parents of ADHD children. J Psychiatr Assoc Thailand. 2001; 47(1): 19-30
16. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision.Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000
17. Swets JA. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems.Science. 1988; 240(4857): 1285-1293
18. Barkley RA, Koplowitz S, Anderson T, McMurray MB.Sense of time in children with ADHD: effects of duration,distraction, and stimulant medication. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 1997; 3(4): 359-369
19. Conners CK, Erhardt D, Epstein JN, Parker JDA, Sitarenios G.Self-ratings of ADHD Symptoms in Adults: Normative Data,Factor Structure, Reliability, and Diagnostic Sensitivity.Durham, NC: Duke University Medical Center. Unpublished
20. Span SA, Earleywine M, Strybel TZ. Confirming the factor structure of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in adult, nonclinical samples. J psychopathol Behav Assess. 2002; 24: 129-136. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015396926356
21. Murphy KR, Barkley RA. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults: Comorbidities and adaptive impairments.Compr Psychiatry. 1996; 37: 393-401. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-440X(96)90022-X
22. Barkley RA, Fischer M, Smallish L, Fletcher K. The persistence of attention- deficit/hyperactivity disorder into young adulthood as a function of reporting source and definition of disorder. J Abnorm Psycho. 2002; 111(2): 279-289. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/108705470300700203
23. Belendiuk KA, Clarke TL, Chronis AM, Raggi VL. Assessing concordance of measures used to diagnose adult ADHD.J Atten Disord. 2007; 10(3): 276-287. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054706289941
24. McGough JJ, Smalley SL, MaCracken JT, Yang M, Del’Homme M, Lynn DE, et al. Psychiatric comorbidities in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: findings from multiplex families. Am J Psychiatry. 2005; 162(9): 1621-1627. doi:https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.9.1621
25. Kolar D, Keller A, Golfinopoulos M, Cumyn L, Syer C,Hechtman L. Treatment of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008; 4(1):107-121
成人ADHD自评量表(ASRS-V1.1泰国版)的信度和效度研究
Kiatrungrit K, Putthisri S, Hongsanguansri S, Wisajan P, Jullagate S, Jullagate S
成人ADHD,筛查,泰国,信度和效度,ASRS-V1.1
Background: The adult ADHD Self–Report Scale Thai version (ASRS-V1.1) (18 items) is a questionnaire for screening adult ADHD.
Aim: To test the validity and reliability of the 18-question ASRS-V1.1 Thai version (ASRS-V1.1 TH) as a screening tool for adult ADHD
Methods: The original 18-question ASRS-V1.1 version was translated into Thai. The process was composed of forward-translation, synthesis of the translation, and back translation. Cross cultural adaptation, field testing, and final adjustment were completed consecutively. The 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH were sent to 1,500 parents of kindergarten and elementary school students in Bangkok, Thailand. The diagnostic interview was randomly selected for 50 parents from the positive result group and 50 parents from the negative result group. The clinical interview for confirming diagnosis was run by 3 psychiatrists who were blinded to the results and used DSM-5 ADHD criteria for diagnosis.
Results: The 18-question ASRS-V1.1 TH had satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha = 0.92:Cronbach’s alpha = 0.87 for inattentive scale, Cronbach’s alpha = 0.84 for hyperactive / impulsive scale). For testing the criteria validity, the questionnaire has an adequate. The AUC from the first 6 questions was 0.80(95% CI: 0.68-0.92) while from the 18 questions was 0.71(95% CI: 0.55-0.86).
Conclusions: The 18-question ASRS-V1.1TH is a psychometrically reliable and valid measure for screening adult ADHD in Thai clinical samples, especially the first 6 questions of the questionnaire.
[Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2017; 29(4): 218-227.
http://dx.doi.org/10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217021]
Department of Psychiatry, Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand
*correspondence: Suwannee Putthisri, mailing address: Psychiatric Department, Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, 270 Rama VI Road, Ratchatewi,Bangkok, Thailand. Postcode: 10400. E-Mail: suwannee.sri@mahidol.ac.th
full approval from the institutional review board of the Mahidol University affiliated Ramathibodi Hospital medical faculty on January 8,2013.

Komsan Kiatrungrit graduated with a bachelor's degree from Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University in 2006. He completed residency training in Mahidol University Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Department in 2012. He is a staff member for the residency training program of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Master of Science Program in Child, Adolescent and Family Psychology at Mahidol University and assistant for the associate Dean for Student Affairs at Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University. His research interests are ADHD in adults and ICT use in children and adolescents.

Appendix 1.

Appendix 2.
- 上海精神医学的其它文章
- Sample Size Calculations for Comparing Groups with Continuous Outcomes
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Rash Fever with Anxiety
- Case Study of An Adopted Chinese Woman with Bulimia Nervosa: A Cultural and Transcultural Approach
- Planning Mental Health Needs of China – A Great Leap Forward
- More is Needed before Alzheimer’s Disease can be Conquered
- New Drug Research and Development for Alzheimer’s Pathology:Present and Prospect

