基于EWT-KMPMR组合模型的光伏电站短期功率预测
李 青,孙谊媊,于永军,王 琛,马天娇
基于EWT-KMPMR组合模型的光伏电站短期功率预测
李 青1,孙谊媊1,于永军1,王 琛1,马天娇2
(1. 国网新疆电力有限公司电力科学研究院,电网技术中心,乌鲁木齐 830000;2. 新疆铁道职业技术学院,乌鲁木齐 830000)
为提高光伏电站短期功率预测的精度,提出一种基于经验小波变换(empirical wavelet transform, EWT))和核最小最大概率回归机(kernel mini max probability machine regression,KMPMR)的组合预测模型,对晴天、阴天和雨天3种天气类型下的光伏电站出力分别进行了预测分析。该文首先采用EWT将相似日光伏功率序列分解为具有特征差异的AM-FM分量,然后根据各AM-FM分量的变化特点建立相应的KMPMR预测模型分别进行预测并叠加得到最终预测结果。试验结果表明,相比SVM方法,该文方法在晴天、阴天和雨天可提高预测精度(MAE)分别为56.19%、54.15%和76.33%;相比EMD-KMPMR方法,在降低近一半左右计算规模的同时,可提高预测精度(MAE)分别为9.42%、38.74%和64.52%。以阿克苏地区光伏电站实际运行数据进行试验验证表明,该文方法在3种天气类型下均可取得较高的预测精度。
发电;模型;功率;光伏电站;组合预测模型;经验小波变换;核最小最大概率回归机
0 引 言
光伏发电已逐渐成为仅次于风力发电的可再生清洁能源利用形式,由于其受光照昼夜交替和气象多变等不可控因素的直接影响,具有难以避免的间歇性特点。然而,随着光伏发电装机容量的逐年增长,大规模的光伏并网对电网安全稳定运行造成了很大的冲击,因此,准确的光伏出力预测对电力系统调度部门合理分配火电等常规能源与光伏发电的比例具有极其重要的意义[1-4]。
目前,中国不同地区的短期光伏功率预测模式和方法均有不同,离市区较近且气象观测站资源丰富地区的光伏电站,一般采用物理方法进行预测,该方法通过光伏组件参数、电厂地理位置信息及气象数据等参数来建立太阳辐照传递方程、光伏组件运行方程等物理方程进行预测,但其建模过复杂,模型自适应性差,难以准确预测突变天气下的光伏电站出力[5-9]。中国大多光伏电站均位于偏远地区,地理位置信息和气象观测数据很难准确获取,因此,以神经网络为主的各种统计分析方法在短期光伏功率预测中应用较多,其本质是通过模拟历史积累数据的运行规律来实现光伏电站出力预测。以SVM和其他各种计算智能方法为主的直接预测方法以及以预测太阳辐照强度为基础进而得到光伏功率的间接预测方法目前已经取得了较为成功的应用[10-13]。然而,在数据变化剧烈的非常规天气状态下,基于神经网络的单一预测方法很难取得较高的预测精度。以小波分析和经验模态分解(empiricalmode decomposition,EMD)为主的各种信号预处理方法已被成功地应用在了光伏功率序列预处理中,可实现对初始光伏功率序列的平稳化处理,进而为智能预测方法提供有利的输入数据,有效改善了单一预测方法在光伏功率波动剧烈区间预测精度不高的问题。然而,小波分析法是一种需要事先设定基函数,依赖于主观经验的非自适应分解方法;EMD存在较为严重的模态混叠现象,容易产生虚假的模态分量,且分解分量个数多,计算规模大,增加了组合预测方法的计算量[14-18]。
在EMD的基础上,文献[19]以小波分析为理论框架,提出了经验小波变换(empirical wavelet transform, EWT)法,其核心思想是通过构造合适的正交小波滤波器组对信号的Fourier谱进行自适应划分,以提取具有紧支撑傅里叶频谱的AM-FM成分。EWT是在小波框架下建立的自适应分解方法,相比于EMD,其具有理论性强,计算量小,分解的模态个数少,不存在难以解释的虚假模态分量的优点[20-21]。
核最小最大概率分类机(kernel minimax probability machine classification, KMPMC)通过引进核函数在高维空间实现非线性分类,是一种基于高阶统计信息的特征提取模型。核最小最大概率回归机(KMPMR)建立在KMPMC的基础上,将回归建模问题看作概率建模的一种形式,对模型分布不作具体假设,仅需给定模型数据分布的均值与协方差矩阵,能够最大化模型的预测输出位于其真实值边界内的最小概率[22-25]。
基于上述,本文在EWT和KMPMR的基础上,提出一种基于EWT与KMPMR的组合预测方法。首先利用EWT将相似日光伏功率时间序列分解为包含原光伏功率序列中不同波动尺度局部特征信息的AM-FM分量,然后根据各分量自身特性建立相应的KMPMR预测模型分别进行预测,叠加各分量预测值以得到最终的预测结果。将EWT-KMPMR方法应用于新疆阿克苏地区的光伏电站功率预测中,并与包括MPMR在内的单一预测方法以及EMD-KMPMR组合预测方法进行比较来验证本文方法的预测效果。
1 经验小波变换
EWT方法吸取了EMD和小波分析各自的优点,具有理论性强,计算量小,分解的模态个数少的优点,计算结果与EMD相似,可将原信号()分解成为+1个固有模态函数f(),一个f()可以定义为一组调幅-调频(AM-FM)信号[26]。即:
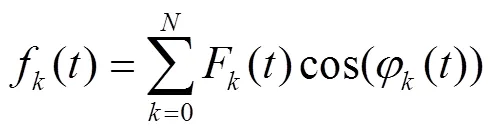
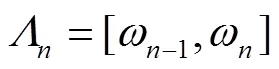
注:Fourier支撑区间[0,π]被分割成个连续的部分,ω选择为信号Fourier谱2个相邻极大值点之间的中点;2τ表示图中阴影部分的宽度。
Note: Section [0,π] of Fourier is devided tosuccessive parts,ωis the midpoints of two adjacent maximum value; 2τis the width of shaded area.
图1傅里叶轴的分割
Fig.1Partitioning of Fourier axis

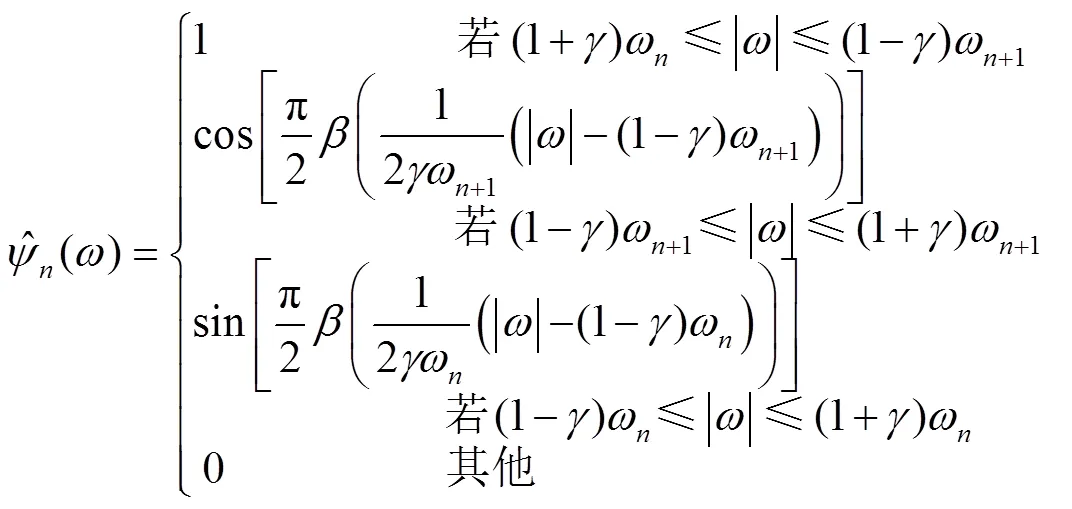
式中


细节系数由经验小波函数与信号内积产生:

近似系数通过尺度函数与信号内积产生:

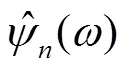

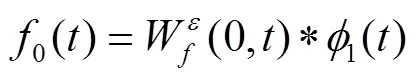

2 核最小最大概率回归机
2.1 回归模型
假定回归数学模型为
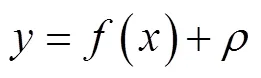


KMPMR是基于引入核函数的最小最大概率分类MPMC建立起来的,形式为
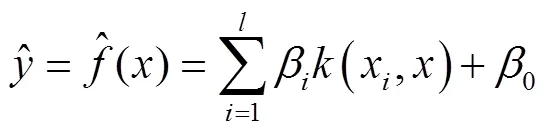
2.2 基于核的最小最大概率分类


即:


可通过式(16)所示的优化问题获得

通过求解式(16)最小化问题得出后,可计算b
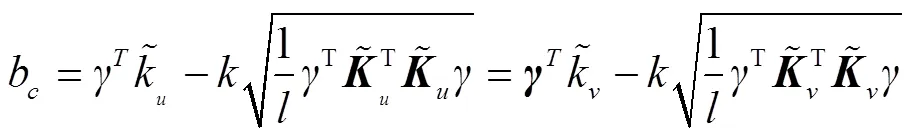
根据式(16)与式(17)分别求得参数,b,可得u,v之间的MPM分界面为

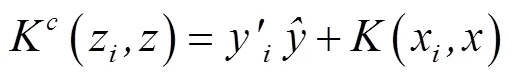

将式(19)所示的核函数代入式(18),通过求解可得式(20)的回归方法:
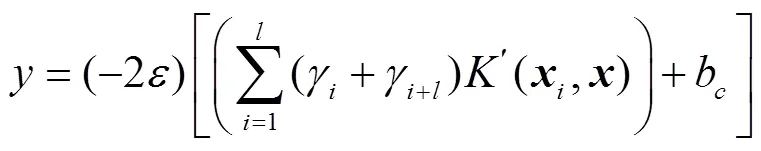


3 EWT-KMPMR方法
3.1 相似日数据选取方法
光伏功率预测中如何有效的获取与待预测日天气类型和光伏出力相似的训练样本直接影响最终预测结果的有效性[28-30]。本文采用Corrcoef函数(计算公式与式(25)一致)提取与待预测日相关度较高的样本来建立预测模型,对降低训练样本规模和提高光伏功率预测精度具有显著的作用。
3.2 算法实现步骤
概言之,EWT-KMPMR方法的实现步骤如下:
1)使用Corrcoef函数筛选与待预测日相关度较高的训练样本。
2)将筛选出的晴天、阴天以及雨天光伏功率序列采用EWT分别进行分解,得到式(7)和式(8)所示的经验尺度分量和经验小波分量。
3)根据各分解分量的不同特点建立不同嵌入维数的KMPMR的预测模型分别进行预测。其中,KMPMR算法实现为:

Step2:通过式(16)和式(17)的分别计算得到和b;
Step3:通过和b的取值结合式(20)可计算得到0、β的取值;
Step4:由计算出的0、β,根据式(12)计算模型的输出;
4)叠加各分量预测结果,得到组合预测结果。
4 短期光伏功率预测试验
4.1 研究概况及方法
阿克苏地区太阳能资源丰富,年均辐射量为5 514.6 MJ/m2,该区域位于新疆中天山南麓,塔里木盆地西北缘,具有典型的暖温带大陆性干旱气候特征,四季分明,冬冷夏热,降水稀少,年、季变化大,日照充足,气温年较差和日较差大;大唐阿克苏光伏一电站位于距阿克苏市直线距离约19 km处,装机总容量为20 MW,厂站光伏阵列安装采用固定支架式安装,倾角为36°,光伏组件类型采用单晶硅太阳电池组件。
本文选取阿克苏光伏一电站实际运行数据做为试验数据来验证EWT-KMPMR方法的预测效果,首先根据气象结果将6、7月份数据划分为晴天、阴天和雨天3种天气类型,然后采用Corrcoef函数分别筛选出3种天气类型下与待预测日相似度较高光伏功率数据作为训练样本,采用EWT对经Corrcoef函数筛选出的相似日光伏功率序列进行分解,使用KMPMR将各分解分量分别进行预测并叠加即可得到最终的预测结果,EWT-KMPMR方法的预测流程如图2所示。
本文按照时间序列建模的方式,由于对原始光伏功率进行了分解,无法准确获得温度及其他气象因素与各分量之间的影响关系,因此仅考虑历史光伏功率值,可建立形如式(22)的KMPMR预测模型:
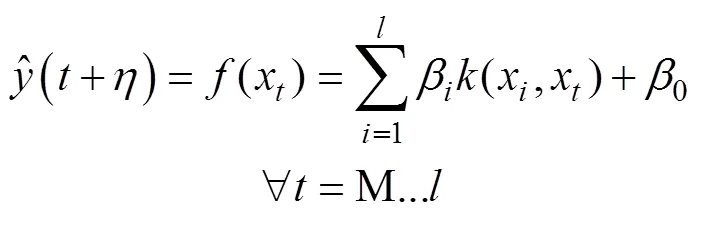

预测评价指标采用均方根误差(root mean square error, RMSE)、平均绝对误差(mean absolute error, MAE)及相关度(),即



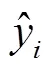

图2 基于EWT-KMPMR预测流程图
4.2 结果与分析
4.2.1 晴天光伏功率预测实例分析
夏日,阿克苏地区的光伏出力大约处在07:45至21:45,采用Corrcoef函数选取阿克苏地区2015年6月中天气类型为晴天的光伏功率数据(图3),以6月23日为基准,可以得到相似度计算结果如表1所示。图3为各相似日光伏出力对比,可以看出,与表1计算结果一致,除6月7日个别样本点外,各相似日的变化趋势和光伏出力基本一致,因此选取表1中前4 d的数据作为训练样本,以15 min为步长,预测6月23日07:45-21:45的光伏发电出力。

表1 相似度计算结果

图3 晴天光伏功率曲线
首先,采用EMD和EWT对5 d(每天07:45至21:45间隔为15 min的57个样本点,共285个样本点)的光伏功率时间序列分别进行分解,分解结果如图4和图5所示,可以看出,EWT和EMD的分解结果差异较大,EWT分解得到3个模态分量(0-2),而EMD分解得到5个模态分量,因此,EWT可以有效地降低构建预测模型的个数,进而降低了组合预测的计算规模。EMD分解得到的IMF分量中产生了一定的虚假模态分量(IMF3-IMF5完全可以用一个模态分量的形式呈现),不利于提取出具有真实物理意义的光伏功率子序列,相比而言,EWT的各分解分量之间具有明显的特征差异。首先,0(经验尺度分量)为平稳分量,几乎可以取得100%的预测精度;1的波动较为规律,与晴天时光伏出力的整个变化趋势相一致,也可以取得很高的预测精度,分量2的变化较为剧烈,会产生一定的预测误差,但其幅值很小,不会为最终的预测结果带来太大的累积误差。

图4 EMD分解结果

图5 EWT分解结果


图6 光伏功率预测结果对比
表2为使用KMPMR对分量(0-2)分别进行预测时超参数()和二分类管道宽度()的取值,各参数均通过交叉验证的方法获取,以得到较优的试验结果。
表3给出了各种预测方法的平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)以及相关度的定量对比,相比其他预测方法。本文方法的预测误差上取得了显著的降低,相比单一预测方法SVM,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了56.19%、55.19%,相比EMD-KMPMR方法,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了9.42%、9.59%。
4.2.2 阴天光伏功率预测实例分析
阴天环境下光伏出力受云层密度等多种因素的影响,具有明显的不规律性和波动性,以7月31日为基准,可以得到2 d(26日和28日)与31日相关度较高的数据(相关度>0.8),相关度计算结果如表1所示。
图7为3个相似日光伏出力对比,可以看出,相比晴天,阴天光伏出力相关度相对不高,但仍然具有一定的相似性,因此选取26日和28日的数据作为训练样本,以15 min为步长,预测7月31日07:45-21:45的光伏发电出力。

表2 不同KMPMR模型的参数取值

表3 EWT-KMPMR与其他预测方法的性能比较

图7 阴天光伏功率曲线
图8和图9为3个相似日光伏序列的分解结果图,本例中,EWT分解得到3个模态分量(0-2),而EMD分解得到6个分量,因此,EWT可以降低一半的组合预测计算规模,而EMD的分解分量中的后4个分量(IMF3-IMF6)中出现了难以解释的虚假模态分量,影响分解效果的同时增加了计算量。在分量0-2的预测模型中,嵌入维分别取值为2、5、7。图10为EWT-KMPMR方法与其他方法的预测结果对比图,可以看出,各种预测方法在变化尖锐的样本点均产生了一定的误差,但相比而言,本文方法的预测效果依然是最好的,相比晴天光伏功率预测(阴天环境下光伏功率的波动性很大),本例中本文方法相比EMD-KMPMR方法预测精度提高程度更加明显。

图8 EMD分解结果

图9 EWT分解结果

图10 光伏功率预测结果对比
通过交叉验证法获取的各KMPMR分预测模型中参数、的取值见表2。
本文方法的预测误差(MAE、RMSE)相比单一预测方法及EMD-KMPMR组合预测方法均降低了很多,相比SVM方法,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了54.15%、53.36%,相比EMD-KMPMR方法,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了38.74%、33.96%(表3)。
4.2.3 雨天光伏功率预测实例分析
图11为包括6月28日在内的共计6 d雨天07:45-21:45时刻的光伏发电出力的序列变化趋势图,可看出雨天的光伏出力整体偏低,结合表1的相似度计算结果,以相关度(>0.8)为选取标准,选取表1中前5日的数据作为训练样本,以15 min为步长,预测6月28日07:45-21:45的光伏发电出力。

图11 雨天光伏功率曲线
图12和图13为6个相似日的光伏序列的分解结果图,同晴天和阴天,EMD仍然分解得到了较多的虚假模态分量,而EWT分解分量中,仅分量2(幅值很小)会为最终的预测结果产生一定的累计误差。

图12 EMD分解结果
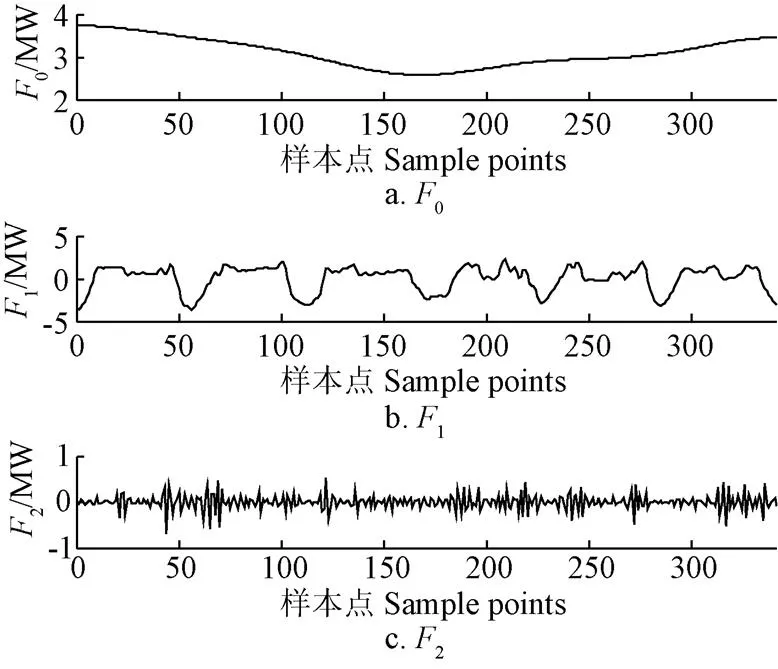
图13 EWT分解结果
超参数()和二分类管道宽度()的取值,各参数均通过交叉验证的方法获取得到见表2。
在分0-2的预测模型中,嵌入维分别取值为3、6、7。图14给出了各种方法方法的预测结果对比图,由图14可见,本文方法的预测效果最好。本文方法的预测误差相比SVM,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了76.33%、78.43%,相比EMD-KMPMR方法,MAE、RMSE指标分别降低了64.52%、65.70%(表3)。

图14 光伏功率预测结果对比
5 结 论
本文提出了一种基于EWT和KMPMR的短期光伏功率组合预测方法。文中以相关度计算结果为依据选取相似日光伏功率作为训练数据,对晴天、阴天和雨天3种光伏电站出力分别进行了预测分析,试验结果表明,相比SVM等单一预测方法,EWT-KMPMR可提高预测精度(MAE)高达(54.15%~76.33%)左右,相比EMD-KMPMR方法,在大量降低组合预测计算规模的同时,可提高预测精度高达(9.42%~64.52%)左右。同时,对比3个试验结果,在阴天和雨天2种数据波动较大的预测实例中,EWT-KMPMR方法预测精度较其他方法提高幅度更大,因此,本文组合预测方法对非常规天气光伏功率出力预测具有很好的应用价值,可有效降低光伏发电功率的随机性对电网的安全可靠运行带来的影响。
[1] 赵争鸣,刘建政,孙晓英. 太阳能光伏发电及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社,2005:34-56.
[2] 龚莺飞,鲁宗相,乔颖,等. 光伏功率预测技术[J]. 电力系统自动化,2016,40(4):140-151.
Gong Yingfei, Lu Zongxiang, Qiao Ying, et al. An review of photovoltaic energy system output forecasting techology[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(4): 140-151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 田春光,田利,李德鑫,等. 基于混合储能系统跟踪光伏发电输出功率的控制[J]. 电工技术学报,2016,31(14):75-83.
Tian Chunguang, Tian Li, Li Dexin, et al. Control strategy for tracking the output power of photovoltaic powergeneration based on hybrid energy storage system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(14): 75-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 汪海瑛,白晓民. 并网光伏的短期运行备用评估[J]. 电力系统自动化,2013,37(5):55-60.
Wang Haiying, Bai Xiaomin. A Very short-term prediction model for photovoltaic power based on ground-based cloud images[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2013, 37(5): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 茆美琴,周松林,苏建徽. 基于风光联合概率分布的微电网概率潮流预测[J]. 电工技术学报,2014,29(2):55-63.
Mao Meiqin, Zhou Songlin, Su Jianhui. Probabilistic power flow forecasting of microgrid based on joint probability distribution about wind and irradiance[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(2): 55-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] Lorenz E, Hurka J, Heinemann D, et al. Irradiance forecasting for the power prediction of grid-connected photovoltaic systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2009, 2(1): 2-10.
[7] 朱想,居蓉蓉,程序,等. 组合数值天气预报与地基云图的光伏超短期功率预测模型[J]. 电力系统自动化,2015,39(6):4-10.
Zhu Xiang, Ju Rongrong, Cheng Xu, et al. A very short -term prediction model for photovoltaic power based on numerical weather predication and ground-based cloud images[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2015, 39(6): 4-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Lorenz E, Hurka J, Heinemann D, et al. Irradiance forecasting for the power prediction of grid-connected photovoltaic systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2009, 2(1): 2-10.
[9] 陈昌松,段善旭,蔡涛,等. 基于模糊识别的光伏出力短期预测系统[J]电工技术学报,2011,26(7):83-89.
Chen Changsong, Duan Shanxu, Cai Tao, et al. Short-term photovoltaic generation forecasting system based on fuzzy recognition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26(7): 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 朱永强,田军. 最小二乘支持向量机在光伏功率预测中的应用[J]. 电网技术,2011,35(7):54-59.
Zhu Yongqiang, Tian Jun. Application of least square support vector machine in photovoltaic power forecasting[J]. Power System Technology, 2011, 35(7): 54-59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Shi Jie, Lee Weijei, Liu Yongqian, et al. Forecasting power output of photovoltaic systems based on weather classification and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2012, 48(3): 1064-1069.
[12] 陈昌松,段善旭,殷进军. 基于神经网络的光伏阵列发电预测模型的设计[J]. 电工技术学报,2009,24(9):153-158.
Chen Changsong, Duan Shanxu, Yin Jinjun. Design of photovoltaic array power forecasting model based on neutral network[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2009, 24(9): 153-158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Shi J, Lee W J, Liu Y, et al. Forecasting power output of photovoltaic systems based on weather classification and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2012, 48(3): 1064-1069.
[14] 张立影,刘智昱,孟令甲,等. 基于小波变换和神经网络的光伏功率预测[J]. 可再生能源,2015,33(2):171-176.
Zhang Liying, Liu Zhiyu, Meng Lingjia, et al. Photovoltaic output power prediction approach based on wavelet transform and neural network[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2015, 33(2): 171-176.
[15] 高相铭,杨世凤,潘三博. 基于EMD和ABC-SVM 的光伏并网系统输出功率预测研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2015,43(21):86-92.
Gao Xiangming, Yang Shifeng, Pan Sanbo. A forecasting model for output power of grid-connected photovoltaic generation systembased on EMD and ABC-SVM[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(21): 86-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 茆美琴,龚文剑,张榴晨,等. 基于EEMD-SVM方法的光伏电站短期出力预测[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2013,33(34):17-24.
Mao Meiqin, Gong Wenjian, Zhang Liuchen, et al. Short-term photovoltaic generation forecasting based on EEMD-SVM combined method [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(34): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Wu Zhaohua, Norden E Huang. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2008, 1(1): 1-41.
[19] Gilles J. Empirical wavelet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(16): 3999-4010.
[20] 黄南天,张书鑫,蔡国伟,等. 采用EWT和OCSVM的高压断路器机械故障诊断[J].仪器仪表学报,2015,36(12):2773-2781.
Huang Nantian, Zhang Shuxin, Cai Guowei, et al. Mechanical fault diadnosis of high voltage circuit breakers utilizing empirical wavelet transform and one-class support vector machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument , 2015, 36(12): 2773-2781. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] Chen J, Pan J, Li Z, et al. Generator bearing fault diagnosis for wind turbine via empirical wavelet transform using measured vibration signals[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 89(5): 80-92.
[22] Lanckriet G R G, Ghaoui L E, Bhattacharyya C, et al. Minimax probability machine[J]. Neural Information Processing
Systems, 2002, 54(22): 801-807.
[23] Strohmann T, Grudic G Z. A formulation for mini max probability machine regression[[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2003, 39(16): 785-792.
[24] Strohmann T R, Grudic G Z. Robust minimax probability machine regression[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 54(5): 1-27.
[25] Kumar M, Mittal M, Samui P. Performance assessment of genetic programming (GP) and minimax probability machine regression (MPMR) for prediction of seismic ultrasonic attenuation[J]. Earthquake Science, 2013, 26(2): 147-150.
[26] Daubechies I, Lu J, Wu H T. Synchrosqueezed wavelet transforms: An empirical mode decomposition like tool[J]. Journal of Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 243-261.
[27] Daubechies I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets[M].Florida: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1992: 117-143.
[28] 傅美平,马红伟,毛建容. 基于相似日和最小二乘支持向量机的光伏发电短期预测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2012,40(16):65-69.
Fu Meiping, Ma Hongwei, Mao Jianrong. Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting based on similar days and least square support vector machine[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2012, 40(16): 65-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 陈通,孙国强,卫志农,等. 基于相似日和CAPSO-SNN 的光伏发电功率预测[J]. 电力自动化设备,2017,37(3):72-77.
Chen Tong, Sun Guoqiang, Wei Zhinong. Photovoltaic power generation forecasting based on similar day and CAPSO-SNN[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2017, 37(3): 72-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 廖卫强,张认成,俞万能,等. 基于相似样本及PCA 的光伏输出功率预测[J]. 太阳能学报,2016,37(9):2377-2385.
Liao Weiqian, Zhang Rencheng, Yu Wanneng, et al. Prediction of output power of photovoltaic based on similar samples and principal component analysis[J]. Acta Energiae Sinica, 2016, 37(9): 2377-2385. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting for photovoltaic power station based on EWT-KMPMR
Li Qing1, Sun Yiqian1, Yu Yongjun1, Wang Chen1, Ma Tianjiao2
(1830000,; 2.830000,)
As one of the renewable energy sources, photovoltaic generation technology has gradually become an important power generation method ranking only the second to the wind power generation technology, however, because of the uncontrollable influence factors that come from the day and night alternation and unstable meteorology condition, the output of photovoltaic power has intermittent and strong nonlinear characteristicsunavoidably. At present, the short-term photovoltaic power forecast models in different areas are not same, and the physical forecasting method was used in the photovoltaic power station that is close to downtown and the area with rich meteorological observatory resources, however, due to its complex modeling and poor adaptivity, it is difficult to predict the photovoltaic station power output accurately when the weather changes suddenly. SVM (support vector machine) and other various computational intelligence methods have been used widely in the short-term photovoltaic power forecast, whose essence is to simulate operation law of the historical data to implement the photovoltaic power station output prediction, so it is still difficult to achieve a higher prediction precision when the data change severely or under abnormal weather conditions by the single forecasting method based on neural network. Based on empirical wavelet transform (EWT) - kernel minimax probability machine regression (KMPMR), a kind of combined forecasting method is proposed to improve the short-term photovoltaic power forecasting accuracy, and the photovoltaic output power on sunny days, cloudy days and rainy days is forecasted and analyzed respectively. EWT inherits the advantages of empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and wavelet transform, and takes the advantages of strong theorization, small amount of computation and fewer decomposed modes. The KMPMR method achieves nonlinear data classification in the high-dimensional space with the help of kernel functions mapping, and minimizes the maximum probability of the classifier which was misclassified. Based on the advantages of EWT and KMPMR, at the same time, in view of the effect of the selection of training sample oneffectiveness of the predicted results, the Corrcoef function is used to obtain the training samples whose photovoltaic power output and change characteristics are parallel to the data of the forecast day, and then the photovoltaic power sequence is decomposed into different AM-FM components with different characteristics by using EWT. Finally, the different KMPMR model is used to forecast each AM-FM component according to their respective characteristics, and the predictive value of each component is superimposed to obtain the final prediction result. The experimental results show that the proposed method can improve the prediction accuracy, with the reduction of MAE (mean absolute error) and RMSE (root mean square error) of 56.19% and 55.19%, 54.15% and 53.36%, and 76.33% and 78.43% compared with the SVM method on sunny days, cloudy days and rainy days. Compared with the EMD-KMPMR method, the MAE and RMSE can be reduced by 9.42% and 9.59%, 38.74% and 33.96%, and 64.52% and 65.70% respectively. In the end, the experimental results show that the proposed method can obtain a higher prediction in 3 kinds of weather by using the actual operation data of photovoltaic power station in Aksu area. Inadditiontothis, through comparing the results of the 3 experiments, the improved prediction accuracy proportion of EWT-KMPMR method in the experiment of cloudy and rainy days is larger than that of sunny days. Therefore, the EWT-KMPMR method has a good application value for the photovoltaic power output prediction under non-conventional weather, which can effectively reduce the influence of randomness on photovoltaic power for the power grid safety and reliable operation.
power generation; models; power; photovoltaic power station; combined forecasting model; empirical wavelet transform; kernel minimax probability machine regression
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.033
TM615
A
1002-6819(2017)-20-0265-09
2017-05-30
2017-07-03
新疆维吾尔自治区重大科技专项发展计划项目:光伏发电关键技术研究与应用(2016A02004);国家电网公司发展计划项目:基于串阻型逆变器的光伏电站并网特性实证性研究与测试(5230DK160006)
李 青,男,甘肃天水人,助理工程师,研究方向为风电及光伏功率预测研究。Email:18699069836@163.com
李 青,孙谊媊,于永军,王 琛,马天娇. 基于EWT-KMPMR组合模型的光伏电站短期功率预测[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(20):265-273. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.033 http://www.tcsae.org
Li Qing, Sun Yiqian, Yu Yongjun, Wang Chen, Ma Tianjiao. Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting for photovoltaic power station based on EWT-KMPMR[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(20): 265-273. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.033 http://www.tcsae.org

