高灵敏度、高稳定度微波辐射计技术研究与实验验证
牛立杰 刘 浩 吴 季
高灵敏度、高稳定度微波辐射计技术研究与实验验证
牛立杰①②刘 浩*①吴 季①
①(中国科学院国家空间科学中心微波遥感重点实验室 北京 100190)②(中国科学院大学 北京 100049)
使用星载综合孔径辐射计进行海洋盐度探测是微波遥感领域的一个研究热点。为了达到海洋盐度探测所需准确度指标,综合孔径辐射计的辐射计单元需要同时具有非常高的灵敏度及定标稳定度。该文研究了一种兼顾高灵敏度和高稳定度的辐射计技术,通过实时定标的方法保证稳定度指标,通过定标数据平均的方法提高灵敏度指标。首次通过频域分析得到最优定标数据平均时间。完成了长时间稳定度实验,实验结果表明:该辐射计稳定度在3天(3 d)内优于0.12 K,灵敏度优于0.1 K,达到了海洋盐度探测综合孔径辐射计对辐射计单元的需求。
高稳定度辐射计;L波段微波辐射计;噪声注入式辐射计;海洋盐度
1 引言
星载微波辐射计技术使全球海洋盐度测量成为可能[1]。海洋盐度探测辐射计需要有很高的灵敏度、稳定度、空间分辨率、刈幅指标。2009年欧空局发射了SMOS卫星,采用Y型阵2维综合孔径体制;2011年美国发射了Aquarius卫星,采用“推帚式”真实孔径体制。两者发挥了重要作用,也发现了一些问题。文献[2,3]介绍了SMOS载荷及最新的数据处理结果,文献[4,5]介绍Aquarius载荷、状态及测量结果。文献[6]对比了两颗卫星数据,总结问题:(1)2颗卫星都未采用海温同步测量手段;(2)都未解决RFI问题;(3) 2维综合孔径辐射计体制可实现大刈幅高分辨率,但系统复杂,误差大;(4)实孔径体制空间分辨率低,观测刈幅小,不能满足应用需求。
中国科学院国家空间科学中心吸取经验,提出“主被动联合微波成像仪”(Microwave Imager Combined Active and Passive: MICAP)方案[7,8]。主载荷是一台L波段1维综合孔径辐射计,可实现高空间分辨率及观测刈幅指标,同时避免复杂度过高的难题。1维综合孔径辐射计由15个辐射计单元组成,要求3天(3 d)内稳定度优于0.12 K,灵敏度优于0.1 K。
国内研究方面,文献[9]提出使用实时定标提高辐射计稳定度。文献[10]采用一种数字增益波动自动补偿微波辐射计,航空实验证明能达到0.2 psu的盐度分辨率。本文研究一种兼顾灵敏度和稳定性的辐射计,实时定标实现高稳定度,定标平均方法提高灵敏度。频域分析得到最优定标平均时间,并完成时序与注入噪声的优化及辐射计实验,指标达到了MICAP的辐射计单元要求。本文研究为MICAP计划奠定基础,同时还将应用于“全球水循环卫星探测计划”(Global Water Cycle Observation Mission: WCOM)的L/S/C三频全极化综合孔径辐射计系统中[11]。
2 高灵敏度、高稳定度辐射计理论基础
2.1辐射计的灵敏度
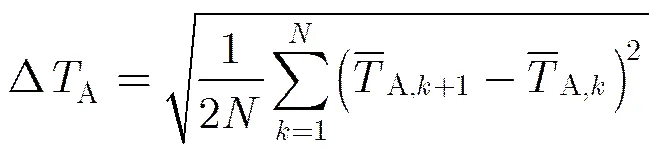
2.2辐射计的稳定度
辐射计的不稳定性主要由系统参数变化带来:增益和接收机噪声温度漂移;定标平面前天线、无源器件及电缆物理温度波动导致的自身噪声波动;定标源(负载、噪声源)噪声温度波动。精密温控、高稳定噪声源、实时定标等可以减小这些不稳定性。
文献[13]中提出了漂移方差的概念,表示辐射计积分时间为时,周期为的漂移的大小:
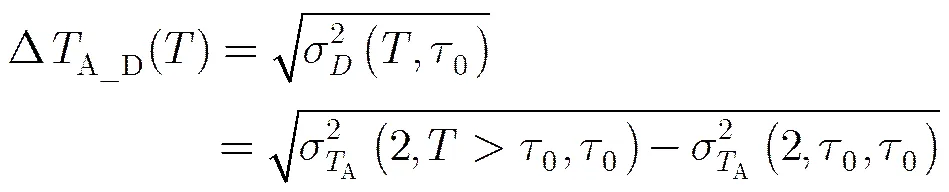
其中,
2.3高灵敏度、高稳定度辐射计类型的选择
辐射计实现高稳定度需要实时定标,但实时定标会增加噪声,降低灵敏度。噪声注入辐射计实时定标修正增益和接收机噪声温度的漂移,稳定度高,但定标噪声导致灵敏度比全功率辐射计差。本文选用噪声注入式辐射计,在获得高稳定度的同时通过特定的定标数据平均方法(详细见3.4节)减小定标噪声,可以兼顾高灵敏度和高稳定性的指标需求。
3 高灵敏度、高稳定度噪声注入式辐射计理论分析
3.1 噪声注入式辐射计原理
传统噪声注入辐射计使用硬件技术实现检波电压抵消,通过脉宽反推天线温度。现在可以使用数字技术对电压采样后直接数字处理,简化系统[14]。原理框图如图1所示。工作时序如图2所示。
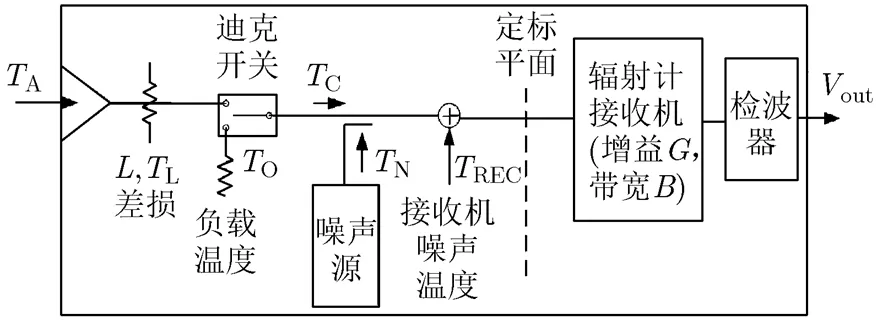
图1 噪声注入式辐射计原理框图

3.2 噪声注入式辐射计灵敏度计算
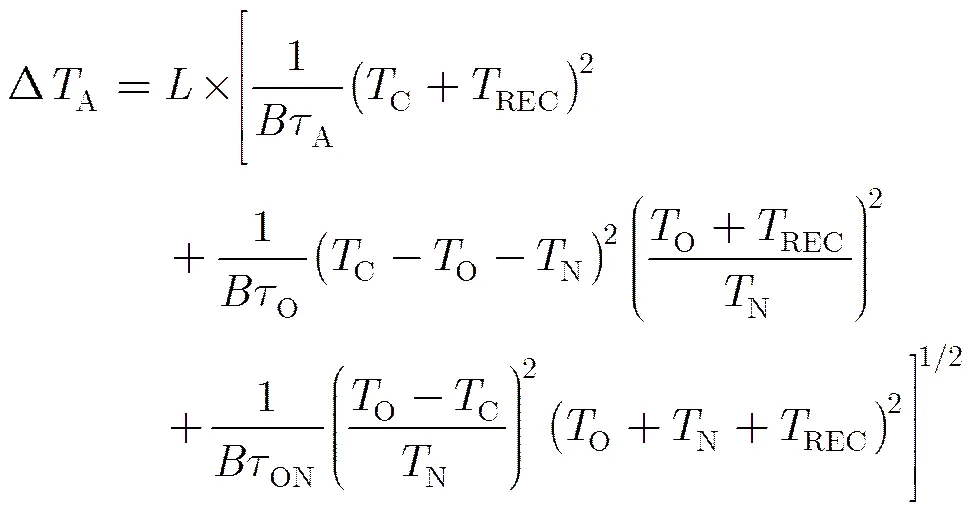
3.3噪声注入式辐射计稳定度计算
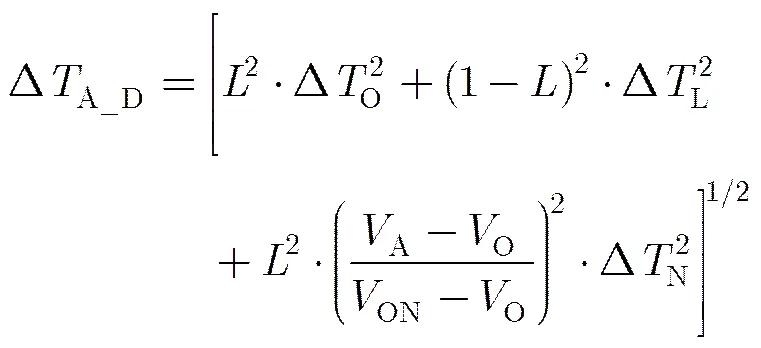
3.4定标数据平均技术

图2 应用定标数据平均技术的辐射计时序
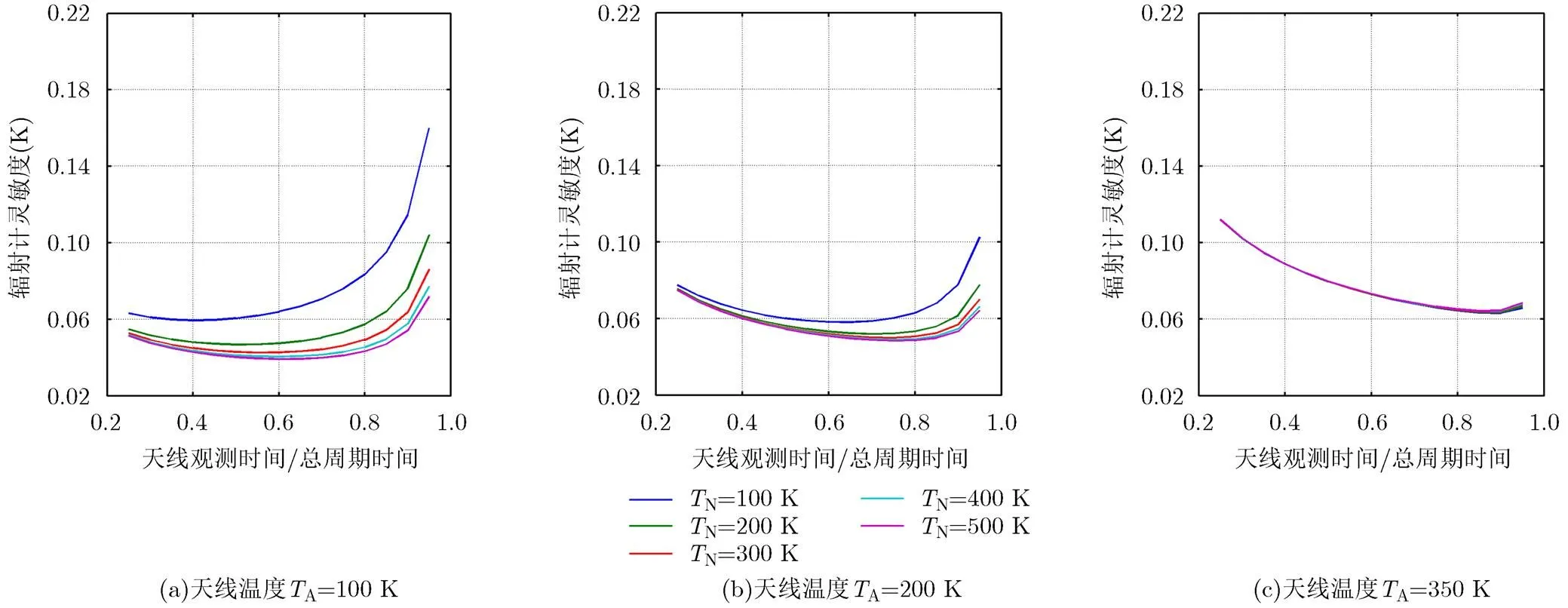
图3 应用定标数据平均技术的辐射计时序与噪声源温度优化
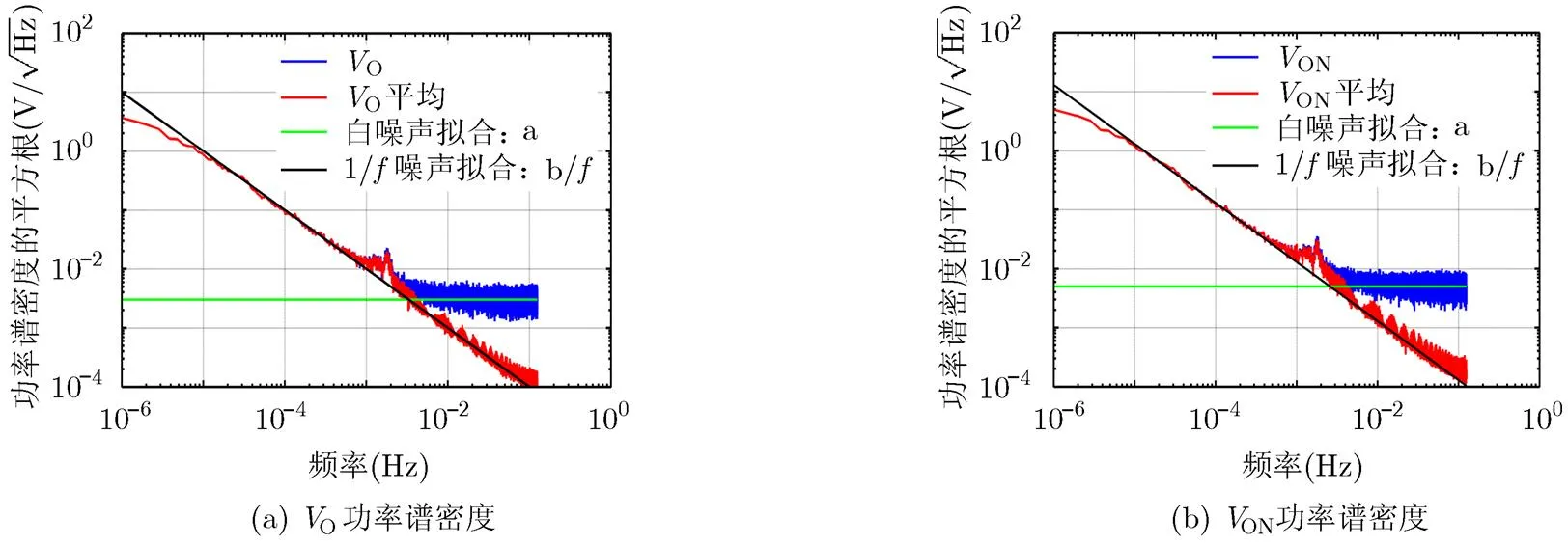
图4 VO与VON的功率谱密度
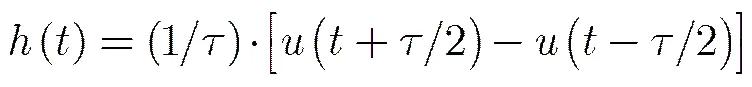
(7)
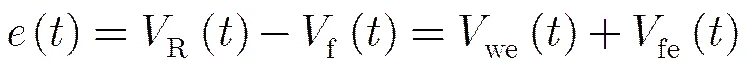
(9)

(11)
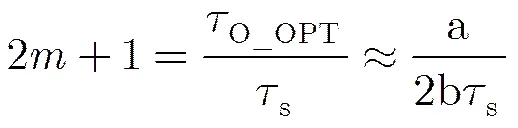
3.5 灵敏度仿真与时序、注入噪声优化

表1 L波段辐射计主要参数
4 辐射计实验验证
4.1辐射计实验过程
实验辐射计参数如表1所示。频率1400~1427 MHz,为50%。完成了8天(8 d)稳定性实验。精密温控系统将辐射计工作温度稳定在范围内。观测目标为一个温控在343 K的恒温匹配负载,温控精度,精密测温实现天线温度补偿。
4.2 实验数据分析
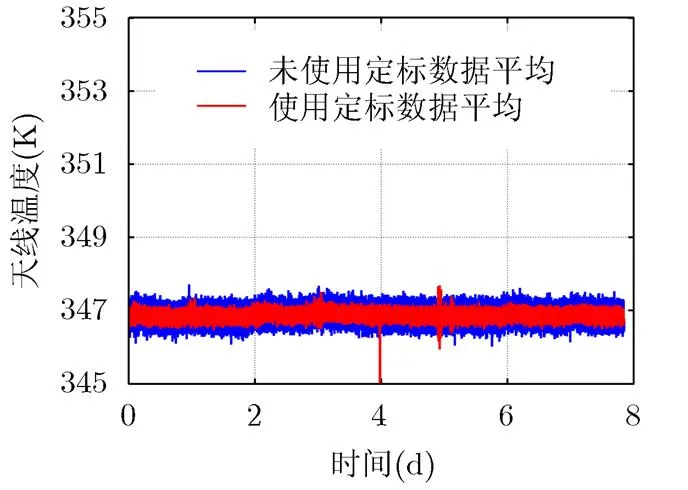
图5 辐射计8天(8 d)稳定性实验得到的天线温度
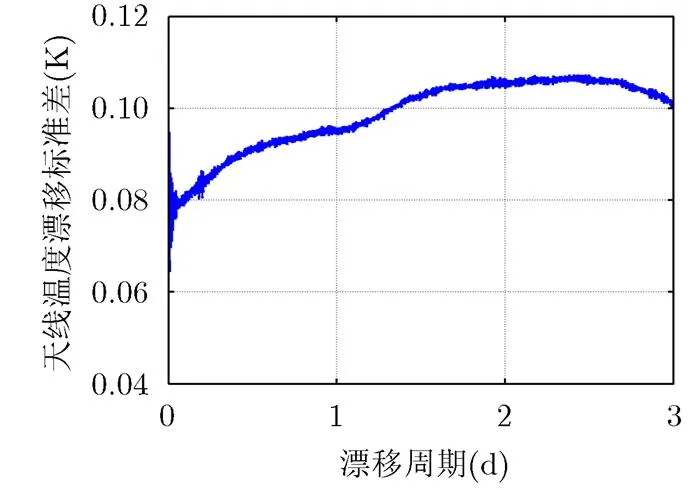
图6 辐射计漂移标准差
5 结束语
本文研究了一种兼有高灵敏度及高稳定度指标的噪声注入辐射计技术,通过实时定标保证高稳定度指标,通过定标平均进一步提高灵敏度指标。通过实验验证了采用精密温度控制,定标平均技术的L波段辐射计灵敏度优于0.1 K(4 s积分时间),3天(3 d)内稳定度优于0.12 K,达到了海洋盐度探测综合孔径辐射计对辐射计单元的需求。
[1] 李青侠, 张靖, 郭伟, 等. 微波辐射计遥感海洋盐度的研究进展[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2007, 26(3): 8-12.
LI Qingxia, ZHANG Jing, GUO Wei,. Research progress of remote sensing of ocean salinity by microwave radiometer [J]., 2007, 26(3): 8-12.
[2] Mcmullan K D, Brown M A, Martin-Neira M,. SMOS: The payload[J]., 2008, 46(3): 594-605.doi: 10.1109/ TGRS.2007.914809.
[3] MartIn-Neira M, Oliva R, Corbella I,. SMOS instrument performance and calibration after 6 years in orbit[J]., 2016, 180(8): 19-39. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.036.
[4] Le Vine D M, Lagerloef G S E, Colomb F R,. Aquarius: An instrument to monitor sea surface salinity from space[J]., 2007, 45(7): 2040-2050. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007. 898092.
[5] Vine D M L, Dinnat E P, Meissner T,Status of Aquarius/SAC-D and Aquarius salinity retrievals[J]., 2015, 8(12): 5401-5415. doi: 10.1109/ JSTARS.2015.2427159.
[6] 殷小军, 张庆君, 王睿, 等. 海洋盐度探测卫星的现状分析和未来趋势[J]. 航天器工程, 2016, 25(1): 119-123. doi: 10.3969/ J.ISSN.1673-8748.2016.01.016.
YIN Xiaojun, ZHANG Qingjun, WANG Rui,Development status and trends of sea surface salt satellite[J]., 2016, 25(1): 119-123. doi: 10.3969/ J.ISSN.1673-8748.2016.01.016.
[7] LIU Hao, ZHU Di, NIU Lijie,MICAP (Microwave Imager Combined Active and Passive): A new instrument for Chinese ocean salinity satellite[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 2015: 184-187.
[8] NIU Lijie, LIU Hao, WU Lin,. Experimental study of an L-band synthetic aperture radiometer for ocean salinity measurement[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 418-421.
[9] 李靖, 张俊荣, 赵凯. 实时定标微波辐射计[J]. 电子科学学刊, 1998, 20(2): 285-288.
LI Jing, ZHANG Junrong, and ZHAO Kai. Real-time calibrated microwave radiometer[J].,1998, 20(2): 285-288.
[10] 赵凯, 史久新, 张汉德. 高灵敏度机载L波段微波辐射计探测海表盐度[J]. 遥感学报, 2008, 12(2): 277–283.
ZHAO Kai, SHI Jiuxin, and ZHANG Hande. High sensitivity airborne L-band microwave radiometer measurements of sea surface salinity[J].,2008, 12(2): 277-283.
[11] LIU Hao, NIU Lijie, WU Lin,IMI(Interferometric Microwave Imager): A L/S/C tri-frequency radiometer for Water Cycle Observation Mission(WCOM)[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 3445-3447.
[12] WU Lin. Contribution to spatial bias mitigation in interferometric radiometers devoted to earth observation: Application to the SMOS mission[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), 2014.
[13] Goodberlet M A and Mead J B. Measuring precision and accuracy drift of radiometer-reported brightness temperature[J]., 2008, 46(11): 3827-3831. doi: 10.1109/ TGRS.2008.2001034.
[14] Goodberlet M A and Mead J B. Two-load radiometer precision and accuracy[J]., 2006, 44(1): 58-67. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.860206.
[15] Wilson W J, Tanner A, and Pellerano F. Ultrastable microwave radiometers for future sea surface salinitymissions[C]. Earth Science Technology Conference, Pasadena, USA,2002: 11-13.
Research and Experimental Verification on High Sensitivity and High Stability Microwave Radiometer
NIU Lijie①②LIU Hao①WU Ji①
①(,,,100190,)②(,100049,)
Global measurement of ocean salinity using satellite borne synthetic aperture radiometer is one of the research focuses in the field of microwave remote sensing. In order to achieve the accuracy of the ocean salinity detection, the radiometer units of the synthetic aperture radiometer need to have very high sensitivity and very high calibration stability. In this paper, the technique of the radiometer with high sensitivity and high stability is researched. High stability is realized by the real-time calibration method, and the sensitivity is effectively improved by the calibration data average technology. The optimal average time is obtained by the frequency domain analysis for the first time. Long time stability experiments are completed to demonstrate its performance. Experimental results show that the stability of this L-band radiometer reaches 0.12 K (in 3 days), and the sensitivity reaches 0.1 K, which can reach the requirement of the synthetic aperture radiometer for ocean salinity detection.
High stability radiometer; L-band microwave radiometer; Noise injection radiometer; Ocean salinity
TP732.1
A
1009-5896(2017)08-2028-05
10.11999/JEIT161112
2016-10-20;
改回日期:2017-02-21;
2017-04-14
刘浩 liuhao@mirslab.cn
牛立杰: 男,1974年生,博士生,副研究员,研究方向为辐射计系统及定标技术.
刘 浩: 男,1978年生,研究员,研究方向为干涉式综合孔径辐射计的系统和信号处理.
吴 季: 男,1958年生,研究员,主要从事微波遥感及空间探测方面研究.

