浙贝母花脂肪油成分和生物活性研究
彭伟, 黎江华, 刘玉杰, 吴纯洁, 蒋淼,廖博,苏轩艺
浙贝母花脂肪油成分和生物活性研究
彭伟, 黎江华, 刘玉杰, 吴纯洁, 蒋淼,廖博,苏轩艺
目的:研究浙贝母花脂肪油(CFD)的化学成分和生物活性。方法:采用气质联用(GC-MS)对CFD化学成分进行分析。采用DPPH自由基清除实验评价CFD的抗氧化活性;采用小鼠醋酸扭体实验对CFD镇痛活性进行研究。结果:实验结果表明CFD中主要为不饱和脂肪酸(46.96%)、饱和脂肪酸(16.83 %):(9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid (26.55 %)、Linoleic acid (20.41 %)、Palmitic acid (16.43 %)。抗氧化实验结果表明CFD有较强的DPPH自由基清除能力,其半数清除率(EC50)为4.57 mg/mL;醋酸扭体实验结果表明,和对照组小鼠相比,CFD灌胃(100 mg/kg和200mg.kg-1)不仅能显著降低小鼠扭体次数(p< 0.05,p< 0.01),还能延长小鼠扭体潜伏时间(p< 0.05,p< 0.01)。结论:浙贝母花脂肪油含有丰富的不饱和脂肪酸,并且具有潜在的抗氧化和镇痛活性。
Fritillaria thunbergiiMiq;贝母花;脂肪油;不饱和脂肪酸;抗氧化;镇痛
浙贝母为百合科(Liliaceae)贝母属植物浙贝母Fritillaria thunbergiiMiq. 的干燥鳞茎,始载于《神农本草经》,列为上品,具有化痰、止咳和平喘等多种功效;收载于历版中国药典,用于治疗痰热咳嗽,咯痰带血、疮疡肿毒[1]等。目前,国内外对于浙贝母鳞茎部分化学成分和药理活性的研究报道很多,但是对于其茎叶花等地上部分研究报道较少。Kawasaki等曾经对浙贝母地上茎叶进行了化学成分研究,仅从中分离得到浙贝甲素、浙贝乙素等几个生物碱[2];国内学者严铭铭等,从中分离得到丁香脂素、2,5-二甲基苯醌等几个化合物[3]。然而,对于浙贝母地上部分脂肪油类成分的化学成分和生物活性研究,尚未有系统研究报道。
1 实验方法和材料
1.1 实验动物
ICR小鼠,体重18~22g,由上海斯莱克实验动物有限责任公司提供;动物饲养在室温21±1℃、12小时昼夜正常交替的环境下,可自由摄取食物和水。每只实验动物在实验中只用一次。动物实验程序均得到第二军医大学动物管理与伦理委员会同意。
1.2 药材和脂肪油的制备
浙贝母花药材采自浙江省磐安县,经第二军医大学秦路平教授鉴定为百合科贝母属植物浙贝母F.thunbergii 的花。取浙贝母花自然干燥后粉碎,用70 %乙醇回流提取,回收溶剂后得到总提物(TE),总提取物与等量的水混悬后用乙酸乙酯萃取得到乙酸乙提取物。将乙酸乙酯部位经硅胶柱色谱,进行洗脱,收集以石油醚-乙酸乙酯(30∶1-15∶1)洗脱下来的脂肪族流分,合并蒸干,即为浙贝母花脂肪油(CFD)。
1.3 GC/MS分析
采用美国Thermo Focus DSQ 气相色谱-质谱联用仪对CFD进行成分分析。色谱柱为:TR-5 (30 m ×0.25 mm × 0. 25 μm) 色谱柱。
具体GC/MS条件如下:
色谱条件:进样口温度220 ℃;起始温度70℃,以10 ℃/ min升至220 ℃,保持5 min;以5 ℃/min 升至280 ℃,保持10 min ;载气:He; 流速:1mL/min;进样方式:分流比 10:1,进样量:1μL。
质谱条件: 电离方式EI :电离能量70 eV ;离子源温度:250 ℃;传输线温度:250℃;扫描范围:30-700amu。结果与质谱标准库(NIST)进行比对,分析CFD中主要化学成分。
1.4 DPPH自由基清除率实验
将CFD用DMSO稀释得到浓度为20、16、12、8、4、2和1 mg/mL的一系列样品溶液。取一块96孔板,加入新鲜配制的DPPH (0.4 mg/mL),100 μL/孔,待筛样品100 μL /孔,空白孔加DMSO溶液100 μL /孔,充分混匀,样品在孔内浓度为:10、8、6、4、2、1和0.5 mg/mL。封板后室温下避光静置30分钟,酶标仪上测定吸光度值,波长540 nm。样品对DPPH清除率按下式计算: DPPH• 清除率 (%) = (AB) / A × 100%,A:空白对照组化学发光强度值,B:加样品组化学发光强度值,最后计算出半数清除率EC50。
1.5 小鼠醋酸扭体实验
将ICR小鼠按体重随机分组,雌雄各半,每组10只。分为空白对照、阳性对照(吲哚美辛)、CFD组(50,100和200 mg/kg)。造模前1h灌胃给药,0.2 mL/10g。灌胃后1h造模,腹腔注射浓度为0.7%的醋酸溶液,0.1 mL/10g。记录15分钟内小鼠的扭体次数和扭体潜伏期。
1.6 数据统计
所有实验数据均表示为x± SD,组间差异采用双尾Student's t-test进行检验,p< 0.05 被认为具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 CFD化学成分分析
如图1和表1所示,共有24个成分从贝母花脂肪油中被鉴定,代表了90.46 %的CFD组成。根据GC-MS结果,CFD中主要成分为(9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid (26.55 %)、linoleic acid (20.41%)、Palmitic acid (16.43 %)、nonacosane (9.33%)、(Z, Z, Z)-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid和methyl ester(2.44%)。对CFD中化学成分进行分类,结果见表2,可知CFD含大量的不饱和脂肪酸类和饱和脂肪酸类成分,分别占脂肪油中比例为46.96%和16.83%。

图1 浙贝母花脂肪油GC–MS 总离子流图
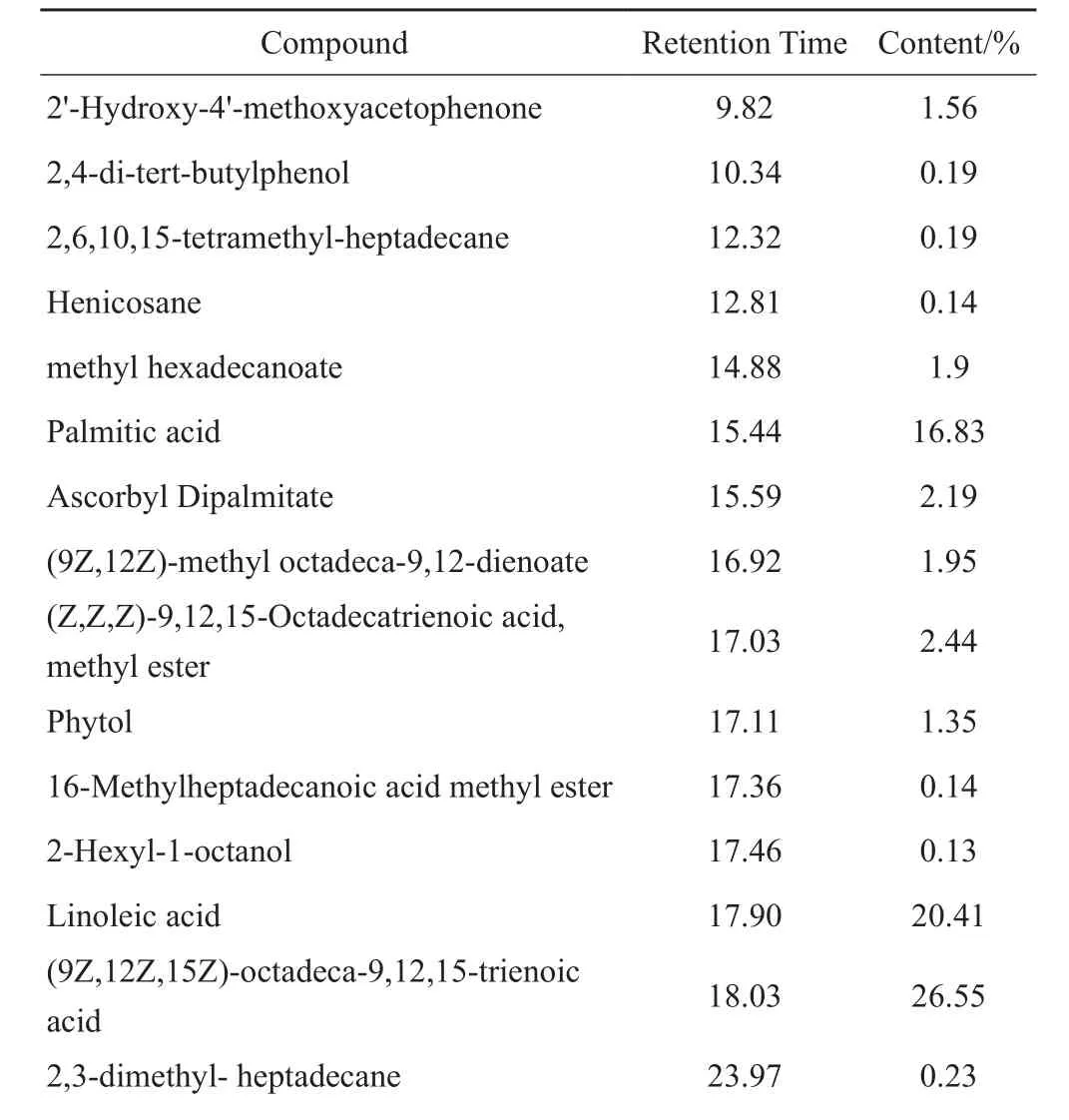
表1 CFD化学成分分析.
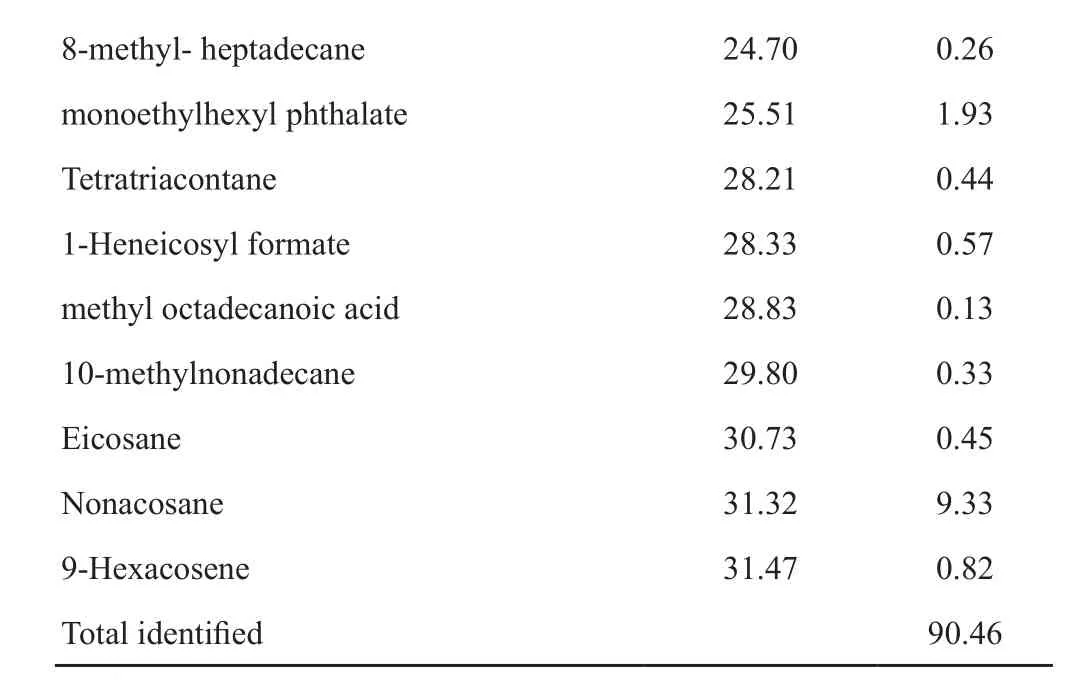
8-m e t h y l- h e p t a d e c a n e 2 4.7 0 0.2 6 m o n o e t h y l h e x y l p h t h a l a t e 2 5.5 1 1.9 3 T e t r a t r i a c o n t a n e 2 8.2 1 0.4 4 1-H e n e i c o s y l f o r m a t e 2 8.3 3 0.5 7 m e t h y l o c t a d e c a n o i c a c i d 2 8.8 3 0.1 3 1 0-m e t h y l n o n a d e c a n e 2 9.8 0 0.3 3 E i c o s a n e 3 0.7 3 0.4 5 N o n a c o s a n e 3 1.3 2 9.3 3 9-H e x a c o s e n e 3 1.4 7 0.8 2 T o t a l i d e n t i f i e d 9 0.4 6
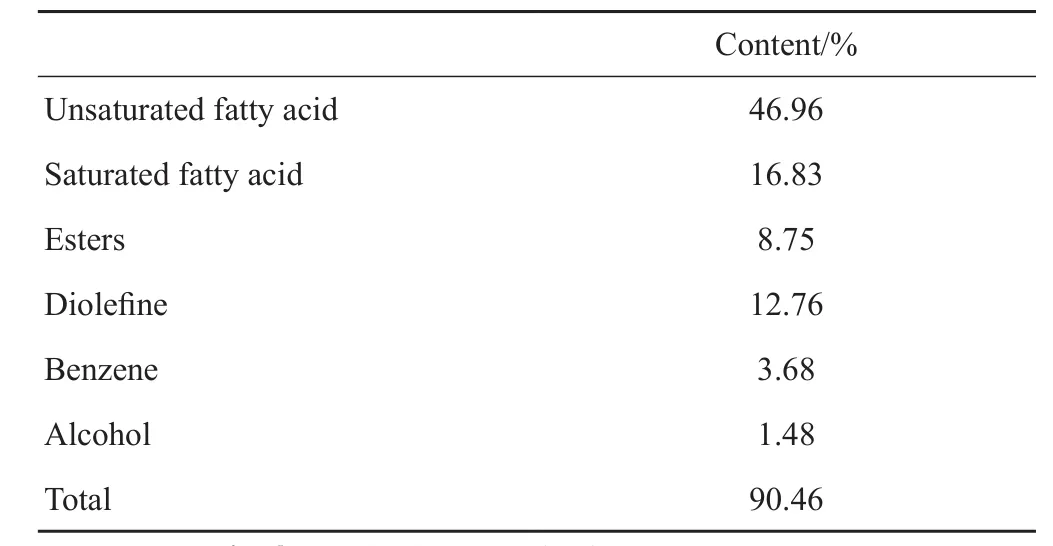
表2 Compositions of the CFD from fl owers ofF. thunbergii.
2.2 DPPH自由基清除能力实验结果
贝母花脂肪油(CFD)DPPH自由基清除实验结果见图3,本次研究表明 CFD具有较强的DPPH自由基清除能力。在0.5~10 mg/mL的浓度范围内,可见明显的浓度依赖关系,经过统计分析后可知,CFD对DPPH自由基的半数清除率EC50为4.57 mg/mL。以上结果提示,CFD具有潜在的抗氧化和抗自由基作用。
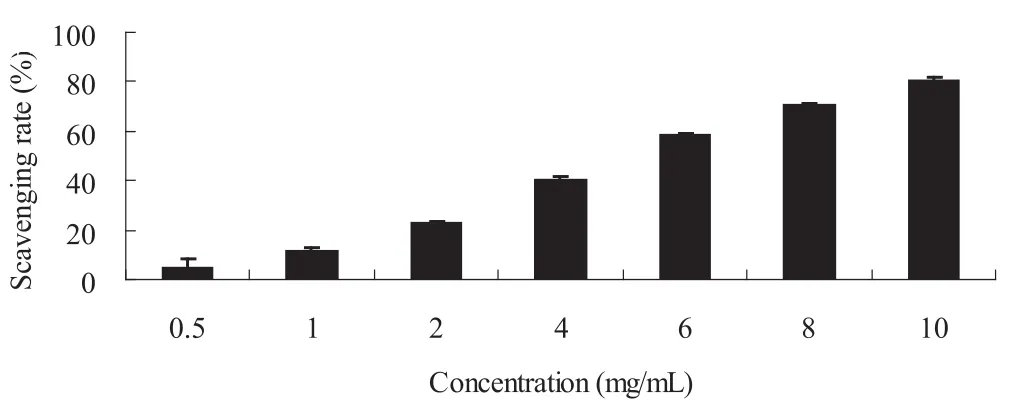
图2 DPPH自由基清除能力实验结果 实验数据表示为SD (n = 4)

图3 CFD对醋酸致痛小鼠扭体扭体次数(A)和 潜伏期(B)的影响. 实验数据表示为SD (n = 10),*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. Control.
2.3 贝母花脂肪油对醋酸致痛小鼠扭体次数和潜伏期的影响
如图3所示,与对照组小鼠相比,灌胃给予CFD(100, 200 mg/kg)能显著减少小鼠在醋酸致痛后的扭体次数(p< 0.05,p< 0.01)并能显著延长小鼠扭体的潜伏期(p< 0.05,p< 0.01)。 以上实验表明,浙贝母花脂肪油具有潜在的镇痛作用。
3 讨论
不饱和脂肪酸具有广泛的生物活性,包括抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降压、降脂以及提高免疫力等,人体摄入足量的脂肪酸有益于保持健康[4,5]。本次研究表明浙贝母花脂肪油中含有大量的不饱和脂肪酸(46.96%)如 (9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid (28.55 %)和linoleic acid(18.41 %);因此,浙贝母花脂肪油有益于人体健康。人体不断的生化反应会带来活性氧(ROS)自由基的产生;在正常的情况下,产生的自由基和人体自身的自由基清除能力是处于动态平衡的,不会造成人体损伤。然而,当人体自身清除能力降低时,ROS会大量积聚在体内而引起细胞和组织损伤,造成人体衰老、慢性心脏疾患甚至癌症[6,7]。近年来,DPPH自由基清除实验被广泛用于评价药物的自由基清除能力和抗氧化能力[7,8]。DPPH自由基是一种稳定的长寿命自由基,溶于有机溶剂呈紫色,在517nm左右有强吸收,有自由基清除剂存在时,DPPH自由基的孤电子被配对,使其颜色变浅,在最大吸收波长处的吸光度变小。因此,可通过在此波长处吸光度的测定来评价抗氧化剂的抗氧化活性,其吸光值愈低,表示试样清除DPPH自由基的能力愈强。本次实验表明,浙贝母花脂肪油具有一定的自由基清除能力,其EC50值为4.57 mg/mL。小鼠醋酸扭体实验是常见的镇痛药物筛选模型,能模拟典型的炎症性疼痛且具备高灵敏性[9,10]。本次实验也结果证明了贝母花脂肪油具备一定的镇痛作用,能抑制醋酸引起的小鼠扭体次数和延长扭体潜伏期。
[1] 国家中医药管理局.中华本草[M].第八册.上海:上海科学技术出版社,1999, 91.
[2] Kitajima J. Basic steroid saponins from aerial parts of Fritillaria thunbergii [J]. Phytochemistry 1982, 21: 187.
[3] 严铭铭,金向群,徐东铭.浙贝母茎叶化学成分的研究[J].中草药,1994,25 (7): 344.
[4] Franke AA, Murphy SP, Lacyey R, et al. Tocopherol andtocotrienol levels of foods consumed in Hawaii [J]. J Agri Food Chem 2007, 55: 769.
[5] Dhakal KH, Jung KH, Chae JH, et al. Variation of unsaturated fatty acids in soybean sprout of high oleic acid accessions [J].Food Chemistry 2014, 164: 70.
[6] Li JL, Zhang M, Zheng TS. The in vitro antioxidant activity of lotus germ oil from supercritical fluid carbon dioxide extraction [J]. Food Chem 2009, 115: 939.
[7] Rengarajan T, Rajendran P, Nandakumar N, et al. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of D-pinitol against 7, 12 dimethylbenz (a) anthracene induced breast cancer in sprague dawley rats [J]. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2014, 4: 384.
[8] Noipa T, Srijaranai S, Tuntulani T, et al. New approach for evaluation of the antioxidant capacity based on scavenging DPPH free radical in micelle systems [J]. Food Res Int 2011,44: 798.
[9] Ali MK, Ashraf A, Biswas NN, et al. Antinociceptive, antiinflammatory and antidiarrheal activities of ethanolic calyx extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. (Malvaceae) in mice [J]. J Integr Med 2011, 9: 626.
[10] Reddy SK, Kumar SA, Kumar VD, et al. Anti-in fl ammatory and analgesic activities of Amorphophallus bulbifer (Roxb)Kunth whole plant [J]. Trop J Pharm Res 2012, 11: 971.
(责任编辑:胡慧玲)
Chemical constituents and bioactivities of the fatty acids of fl owers of Fritillaria thunbergii Miq./
PENG Wei, LI Jiang-Hua, LIU Yu-Jie, WU Chun-Jie, JIANG Miao, LIAO Bo, SU Xuan-Yi//(School of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine; Key Laboratory of Standardization for Chinese Herbal Medicine, Ministry of Education; National Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Systematic Research, Development and Utilization of Chinese Medicine Resources, Chengdu 611137,Sichuan)
Objective:To investigate chemical constituents and bioactivities of fatty acids from the fl owers ofFritillaria thunbergiiMiq. (CFD).Method:GC-MS was used to analyze compositions of CFD. DPPH radical scavenging assay was used to evaluate its antioxidant properties, and the acetic acid-induced abdominal writhing test in mice was performed to investigate its antinociceptive effects.Result:The results revealed that main components of CFD were (9Z, 12Z, 15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid (26.55 %), linoleic acid (20.41 %), Palmitic acid (16.43 %), indicating that CFD contained plenty of unsaturated fatty acid(46.96%) and saturated fatty acids (16.83 %). In addition, results also demonstrated that CFD possessed signi fi cant DPPH radical scavenging activity (EC50= 4.57 mg/mL). Furthermore, CFD (100 and 200 mg.kg-1) can not only significantly decreased the number of writhing episodes induced by acetic acid (p < 0.05, p < 0.01), but also increased the latencies of the writhing (p < 0.05,p < 0.01).Conclusion:CFD possess signi fi cant anti-oxidant and antinociceptive effects, and unsaturated fatty acid is the main constituent of CFD.
Fritillaria thunbergiiMiq; fl owers;fatty acids;unsaturated fatty acid;antioxidant;antinociceptive
R 282
A
1674-926X(2017)03-006-03
成都中医药大学药学院 中药材标准化教育部重点实验室 四川省中药资源系统研究与开发利用重点实验室省部共建国家重点实验室培育基地,四川 成都 611137
彭伟,男,博士研究生在读,从事中药炮制及新制剂研究 Email:pengwei002@126.com
蒋淼(1982-),女,讲师,主要从事中药基础理论及应用研究
Tel:028-61800231 Email:jiangmiaocc@163.com
2016-12-20

