渠道渗漏HYDRUS模拟验证及影响因素分析
付 强,李 玥,李天霄,崔 嵩,刘 东(东北农业大学水利与土木工程学院,哈尔滨 150030)
渠道渗漏HYDRUS模拟验证及影响因素分析
付 强,李 玥,李天霄,崔 嵩,刘 东
(东北农业大学水利与土木工程学院,哈尔滨 150030)
渠道渗漏影响灌溉水利用效率,分析影响渗漏的主要因素,评估各影响因素对渠道渗漏的影响程度,可以为提高灌溉水利用效率提供理论参考。为了得到渠道渗漏的主要影响因素,进行了渠道渗漏室内模拟试验,观测不同边坡系数、入渗水头、渠道底宽下的累积入渗量和湿润锋推进过程,建立试验条件下的土壤水分运动模型,选用HYDRUS-2D软件求解所建模型,并将求解得到的模拟值与实测值进行比较,结果表明,模型模拟R2均高于0.9、均方根误差为0.43~4.99 L,检验了所建模型可以用于模拟渠道渗漏的土壤水分入渗过程。模拟表明,边坡系数对湿润锋运移距离和累积入渗量的影响很小,渠道底宽对渠道土壤水分入渗过程的影响较大,通过双因素方差分析,渠道底宽对累积入渗量和湿润锋运移距离的影响极显著(P<0.01),而入渗水头对水平距离的影响显著(P<0.05),渠道底宽和入渗水头之间不存在显著的交互影响(P>0.05)。研究结果可以为提高灌溉水利用效率、对灌溉渠道防渗提供技术参考。
渠道;入渗;数值分析;HYDRUS-2D;湿润锋;渗漏
0 引 言
灌溉水损失的一大部分来自渠道渗漏,渠道水渗漏会降低灌区的灌溉水利用效率,造成水资源的浪费。由于通过大田试验研究渠道渗漏土壤入渗规律比较困难,室内模拟试验开始受到关注:孙美等进行了夹砂层状土的渠道渗漏室内模拟试验,发现夹砂层会使湿润锋出现不连续的现象,具有一定的阻水减渗效果[1];张锐等开展了室内土箱模拟试验,发现土壤体积质量越大,入渗水头越高,灌溉需水量越少[2];Zhang等[3]实施了不同土壤类型、初始含水量和垄沟尺寸下的6组室内试验,观测了累积入渗量、湿润锋分布的变化,为设计垄沟种植系统提供了参考;Phogat等[4]利用土箱试验验证了二维水平衡模型,并分析了渠床高程对渗流和地下水位上升的影响;冀荣华等[5]在室内模拟了负压灌溉下的土壤水分运动,得到了灌水器半径对土壤入渗有显著影响的结论;聂卫波等[6]通过模拟沟灌入渗,建立了沟灌土分运动数值模型,并以此为基础,推导出沟灌条计算累积入渗量的方法。数值模拟方面,有限元计算机模型HYDRUS具有丰富的功能[7-12]:Bufon等[13]用HYDRUS-2D计算了滴灌条件的棉花含水量,发现计算结果与测量数据拟合程度较高;Kandelous等[14]用HYDRUS-2D模拟了地下滴灌系统的室内和大田试验,并用均方根误差对试验结果和模拟结果进行了评价,认为其对应关系非常好;张勇勇[15]建立了垄沟灌溉下的土壤水动力学模型,用HYDRUS-2D软件进行求解,得到了不同试验条件下的土壤含水量、累积入渗量和湿润锋运移距离并验证了设立模型的合理性。以上研究成果表明,用HYDRUS-2D模拟土壤水分入渗过程具有较高的可靠性,但并未考虑渠道边坡系数对土壤入渗的影响及各因素之间的交互特性;边坡系数作为渠道的重要参数,其变化对渠道入渗的影响非常重要,而各因素之间的交互影响对渠道断面的优化设计也起着决定性的作用。本文开展渠道渗漏室内模拟试验,建立试验条件下的土壤水分运动方程,通过试验和模拟方法分析边坡系数、入渗水头和渠道底宽及其交互作用对湿润锋运移距离和累积入渗量的影响,研究渠道土壤水分运动的主要影响因素,以期为减少渠道水渗漏,提高灌溉水利用效率提供理论支持。
1 材料与方法
1.1 室内试验
1.1.1 试验设备
试验设备由模拟土箱和供水设备2部分构成,模拟土箱规格为60 cm×20 cm×110 cm,由有机玻璃制成,为了防止气阻,土箱侧面和正面均留有排气孔;为了读数方便,土箱后侧玻璃板贴有刻度条。试验由马氏瓶供水,马氏瓶直径20 cm,高80 cm[16-17]。试验土箱内按照试验设计要求,设置恰当的渠道断面尺寸,试验装置如图1。
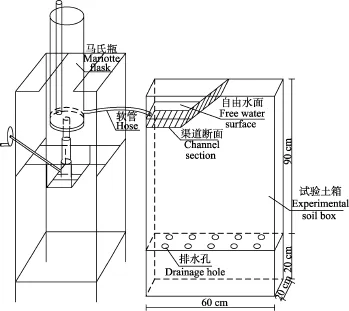
图1 室内模拟试验装置Fig. 1 Indoor simulation experimental setup
1.1.2 供试土样
试验土样于2016年7月取自哈尔滨市东北农业大学水利学院试验田(126°45′32″E、45°44′41″N)[18]。取样深度为10~30 cm,土壤质地为壤土,颗粒比较均匀,试验前,土样风干破碎,过2 mm筛,配置初始质量含水率7%,按设计干容重1.4 g/cm3分层(10 cm)装入试验土箱中,层间打毛[19]。
1.1.3 试验设计
室内试验于2016年夏季在东北农业大学水利学院水工厅内进行。试验采用三因素完全试验设计,设计的渠道底宽分别为5、10、15 cm;入渗水头分别为3、6、9 cm;边坡系数分别为1、1.2、1.5,共27个处理,各3次重复,需进行81次试验。考虑到工作量较大,而且试验目的是为了模型合理性分析,实际进行了15个处理试验。每次试验持续时间为480 min。
试验开始时首先按照设计的渠道断形状装填土样,随后调节马氏瓶进气管低端至设计入渗水头高度,快速向土箱内加水至设计水位,同时打开其止水夹,再对进气管低端高度进行微调。试验开始后每隔5 min记录马氏瓶读数,每隔10 min在土箱贴有刻度条的一侧描绘湿润峰曲线;试验进行一段时间后根据湿润锋运移距离和入渗速度适当延长读数、描绘时间间隔。试验结束后用分辨率为1334×750像素的相机拍下绘制的湿润峰曲线,整理数据。
1.2 模型建立
1.2.1 渠道水分运动模型
设计试验条件下的渠道水分入渗过程可以简化为二维非饱和水平及垂直入渗土壤水分运动问题,采用Richards方程进行描述[20]。
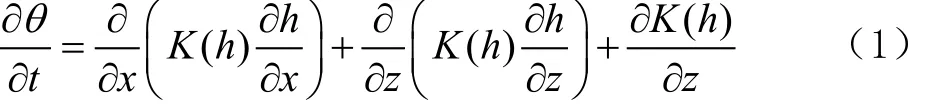
式中θ为土壤体积含水率,cm3/cm3;t为入渗时间,min;h为基质势,cm;x、z分别水平坐标和垂直距离,cm;K(h)为土壤非饱和导水率,cm/min。
上述Richards方程中提及的非饱和导水率、土壤基质势及含水率的关系采用VG-M模型进行描述[21-22]。
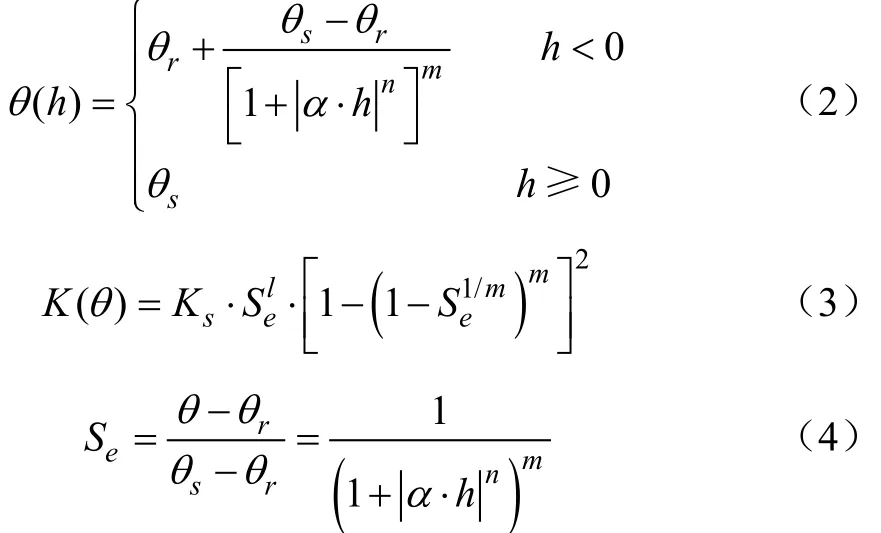
式中θr为残余含水率,cm3/cm3;θs为饱和含水率,cm3/;KS为饱和导水率,cm/min;m、n、α为经验系数,m=1-1/n。
根据离心机实测的土壤水分特征曲线,环刀法实测的饱和导水率等数据,采用MATLAB2012a拟合得到相关模型参数[23-26]:饱和含水率0.438 cm3/cm3;残余含水率0.042 cm3/cm3;α为 0.029;n为1.274;饱和导水率0.049 cm3/cm3。
1.2.2 定解条件
所建模型的初始和边界条件如图2所示。
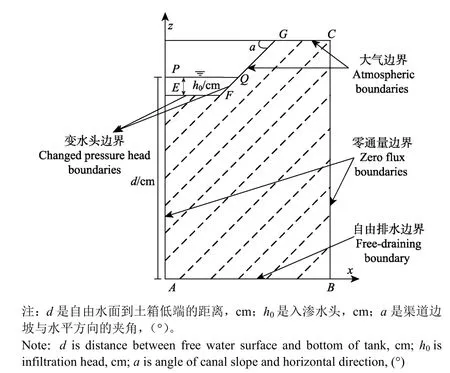
图2 模型求解的边界条件Fig. 2 Boundary conditions for model solving
初始条件:在设计的试验条件下,土壤水分剖面为稳定剖面。因此,模型的初始条件为计算区域内各点具有相同的水土势。
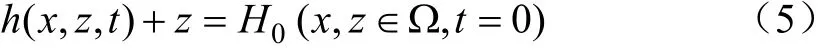
式中H0为初始水土势,cm;Ω为计算区域(即图2中的阴影部分);模拟区域最低点的z=0。
边界条件:试验过程中EFQ保持恒定入渗水头h0(cm);上边界QG和GC覆盖塑料薄膜,可以忽略蒸发,视为零通量边界;左边界EA为对称轴,水平通量为0;右边界CB视为零通量面;下边界AB设置了排水孔,而且在试验过程中湿润锋未到达土槽底部,不影响土壤水分入渗过程,保持恒定初始条件,设为自由排水边界。
综上,其边界条件可表述为

式中t0为试验延续时间,min。
1.2.3 数值计算
为了求解上述偏微分方程,采用HYDRUS-2D软件对试验设计方案下的湿润锋运移水平、竖直距离和累积入渗量进行数值模拟[27-29],并将所得结果与试验结果进行对比分析,采用均方根误差(root mean square error,RMSE)和决定系数(R2)[30]检验所建立的土壤水分运动方程的合理性。
2 结果与分析
2.1 模型验证
2.1.1 累积入渗量对比
从15组试验中随机选取9组试验组合研究其累积入渗量实测值和模拟值动态变化(图3)。结果表明,模拟值与实测值变化趋势一致,均表现出初期入渗较快,随入渗时间的延长入渗速率逐渐降低,并趋向稳定的状态。各次试验累积入渗量的模拟值和实测值的RMSE和 R2如表1所示。由表1可知,RMSE的值在0.43~4.99 L之间变化,R2值在0.91~0.97之间变化(均高于0.9),说明实测值与模拟值之间的对应关系较好,所建立的土壤水分运动方程合理。
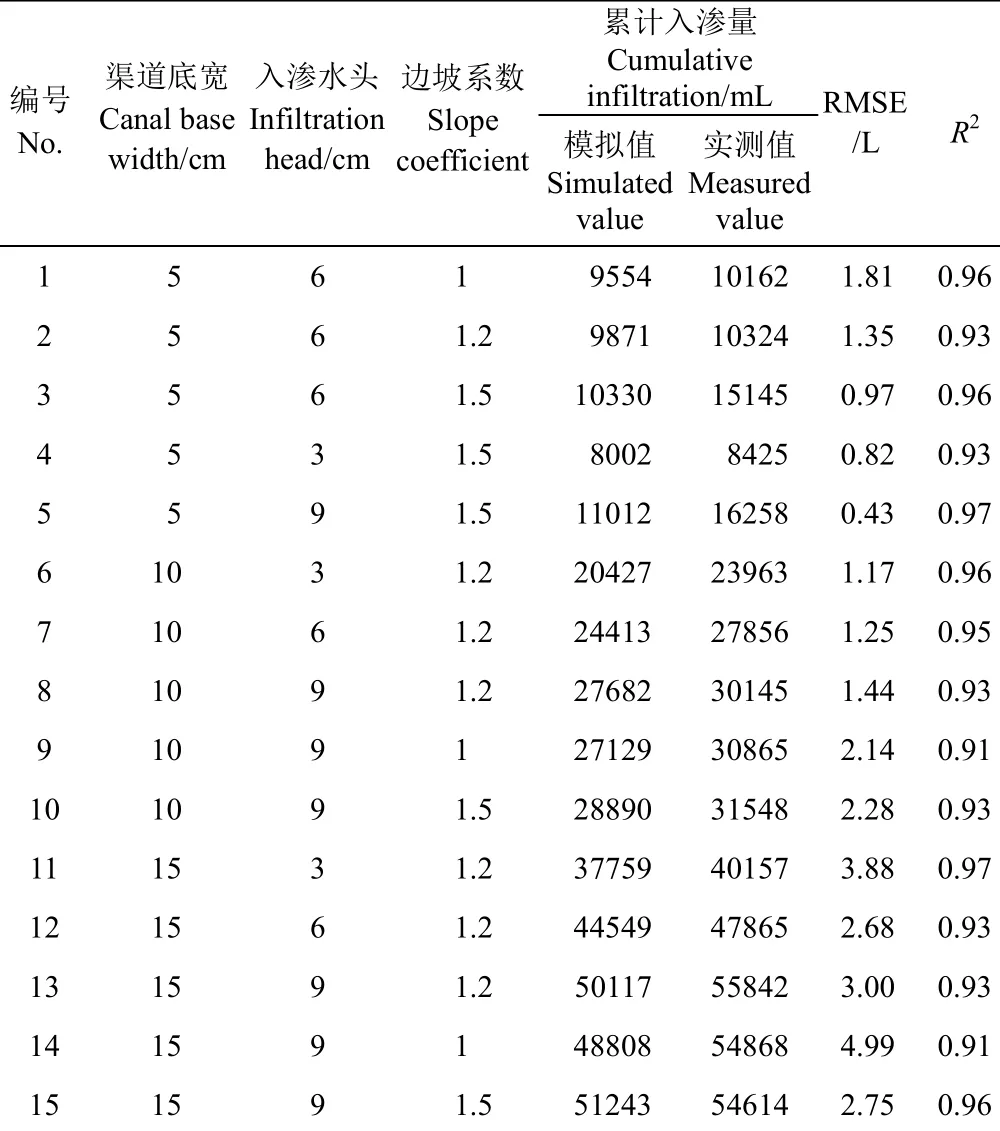
表1 累积入渗量实测值和模拟值的统计分析Table 1 Statistical analysis of measured and simulated cumulative infiltration
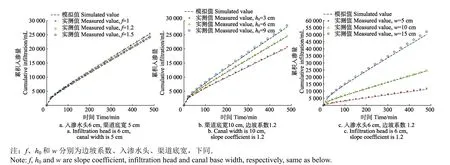
图3 各试验条件下累积入渗量的模拟值与实测值对比Fig. 3 Comparison of simulated and measured cumulative infiltration under various experimental conditions
2.1.2 湿润锋运移距离对比
以4种组合试验为例(图4),对比480 min内湿润锋运移距离模拟值和实测值,结果表明,各处理条件下湿润锋运移距离的实测值与模拟值基本吻合,均表现出初期运移速度较快,随试验时间的延长渐渐减缓,并趋于稳定。
综上,实测数据与模拟结果吻合较好,可以认为本文建立的土壤水动力学模型是可靠的,选取的相关参数值是适当的,用于模拟试验条件下的累积入渗量和湿润锋运移过程是可行的。
2.2 基于HYDRUS模拟的累积入渗量影响因素分析
为了分析渠道底宽w、入渗水头h0、边坡系数f对累积入渗量的影响,用HYDRUS软件模拟了27组渠道渗漏试验。以图5为例表明累积入渗量随三者的变化。由图可知,累积入渗量随渠道底宽和入渗水头变化较大,但边坡系数f对累积入渗量的影响很小。

图4 各试验条件下湿润峰的模拟值与实测值对比Fig. 4 Comparison of simulated and measured wetting front under various experimental conditions
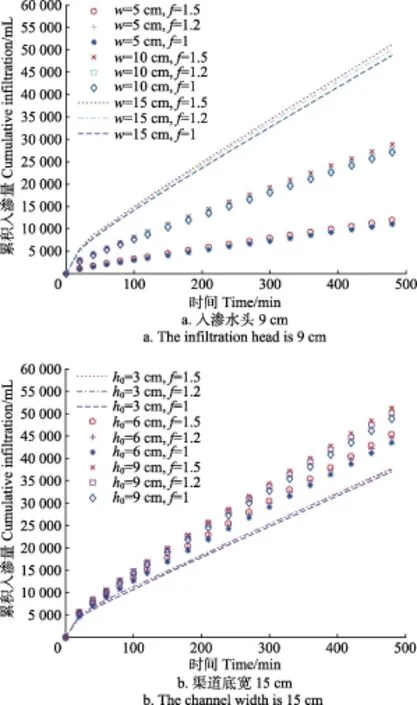
图5 各试验条件下的累积入渗量对比Fig. 5 Comparison of cumulative infiltration under different experimental conditions
对w和h0下渠道480 min累积入渗量做双因素方差分析,结果见表2。由表2可以看出,w对累积入渗量影响的F值为59.46,远大于临界值4.78,说明渠道底宽对入渗量的影响极显著(P<0.01)。当f=1、h0=3 cm时,若w由5 cm增加到15 cm时,累积入渗量由7 688 mL增加到37 027 mL,增加了382%。表2还表明h0对累积入渗量影响的F值为2.612,小于临界值4.778,说明其对累积入渗量的影响不显著(P>0.05)。二者之间交互影响F值为0.30,说明w和h0的交互作用不显著(P>0.05)。这是因为,随着f、h0和w的增加,湿周增加,入渗界面受水面积增加,因而累积入渗量增加。而f对湿周的影响很小,因此其对渠道入渗的影响不作考虑。且由表2可以看出,湿周随w的增幅比随h0的增幅大,因此w对累积入渗量的影响比h0显著。
2.3 基于HYDRUS模拟的湿润锋运移距离影响因素分析
不同水头下底宽、边坡系数对湿润锋运移影响类似,故以水头为9 cm表明不同底宽和边坡系数对湿润锋运移的影响,如图6所示。可以看出,边坡系数对湿润锋运移距离几乎没有影响,而渠道底宽、入渗水头与湿润锋运移距离呈正相关。
方差分析表明(表2),w对水平距离影响的F值为59.55,垂直距离为7.42,均大于临界值4.78,而且水平距离的F值远大于垂直距离,说明w对湿润锋运移距离的影响显著(P<0.01),且对水平距离的影响特别显著(P<0.01),比如在t=480 min,f=1、h0=3 cm的条件下,当w由5 cm增加到15 cm时,湿润锋运移水平、垂直距离分别增加了55.89%和47.82%。这是因为在f和h0不变的情况下,随着w的增加,入渗界面湿周增加,湿润锋运移距离有所增加,而w的增加直接导致垂向入渗面积增加,因而对水平距离的影响更为显著。入渗水头对水平距离影响的F值为19.14,垂直距离为3.0。说明h0对水平距离的影响显著(P<0.05),如在w=5 cm的条件下,
当h0由3 cm增加到9 cm时,湿润锋运移水平增加了33.45%。在w和f不变的条件下,随着h0增加,入渗界面压力势和受水面积增加,而h0的增加对垂向入渗面的影响较大,因而对水平距离的影响比较显著。w、h0对湿润锋运移水平、垂直距离的交互影响F值分别为0.15和0.004,说明w、h0对湿润锋运移距离不存在显著的交互作用(P<0.05)。
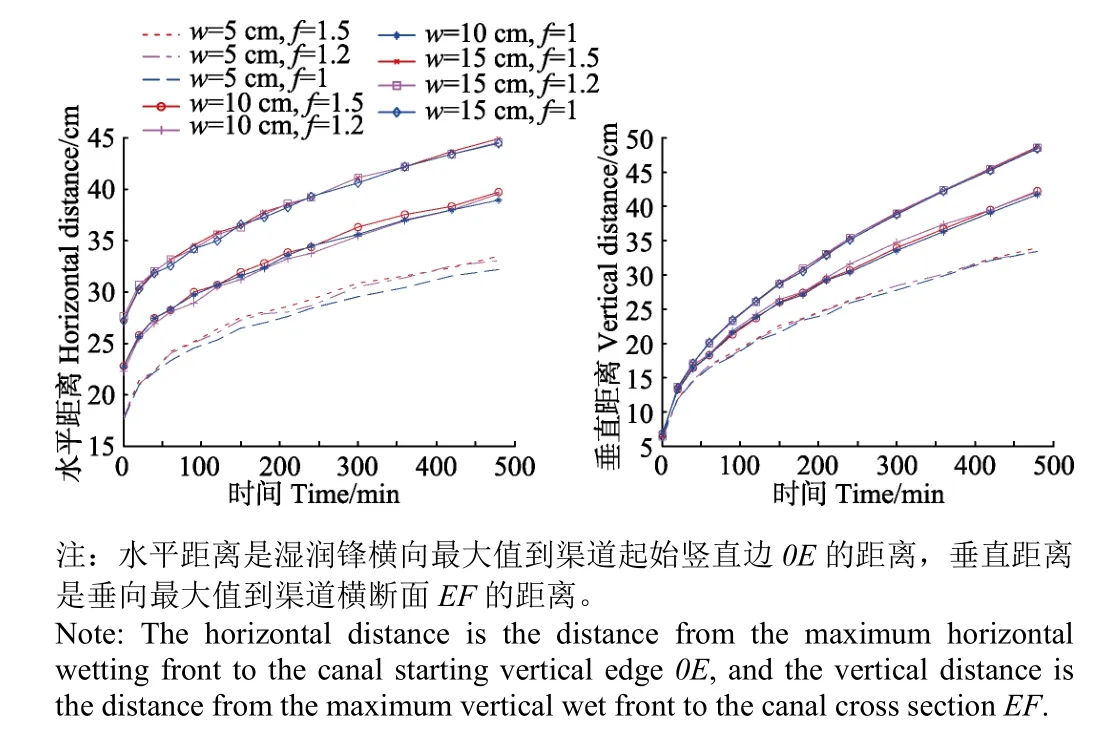
图6 各试验条件下的湿润锋运移距离对比Fig. 6 Comparison of wetting front migration distance under different experimental conditions
2.4 入渗速率变化
所有试验条件下的入渗速率均展现出随时间的延长渐渐减小并趋向稳定的征象;在试验开始初期,入渗速率下降得较快,随着时间的延长,土壤水土势梯度渐渐减小,入渗速率也随之减小并趋向一个定值。以f =1.5为例(图7),在w和f相同的条件下,随h0的增加,入渗速率增加。其原因为,h0增加时,入渗界面处压力势增大导致入渗速率增加;随入渗时间的推移,土壤湿润区域变大,水土势不断减小,并趋于稳定,因此入渗速率渐渐趋于稳定。在相同h0和f条件下,入渗速率随渠道底宽的增加而增加,且增幅较大。其原因为,渠道底宽增加,入渗界面湿周增加,受水面积变大,使得入渗速率增大。在w和h0相同的条件下,由于f对入渗断面湿周的影响很小,因此f对入渗速率几乎没有影响。
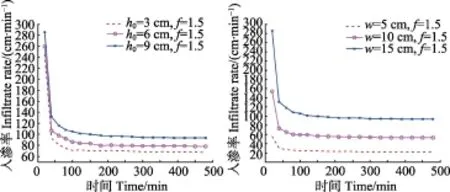
图7 边坡系数为1.5时不同底宽和入渗水头下的入渗率对比Fig. 7 Comparison of infiltration rates under different canal base width and infiltration head with slope coefficient of 1.5
3 结 论
选用基于Richards方程的有限元模拟软件HYDRUS-2D进行数值模拟得到的模拟值和实测值的的拟合程度较高(R2均高于0.9),可以契合地模拟试验条件下的渠道渗漏土壤水分入渗规律。
模拟结果均表明,边坡系数对土壤水分入渗过程的影响较为微弱;累积入渗量、湿润锋运移距离及入渗速率均随入渗水头增加而增加,且入渗水头对湿润锋运移水平距离的影响显著(P<0.05);随渠道底宽的增加,湿润锋运移距离、累积入渗量以及入渗率均表现出增加的趋势,且渠道底宽增加对累积入渗量和运移距离的影响极显著(P<0.01)。当边坡系数为1、入渗水头为3 cm时,若底宽由5 cm增加到15 cm时,480 min累积入渗量增加了382%,湿润锋运移水平、垂直距离分别增加了55.89%和47.82%。通过双因素方差分析,发现渠道底宽和入渗水头之间的没有显著的交互作用。
本文只针对各影响因素对渠道渗漏的影响做了定性分析,如何确定各试验条件下累积入渗量和湿润锋运移距离随影响因素变化的定量关系,寻求最优经济效益下的渠道断面设计,将作为下一步研究的重点。
[1] 孙美,毛晓敏,陈剑,等. 夹砂层状土条件下渠道渗漏的室内试验和数值模拟[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(8):33-38. Sun Mei, Mao Xiaomin, Chan Jian, et al. Laboratory experiment and simulation on canal seepage through sand interlayer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(8): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 张锐,闫超,刘博,等. 入渗水头及土壤体积质量对垄作沟灌土壤水分入渗和分布的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2016,35(6):37-41. Zhang Rui, Yan Chao, Liu Bo, et al. Effects of infiltration heads and soil volume-quality on soil water infiltratrion and distribution under ridge tillage furrow irrigation[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2016, 35(6): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Zhang Yongyong, Wu Pute, Zhao Xining, et al. Simulation of soil water dynamics for uncropped ridges and furrows under irrigation conditions[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2013, 93(1): 85-98.
[4] Phogat V, Malik R S, Kumar S. Modelling the effect of canal bed elevation on seepage and water table rise in a sand box filled with loamy soil[J]. Irrigation Science, 2009, 27(3): 191 -200.
[5] 冀荣华,王婷婷,祁力钧,等. 基于HYDRUS-2D的负压灌溉土壤水分入渗数值模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(4):113-119. Ji Ronghua, Wang Tingting, Qi Lijun, et al. Numerical simulation of soil moisture infiltration under negative pressure irrigation based on HYDRUS-2D[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(4): 113-119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 聂卫波,马孝义,王术礼. 沟灌土壤水分运动数值模拟与入渗模型[J]. 水科学进展,2009,20(5):668-676. Nie Weibo, Ma Xiaoyi, Wang Shuli. Infiltration model andnumerical simulation of the soil water movement in furrow irrigation[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2009, 20(5): 668-676. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Deb S K, Shukla M K, Mexal J G, et al. Evaluation of spatial and temporal root water uptake patterns of a flood-irrigated pecan tree using the HYDRUS (2D/3D) model[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 2013, 139(8): 599-611.
[8] Han Ming, Zhao Chengyi, Feng Gary, et al. Evaluating the effects of mulch and irrigation amount on soil water distribution and root zone water balance using HYDRUS-2D[J]. Water, 2015, 7(6): 2622-2640.
[9] Saso J K, Parkin G W, Drury C F, et al. Chloride leaching in two Ontario soils: Measurement and prediction using HYDRUS-1D[J]. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 92(2): 285-296.
[10] 李耀刚,王文娥,胡笑涛. 基于HYDRUS-3D的涌泉根灌土壤入渗数值模拟[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2013,31(6):546-552. Li Yaogang, Wang Wen′e, Hu Xiaotao. Numerical simulation of soil water infiltration under bubbled root irrigation based on HYDRUS-3D[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2013, 31(6): 546-552. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 潘红霞,付恒阳,贺屹. 基于HYDRUS-2D的地下滴灌下水分运移数值模拟研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2015,34(3):52—55. Pan Hongxia, Fu Hengyang, He Yi. Numerica simulation of water movement under subsurface drip irrigation using HYDRUS-2D[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2015, 34(3): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] El-Nesr M N, Alazba A A, Šimůnek J. HYDRUS simulations of the effects of dual-drip subsurface irrigation and a physical barrier on water movement and solute transport in soils[J]. Irrigation Science, 2014, 32(2): 111-125.
[13] Bufon V B, Lascano R J, Bednarz C, et al. Soil water content on drip irrigated cotton: Comparison of measured and simulated values obtained with the Hydrus 2D model[J]. Irrigation Science, 2012, 30(4): 259-273.
[14] Kandelous M M, Šimůnek J. Numerical simulations of water movement in a subsurface drip irrigation system under field and laboratory conditions using HYDRUS-2D[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, 97(7): 1070-1076.
[15] 张勇勇. 垄沟灌溉土壤水分入渗模拟研究[D]. 北京:中国科学院大学,2013. Zhang Yongyong. Simulation Research on Soil Water Infiltration under Ridge-furrow Irrigation[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 张锐. 垄作沟灌土壤水分入渗规律的试验研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2016. Zhang Rui. Research on the Infiltration Law of Ridge Tillage Furrow Irrigation Soil Water[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孙美,毛晓敏,陈剑. 渠道渗漏室内试验土壤水分运动数值模拟[C]. 纪念中国农业工程学会成立30周年暨中国农业工程学会2009年学术年会,2009.
[18] 付强,侯仁杰,王子龙,等. 冻融期积雪覆盖下土壤水热交互效应[J]. 农业工程学报2015,31(15):101-107. Fu Qiang, Hou Renjie, Wang Zilong, et al. Soil moisture thermal interaction effects under snow cover during freezing and thawing period[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(15): 101-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 聂卫波. 畦沟灌溉水流运动模型与数值模拟研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2009. Nie Weibo. Research on Water Flow Model and Numerical Simulation for Border and Furrow Irrigation[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 雷志栋,杨诗秀,谢森传. 土壤水动力学[M]. 北京:北京清华大学出版社,1988.
[21] Genuchten M T V. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898.
[22] Mualem Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 1976, 12(3): 513-522.
[23] 彭建平,邵爱军. 用Matlab确定土壤水分特征曲线参数[J].土壤,2007,39(3):433-438. Peng Jianping, Shao Aijun. Determination of parameters of soil water characteristic carve by Matlab[J]. Soils, 2007, 39(3): 433-438. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 杨改强,霍丽娟,杨国义,等. 利用MATLAB拟合vanGenuchten方程参数的研究[J]. 土壤,2010,42(2):268 -274. Yang Gaiqiang, Huo Lijuan, Yang Guoyi, et al. Research on fitting van Genuchten equation parameter with MATLAB Software[J]. Soils, 2010, 42(2): 268-274. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 付强,蒋睿奇,王子龙,等. 基于改进萤火虫算法的土壤水分特征曲线参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(11):117-122. Fu Qiang, Jiang Ruiqi, Wang Zilong, et al. Optimization of soil water characteristic curves parameters by modified firefly algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(11): 117-122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 刘洪波,张江辉,虎胆·吐马尔白,等. 土壤水分特征曲线VG模型参数求解对比分析[J]. 新疆农业大学学报,2011,34(5):437-441. Liu Hongbo, Zhang Jianghui, Hudan Tuma'erbai, et al. Contrast analysis on soil water characteristic curve of VG model parameters[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2011, 34(5): 437-441. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Iqbal S, Guber A K, Khan H Z. Estimating nitrogen leaching losses after compost application in furrow irrigated soils of Pakistan using HYDRUS-2D software[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2016, 168: 85-95.
[28] 李睿冉. HYDRUS-2D模型在渠道渗漏数值模拟中的应用[J]. 节水灌溉,2012(11):71-74.
[29] 毛晓敏,姚立强,冯绍元,等. 层状土条件下混凝土衬砌渠道渗漏及土壤水分分布的数值模拟[J]. 水利学报,2011,42(8):949-955. Mao Xiaomin, Yao Liqiang, Feng Shaoyuan, et al. Numerical simulation on canal seepage and soil water distribution for concrete lining canal with layered soil structure[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2011, 42(8): 949-955. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Singh D K, Rajput T B S, Singh D K, et al. Simulation of soil wetting pattern with subsurface drip irrigation from line source[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2006, 83(12): 130-134.
HYDRUS simulation and verification of canal leakage and its influencing factors analysis
Fu Qiang, Li Yue, Li Tianxiao, Cui Song, Liu Dong
(School of Water Conservancy & Civil Engineering, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China)
Canal leakage is the main factor affecting the efficiency of irrigation water. In this paper, the main factors of canal leakage (referring to infiltration) were analyzed and numerical analysis was carried out. In order to obtain the main factors that affected canal leakage, the indoor leakage simulation experiment was carried out. The experimental site was located in Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin(126°45′32″E、45°44′41″N). The test case was made of Plexiglas material, with the size 60 cm ×20 cm×110 cm (length×width×height). Mariotte flask was used to ensure water supply and its diameter was 20 cm and the height was 80 cm. A total of 15 treatments with 3 replicates were conducted. During the experiment, the cumulative infiltration and wet front migration distance of each experiment were recorded. In addition, the soil water characteristic curve of the soil samples was tested and the relevant parameters in the VG model were fitted. The parameters of the fitting and the saturated hydraulic conductivity measured by the ring knife method were input into the HYDRUS-2D software to solve the soil water movement model under the experimental conditions, and the simulate values were obtained. The error analysis of the simulated and measured values was carried out. The root mean square error and the determination coefficient of each experiment were calculated. The results showed that the model was reasonable with the root mean square error of 0.43-4.99 L and the R2higher than 0.9, and the model could simulate the soil water movement process under the experimental conditions. Based on the measured and simulated values, the influence of the 3 factors on the canal leakage and the influence of these factors on the infiltration process were analyzed. The influence of the slope coefficient on the infiltration process was weak and its influence on the infiltration process could be ignored. Two-way analysis of variance was performed in order to analyze the influence of canal base width and infiltration head and its interaction on cumulative infiltration and wetting front migration distance. The results showed that the statistic value of the canal base width was 55.62 for the cumulative infiltration, 59.46 for the horizontal distance of wet front migration, and 7.42 for the vertical distance. All the 3 statistic values were greater than the critical value of 4.78 under the significance level of 0.01. It indicated that the canal base width had a significant impact on the cumulative infiltration and the wetting front migration distance. The statistic value of the infiltration head at the cumulative infiltration was 2.612, the statistic value of the horizontal distance of wet front migration was 19.14, and the vertical distance was 3.00. The infiltration head had a significant effect on the horizontal distance. The statistic values of the effects of canal width and infiltration head on the cumulative infiltration and the horizontal and vertical distance were 0.30, 0.15 and 0.004, respectively. They were less than the critical value of 3.47, indicating that there was no significant interaction between the canal width and infiltration head (P>0.05). The results of the study can provide technical support for improving the utilization efficiency of irrigation water from the aspect of canal seepage control.
canals; infiltration; numerical analysis; HYDRUS-2D; wetting front; leakage
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.015
TV732.6; S152.7+2
A
1002-6819(2017)-16-0112-07
付 强,李 玥,李天霄,崔 嵩,刘 东. 渠道渗漏HYDRUS模拟验证及影响因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(16):112-118.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.015 http://www.tcsae.org
Fu Qiang, Li Yue, Li Tianxiao, Cui Song, Liu Dong. HYDRUS simulation and verification of canal leakage and its influencing factors analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(16): 112-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.015 http://www.tcsae.org
2017-02-24
2017-06-10
国家自然科学基金(51479032、51579044);国家重点研发计划(2017YFC0406002)
付 强,男,辽宁锦州人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业水土资源系统分析、冻融土壤水热作用机理等方面研究。哈尔滨 东北农业大学水利与土木工程学院,150030。Email:fuqiang0629@126.com。

