马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机设计
孙 伟,刘小龙,张 华,王虎存,田 斌
马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机设计
孙 伟,刘小龙,张 华,王虎存,田 斌※
(甘肃农业大学机电工程学院,兰州 730070)
为实现全膜覆盖种行覆土马铃薯机械化种植,针对地膜全域覆盖膜上对行覆土等难题,设计了马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机。对样机关键部件进行了分析与设计,确定了液压偏置悬挂装置、跨越式膜上覆土装置、排种系统、碎土整形装置结构及工作参数,解析了核心部件作业机理。田间试验表明,马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机膜下播种深度合格率为86%,种薯间距合格指数为89%,重种指数为5%,漏种指数为4%,种行覆土宽度合格率为92%,种行覆土厚度合格率为94%,邻接行距合格率为86%,地膜采光面机械破损程度为48.1 mm/m2,渗水孔间距合格率为96%。田间性能试验指标均达到国家和行业标准要求,试验结果满足设计要求,能够实现施肥、播种、起垄、全膜覆盖、种行覆土一体化作业。
机械化;设计;农作物;全膜双垄沟;种行覆土;马铃薯种植机
0 引 言
马铃薯地膜全域覆盖沟垄栽培是近年来西北黄土高原旱作区普遍采用的抗旱种植模式,研究表明,该技术比露地栽培增产20%以上[1-3]。但是由于无配套种植机具,目前采用先覆膜、后人工点播的分段作业方式,劳力消耗大,作业质量差,急需实现机械化联合作业。
自20世纪50年代开始,欧美许多发达国家马铃薯生产装备开始向自动化方向发展,马铃薯种植机经历了由小到大、由低级半机械化到高级自动化的发展过程,在技术水平和基础理论研究方面都取得了巨大的成果。典型机具有:英国STANDEN ENGINEERINGLTD公司开发的SP系列马铃薯播种机列马铃薯播种机,德国Grimme-UK公司生产的GL、VL系列马铃薯播种机,美国Crary公司开发了Lockwood 504Pick、506 Pick、508 Pick系马铃薯播种机[4]。这些机型可一次性完成开沟、施肥、播种、起垄、镇压等多项作业,智能化程度高,但基本不设计覆膜功能。20世纪80年代以后,中国马铃薯播种机械发展迅速,先后有十几家科研或教学生产单位开始研制生产马铃薯播种机,技术上日渐成熟[5-9]。如内蒙古农业大学研制的2BSL-2型马铃薯起垄播种机[10],黑龙江八一农垦大学研制的2CM-2型马铃薯播种机[11],黑龙江省农业机械工程科学研究院研制的2CMF-4型悬挂式马铃薯种植机[12],中机美诺科技股份有限公司开发的1240A马铃薯种植机,这些机型基本满足北方不同地域大面积露地栽培农艺要求。青岛洪珠农业机械有限公司研发的2CM-1/2马铃薯播种机,一次性可以完成施肥、播种、起垄、覆膜作业;甘肃酒泉铸陇机械制造有限责任公司研发的2CMLF-2A马铃薯播种机[13],增加了膜上覆土功能,作业后整个膜面上覆盖3~5 cm左右土壤,这2款机型适合半覆膜垄作种植模式。
马铃薯地膜全域覆盖沟垄栽培要求相邻膜边对接,沟垄完全被地膜覆盖。现有覆膜种植技术基本上采用膜侧取土,要求膜与膜之间留有裸露条带,以便覆土机构取土和作业机具行走,不符合地膜全域覆盖沟垄栽培农艺要求。为此,设计了马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机,并进行了田间试验。
1 整机结构及工作原理
1.1 技术要求
研究表明,马铃薯幼芽具有自动破膜能力[14-16],即在播种后膜上覆一层3~5 cm土壤,利用作物发芽时芽不见光,子叶就不散开的特性,依靠膜上的土壤重力和幼芽自然向上作用使幼苗自动破膜,自然出苗。为此,将该特性应用于马铃薯地膜全域覆盖高产栽培技术。图1为马铃薯全膜覆盖种行覆土种植垄形,大小垄总宽120 cm,大垄宽80 cm,小垄宽40 cm,高10~13 cm,用幅宽135 cm地膜全覆盖,大垄上种植马铃薯,播种深度13 cm,种行上方覆盖一层宽度17 cm、厚度3~5 cm土壤。
1.2 总体结构
如图2所示,马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机主要由机架、排肥系统、排种系统、变速箱、开沟器、地轮、跨越式膜上覆土装置、整形碎土装置、覆膜机构构成。

1.排种系统 2.种箱 3.肥箱 4.悬挂机构 5.覆土器 6.开沟器 7.跨越式膜上覆土装置 8.整形碎土装置 9.覆膜机构 10.地轮
1.3 工作原理
工作时,种植机通过液压偏置悬挂装置与拖拉机三点悬挂架连接,在拖拉机牵引下种植机地轮驱动排肥系统和排种系统工作,勺链式排种器将种薯投掷至尖角翼形开沟器开出的“V”型种沟内。位于开沟器侧后方的跨越式膜上覆土装置将土壤铲起并提升越过覆膜机构输送至覆土器,跨越式膜上覆土装置起土后在地表形成2个垄沟,垄沟中间为小垄,两边各形成半个大垄。整形碎土装置进一步修整垄形,覆膜机构将膜铺放到已成形的种床上面。覆土器将跨越式膜上覆土装置输送来的土壤铺洒到种植种行正上方及膜边。机组一趟作业形成中间1个小垄和两侧半个大垄,下趟作业相邻两行半个大垄相接,在大垄垄面中间膜边相接,不留空白带。
2 主要工作部件设计
2.1 液压偏置悬挂装置
马铃薯地膜全域覆盖沟垄栽培机械作业存在幅宽配套问题,即拖拉机轮辐宽度大于种植机作业幅宽,为此,设计了液压偏置悬挂装置。
如图3所示,液压偏置悬挂装置主要由磁感应液压油缸、上滑动支杆、下滑动支杆和悬挂架组成。其中,悬挂架通过上、下滑动支杆和上、下滑动套筒与机架连接,磁感应液压油缸安装在机架与悬挂架之间。工作时,通过调整磁感应液压油缸长度改变机架与悬挂架相对位置,从而实现种植机偏置。
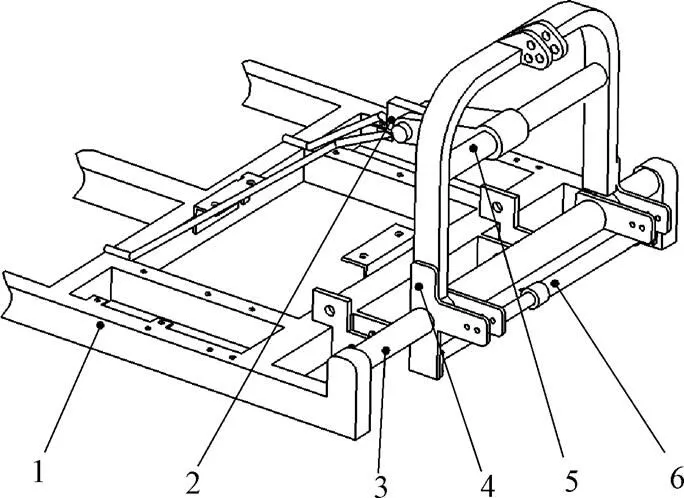
1.机架 2.拉杆 3.下滑动支撑杆 4.悬挂架 5.上滑动支杆 6.磁感应液压油缸
控制系统和液压油缸分别由拖拉机蓄电池和液压系统提供动力。如图4所示,工作时,驾驶员按下按钮开关A1,D1导通,油缸活塞向右移动,活塞杆推动机架向右偏置,当活塞移动至感应开关K2,电路切断,D1停止工作;驾驶员按下按钮开关A2,D2导通,油缸活塞向左移动,活塞杆推动机架向左偏置,当活塞移动至感应开关K1,电路切断,D2停止工作,机架停留在偏置位置。
加肥、加种后,播种机质量为410 kg,偏置时液压油缸需提供的推拉力min=,式中,为钢之间的摩擦系数;为滑动杆提供的支撑力,与播种机质量相等,则液压油缸需提供的推拉力>602.7 N。磁感应开关K1、K2之间的距离为拖拉机轮辐宽度与播种机作业幅宽之差。该机配套25.7 kW轮式拖拉机,拖拉机轮辐宽度为1.5 m,则油缸行程为0.3 m,选择MOB40-300型磁感应液压油缸。
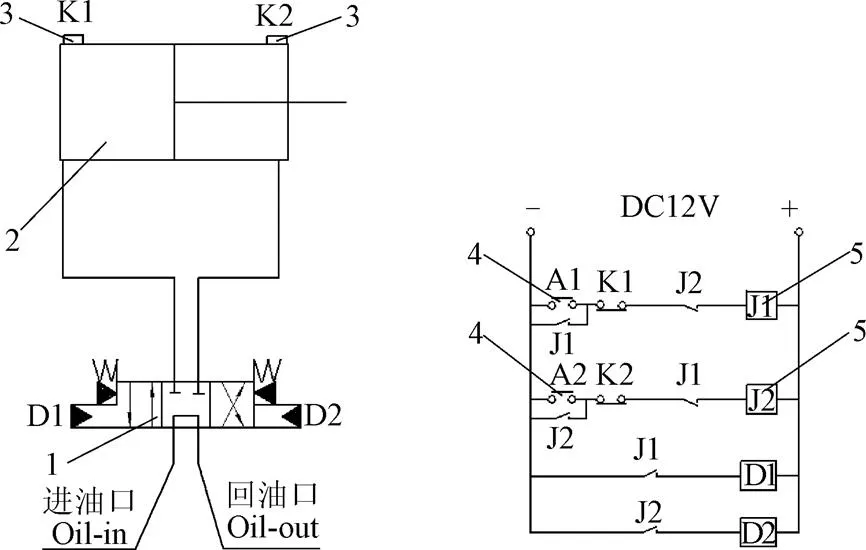

a.液压油路a. Hydraulic circuitb.控制电路b. Control circuit
1.电磁阀 2.磁感应液压油缸 3.磁感应开关 4.按钮开关 5.小型继电器
1.Electromagnetic valve 2.Magnetic induction hydraulic cylinder 3.Magnetic induction switch 4.Button switch 5. Miniature relay
注:A1、A2为按钮开关;K1、K 2为磁感应开关;D1、D2为电磁阀;J1、J2为继电器触点。
Note: A1 and A2 are button switches; K1 and K2 are magnetic induction switches; D1 and D2 are electromagnetic valves; J1 and J2 are relay contacts.
图4 液压偏置悬挂机构原理图
Fig.4 Principle diagram of hydraulic offset suspension mechanism
2.2 跨越式膜上覆土装置
国内对膜上覆土机构的研究主要是针对半膜种植模式,有滚轮式、滚筒式和旋耕式[17-19],这几种膜上覆土机构均采用膜侧取土,横向输送覆土的方式,地膜之间须有裸露条带,不符合全膜覆盖的要求,故采用膜前取土的方式设计了跨越式膜上覆土装置。如图5a所示,跨越式膜上覆土装置由开沟取土铲、刮板升运带、升运器张紧机构、侧向输送器、覆土器、主动轮和从动轮等构成。膜上覆土装置通过正反扣调节器与种植机机架联接,整体装置的安装角度确保作业状态下刮板升运带与水平面的夹角为45°。


a.机构简图a. Mechanism diagramb.轴测图b. Axonometric drawing
1.开沟取土铲 2.张紧机构 3.从动轮 4.刮板 5.升运带 6.整形器 7.膜辊 8.正反扣调节器 9.主动轮 10.护罩 11.侧向输送器 12.覆土器 13.清土装置
1.Shovel for ditching and taking soil 2.Tightening devices 3.Driven wheel 4.Scraper 5.Lifting belt 6.Shaping device 7.Plastic film roller 8.Pros and cons button adjuster 9.Driving wheel 10.Shield 11.Lateral conveyor 12.Covering soil device 13.Cleaning soil device
图5 跨越式膜上覆土装置机示意图
Fig.5 Diagram of spanning type device of covering soil on plastic film
2.2.1 开沟取土铲
开沟取土铲主要作用是将土壤掘起后送至刮土板,起土后在地表形成集雨沟,2个开沟取土铲之间形成集雨面。按农艺要求,2个开沟取土铲间距为400 mm。将开沟取土铲铲面设计成梯形,升运带宽度与升运带一致,取150 mm,为减小刮板升运带工作阻力,避免刮土板直接刮取集雨沟底部土壤,当刮土板运动至从动轮正下方呈竖直状态时,开沟取土铲前端应低于刮土板顶点,两者垂直距离取20 mm。为防止刮板在作业过程中与开沟取土铲尾部干涉,间隙取25 mm。为保证土壤在开沟铲上流动通畅,不产生堆积,经过反复试验,开沟取土铲的入土角取30°,长度取80 mm。
在两刮板相继取土的时间间隔内,机组前进的距离=/,则起土量
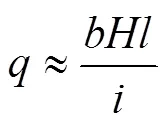
式中为升运带宽度,mm;为挖掘深度,mm;为刮板间距,mm;为升运带速度与前进速度之比。
起土量应大于刮板的输土量,则

式中为刮板升运带与水平面的夹角,(°);为土壤内摩擦角,(°);为刮板高度,mm。
由此可知,起土铲入土深度影响起土量。作业中,由于土壤类型及耕整地方式差异,相同结构参数下机组下陷深度不同导致入土深度不一致,为适应不同工况,如图5b所示,设计了正反扣调节器调整深度。若土壤松软机组下陷较大,可以旋转丝套,使丝套2端的正反丝杆旋入丝套,正反扣深度调节器变短,起土铲入土深度变浅,反之亦然。
2.2.2 刮板升运带
图6为刮板的运动分析,刮板上的土壤表面与水平面呈一夹角,该夹角为土壤内摩擦角。每个刮板上的土壤量即为升运带长度的输送量,体积由端面面积与刮板宽度相乘求得,则一定长度的膜上覆土量为[20]

式中为输送效率,主要与充满系数、升运带打滑率有关。
按种行覆土栽培要求,种行膜面需覆盖宽度17 cm、厚度3~5 cm的土壤,单侧膜边覆盖宽度10 cm、厚度3~5 cm的土壤,则单位长度膜面覆土量8.1×10-3~1.4×10-2m3。该装置采用5×150 mm橡胶帆布传动带,刮板间距取100 mm,刮板高度取60 mm,升运带速度与前进速度之比为1.35。根据(3)式可以算得升运带理论输土量为0.016 m3,故满足设计要求。
为调整升运带的松紧,如图5所示,设计了张紧机构,通过调节两侧拉杆长度带动从动轮轮轴前后移动实现松紧调整。为避免进入升运带背部的土壤随粘附在从动轮上,改变从动轮半径破坏装配关系,设计了清土装置。清土装置安装在张紧机构上,主要由2块橡胶刮片构成,一块抵靠在从动轮上,清理粘附在从动轮上的土壤,另一块抵靠在升运带背部,清理进入升运带背部的土壤。
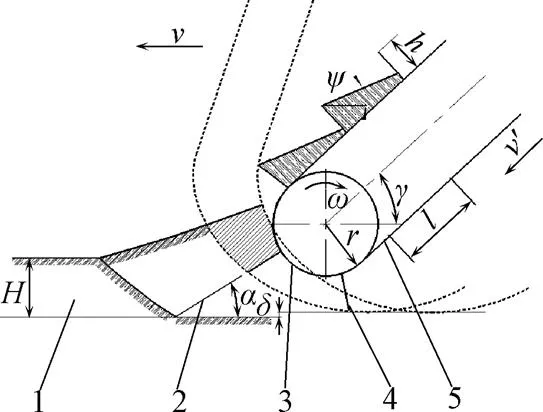
1.土壤 2.开沟取土铲 3.从动轮 4.刮板 5.升运带
1.Soil 2.Shovel for ditching and taking soil 3.Driven wheel 4.Scraper 5.Lifting belt
注:为从动轮角速度,rad·s-1;为前进速度,m·s-1;为起土深度,mm;为升运带与水平面的夹角,(°);为土壤内摩擦角,(°);为从动轮半径,mm;为刮板高度,mm;为刮板间距,mm;为升运带速度,m·s-1;为刮板与沟底间隙;为开沟取土铲的入土角,(°)。
Note:is angular velocity of driven wheel, rad·s-1;is forward velocity, m·s-1;is depth of plowing, mm;isthe angle between the lifting belt and the horizontal plane, (°);is soil internal frictional angle, (°);is radius of driven wheel, mm;is the height of scraper, mm;is scraper spacing, mm;is velocity of lifting belt, m·s-1;is clearance between scraper and bottom, mm;.is penetration angle of shovel for ditching and taking soil, (°).
图6 刮板的运动分析
Fig.6 Motion analysis of scraper
2.2.3 侧向输送器
起土铲作业后在地表形成小垄沟,垄沟间距400 mm,即两套膜上覆土装置中心距为400 mm,而种行间距(2个开沟器之间距离)为700 mm,为了将土壤覆盖在种行正上方,升运带提升的土壤须侧向输送一定距离。该机采用螺旋输送器侧向输送土壤,结构如图7所示。由于刮板升运带宽度为150 mm,覆土宽度为170 mm,则输送器长度为320 mm;为提高输送器排杂能力,防止上季作物根茬和石块堵塞,螺旋输送器外径取150 mm,输送器轴径取48 mm,螺距取150 mm,叶片与底壳的间隙取5 mm;为提高输送器结构强度,防止根茬和石块对叶片的破坏,采用不等厚叶片,厚度1取2.5 mm,取5 mm[21]。

1.升运带 2.护罩 3.螺旋输送器 4.种行覆土 5.覆土器
1.Lifting belt 2.Shield 3.Screw conveyer 4.Covering soil of seedling belt 5.Covering device
注:为叶片厚度,mm;为输送器长度,mm;为螺旋输送器外径,mm;为输送器轴径,mm;为螺距,mm。
Note:is blade thickness, mm;is conveyor length, mm;is outer diameter of the screw conveyor, mm;is shaft diameter of the screw conveyor, mm;is pitch, mm.
图7 侧向输送器结构示意图
Fig.7 Structure diagram of lateral conveyor
螺旋输送器推运量为[22]:
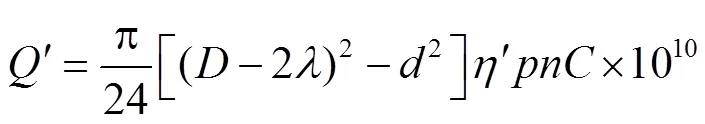
式中为叶片与底壳的间隙,mm;为充满系数,取0.3;为转速,r/min;为输送器倾斜输送系数,由于螺旋输送器水平布置,取1。
在机组1 m/s的作业速度下,螺旋输送器推运量要与升运带输土量匹配,由式(4)可得,螺旋输送器转速取140 r/min,螺旋输送器推运量为0.016 m3,符合设计要求。
2.3 排种系统
勺链式排种器是目前中小型马铃薯播种机普遍采用的一种排种装置,其性能直接影响播种作业质量和效率[23-26]。该机排种器采用12A型链条,每6节布置双侧弯板,用来安装种勺,则种勺间距为114.3 mm,如图8所示。影响勺链式排种器性能的诸多因素中,种勺尺寸和容种高度(即排种链埋入种子层中的长度)最为关键。切块薯质量在50 g左右,马铃薯密度在1 000~1 200 kg/m3之间,则切块薯的当量直径在34.2~36.2 mm之间,考虑到切块薯形体差异较大,种勺内壁为SR30 mm球面,深度为18 mm,为提高充种性能,勺口高度大于两侧高度,勺口采用大半径弧线过渡。
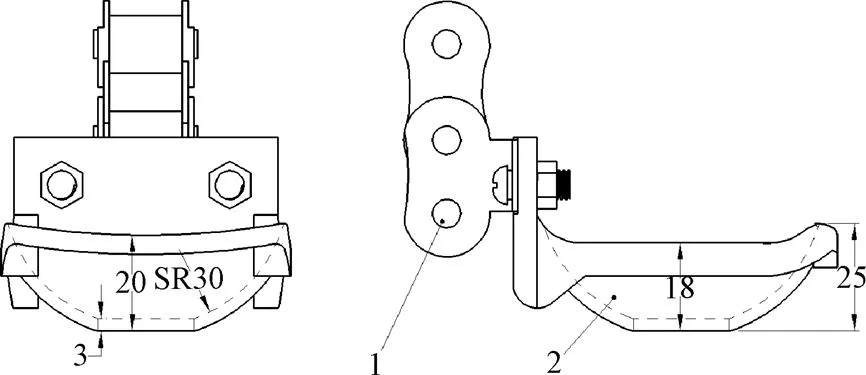

a. 主视图a. Front viewb. 侧视图b. Lateral view
1. 12 A侧板链 2. 取种勺
1. 12 A lateral plate chain 2. Taken seed spoon
图8 勺链式排种器结构示意图
Fig.8 Structure diagram of spoon chain type metering device
实践表明,随着容种高度增加,勺链式排种器漏种率降低,重播率升高。传统单种箱排种系统存在重播率、漏种率不稳定的情况。作业前期种箱薯块数量多,容种高度高,重播率高,后期随薯块数量减少,容种高度降低,漏种率升高。根据实际情况,为便于调整容种高度,对传统种箱进行了优化和改进。如图9所示,种箱主要由补种箱、排种箱、隔板和破拱装置构成,其中,隔板安装在补种箱、排种箱之间,破拱装置安装在排种箱下部。作业时,勺链式排种器顺时针转动,处于种薯内的排种勺在充种、取种过程中带动周围种薯向上运动,在其周围形成一定厚度的带动层。同时,副种箱下部种薯向主排种箱流动,用以补偿取种勺带走种薯。通过调整隔板上下位置,可以改变容种高度。由于切块薯流动性较差,会出现架空现象,为避免补种箱向排种箱补薯不及时导致容种高度下降的问题,在补种箱下面设计了破拱装置。该装置在地轮带动下冲击安装在种箱上的橡胶板,橡胶板振动破拱,解决切块薯由于流动性差造成的架空问题。

1.补种箱 2.排种箱 3.取种勺 4.种薯运动方向 5.调整隔板 6.橡胶板 7.破拱装置
2.4 尖角翼形开沟器
膜顶坐土促生技术要求覆土条带与种行上下对正,防止茎芽顶到裸露地膜造成高温烧苗,为此,设计了尖角翼形开沟器。如图10所示,开沟器由前刀刃、侧翼板和铲柄构成,其中,前刀刃划开根茬(西北黄土高原旱作区多采用马铃薯、玉米轮作),侧翼形成“V”型种沟,保证薯块在沟底的稳定性。前刀刃高度2取130 mm,与播种深度一致;侧翼板高度1取270 mm,后翼高度3取100 mm;开沟器宽度b略大于护种槽宽度,取85 mm;为保证前刀刃对土壤的滑切作用,1>π/2+1,1为土壤与刀刃间的摩擦角,1=14°~38°,1取128°;为使侧翼面上的土壤向后滑移,减小工作阻力,1<π−21,1取104°[22]。
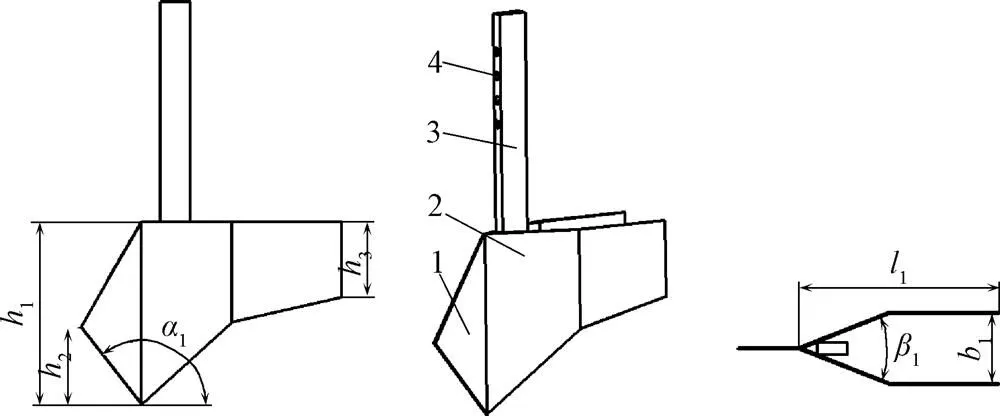

a. 主视图a. Front viewb. 轴测图b. Axonometric drawingc. 俯视图c. Top view
1.前刀刃 2.侧翼板 3.铲柄 4.定位孔
1.Front edge 2.Side wing 3.Handle 4.Location hole
注:1为侧翼板高度,mm;2为前刀刃高度,mm;3为后翼高度,mm;1为刀刃前角,(°);1为侧翼板张角,(°)。
Note:1is height of flank plate, mm;2is height of front edge, mm;3is height of rear wing, mm;1is rake angle of front edge,(°);1is flare angle of flank plate, (°).
图10 尖角翼形开沟器结构示意图
Fig.10 Structure diagram of pointed wing furrower
2.5 碎土整形装置
马铃薯覆膜种植不仅有保墒增温作用,还有灭草功能。这就要求地膜与垄面紧密贴合且无破损。垄面不平整及垄面上的土块是引起地膜破损的原因之一。为保证垄型和垄面平整,防止表层板结土块破坏地膜完整性,设计了碎土整形装置。碎土整形装置结构如图11所示,由轮架、预紧装置、碎土整形辊等构成。作业时,碎土整形辊滚动过程中栅条对土块有破碎功能,在预紧装置压力作用下镇压土壤形成垄型。

1.轴承 2.预紧装置 3.碎土整形辊 4.轮架
2.6 打孔器
为有效利用集雨面收集的降水,需要在沟底膜面上打渗水孔。为了简化结构,在展膜辊上附加了打孔功能。如图12所示,打孔器穿套在展膜辊上,由打孔针、橡胶伸缩套组成。打孔针直径为5 mm,长度25 mm,顶部加工成锥形。为防止打孔针撕膜,同时在打孔位置更好地展膜,在打孔针周围设计了长度100 mm的泡绵护套,打孔针底部插在泡绵护套预留孔内。

1.展膜辊 2.泡绵护套 3.打孔针
3 田间试验
3.1 试验条件
覆土装置田间试验于2017年5月在陇中黄土高原旱农区兰州市西固区西柳沟街道柴家台进行。试验土壤为黄绵土,含水率为17.54%,容重为1.30~1.35 g/cm3,坚实度<250×103Pa,田面较平整、松碎且杂草较少,试验地长度为75 m。使用种薯物理机械特性为平均尺寸56.4 mm×44.3 mm×31.8 mm,含水率为71.3%,每个种薯的平均质量为39.8 g。配套动力为22.1 kW东方红-300型拖拉机。
3.2 试验方案与方法
作业完成后,参照GB/T 25417-2010《马铃薯种植机技术条件》、NY/T 1415-2007《马铃薯种植机质量评价技术规范》和NY/T 987-2006《铺膜穴播机作业质量》标准对播种机作业性能的测定要求,测定种植深度合格率、种行覆土宽度合格率、种行覆土厚度合格率、邻接行距合格率、地膜采光面机械破损程度、渗水孔间距合格率的试验数值[27-30]。
种植深度合格率测定方法:在一块地内沿地块的长度和宽度中点连十字线,将地块划分为4块,随机抽取对角2块作为检测样本。在样本地块中,按对角线取5个小区,每个小区长度为4.2 m(约12个穴距),测定3行,以穴为测点,共测20点。垂直切开种床土壤,在剖面上测量播种深度、种薯间距。


式中为种植深度合格率,%;为种薯间距合格指数,%;0为总测定个数;1为种植深度合格数;2为种薯间距合格数。
地膜采光面机械破损程度测定方法:随机抽取5 m作业垄长,测量采光面机械破损的缝长或边长、采光面展平宽度,以10个测试区的测定平均值为测试结果。
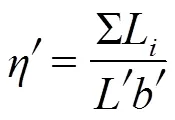
式中为地膜采光面机械破损程度,mm/m2;L为测试区内第处采光面机械破损的缝长或边长,mm;为测试区长度,m;为测试区内采光面展平宽度平均值,m。
种行覆土宽度合格率、种行覆土厚度合格率测定方法:随机选取测定点,在每个测定点上测定种行覆土宽度和种行覆土厚度,求平均值
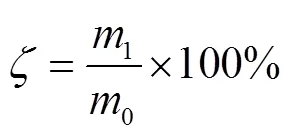

式中为种行覆土宽度合格率,%;为种行覆土厚度合格率,%;0为总测定点数;1为种行覆土宽度合格点数;2为种行覆土厚度合格点数。
邻接行距合格率测定方法:出苗后测定,在邻接行处设定小区,每个小区长5 m,每个小区内在邻接行处均布测10点,测定邻接行距
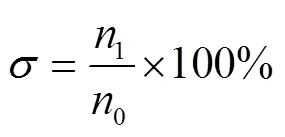
式中为邻接行距合格率,%;0为邻接行距测定总点数;1为邻接行距合格点数。
渗水孔间距合格率测定方法:随机抽取5 m作业垄长,测量渗水孔间距,(300±10)mm为合格,以10个测试区的测定平均值为测试结果。
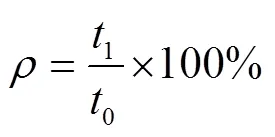
式中为渗水孔间距合格率,%;0为测定总点数;1为间距合格点数。
在测定马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机作业性能指标的同时,与2CM-2马铃薯播种机进行了对比试验,其中,后者采用半覆膜垄作种植模式,试验结果见表1。田间试验表明,马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机膜下播种深度合格率为86%,种薯间距合格指数为89%,重种指数为5%,漏种指数为4%,种行覆土宽度合格率为92%,种行覆土厚度合格率为94%,邻接行距合格率为86%,地膜采光面机械破损程度为48.1 mm/m2,渗水孔间距合格率为96%。由表1可知,设计的马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机满足地膜全域覆盖高产栽培技术要求,田间性能试验指标均达到国家和行业标准要求,排种性能指标均高于2CM-2马铃薯播种机。图13为马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机田间试验及效果。

表1 田间试验结果

a. 播种试验a. Sowing testsb. 苗期效果b. Effect of seedling stage
注:地膜厚度0.008 mm;覆土厚度55 mm;渗水孔间距300 mm。
Note: The thickness of plastic film is 0.008 mm; the thickness of covering soil is 55 mm; the spacing of seepage hole is 300 mm.
图13 马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机田间试验及效果
Fig.13 Field experiments and cultivation effect of potato casingsoil planter in all-in-one machine combined with fertilizing, sowing, ridging, complete film mulching and planting line covering
4 结 论
基于全膜双垄沟马铃薯种植农艺要求与膜顶坐土促生机理,设计了马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机。
1)对样机关键部件进行了分析与设计,确定液压偏置悬挂装置、跨越式膜上覆土装置、排种系统、碎土整形装置结构及工作参数。设计的跨越式膜上覆土装置满足全膜种行覆土农艺要求,由补种箱、排种箱、破拱装置等组成的排种系统,可以调整排种箱容种高度,提升排种系统性能。
2)田间试验表明,马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机膜下播种深度合格率为86%,种薯间距合格指数为89%,重种指数为5%,漏种指数为4%,种行覆土宽度合格率为92%,种行覆土厚度合格率为94%,邻接行距合格率为86%,地膜采光面机械破损程度为48.1 mm/m2,渗水孔间距合格率为96%。田间性能试验指标均达到国家和行业标准要求。
[1] Zhao Hong, Wang Runyuan, Ma Baoluo, et al. Ridge-furrow with full plastic film mulching improves water use efficiency and tuber yields of potato in a semiarid rainfed ecosystem[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 161: 137-148.
[2] Qin Shuhao, Zhang Junlian, Dai Hailin, et al. Effect of ridge-furrow and plastic-mulching planting patterns on yield formation and water movement of potato in a semi-arid area[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2014, 131: 87-94.
[3] 秦舒浩,张俊莲,王蒂,等. 覆膜与沟垄种植模式对旱作马铃薯产量形成及水分运移的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2011,22(2):389-394.
Qin Shuhao, Zhang Junlian, Wang Di, et al. Effects of plastic film mulching and furrow planting pattern formation and water transport on potato yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(2): 389-394. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 毛琼. 国内外大田马铃薯播种机械化的发展现状与未来预测[C]//中国农业工程学会2011年学术年会论文集. 重庆:中国农业工程学会,2011:1-5.
[5] 吕金庆,王英博,李紫辉,等. 加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):19-28.
Lü Jinqing, Wang Yingbo, Li Zihui, et al. Performance analysis and experiment of cup-belt type potato seed-metering device with flow deflector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 19-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 吕金庆,杨颖,尚琴琴,等. 气吸式马铃薯排种器正压吹种零速投种性能优化试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(20):40-48.
Lü Jinqing, Yang Ying, Shang Qinqin, et al. Performance optimization test on air-suction potato seed metering device with positive pressure airflow and zero-speed seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(20): 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 牛康,苑严伟,罗敏,等. 双层种箱式马铃薯排种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(20):32-39.
Niu Kang, Yuan Yanwei, Luo Min, et al. Design and experiment of potato metering device with double-deck seed tank[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(20): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 王希英,唐汉,王金武,等. 双列交错勺带式马铃薯精量排种器优化设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(11):82-90.
Wang Xiying, Tang Han, Wang Jinwu, et al. Optimized design and experiment on double-row cross spoon-belt potato precision seed metering device[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(11): 82-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] Sun Wei, Shi Linrong, Wang Di, et al, Design and test of whole plastic-film mulching on double ridges potato planter[J]. Energy Education Science and Technology Part A: Energy Science and Research, 2014, 32(2): 1317-1324.
[10] 赵满全,窦卫国,赵士杰,等. 2BSL-2型马铃薯起垄播种机的研制[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报,2001,22(1):101-104.
Zhao Manquan, Dou Weiguo, Zhao Shijie, et al. The devolopment of the 2BSL-2 model of potato ridging planter[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2001, 22(1): 101-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 周桂霞,张国庆,张义峰,等. 2CM-2型马铃薯播种机的设计[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2004,16(3):53-56.
Zhou Guixia,Zhang Guoqing,Zhang Yifeng, et al. Design of the potato seeder of model 2CM-2[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang August First Land Reclamation University, 2004, 16(3): 53-56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 杨金砖,吕金庆,李晓明,等. 2CMF-4 型悬挂式马铃薯种植机的研究[J].农机化研究,2010,32(1):127-130.
Yang Jinzhuan, Lü Jinqing, Li Xiaoming, et al. Research of 2CMF-4 potato-planting machine with hanging configuration[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(1): 127-130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 戴飞,辛尚龙,赵武云,等. 全膜面覆土式马铃薯播种联合作业机设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(3):76-83.
Dai Fei, Xin Shanglong, Zhao Wuyun, et al. Design and experiment of combined potato planting machine for covering soil on top of full film surface[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2017, 48(3): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨来胜,王程,何培洪,等. 西北地区马铃薯膜上覆土最佳土层厚度试验[J]. 农学学报,2016,6(7):60-63.
Yang Laisheng, Wang Cheng, He Peihong, et al. Optimum thickness of covering soil on plastic films of potato cultivation[J]. Journal of Agricultural, 2016, 6(7): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 陈建保,张祚恬,郝伯为,等. 膜上覆土对旱作覆膜马铃薯生长的影响[J]. 农业科技通讯,2013(4):55-57.
Chen Jianbao, Zhang Zuotian, Hao Bowei, et al. Effect of soil covering on the growth of potato covered with film on dry land[J]. Agricultural Science and Technology Communication, 2013(4): 55-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 孙伟. 马铃薯自动破膜效应及全膜覆土技术研究[D]. 兰州:甘肃农业大学,2014.
Sun Wei. Study on Effect of the Potato Self-Puncture and the Full Film Covering Soil Technology[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2014.
[17] 李革,艾力·哈斯木,康秀生,等. 地膜播种机螺旋覆土滚筒的参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(6):135-137.
Li Ge, Aili Hasmu, Kang Xiusheng, et al. Parametric optimization of the spiral cylinder of a plastic-film mulch seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(6): 135-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈学庚,赵岩. 棉花双膜覆盖精量播种机的研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(4):106-112.
Chen Xuegeng, Zhao Yan. The research and development of cotton double film mulch sowing machine [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(4): 106-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 邵承会,阚君武,唐可洪. 基于因次分析的盐田铺膜机动力参数研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2003,34(1):121-123.
Shao Chenghui, Kan Junwu, Tang Kehong. Research on power consumption of salt-field filming machine by dimension analysis methods[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2003, 34(1): 121-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 孙伟,刘小龙,石林榕,等. 刮板升运带式膜上覆土装置覆土特性[J]. 机械工程学报,2016,52(7):38-45.
Sun Wei, Liu Xiaolong, Shi Linrong, et al. Covering soil on plastic-film characteristics of scraper lifting belt mechanism[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(7): 38-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 北京农业机械化学院主编. 农业机械学(下)[M]. 北京:农业出版社,1981.
[22] 中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册[M]. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2007.
[23] 吕金庆,杨颖,李紫辉,等. 舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(16):17-25.
Lü Jinqing, Yang Ying, Li Zihui, et al. Design and experiment of cup-belt type potato seed-metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(16): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 孙伟,王关平,吴建民. 勺链式马铃薯排种器漏播检测与补种系统的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):8-15.
Sun Wei, Wang Guanping, Wu Jianmin. Design and experiment on loss sowing testing and compensation system of spoon-chain potato metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 牛康,周利明,苑严伟,等. 勺链式马铃薯排种器自补种系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(增刊1):76-83.
Niu Kang, Zhou Liming, Yuan Yanwei, et al. Design and experiment on automatic compensation system of spoon- chain potato metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(Supp.1): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 王关平,孙伟. 一种马铃薯漏播检测及补偿装置的研制[J]. 农业现代化研究,2016,37(5):1008-1014.
Wang Guanping, Sun Wei. Development of a kind of potato loss sowing detection and compensation device[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2016, 37(5): 1008-1014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] NY/T 1415-2007.马铃薯种植机质量评价技术规范[S].
[28] GB/T 6242-2006. 种植机械马铃薯种植机试验方法[S].
[29] NY/T 987-2006. 铺膜穴播机作业质量[S].
[30] 杨丽,史嵩,崔涛,等. 气吸与机械辅助附种结合式玉米精量排种器[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(增刊):48-53.
Yang Li, Shi Song, Cui Tao, et al. Air-suction corn precision metering device with mechanical supporting plate to assist carrying seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(Supp.): 48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design of potato casingsoil planter in all-in-one machine combined with fertilizing, sowing, ridging, complete film mulching and planting line covering
Sun Wei, Liu Xiaolong, Zhang Hua, Wang Hucun, Tian Bin※
(College of Electromechanical Engineering, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou 730070, China)
Whole plastic mulching and furrow planting has been widely adopted as a drought resistant cultivation model of potato in the arid areas on the Loess Plateau of Northwest China in recent years. Research has shown that the technique increases the production by more than 20% compared with the open field cultivation. However, due to the lack of matching planting machine, the sectional operation is currently adopted, with film mulching and artificially dropping seeds. The mode is labor-consuming and has poor-quality work, which urgently calls for mechanized combined operation. Since the 1950s, potato production equipment has begun to develop in the direction of automation in many developed countries in Europe and America, potato planting machine has changed from the elementary semi-mechanization to the senior automation, and meanwhile great achievements have been made in technical level and basic theory research. After 1980s, potato planter has rapidly progressed in China. More than a dozen scientific research institutes or production units began to develop and produce potato seeder, and with the passage of time, the technology is maturing. Whole plastic mulching and furrow planting requires that adjacent film edge butts and the ridge as well as furrow should be completely covered with plastic film. The existing mulch film planting technology basically takes the way shoveling soil from membrane side. There is a bare strip between the films so as to shovel soil and to operate potato planter. It does not meet the requirement of whole plastic mulching and furrow planting. In order to solve the problems of releasing seedlings and dibbling artificially in potato mulching film cultivation, the growth-promoting mechanism of covering soil on plastic film is applied to potato high-yielding cultivation techniques of whole plastic-film mulching, and a potato planter combined with fertilizing, sowing, ridging, complete film mulching, planting line covering is designed. Aiming at the matching problem of widths that the width of the tractor is larger than the width of the planter, a hydraulic offset suspension device is designed. To solve the problems of wind damage, cavity dislocation and seedlings burnt caused by not having enough volume of covering soil, the device is designed which is suitable for whole plastic-film mulching machine, namely spanning type device of covering soil on plastic film. In view of the problem of poor seeding stability of traditional chain metering device, the seed metering system is optimized and improved. Sharp wing furrower is designed to make the soil strip and the seedlings belt aligned both up and down. A soil-crushing and reshaping device is designed to ensure the shape of ridges. A punch is designed to drill the holes for water seepage on the film surface of the ditch bottom and to effectively make use of the rainfall collected by rainwater collecting surface. The key components of the prototype are analyzed to determine the structure and working parameters of hydraulic offset suspension device, spanning type device of covering soil on plastic film, seed metering system, and soil-crushing and reshaping device. The working mechanisms of the key components are clarified too. Field experiments show that, the qualified rate of sowing depth under the mulching film is 86%, the qualified index of seed potato spacing is 89%, the reseeding and miss-seeding index are 5% and 4% respectively, the qualified rates of soil width and soil depth covered on planting line are 92% and 94% respectively, the qualified rate of adjacent row spacing is 86%, the mechanical damage degree of day lighting surface of plastic film is 48.1 mm/m2, and the spacing qualification rate of water-leaking hole is 96%. Field performance test indices have reached the requirements of the national and industry standards; moreover, the results meet the design requirements, and the machine can realize integrated operation of fertilization, sowing, ridging, whole film mulching and covering soil on planting line.
mechanization; design; crops; complete film mulching on double ridges; covering soil on planting line; potato planter
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.002
S223.2
A
1002-6819(2017)-20-0014-09
2017-06-07
2017-08-14
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51765004);甘肃农业大学伏羲人才项目(GAUFX-02J01);甘肃省科技支撑计划(1504NKCA002)。
孙 伟,副教授,主要从事旱作农机装备技术研究。 Email:sunw@gsau.edu.cn
※通信作者:田 斌,教授,主要从事农业机械设计制造及理论。 Email:tianb@gsau.edu.cn
孙 伟,刘小龙,张 华,王虎存,田 斌. 马铃薯施肥播种起垄全膜覆盖种行覆土一体机设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(20):14-22. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Sun Wei, Liu Xiaolong, Zhang Hua, Wang Hucun, Tian Bin. Design of potato casingsoil planter in all-in-onemachine combined with fertilizing, sowing, ridging, complete film mulching and planting line covering[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(20): 14-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.20.002 http://www.tcsae.org

