具有截断控制参数学习效应的单机排序问题
罗成新, 翟雯瑾
(沈阳师范大学 数学与系统科学学院, 沈阳 110034)
具有截断控制参数学习效应的单机排序问题
罗成新, 翟雯瑾
(沈阳师范大学 数学与系统科学学院, 沈阳 110034)
讨论具有截断控制参数学习效应和退化效应且工件的加工时间依赖于资源分配的单机排序问题。分别在线性资源和凸资源消费函数条件下研究问题。每个任务有一个松弛工期窗口,任务的实际加工时间依赖于截断控制参数、工件的开始加工时间和分配方案的资源数量。目标是求出任务的最优排序、每个任务的工期窗口位置、最优资源分配,使由任务总提前、延误、工期窗口的开始时间、窗口大小、时间表长、总完工时间及资源总费用的加权和最小。将问题转化为指派问题,证明了该问题是在多项式时间内可解的,并分别给出了2个多项式时间的最优算法。
排序; 资源分配; 截断控制参数; 退化效应; 指派问题
0 引 言
近20年,由于现代运营管理等产业的引进,具有工期的排序问题陆续进入人们的视野。如果一个工件在它的工期之前完成加工,那么它需要承担一部分的提前惩罚费用;相应的,如果一个工件在它的工期之后完成加工,那么它需要承担一部分的延误惩罚费用。Li[1]研究了工件的交货期与工件位置相关的单机排序问题。
经典排序模型中,任务的加工时间通常都是固定的常数,然而考虑到学习效应、退化效应、资源分配等情况,任务的加工时间不再是固定不变的。Cheng[2-3]研究带有退化效应的工期指派问题,目标是确定最优工期及最优的排序使目标函数值最小。由于实际生产需要,具有学习效应与退化效应问题越来越受重视。Yang[4]等研究了带有退化效应与维修活动的工期指派问题。文献[5-13]讨论了带有提前、延误的工期指派问题。
Wang[13]等研究了具有截断控制参数学习效应和退化效应且工件的加工时间依赖于资源分配的单机排序问题,并求得最大加工时间与总完工时间最小值时的最优算法。本文在文献[13]的基础上,研究工件实际加工时间的线性资源消耗函数与凸资源消耗函数下的带有提前、延误、交货期开始时间、交货期大小、最大完工时间、总完工时间及总资源分配的总费用的最小化问题。工件的实际加工时间是关于位置与资源的具有截断参数学习效应与退化效应的线性函数与凸函数,通过将问题转化为指派问题得到了多项式时间的最优算法。
1 问题描述
考虑如下的问题:n个独立且在零时刻到达的工件N={J1,J2,…,Jn},需要在一台机器上加工,在同一时刻机器最多只能加工一个工件,工件必须连续加工不允许中断。在本文中,考虑2种资源分配分别为退化效应与具有截断控制参数的学习效应模型。在本文里线性资源消耗函数模型中工件的实际处理时间表达式如下:
其中:pj为工件Jj的基本加工时间;工件Jj的学习指数为aj(aj≤0);工件Jj的截断控制参数为bj(0
本文里凸资源消耗函数模型中工件的实际处理时间表达式如下:

其中:α>0,β>0,γ>0,δ1≥0,δ2≥0,μ≥0为给定常数;Gj(>0)为资源分配的单位费用。
使用三参数[7]表示法可将上述问题分别表示为
(1)
(2)
2 最优算法


因此引理结论成立。证毕。

证明 与引理1证明类似。证毕。
引理3 对于任意给定的排序π=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]),存在最优的q1和q2,分别是第k个和第l个工件的完工时间(l≥k),即

证明 仅就问题(1)来证明引理,问题(2)可用相同方法证明。如果最优排序π不具有这个性质,即
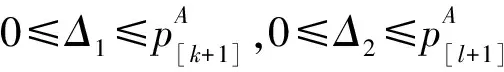
1) 工件J[j](j=1,2,…,k+1) 提前的总费用为
2) 工件J[j](j=l+2,l+3,…,n)延迟的总费用为
3) 窗口开始时间总费用为
4) 窗口大小的总费用为

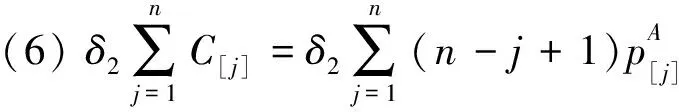
因此,总费用可以表示为Z=AΔ1+BΔ2+C,其中
显然A,B与C都是不依赖Δ1与Δ2的常数。要使Z最小必须使
因此,对于任意给定的排序π,存在最优的q1和q2,分别是第k个和第l个工件的完工时间。证毕。

证明 给出一个适合于引理3的最优排序,考虑以下的费用:
1) 工件J[j](j=1,2,…,k)提前的总费用为
2) 工件J[j](j=l+2,l+3,…,n)延迟的总费用为
3) 窗口开始时间总费用为
4) 窗口大小的总费用为


引理5 给定排序π=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]),问题(1)中工件J[k](k=1,2,…,n)的实际加工时间为
(3)
证明 用数学归纳法,此处省略。证毕。
根据引理3、4与5,可以得出
(4)
其中
(5)

(6)
对于任意的排序π=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]),由式(4)可以得出最优资源为
(7)
为了求出最优解,将问题(1)转化为指派问题。对j,r=1,2,…,n令
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
因此,对于问题(1)可以给出如下最优算法。
算法1
第1步 根据引理4,计算出k与l;
第2步 根据(8)计算出λjr,j,r=1,2,…,n;
第3步 求解指派问题(9)-(12),得到最优排序π*=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]);

定理1 对于问题(1)可以通过求解指派问题在O(n3)时间内得到最优解。
证明 上述分析保证了定理结论的正确性。算法1中的第1、4、5步可以在O(1)时间内完成,第2、3步需要O(n3)时间内完成,所以算法的时间复杂性为O(n3)。证毕。
引理6 给定排序π=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]),问题(2)工件J[k](k=1,2,…,n)的实际加工时间为
(13)
由此可以得出
(14)
引理7 问题(2)对于工件排序π=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]),最优资源分配如下:
(15)
将式(15)代入式(14)得
(16)
为了求出最优解,将问题(2)化为指派问题。引入
(17)
则问题(2)转化为如下指派问题:
(18)
(19)
(20)
(21)
因此,对于问题(2)可以给出如下最优算法。
算法2
第1步 根据引理4,计算出k与l;
第2步 根据(17)计算出ϑjr,j,r=1,2,…,n;
第3步 求解指派问题(18)~(21),得到最优排序π*=(J[1],J[2],…,J[n]);
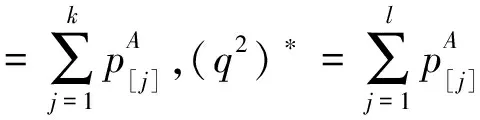
定理2 对于问题(2)可以通过求解指派问题在O(n3)时间内求得最优解。
证明 证明过程与定理1证明过程类似。此处省略。证毕。
3 结 论
本文研究了具有截断控制参数的单机排序问题。加工时间是关于资源的线性函数与凸函数,目标是求带有提前、延误、交货期开始时间、交货期大小、最大完工时间、总完工时间及总资源分配的总费用的最小值。通过将问题转化为指派问题,证明问题多项式时间内是可解,并给出了多项式时间最优算法。
[ 1 ]LI Gang,LUO Meiling,ZHANG Wenjie,et al. Single-machine due-window assignment scheduling based on flow allowance,learning effect and resource allocation[J].International Journal of Production Research, 2015,53(4):1228-1241.
[ 2 ]CHENG T C E,KANG Liying,NG C T. Single machine due-date scheduling of jobs with decreasing start-time dependent processing times[J]. Int T Oper Res, 2005,12(3):355-366.
[ 3 ]CHENG T C E,KANG Liying,NG C T. Due-date assignment and single machine scheduling with deteriorating jobs[J]. J Oper Res Soc, 2004,55(2):198-203.
[ 4 ]YANG S J,YANG D L,CHENG T C E. Single-machine due-window assignment and scheduling with job-dependent aging effect and deteriorating maintenance[J]. Comput Oper Res, 2010,37(8):1510-1514.
[ 5 ]GRAHAM R L,LAWLER E L,LENSTRA J K,et al. Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey[J]. Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 1979,5:287-326.
[ 6 ]BAKER K R,SCUDDER G D. Sequencing with earliness and tardiness penalties: a review[J]. Oper Res, 1990,38(1):22-36.
[ 7 ]GORDON V S,TARASEVICH A A. A note: Common due date assignment for a single machine scheduling with the rate-modifying activity[J]. Comput Oper Res, 2009,36(2):325-328.
[ 8 ]BISKUP D,JAHNKE H. Common due date assignment for scheduling on a single machine with jointly reducible processing times[J]. Int J Prod Econ, 2001,69(3):317-322.
[ 9 ]SHABTAY D,STEINER G. The single-machine earliness-tardiness scheduling problem with due date assignment and resource-dependent processing times[J]. Ann Oper Res, 2008,159(1):25-40.
[10]KUO W H,YANG D L. A note on due-date assignment and single-machine scheduling with deteriorating jobs[J]. J Oper Res Soc, 2008,59(6):857-859.
[11]YANGS J,LEE H T,GUO J Y. Multiple common due dates assignment and scheduling problems with resource allocation and general position-dependent deterioration effect[J]. Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 2013,67(1/2/3/4):181-188.
[12]WANG Jibo,WANG Jianjun. Research on scheduling with job-dependent learning effect and convex resource-dependent processing times[J]. Int J Pro Res, 2015,53(19):5826-5836.
[13]WANG Jibo,LIU M Q, YIN N,et al. Scheduling Jobs with Controllable Processing Time, Truncated Job-Dependent Learning and Deteriortion Effects[J]. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 2017,13(2):1025-1039.
Single machine scheduling problem with the truncated control learning effect
LUOChengxin,ZHAIWenjin
(School of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shenyang Normal University, Shenyang 110034, China)
In this paper, we study a single machine scheduling problem with truncated job-dependent learning effect and deterioration effects and processing time dependent on resource. Each job has a slack due-window. The actual processing time of a job is a linear function and a convex function of the resource amount allocated to it, respectively. The actual processing time of each job depends on a truncated control parameter, the starting time and the resource amount allocated to it. The objective is to find the optimal sequence of jobs, slack due-window and the optimal resource allocation scheme to minimize the weighted costs of earliness, tardiness, the starting of due-window, and the size of the due windows, makespan, the total completion times and the resource allocation. We show that the problem is polynomial solvable by transforming this it into an assignment problem. Two polynomial time optimal algorithms are presented, respectively.
scheduling; resource allocation; truncated control parameter; deterioration effect; assignment problem
2017-06-02。
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11171050); 辽宁省教育厅科学研究一般项目(L2014433)。
罗成新(1958-),男,辽宁新宾人,沈阳师范大学教授,博士。
1673-5862(2017)03-0305-06
O223
A
10.3969/ j.issn.1673-5862.2017.03.009