基于驻波率原理的农药雾滴沉积量检测系统设计与试验
吴亚垒,祁力钧※,张 亚,高春花,李 帅,Elizabeth Musiu
基于驻波率原理的农药雾滴沉积量检测系统设计与试验
吴亚垒1,祁力钧1※,张 亚2,高春花1,李 帅3,Elizabeth Musiu1
(1. 中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083; 2. 中国农业大学信息与电气工程学院,北京 100083;3. 华北电力大学机械工程系,保定 071051)
为实现施药后雾滴地面沉积量的快速获取,该文提出一种基于驻波率原理的叉指型雾滴采集极板结构。为验证该极板结构的合理性,应用三维电磁仿真软件HFSS对此系统进行电磁仿真。HFSS模型求解的结果表明,叉指型极板内部出现了静电屏蔽,极板间通过雾滴能够实现电磁耦合,可用于雾滴沉积量检测,系统灵敏程度将随着极板间距的增大而减小。通过标定试验,建立了检测系统输出电压与试剂溶液沉积量关系的回归方程,测试后2种不同介电常数的胭脂红溶液和丙三醇溶液决定系数R2分别为0.982 1和0.997 6。通过对3W-ZW10型温室自走式喷雾机应用测试,结果表明:该系统在采样点上沉积量的模拟值最大相对误差率不超过7.95%,且模拟值与实测值均方根误差RMSE最大为0.076 7 mg/cm2,雾滴沉积检测准确率高,方便实用,可用于田间雾滴沉积率的快速测量。
设计;计算机仿真;喷雾;驻波率原理;叉指型极板探头;雾滴沉积量测量;HFSS仿真
吴亚垒,祁力钧,张 亚,高春花,李 帅,Elizabeth Musiu. 基于驻波率原理的农药雾滴沉积量检测系统设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(15):64-71. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.008 http://www.tcsae.org
Wu Yalei, Qi Lijun, Zhang Ya, Gao Chunhua, Li Shuai, Elizabeth Musiu. Design and experiment of pesticide droplet deposition detection system based on principle of standing wave ratio[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(15): 64-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.008 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
雾滴沉积分布特性与规律的快速、有效获取不仅能够减少施药实验成本、降低操作难度和实验复杂度[1-3],而且对于评估施药作业质量,提高农药利用率有重要意义[4-6]。优化雾滴沉积检测技术,解决田间雾滴沉积分布测量方法单一和效率不高的问题是该领域学者追求的目标[7-8]。
王昌陵等[9]研发了一套雾滴空间质量平衡收集装置用于接收喷雾雾滴,采用多通道智能微气象测量系统测量无人机下旋气流场,分析精准作业高度和速度下无人机喷雾雾滴空间质量分布和下旋气流场特性及其内在关系。张瑞瑞等[10]基于变介电常数电容器原理和传感器网络技术,设计航空施药雾滴地面沉积实时监测系统,并探究该系统用于雾滴地面沉积量测量的实用性。Zhu等[11]研究了基于图像分析技术和水敏试纸的药液沉积分析系统。Salyani等[12]通过研究药液沉积量对导体电阻率的影响,设计了一种基于可变电阻器原理的药液沉积传感器,并建立了传感器输出电压与药液沉积量关系模型。王景旭等[13]利用CFD模拟技术研究了温室风送式喷雾机雾滴的沉积模型。高志涛等[14]借助矢量网络分析仪与HFSS电磁场仿真软件对传感器电极的阻抗特性与电场分布状况进行了分析,为实时获取多层土壤墒情及土壤温度提供了一种高效方法。总的来说,针对雾滴沉积量与在线快速检测技术研究还相对较少[15-16]。
本文基于变介电常数理论中的驻波率原理和传感器网络技术,旨在设计雾滴地面沉积实时检测系统,以仿真试验分析为手段,探索电场的分布特性,逐步仿真优化得到叉指型极板结构形状及最佳参数,同时结合温室自走式喷雾机系统进行了应用测试与试验验证,以期为实现在线准确、快速获取雾滴沉积分布特性提供参考。
1 叉指型雾滴采集系统测量原理
本文设计的叉指型雾滴沉积量采集系统基于驻波率原理,由100 MHz信号源、50 Ω同轴传输线、高频检波与差分运算放大电路、叉指型雾滴采集极板探头及无线网络传输装置组成。利用驻波率法测量雾滴沉积量实际上反映的是喷雾环境下叉指型雾滴采集板探头的特性阻抗变化。图1为雾滴沉积量实时检测装置系统原理图。
当信号源产生的高频电磁波沿着传输线被传送到叉指型雾滴采集探头,由于探头的阻抗与传输线的阻抗不匹配,一部分信号将被反射回来。在传输线上,高频入射波与反射波叠加形成驻波,传输线上各点的电压幅值存在变化[17-18]。
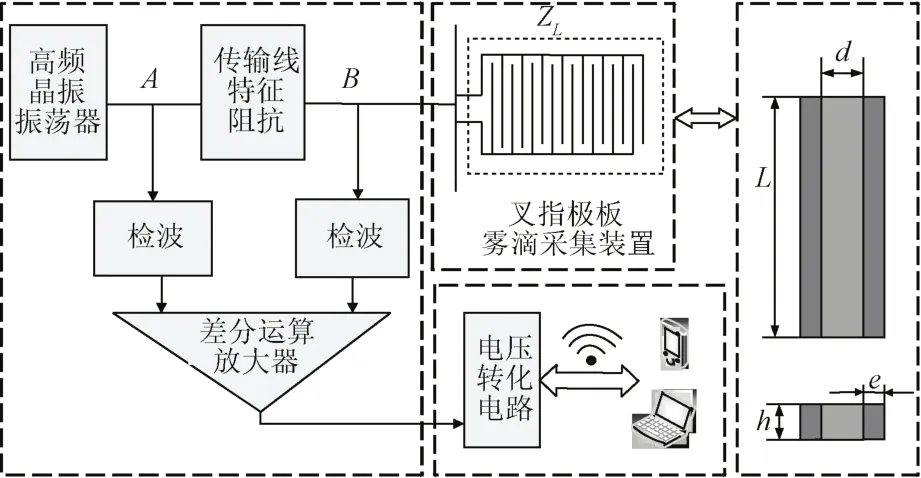
图1 雾滴沉积量系统原理图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of droplets deposition system
根据基本传输线理论[19],其等效参数均匀分布可得等效电路如图2所示。
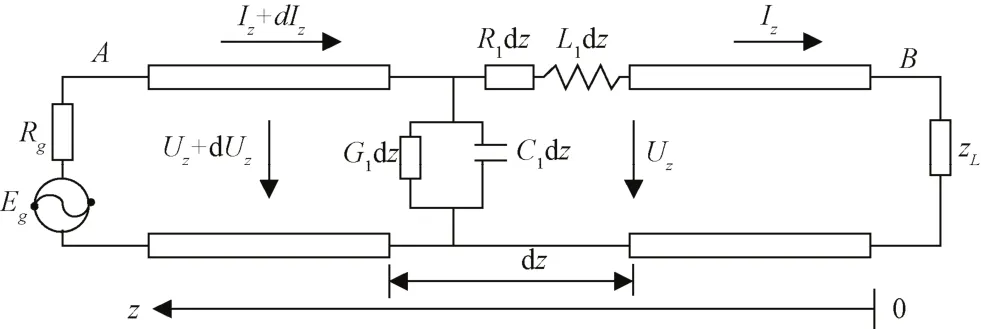
图2 测量装置等效电路图Fig.2 Equivalent circuit of measuring device
其中考虑高频状态下分布电容、电抗的影响,在传输线上任意点处取微元dz,得其电压与电流的微分表达式
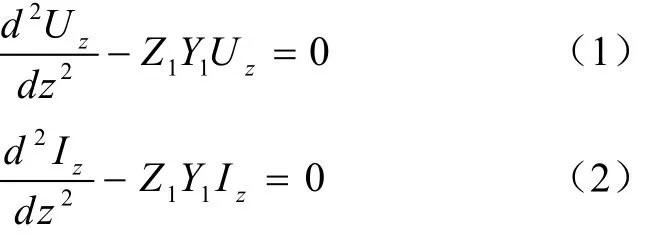
其瞬时解表达式为
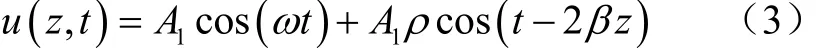
式中A1为高频振荡器的信号幅值;ρ为反射系数;β为相移系数;ω为信号源角频率;z为传输线阻抗瞬时值。


式中k为物质豫驰时间;f为信号源测试频率;λ为信号波波长。
根据驻波率测量原理,图2中取A、B两点的差动信号作为叉指型雾滴采集板探头变换电路的输出,传输线两端的电压UAB表达式为

式中ZC为同轴传输线的特征阻抗,Ω。
本研究中ZC为50 Ω的标准同轴电缆。在A1和ZL恒定的情况下,传输线两端的电位差UAB只与叉指型装置阻抗ZL有关,当ZC=ZL时,传输线上不会产生驻波,传输线两端电压为0。因此,确定叉指型极板探头的阻抗ZL尤为重要。叉指型极板探头的检测阻抗值ZL与导纳Y关系如式(7)所示。

式中ωs为叉指型极板测试角频率,rad/s;Cs为叉指型极板总的电容,F;Y为传输线导纳;j表示虚部。
叉指型极板探头的阻抗特性与间隙内铺洒物质的介电常数有关,其电容C为

式中ε为极板间介电常数;S为平行板覆盖面积,mm²;d为叉指型极板间距,mm。
叉指型雾滴采集板探头为具有一定间距d、一定宽度e、一定厚度h和一定长度L的敷铜板,将多个极板并联且等间距固定,即可用于雾滴沉积测量的叉指型极板,极板底侧与树脂板固化,树脂板总面积S0,包括叉指型极板的表面积S1及极板间面积S2,极板间面积可以根据介质不同,分割成空气介质面积S3和药液介质面积S4,其中:
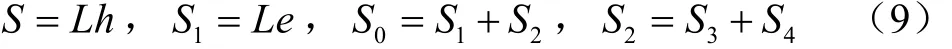
式中S0为树脂板的总面积,mm²;S1和S2分别为极板上与极板间的表面积,mm²;S3和S4分别为空气与药液介质的表面积,mm²。
当所设计叉指型极板覆盖面积S不可变,通过极板间介电质改变引起介电常数变化,从而改变电容器电容。设定空气介电常数为ε1,叉指型极板间无雾滴沉降时,电容量为Cz。当叉指型极板间有雾滴沉降时,因介质变成由液滴和空气组成的混合体,液滴的介电常数与空气不同[10],所以电容等效介电常数值发生变化,从而电容变为Ce。施药过程中,药液浓度一旦固定,在忽略环境温差变化对溶液介电常数影响时,药液的介电常数是定值,设定药液的介电常数为ε2,电容量为
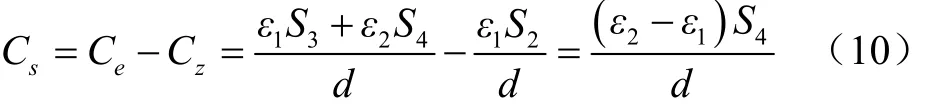
式中Cz和Ce分别为极板间雾滴无沉降与有沉降时的电容量,F;ε1和ε2分别为空气与药液的介电常数。
施药过程中,雾滴体积中径较小,雾滴径谱一致性较好,且沉积在靶标上的药液相对较少,由此推测其雾滴的沉积面积S4与其沉积量m在一定的沉积量范围内具有较好的相关性,相关系数为k*。雾滴喷施前后电压值变化与雾滴沉积量的理论关系表达式为
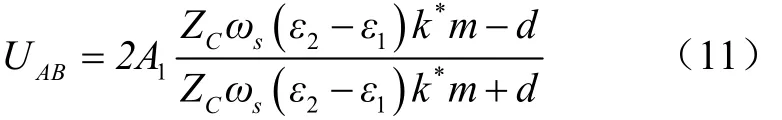
式中m为农药雾滴沉积量,mg/cm2;k*为相关系数。
故基于以上式(1)-式(11)公式推导,可以通过喷雾环境下叉指型雾滴采集板探头的特性阻抗变化来表征实际雾滴沉积量的变化,所以从理论分析来看,可以利用介电理论中的驻波率原理的电压变化来反映喷施前后雾滴在叉指型雾滴采集板的沉积量变化。
2 叉指型极板参数确定与电场分布特性研究
选取合适的试验控制参数是叉指型雾滴采集板设计的关键,其目的是通过采集板上面药液与空气的混合介电常数的变化转换为传输线上驻波率的变化。
2.1 测量频率参数的确定
在叉指型雾滴采集极板间距固定的情况下,负载阻抗由信号源频率和药液与空气混合的介电常数决定,而介电常数是与信号源频率相关,所以信号源频率的选择对测量结果会造成一定影响。Topp等[20]研究发现,在1 MHz~1 GHz频率范围内,有效介电常数主要取决于介质中的水分含量。
介电常数可以分解为

式中ε′和ε″分别为介电常数的实部和虚部。
经数学推导[21],得
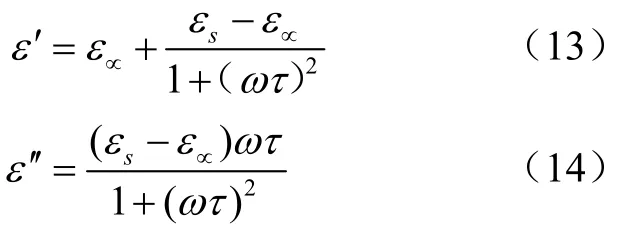
式中ε∝为电子位移极化对应的高频介电常数;εs为静电场中的介电常数;τ为水常温下的弛豫时间,s。
由式(13)和(14)可知,当外加电场的角频率1ωτ=时,ε″具有极大值;当1τω≤时,ε′趋近于εs,此时介质没有电导产生的损耗。水分子是一种极性很强的偶极子,在外电场作用下,水的极化程度远大于其他物质。在微波频段,不同波长对应水的介电常数不同[21]。水的介电常数与波长的关系如图3所示。
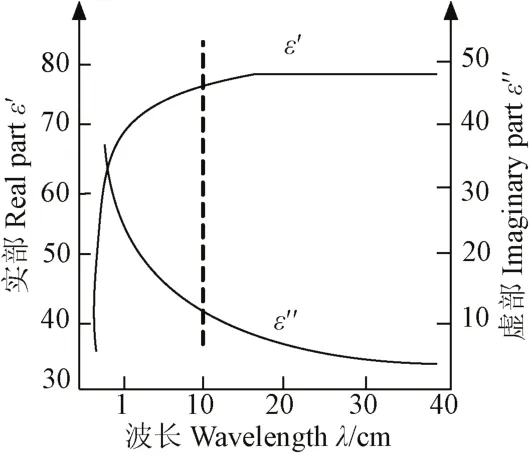
图3 水的介电常数与波长的关系Fig.3 Relationship between dielectric constant of water and wavelength
由图3可知,当信号源波长在10 cm以上即频率小于3 000 MHz时,介电常数的实部远大于虚部。当波长为10 cm时,水的ε′为77.2,空气的介电系数为1,在此频段内水比空气状态下介电常数大很多。由于过高的频率易受到外界电磁环境的干扰,本文综合其他基于驻波率法测量含水率的研究,选用电磁波频率为100 MHz的信号源[22]。
2.2 叉指型极板电场仿真分析
2.2.1 不同极板间距处电场分布状况
利用Ansoft HFSS电磁仿真软件[23]建立了叉指型雾滴采集极板几何模型如图4所示。1)极板的上表面宽度e设为1 mm,上表面长度L设为38 mm,侧表面高度h设为100 μm,一极板末端距离另一极板设为1 mm,叉指型雾滴采集极板间距d分别设为0.5、1、3、6 mm;2)设定极板间距内填充介质的介电常数为18,树脂板及辅助支架的介电常数设为4,设定叉指型铜极板为理想电场边界,选取半径为40 mm的球体作为辐射边界的条件;3)选择求解类型为Driver Model,其次设置波端口激励为集总端口激励方式,最后添加求解设置,设定求解模型频率为100 MHz。运行Analyze-All,HFSS电磁软件在叉指型雾滴采集极板上的电场分布状况仿真结果如图5所示。
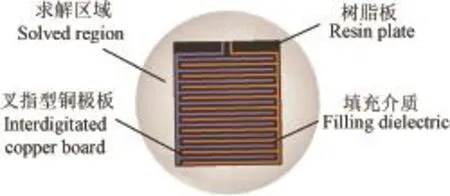
图4 叉指型雾滴采集极板电磁模型Fig.4 Electromagnetic model of interdigitated droplet collection board
由图5可以看出叉指型不同间距的极板主要影响雾滴沉积区域的XY和YZ截面方向的电场分布,XY和YZ截面分别为电磁模型主视图与左视图,图中淡黄色区域的电场强度满足测试的要求。根据达到淡黄色区域的电场强度的作用进行分析:1)0.5和1 mm间距情况下,叉指型雾滴采集极板检测区域电场分布差异不明显,且0.5和1 mm情况下XY和YZ截面上极板之间均匀分布,周围电场紧凑,没有出现分离现象。但是随着极板间距的逐渐增大,电场分布差异性越来越明显;2)3 mm情况下,XY截面上基本满足电场强度的要求,但是出现了不均匀的现象,且YZ截面的场强不连续性也随之显现;3)6 mm情况下,XY截面上不满足电场强度的要求,出现了严重不均匀的现象,且YZ截面的场强间断性明显,强度明显变弱。由上述现象发现:0.5和1 mm间距的极板均适用于雾滴的检测,考虑到敷铜极板的加工难易程度以及喷雾中雾滴沉积量造成的系统灵敏度问题。综上所述,本文选用间距为1 mm的叉指型雾滴采集极板探头。
2.2.2 叉指型极板表面电场分布特性
同时图5仿真结果表明:叉指型雾滴采集极板边缘电场的强度在水平和垂直方向上均沿着远离电极的方向而减小,电场的能量主要集中在两极板探头之间。两电极相对的空间内颜色最深,表现为红色,具有最大强度的电场,尤其是电极边缘处。应该注意到,两个电极板的中心部位表现为电场最弱的蓝色,这是由于带电导体的静电屏蔽现象造成的[24]。在两极板相对之外的空间内,随着远离电极的方向,电场颜色逐渐减弱为绿色、天蓝色直至最后与远处融为一色,变成深蓝。这一结果表明,电场能够在两极板间距的范围内实现耦合。
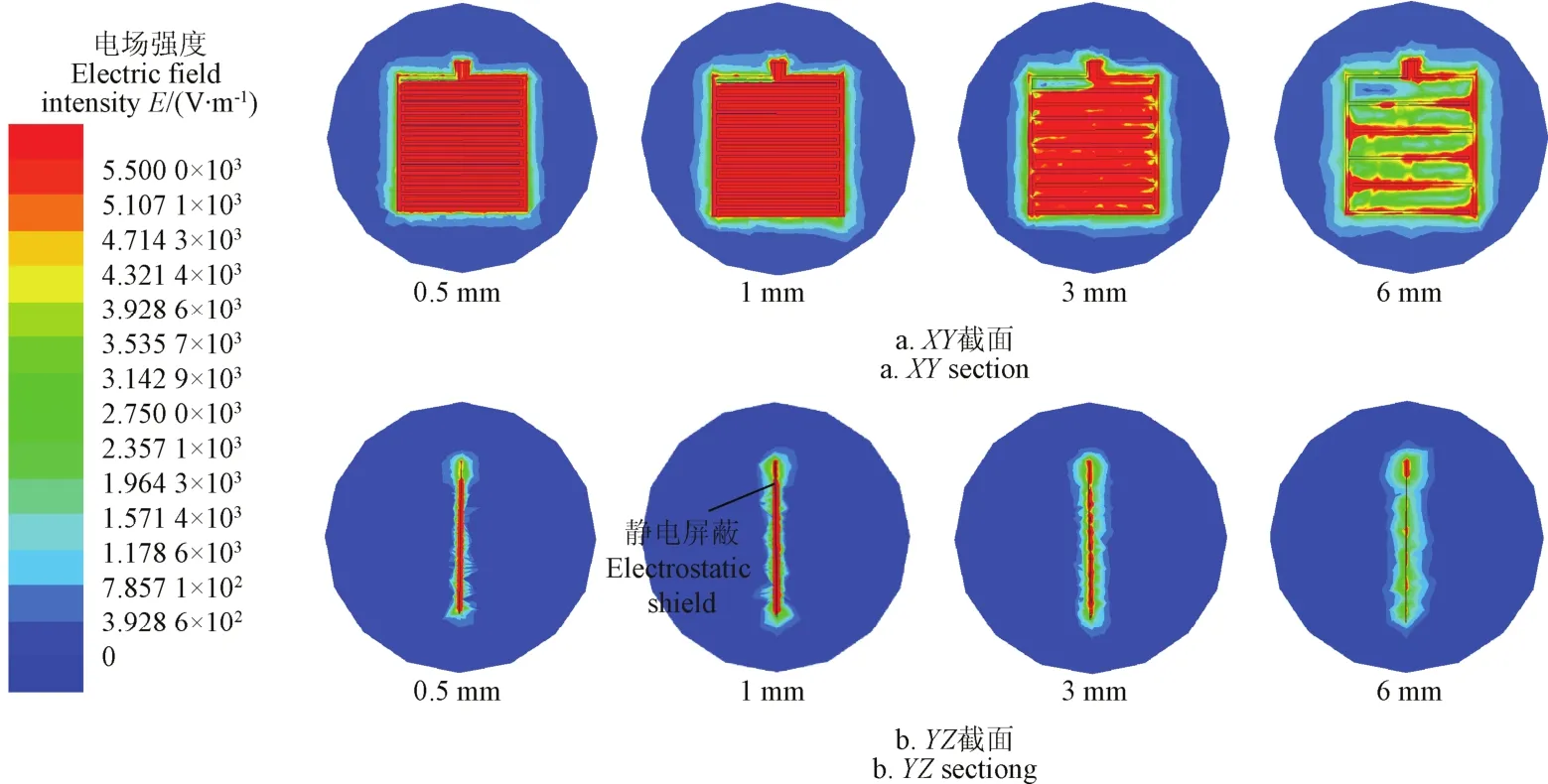
图5 叉指型雾滴采集极板不同间距下的电场强度分布图Fig.5 Electric field intensity distribution of interdigitated droplet collection board under different spacing
3 试验与测试
3.1 试验材料
试验试剂:胭脂红试剂、自来水及丙三醇溶液。试验仪器:0.1~2.5 μL移液枪(上海注射器三厂Biohit proline W-103,精度0.05 μL),容量瓶、滴管、烧杯、温湿度传感器、德利斯公司玻璃手套箱、乳胶手套,英衡电子天平(精度0.001 g),SA-50W-12V/4A模块,在线采集装置,采样滤纸规格(4 cm×4.2 cm),UV-5200分光光度计(上海元析公司),MSS-33544激光粒度仪。
3.2 试验处理
考虑到药液不同的介电常数,试验选取0.5 g/L胭脂红溶液(介电常数79.2)与丙三醇溶液(介电常数47.8)。滴取前,叉指型极板表面擦拭干净,放进玻璃手套箱,且平置于天平上,天平与电压示数调至初始值。试验开始,利用微量移液枪连续产生体积为0.05 μL大小的单个雾滴进行试验,使雾滴充分滴落到叉指型雾滴采集极板间隙中,电压示数趋于稳定后停止。滴取中,不断记录天平与在线采集装置中电压的示数变化。滴取后,整个过程重复25次试验。温度为(24±0.5)℃,湿度为22%±0.8%,试验布置(可忽略蒸发对本试验的影响)示意图如图6所示。
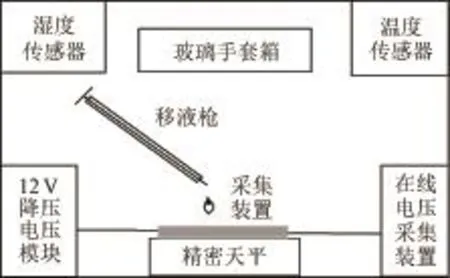
图6 实验室试验装置示意图Fig.6 Schematic diagram of test device in lab
3.3 叉指型雾滴采集装置标定试验及结果分析
试验在玻璃手套箱环境下进行,为更好地定量分析叉指型雾滴采集装置输出电压与滴取前后雾滴沉积量之间的关系,对所测的数据进行多项式拟合,测量数据中滴取前后在线采集电压输出变化值Δy为自变量,滴取前后的质量变化值Δx为因变量,绘出了如图7所示的曲线。
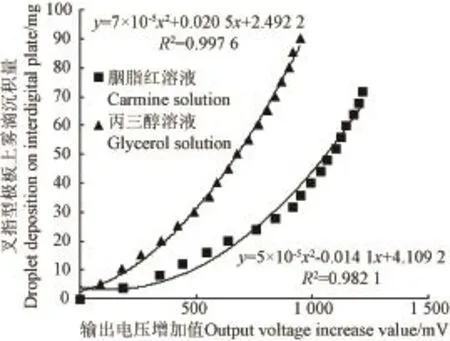
图7 胭脂红溶液与丙三醇溶液沉积回归方程Fig.7 Regressive equation of carmine solution and glycerol solution in deposition
溶液的介电常数是和溶质的浓度有关系的[25]:1)一般果蔬农药稀释倍数介于800~1 600之间[26],药液介电系数较大且接近水的介电常数80,因此该文选用胭脂红药液进行试验;2)植保无人机喷洒多采用超低量喷雾,药液浓度高,介电系数较小,因此选用丙三醇溶液进行试验。所选的这2种用于标定的试剂的介电常数可以代表一般农药的介电常数。
图7中2条曲线对比发现,在相同沉积量情况下,胭脂红溶液电压输出值波动范围较丙三醇溶液明显,且灵敏度较好,但二者滴取前后的电压与药液沉积量的回归相关性均较好,2种不同介电常数的溶液决定系数R2分别为0.982 1和0.997 6。该基于驻波率原理的雾滴沉积量检测系统实时采集的数据可以用于雾滴沉积量测量,同时可用于雾滴在作物靶标上分布参数优化。
3.4 应用测试
2017年2月15日,系统在中国农业大学植保机械实验室3 m×6 m区域内测试,建立直角坐标系,区域布置在第一象限,坐标点标记(一个单位长度为1 m),喷雾机由坐标点(0,0)作业至(0,2)处,试验中喷雾机的喷雾技术参数如表1所示。
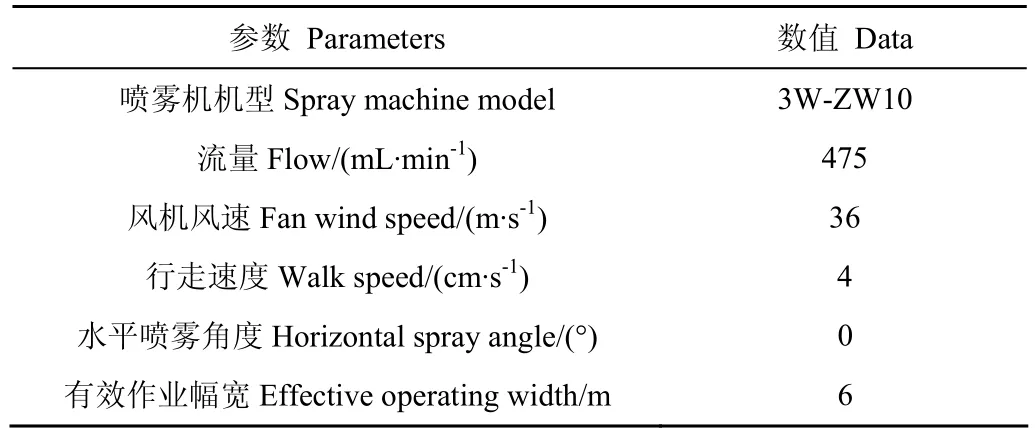
表1 喷雾机的技术参数Table 1 Parameters of sprayer
叉指型雾滴采集极板布置分布在(1.5,1.5)、(3,1.5)、(4.5,1.5)的3个坐标点处,每块雾滴采集极板周围布置4张同样大小的4 cm×4.2 cm滤纸,目的是在保证相同测试条件下,对4张测量结果取均值,用于与该系统的雾滴沉积量测量对比,试验布置如图8a所示。同时本研究设计的叉指型雾滴沉积量实时在线采集系统由带有AD芯片数据采集的STM32单片机、ZigBee无线数传模块及12V欧力能供电模块组成,传感器节点安装如图8b所示。
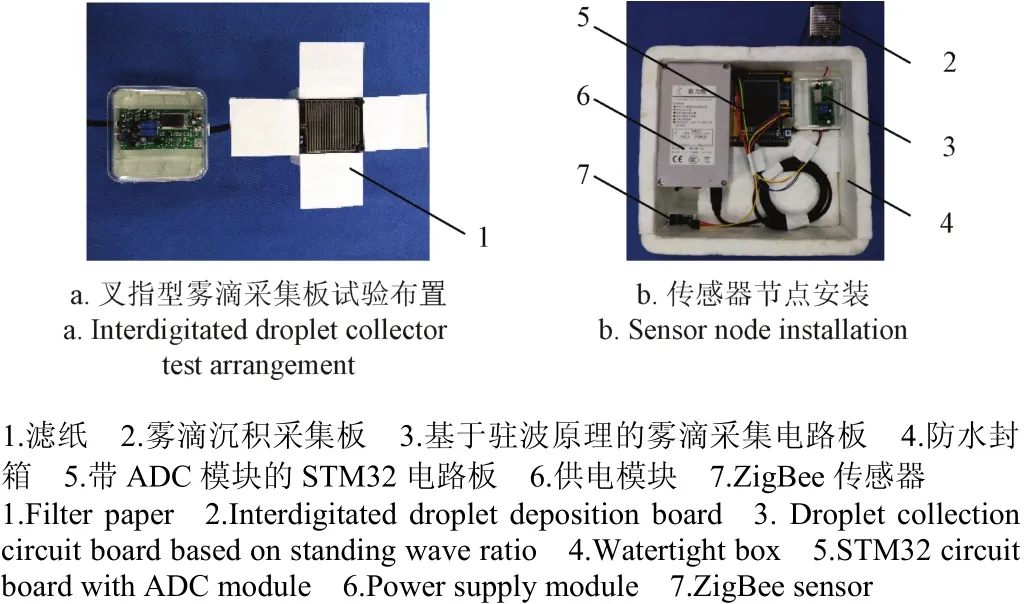
图8 叉指型雾滴采集板安装与试验布置Fig.8 Interdigitated droplet collector installation and test arrangement
喷施液体选用0.5 g/L胭脂红溶液,试验过程重复6次,分别得到18组采集样本,喷雾测试环境温度24°,湿度为22%,同时在此条件下利用激光粒度仪分别对不同喷雾距离处的雾滴体积中径大小进行9次测定,取均值。基于在波长为508 nm下吸光度随胭脂红溶液浓度增大而增大的规律,本文借鉴了吸光度测量法在雾滴沉积量上的方法[27-31],见式(15)。利用模拟方法与吸光度法分别对18组采集样本进行计算,试验结果见表2。
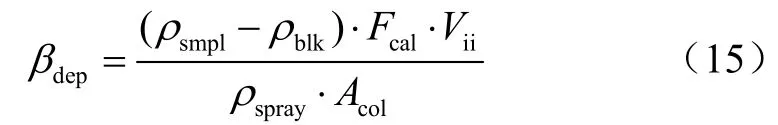
式中βdep为雾滴沉积量,mg/cm2;ρsmpl为待测样品的浓度读数;ρblk为空白对照的浓度读数;Vii为用于洗脱滤纸收集的胭脂红的稀释液的体积,L;ρspray为药箱内胭脂红喷洒液浓度,g/L;Acol为滤纸面积,cm2;Fcal为校正因子。
为评估系统测量法和吸光度法对于雾滴沉积量检测的效果,将不同喷雾距离处的模拟值和实测值进行比较(如表2所示),式(16)表述均方根误差RMSE,反映了模拟值距偏离真实值的离散度与精密度,为进一步分析采样点偏差程度,式(17)表述采样点中最大相对测量误差emax[32]。式中Xmodel,i为使用系统法所获得的雾滴沉积量(简称“模拟值”),mg/cm2;Xobs,i为使用吸光度法所获得雾滴沉积量(简称“实测值”),mg/cm2;N为所对应喷雾距离处的样本数。
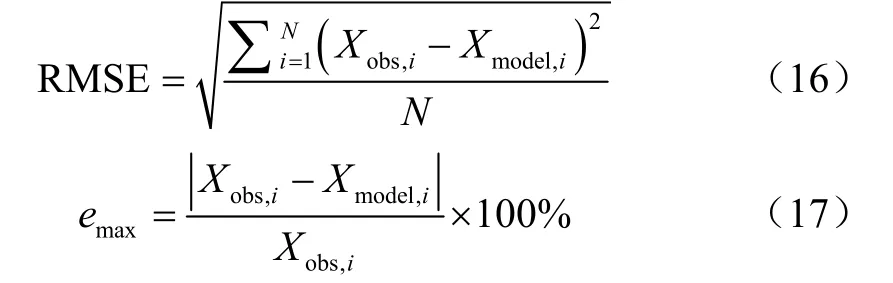
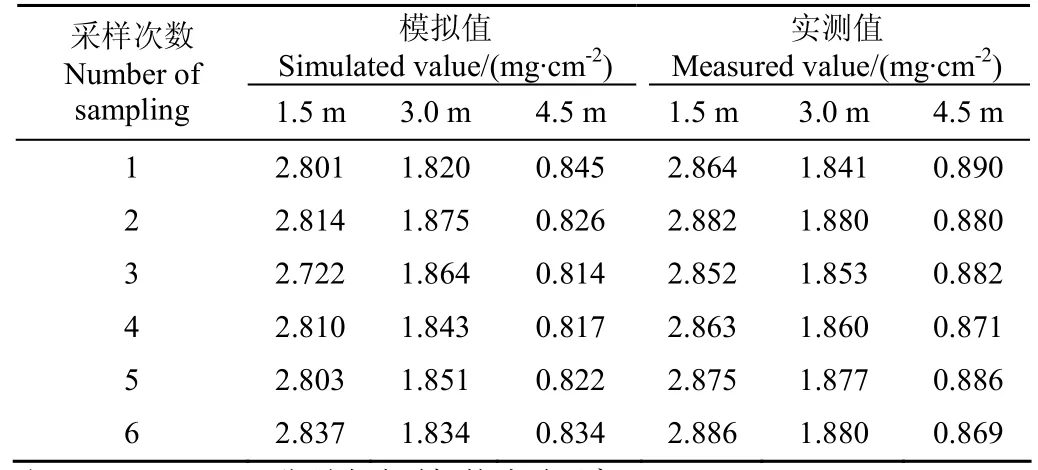
表2 在喷雾距离1.5、3、4.5 m处模拟值与实测值试验结果Table 2 Results of simulated values and measured values at spray distance of 1.5,3,4.5 m
将6次采集的试验样本筛选,并以不同喷雾距离处雾滴粒径大小分布进行归类,以采样滤纸吸光度法获得的数据为参考指标,结合激光粒度仪对不同距离处的雾滴大小测定结果,由试验分析可知,表2中距离在1.5 m处时,雾滴体积中径VMD在136.5至288.7 μm之间,采样点均方根误差RMSE为0.076 7 mg/cm2(系统的模拟值),最大相对测量误差4.56%,按照Miller PH模型,1.5 m处由于距离喷嘴口较近,产生较多大粒径雾滴,一方面由于动量较大,撞击树脂板较滤纸产生反弹作用更为明显,另一方面由于采集板表面光滑,使得雾滴在树脂板上铺展面积相对较大,阻抗发生变化,使得气液混合介电系数高于试验标定数值;距离在3 m处时,雾滴体积中径VMD在84.2至112.5 μm之间,采样点均方根误差RMSE为0.025 5 mg/cm2,最大相对测量误差仅2.65%,原因是雾滴体积中径减小,一方面动能急剧减少,反弹作用趋于减弱,另一方面,该粒径下的雾滴粘连情况减少,铺展面积符合标定试验要求,在树脂板上的沉积性趋于平稳;距离在4.5 m处时,雾滴体积中径VMD在23.5至50.8 μm之间,采样点均方根误差RMSE为0.056 4 mg/cm2,最大相对测量误差7.95%,因为采样点距离喷嘴口较远,雾滴粒径很小,一方面该粒径下雾滴铺展性较差,使得气液混合介电系数低于试验标定数值,另一方面液膜较薄,蒸发因素影响显著。
系统模拟值与吸光度实测值在喷雾距离1.5、3、4.5 m处的雾滴沉积量测量对比,系统模拟值均小于吸光度实测值,这与采集板的表面材料属性相关性较大,雾滴易在其表面形成弹跳、飞溅,而雾滴相对容易在滤纸表面附着。另外,雾滴的蒸发也是重要的影响因素,需对系统采集频率进行校正,减少系统测量误差。
综上所述,本文所设计的雾滴采集系统可以适用于300 μm粒径范围内不同雾滴大小的沉积量测定,满足雾滴喷雾质量检测的应用需求。
4 结 论
1)本文理论推导了雾滴沉积量与叉指型采集系统参数的回归关系和计算方程,进一步证明了利用变介电常数驻波率原理进行雾滴沉积量测量的可行性。
2)针对叉指型雾滴采集系统测试频率与极板间距进行了深入研究,借助HFSS三维电磁仿真软件,对4种不同间距的极板进行了仿真与电场特性分析,最终确定了极板的间距,并阐释了铜极板内部静电屏蔽的机理。
3)从实验室标定与应用测试结果可以得出,设计的叉指型雾滴采集系统在300 μm粒径范围内具有可行性,参照吸光度法与系统测量法的均方根误差RMSE最大为0.076 7 mg/cm2及其最大相对测量误差不超过7.95%,分析表明,雾滴沉积趋势结果基本一致,可以用于雾滴沉积量的测量。
4)提出的利用驻波率法叉指型雾滴采集系统可实现对温室中雾滴沉积量的实时检测,具有较高的可靠性,同时对于大田雾滴喷雾质量的检测及研究雾滴分布特性与规律(如雾滴分布变异系数、有效幅宽等测量等方面)具有较大的实际意义。
[1] Qin W C, Xue X Y, Zhou L X, et al. Effects of spraying parameters of unmanned aerial vehicle on droplets deposition distribution of maize canopies[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(5): 50-56.
[2] Wang S, Dorr G J, Khashehchi M, et al. Performance of selected agricultural spray nozzles using particle image velocimetry[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science & Technology, 2015, 17(3): 601-613.
[3] 莽璐,祁力钧,冀荣华,等. 温室自动变量施药系统设计[J].中国农业大学学报,2009,14(4):114-118.
Mang Lu, Qi Lijun, Ji Ronghua, et al. Design of variable rate spray system in greenhouse[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2009, 14(4): 114-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 廖娟,臧英,周志艳,等. 作物航空喷施作业质量评价及参数优选方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(增刊2):38-46.
Liao Juan, Zang Ying, Zhou Zhiyan, et al. Quality evaluation method and optimization of operating parameters in crop aerial spraying technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(Supp.2): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 邱白晶,闫润,马靖,等. 变量喷雾技术研究进展分析[J].农业机械学报,2015,46(3):59-72.
Qiu Baijing, Yan Run, Ma Jing, et al. Research progress analysis of variable rate sprayer technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(3): 59-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张京,何雄奎,宋坚利,等. 无人驾驶直升机航空喷雾参数对雾滴沉积的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(12):94-96.
Zhang Jing, He Xiongkui, Song Jianli, et al. Influence of spraying parameters of unmanned aircraft on droplets deposition[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(12): 94-96. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Wang Z H, Wang F P, Fan J R, et al. The spraying field characteristics and distribution of deposition of droplets of electrostatic oiler[J]. Journal of Engineering and Technology Research, 2016, 8(4): 31-46.
[8] 陈盛德,兰玉彬,李继宇,等. 小型无人直升机喷雾参数对杂交水稻冠层雾滴沉积分布的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(17):40-46.
Chen Shengde, Lan Yubin, Li Jiyu, et al. Effect of spray parameters of small unmanned helicopter on distribution regularity of droplet deposition in hybrid rice canopy[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(17): 40-46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 王昌陵,何雄奎,王潇楠,等. 无人植保机施药雾滴空间质量平衡测试方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):54-61.
Wang Changling, He Xiongkui, Wang Xiaonan, et al. Testing method of spatial pesticide spraying deposition quality balance for unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张瑞瑞,陈立平,兰玉彬,等. 航空施药中雾滴沉积传感器系统设计与实验[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(8):123-127.
Zhang Ruirui, Chen Liping, Lan Yubin, et al. Development of a deposit sensing system for aerial spraying application[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(8): 123-127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Zhu H P, Salyani M, Fox R D. A portable scanning system for evaluation of spray deposit distribution[J]. Co-mputers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2011, 76(1): 38-43.
[12] Salyani M, Serdynski J. Development of a sensor for spray deposition assessment[J]. Transactions of the Asae, 1990, 33(5): 1464.
[13] 王景旭,祁力钧,夏前锦. 靶标周围流场对风送喷雾雾滴沉积影响的CFD模拟及验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(11):46-53.
Wang Jingxu, Qi Lijun, Xia Qianjin. CFD simulation and validation of trajectory and deposition behavior of droplets around target affected by air flow field in greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(11): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 高志涛,刘卫平,赵燕东,等. 多层土壤剖面复合传感器设计与性能分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(1):108-117.
Gao Zhitao, Liu Weiping, Zhao Yandong, et al. Design and performance analysis of composite sensor for multilayer soil profile[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(1): 108-117. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Giles D K, Downey D, Crowe T G. Digital device and technique for sensing distribution of spray desposition[J]. Transactions of the Asae, 2005, 48(6): 2085-2093.
[16] 祁力钧,马伟. 一种作物根区土壤肥药注施靶标在线预测定点方法:CN104076711A[P]. 2014-10-01.
[17] 刘贺,赵燕东. 基于驻波原理的短探针小麦茎水分传感器[J].农业工程学报,2011,27(11):140-144.
Liu He, Zhao Yandong. Wheat stem moisture sensor using short probes based on SWR principle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(11): 140-144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 岳志勤,姚志明,宋岩,等. 同轴电缆转接中特性阻抗的错位补偿计算方法[J]. 现代应用物理,2014,5(1):64-70.
Yue Zhiqin, Yao Zhiming, Song Yan, et al. Calculation of impedance compensation for design of coaxial cable connectors[J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2014, 5(1): 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 赵燕东,高超,张新,等. 基于驻波率原理的植物茎体水分无损检测方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(1):310-316.
Zhao Yandong, Gao Chao, Zhang Xin, et al. Non-destruc-tive measurement of plant stem water content based on standing wave ratio[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(1): 310-316. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] Topp G C, Davis J L, Annan A P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content using TDR: I. Applications to wetting fronts and steep gradients1[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1982, 46(4): 672-678.
[21] 白陈祥. 基于驻波原理的乔木茎干含水率检测方法研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2008.
Bai Chenxiang. The Study on Measurement of Stem Water Content Based on Standing Wave Theory[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王海兰,张新,盛文溢,等. 基于TDT原理的灌木水分传感器探头设计与实验[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(5):259-264.
Wang Hailan, Zhang Xin, Sheng Wenyi, et al. Experiment research on shrubs moisture sensor probe structure by TDT principle[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(5): 259-264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] Singh A K, Gangwar R K, Kanaujia B K. Wideband and compact slot loaded annular ring microstrip antenna using L-probe proximity-feed for wireless communications[J]. International Journal of Microwave & Wireless Technologies, 2015, 1(7): 1-9.
[24] 王巧利. 基于介电原理的浅层土壤水分测量方法研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2015.
Wang Qiaoli. Topsoil Moisture Measurement Using a Directric Constant Method[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 徐士鸣,刘欢,吴曦,等. KI/LiCl/LiBr-水-乙醇三元体系电导率特性研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报,2017,57(1):23-28.
Xu Shiming, Liu Huan, Wu Xi, et al. Study of conductivity charcteristics of ternary solutions KI/LiCl/Li Br-water-ethanol[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2017, 57(1): 23-28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 傅泽田,祁力钧,王秀. 农药喷施技术的优化[M]. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2002.
[27] 邱白晶,王立伟,蔡东林,等. 无人直升机飞行高度与速度对喷雾沉积分布的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(24):25-32.
Qiu Baijing, Wang Liwei, Cai Donglin, et al. Effects of flight altitude and speed of unmanned helicopter on spray deposition uniform[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(24): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] Qin W C, Xue X Y, Cui L F, et al. Optimization and test for spraying parameters of cotton defoliant sprayer[J]. International Journal of Agricultural & Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(4): 63-72.
[29] 祁力钧,杜政伟,冀荣华,等. 基于GPRS的远程控制温室自动施药系统设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(23):51-57.
Qi Lijun, Du Zhengwei, Ji Ronghua, et al. Design of remote control system for automatic sprayer based on GPRS in greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(23): 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Xue X Y, Tu K, Qin W C, et al. Drift and deposition of ultra-low altitude and low volume application in paddy field[J]. International Journal of Agricultural & Biological Engineering, 2014, 7(4): 23-28.
[31] 王沛,祁力钧,李慧,等. 植物叶片表面结构对雾滴沉积的影响分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(10):75-79.
Wang Pei, Qi Lijun, Li Hui, et al. Influence of plant leafsurface structures on droplet deposition[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(10): 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李明,赵春江,李道亮,等. 日光温室黄瓜叶片湿润传感器校准方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(2):224-230.
Li Ming, Zhao Chunjiang, Li Daoliang, et al. Calibration method of leaf wetness sensor for cucumber in solar greenhouse[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(2): 224-230. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Design and experiment of pesticide droplet deposition detection system based on principle of standing wave ratio
Wu Yalei1, Qi Lijun1※, Zhang Ya2, Gao Chunhua1, Li Shuai3, Elizabeth Musiu1
(1. College of Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China; 2. College of Information and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China; 3. Department of Mechanical Engineering; North China Electric Power University, Baoding 071051, China)
In order to realize the rapid acquisition of droplet deposition after application, this study proposed an interdigitated droplet collecting board structure based on standing wave ratio principle. The purpose of this study was to quickly and effectively obtain the characteristics and regularity of the droplet deposition distribution. On one hand, the system could reduce the experiment cost, the difficulty of operation and the complexity of the experiment. On the other hand, the system was important to evaluate the quality of pesticide application and improve the utilization rate of pesticide. Optimized droplet deposition detection technology could solve the problem of single measurement method and low efficiency of droplet deposition distribution in field, which was a goal pursued by scholars in this research field. Based on the principles of standing wave ratio and sensor network technology, the real-time detection system of droplet deposition on the ground was designed. The droplet distribution characteristics of the electric field were explored by the method of simulation, and then the optimal parameters of the interdigitated droplet collecting board were obtained. At the same time, combined with the greenhouse self-propelled sprayer system, the application test and verification test were carried out to obtain the distribution characteristics of droplet deposition accurately and quickly. The real-time detection system of droplet deposition in the greenhouse could be realized by using the method of standing wave ratio, and the reliability was very high. At the same time, the system had great practical significance in the field of droplet spray quality detection and regularity research. In order to verify the rationality of the interdigitated droplet collecting board structure, the electromagnetic simulation of the system was carried out by using the three-dimensional electromagnetic simulation software HFSS (high frequency structure simulator). The device took the STM32 single chip microcomputer as its core to build the ZigBee network, and the signal of the droplet collection sensor was transmitted to the remote terminal based on LabView2014 through the RS232 serial port, which realized the real-time monitoring of the droplet deposition. The results of the HFSS model showed that the electrostatic shielding appeared inside the interdigitated droplet collection board. The electromagnetic coupling could be realized by the droplets between the boards, which could be used to detect the droplet deposition. The sensitivity of the system would be decreased with the board spacing broadening. The regression equation of the relationship between the output voltage of the detection system and the deposition amount of the reagent solution was established through the calibration experiment. The determination coefficients under 2 different dielectric constants were 0.982 1 and 0.997 6 respectively. The 3W-ZW10 type self-propelled sprayer application test in greenhouse showed that the maximum relative error rate of the simulated value of the deposition amount of the system at the sampling point was not more than 7.95%. The RMSE (root mean square error) of the measured value was 0.076 7 mg/cm2. The detection accuracy of droplet deposition was high. The droplet deposition amount detection system can be used for rapid measurement of field droplet deposition rate based on the principle of standing wave ratio. From the laboratory calibration and application test results, it can be concluded that the design of the interdigitated droplet collection system is feasible within the range of 300 μm particle size. The proposed real-time detection method of droplet deposition in greenhouse based on the standing wave ratio is suitable for the detection of the droplet spray quality and the characteristics of droplet distribution. This research can provide reference for the measurement of droplet deposition.
design; computer simulation; spraying; standing wave ratio principle; interdigitated droplet collection board probe; droplets deposition quantity measurement; HFSS simulation
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.008
TP212.9; S491
A
1002-6819(2017)-15-0064-08
2017-03-03
2017-07-16
科技部国家重点研发计划项目“地面与航空高工效施药技术及智能化装备”(2016YFD0200700);科技部国家重点研发计划项目“现代果园智能化精细生产管理技术装备研发”(2017YFD0701400)
吴亚垒,男,博士生,研究方向为主要从事植保机械研究。北京中国农业大学工学院,100083。Email:kevin_wuyalei@cau.edu.cn
※通信作者:祁力钧,男,博士,教授,研究方向为从事植保机械研究。北京 中国农业大学工学院,100083。Email:qilijun@cau.edu.cn

