培美曲塞联合顺铂与紫杉醇联合顺铂一线治疗转移性肺腺癌的疗效对比观察
陈 萍 胡 平
江苏省盐城市第一人民医院肿瘤科,江苏盐城 224000
培美曲塞联合顺铂与紫杉醇联合顺铂一线治疗转移性肺腺癌的疗效对比观察
陈 萍 胡 平
江苏省盐城市第一人民医院肿瘤科,江苏盐城 224000
目的探讨培美曲塞联合顺铂与紫杉醇联合顺铂治疗转移性肺腺癌的疗效﹑无进展生存期和毒副反应。方法培美曲塞联合顺铂组(PC组):培美曲塞500mg/m2,第1天静脉滴注30min,顺铂75mg/m2,第1~3天每天静脉滴注2h。培美曲塞用药前1周常规预处理,肌肉注射维生素B12 1000μg 1次,叶酸400μg/d,用药前一天,用药当天﹑用药后一天口服地塞米松4mg,每日2次。紫杉醇联合顺铂组(TP组):紫杉醇135mg/m2,第1天静脉滴注2h,顺铂75mg/m2,第1~3天每天静脉滴注2h。两种方案均21d为1个化疗周期,至少完成4周期以上化疗。按照RECIST标准评价化疗疗效和毒性。结果PC组和TP组的有效率分别为45.8%﹑41.7%(P>0.05)。48例患者均可评价疗效,PC组部分缓解11例,稳定8例,进展5例,有效率45.8%,疾病控制率79.2%;TP组部分缓解10例,稳定7例,进展7例,有效率41.7%,疾病控制率70.8%。中位无进展生存期(PFS)分别为5.7个月和4.6个月(P=0.021)。两组主要毒副反应主要为骨髓抑制﹑胃肠道反应和周围神经毒性。紫杉醇联合顺铂组的骨髓毒性及胃肠道不良反应发生率较高。结论培美曲塞联合顺铂治疗转移性肺腺癌的近期疗效与紫杉醇联合顺铂方案相当,但培美曲塞联合顺铂方案无进展生存期延长,毒副反应轻,安全性高,是较理想的化疗方案。
肺腺癌;培美曲塞;紫杉醇;顺铂;化学治疗
近年来,肺癌的发病率和死亡率均排在恶性肿瘤的首位[1-2]。其中,肺腺癌的发病率逐年升高,超过70%的患者为中晚期,常失去手术机会,因此化疗是治疗进展期和转移性肺腺癌的主要手段之一。培美曲塞(pemetrexed)是一种新型的多靶点抗叶酸制剂,作用于叶酸依赖性代谢途径中的多个酶,包括胸苷酸合成酶(TS),二氢叶酸还原酶(DHFR)和甘氨酰胺核苷甲酰基转移酶(GARFT)等,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的生长[3-4]。由于其耐受性较好,不良反应小,与铂类药物联合应用治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)受到推崇。因此,本研究于2013年1月~2016年12月期间,采用培美曲塞或紫杉醇(paclitaxel)联合顺铂(cisplatin)的方案,治疗转移性肺腺癌患者48例,进行对比研究,观察和比较两种联合化疗方案的疗效﹑无进展生存期(PFS)及不良反应。

表1 48例患者的近期疗效
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
我们在2013年1月~2016年12月期间,采用培美曲塞或紫杉醇联合顺铂的方案,治疗转移性肺腺癌患者48例。PC组24例患者,其中女13例,男11例;年龄45~73岁,平均(59.9±8.6)岁;按照病情程度:多处病灶转移9例,单处病灶转移15例。TP组24例患者,其中女14例,男10例;年龄48~72岁,平均(60.5±7.1)岁;按照病情程度:多处病灶转移8例,单处病灶转移16例。48例转移性肺腺癌患者均为初治,所有患者均经病理学或细胞学确诊为肺腺癌,有可测量评价的病灶。对两组患者性别﹑年龄﹑病情程度资料进行比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 治疗方法
PC组:培美曲塞(江苏森豪药业股份有限公 司,H20051288)500mg/m2,第 1天静 脉 滴 注30min,顺铂(齐鲁制药有限公司,H20073653)75mg/m2,第1~3天每天静脉滴注2h。培美曲塞用药前1周常规预处理,肌肉注射维生素B121000ug 1次,叶酸400μg/d,用药前一天,用药当天﹑用药后一天口服地塞米松4mg,每日2次。TP组:紫杉醇(扬子江药业集团有限公司,H20053001)135mg/m2,第1天静脉滴注2h,顺铂75mg/m2,第1~3天每天静脉滴注2h。两种方案均21d为1个化疗周期,化疗前后患者查血常规﹑肝肾功能。每进行2周期化疗后做胸腹部CT,头颅MRI等评价疗效。
1.3 评价标准
近期疗效按RECIST疗效评价标准分为完全缓解(CR)﹑部分缓解(PR)﹑稳定(SD)和进展(PD)。RECIST标准如下[5-6]:CR:所有目标病灶均消失,4周后复测确认;PR:基线病灶最大径之和至少减小30%,4周后复测确认;SD:基线病灶最大径之和有减小但未达PR或有增加但未达PD,4周后复测确认;PD:基线病灶最大径之和至少增加20%,或出现新病灶。CR+PR为总有效率(RR);CR+PR+SD为疾病控制率(DCR)。毒副反应按WHO标准分0~Ⅳ度。无进展生存期(PFS)定义为自首次入组化疗开始至疾病进展或死亡的时间。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS20.0软件进行统计学处理。计量资料以()表示,采用t检验,计数资料以百分比表示,采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 近期疗效
符合入组条件的病例48例,均完成4~6周期化疗,全部病例进入疗效评价及不良反应的评价。PC组24例:部分缓解(PR)11例,稳定(SD)8例,总有效率为45.8%,疾病控制率79.2%;TP组24例:部分缓解10例,稳定7例,总有效率为41.7%,疾病控制率70.8%。两组总有效率和疾病控制率比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.085,0.444,P> 0.05),见表 1。
2.2 毒副反应
培美曲塞联合顺铂组和紫杉醇联合顺铂组的主要毒副反应为骨髓抑制﹑消化道反应等。培美曲塞联合顺铂组出现I度骨髓抑制6例,II度骨髓抑制2例,III度骨髓抑制6例。紫杉醇联合顺铂组出现I度骨髓抑制9例,II度骨髓抑制4例,III度骨髓抑制3例,IV度骨髓抑制1例,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=4.148,P=0.042);其次是消化道反应,培美曲塞联合顺铂组I-II度呕吐6例,III度呕吐2例,紫杉醇联合顺铂组I-II度呕吐15例,4例出现III度呕吐现象,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=10.243,P=0.001),经对症,止吐治疗后均在5d内好转。其中培美曲塞联合顺铂组骨髓抑制和消化道反应的发生率显著低于紫杉醇联合顺铂组。见表2。
2.3 中位生存时间(PFS)
PC组患者的中位无进展生存时间为5.7个月,TP组患者的中位无进展时间为4.6个月,两组的生存曲线比较有统计学意义(χ2=5.349,P=0.021),PC组患者的无进展生存时间比TP组的长。见图1。
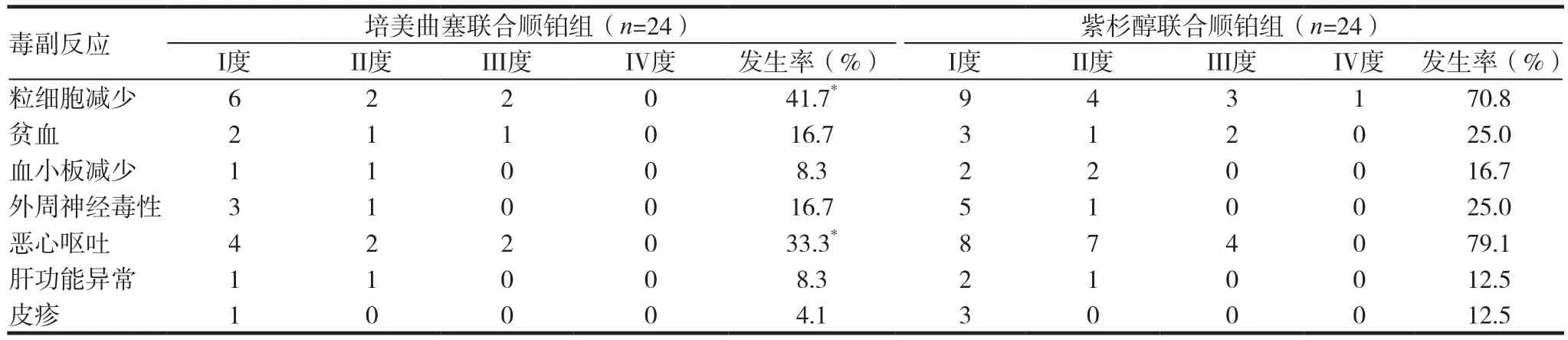
表2 48例患者的毒副反应情况
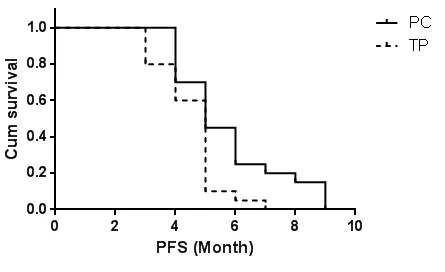
图1 两组患者无进展生存时间曲线比较
3 讨论
肺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤,全球每年肺癌新发病例和相关死亡病例均超过一百万例,非小细胞肺癌占所有肺癌80%以上,70%以上患者发现时已伴有局部或远处转移,已失去手术切除机会,以化疗为主的综合治疗是其主要治疗手段。以铂类为基础的联合化疗方案成为标准的治疗方案,中位生存期约8~11个月[7]。
培美曲塞系多靶点抗叶酸制剂,它作用于叶酸依赖性代谢途径中的多个酶,为多靶点抗叶酸药物。通过破坏细胞内叶酸依赖性的正常代谢过程,抑制细胞复制,从而抑制肿瘤生长,培美曲塞可抑制胸苷酸合成酶﹑二氢叶酸还原酶和甘氨酰胺核苷酸甲酰转移酶的活性,使细胞分裂停止于S期,从而影响胸腺嘧啶核苷酸和嘌呤核苷酸的生物再合成[8-9]。其抗瘤谱广,在肺癌﹑恶性胸膜间皮瘤﹑乳癌﹑妇科肿瘤中应用广泛,毒副反应较低,在NSCLC除鳞癌外的疗效均明显优于其他常用化疗药物[10-13]。因此,FDA在2008年9月30日正是批准培美曲塞可联合顺铂作为局部恶化和转移并伴有非鳞状组织学特征的NSCLC的一线治疗方案。Scagliotti等[14-15]发表了培美曲塞联合顺铂一线治疗晚期NSCLC的研究,结果表明培美曲塞联合顺铂的方案与对照组相比更加具有安全性,同时,腺癌患者和大细胞癌患者的总生存期长于对照组。
本研究应用培美曲塞联合顺铂一线治疗转移性肺腺癌,近期有效率达45.8%,疾病控制率79.2%,中位无进展生存期5.7个月,患者临床获益优于紫杉醇联合顺铂治疗组。骨髓抑制是培美曲塞和紫杉醇最常见的毒副反应,PC组未见IV度骨髓抑制,TP组III-IV度骨髓抑制达16.7%,经积级治疗后均可恢复,未出现治疗相关性死亡。PC不良反应发生率低,耐受性更好,安全性更高,更适宜于老年高龄,体力状况稍差的患者。
综上所述,培美曲塞联合顺铂的方案,用于治疗转移性肺腺癌疗效确切,可延长患者的无进展生存时间,改善患者生活质量,耐受性良好,安全性高,可用于晚期肺腺癌患者的一线治疗。
[1] Siegel R,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2017[J].CA Cancer J Clin.2017,67(1):7-30.
[2] Chen W,Zheng R,Baade PD,et al.Cancer statistics in China,2015.CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(2):115-132.
[3] BlascoA.Sirera R,Terrasa J,et al.Pemetrexed as secondline treatment for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC):Efficacy and correlation with molecular markers[J].J Clm Oncol,2008,26(15 supple):a 8095.
[4] Shaw AT,Varghese AM,Solomon BJ,et al.Pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced,ALK-positive nonsmall cell lung cancer[J].Ann Oncol,2013,24(1):59-66.
[5] Therasse P,Arbuck SG,Eisenhauer EA,et al.New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors.European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer,National Cancer Institute of the United States,National Cancer Institute of Canada[J].J Natl Cancer Inst,2000,92(3):205-216.
[6] Nishino M,Jackman DM,Hatabu H,et al.New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) guidelines for advanced non-small cell lung cancer:comparison with original RECIST and impact on assessment of tumor response to targeted therapy[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol,2010,195(3):221-228.
[7] Yamaguchi T,Nakanishi T,Hayashi M,et al.Efficacy and safety of cisplatin plus pemetrexed as a first-line treatment for Japanese patients with advanced non-squamous nonsmall cell lung cancer-a retrospective analysis[J].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho,2015,42(2):183-187.
[8] Wu M,Yuan Y,Pan YY,et al.Combined gefitinib and pemetrexed overcome the acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in nonsmall cell lung cancer[J].Mol Med Rep,2014,10(2):931-938.
[9] Tièche CC,Peng RW,Dorn P,et al.Prolonged pemetrexed pretreatment augments persistence of cisplatininduced DNA damage and eliminates resistant lung cancer stem-like cells associated with EMT[J].BMC Cancer,2016,16(1):125.
[10] Hanna N,Shepherd FA,Fossella FV,et al.Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy[J].J Clin Oncol,2004,22(9):1589-1597.
[11] Blackhall F,Kim DW,Besse B,et al.Patient-reported outcomes and quality of life in PROFILE 1007:a randomized trial of crizotinib compared with chemotherapy in previously treated patients with ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J].J Thorac Oncol.2014, 9(11):1625-1633.
[12] Vogelzang NJ,Rusthoven JJ,Symanowski J,et al.Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma[J].J Clin Oncol,2003,21(14):2636-2644.
[13] Egloff H,Jatoi A.Pemetrexed for ovarian cancer: a systematic review of the published literature and a consecutive series of patients treated in a nonclinical trial setting[J].Case Rep Oncol,2014,7(2):541-549.
[14] Scagliotti GV,Parikh P,von Pawel J,et al.Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer[J].J Clin Oncol,2008,26(21):3543-3551.
[15] 刘延霞,刘峰.培美曲塞或吉西他滨联合顺铂治疗晚期NSCLC随机对照研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2013,20(22):1748-1750.
Clinical effect of Pemetrexed with cisplation and Paclitaxel with cisplation in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer
CHEN Ping HU Ping
Department of Oncology,Yancheng 1st Hospital of Jiangsu Province,Yancheng 224001,China
Non-small cell lung cancer;Pemetrexed;Paclitaxel;Cisplatin;Chemotherap
R734.2
A
2095-0616(2017)19-28-04
2017-07-03)
[Abstrcat] ObjectiveTo observe the efficacy and toxicity of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated by pemetrexed combined with cisplatin and paclitaxel combined with cisplatin.MethodsPemetrexed with cisplation group(pc):pemetrexed 500mg/m2for 30minutes on the first day and cisplatin 75mg/m2for 2 hours on the first day to the three day by intravenous in fusion.Pretreatment of pretreatment of Permian was pretreated 1 week before,intramuscular injection of 1000μg VB12,folic acid 400μg/d,Oral dexamethasone 4mg at the day before medication,the day after medication and the day after medication,bis in die.Paclitaxel combined with cisplatin group:Patients reveived paclitaxel 135mg/m2for 2 hours on day 1 and cisplatin 75mg/m2for 2 hours on day 1 to day 3 by intravenous in fusion.Each patients was given 4 cycles at least.The chemotherapy was repeated every 21 days and the efficacy and toxicity were then evaluated. ResultsThe total effective of the PC group and TP group is separate 45.8% and 41.7%,(P>0.05).The response rate of all the patients were evaluated.There were 11 partial remission(PR),8 stable disease(SD) and 5 progressive disease(PD)in the PC group,the overall response rate was 45.8% and disease control rate (DCR)was 79.2%.While,there were 10 partial remission(PR),7 stable disease(SD) and 7 progressive disease(PD)in the TP group,the overall response rate was 41.7% and disease control rate (DCR)was 70.8%.The PFS of each group were 5.7 month and 4.6 month(P=0.021).The major toxic reaction included marrow depression, gastrointestinal reaction and peripheral neurotoxicity.Marrow depression,gastrointestinal reaction are more pronounced in paclitaxel combined with cisplatin group.ConclusionChemotherapy with pemetrexed combined with cisplatin in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer is effective and safe,which can improve the patient quality of life.

