高迁移率族蛋白-1、糖基化终产物受体及Toll样受体-4通路对爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤影响研究
佟昌慈, 柳云恩, 张玉彪, 施 琳, 丛培芳, 刘 颖, 史秀云, 金红旭, 侯明晓
沈阳军区总医院 急诊医学部 全军重症(战)创伤救治中心实验室 辽宁省重症创伤和器官保护重点实验室,辽宁 沈阳 110016
·爆震伤·
高迁移率族蛋白-1、糖基化终产物受体及Toll样受体-4通路对爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤影响研究
佟昌慈, 柳云恩, 张玉彪, 施 琳, 丛培芳, 刘 颖, 史秀云, 金红旭, 侯明晓
沈阳军区总医院 急诊医学部 全军重症(战)创伤救治中心实验室 辽宁省重症创伤和器官保护重点实验室,辽宁 沈阳 110016
目的 探讨高迁移率族蛋白(HMGB)-1、糖基化终产物受体(RAGE)及Toll样受体(TLR)-4通路对爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤的调控机制。方法 选取40只SD大鼠,10只纳入对照组;其余30只在建立爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤模型后,分别纳入6 h组、12 h组、24 h组。ELISA检测大鼠血清炎症因子HMGB-1、白细胞介素(IL)-1α、IL-8;Real Time PCR、Western Blot及免疫荧光检测大鼠肺组织炎症因子HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8及通路相关蛋白RAGE、TLR-4、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)、两面神激酶(JAK)-2、信号传导及转录激活因子(STAT)-3。结果 ELISA结果显示,与对照组比较,12 h组、24 h组HMGB-1与IL-1α表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组IL-8表达增高,12 h组表达量最高(P<0.05)。Real Time PCR、Western Blot及免疫荧光结果显示,与对照组比较,12 h组、24 h组HMGB-1与IL-1α表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组IL-8表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;12 h组RAGE表达增高;12 h组、24 h组TLR-4、p38 MAPK表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组、24 h组JAK-2、STAT-3表达增高,12 h组表达量最高(P<0.05)。结论 爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤诱导HMGB-1释放,结合RAGE与TLR-4受体,激活p38 MAPK与JAK/STAT通路,促进炎症因子IL-1α、IL-8的作用,调节炎症反应。
爆震伤; 急性肺损伤; 大鼠; 高迁移率族蛋白; 糖基化终产物受体; Toll样受体
随着现代局部军事冲突的增加,高能武器的大量使用,恐怖事件、瓦斯与地铁内爆炸等事故的发生率上升,爆震伤已经成为青壮年死亡的重要原因,造成了严重的生命损害,消耗了大量的医疗资源。爆震伤是一种复杂的物理损伤,冲击波直接或间接作用机体并释放出能量造成损伤,常累及多个重要器官,具有伤情复杂、死亡率较高、临床伤情变化较快、休克率高等特点[1-3]。因此,对爆震伤的合理救治不仅是当前医学研究的热点,更是社会安全稳定发展的迫切需要。肺是爆震伤的主要累及器官,也是导致伤员死亡最常见的致命伤之一。爆炸形成的冲击波作用于机体,引起胸廓变形,胸腔内压增加,并通过肺实质传播,导致即刻或迟发性的大出血与肺泡、肺毛细血管破裂,出现肺部出血、肺组织挫伤及肺水肿等[3-5]。随着病情的恶化,会发展为急性肺损伤(acute lung injury,ALI)、急性呼吸窘迫综合征(acute respiratory distress syndrome,ARDS)及多器官功能障碍综合征(multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,MODS)[6-7]。有研究表明,ALI常伴随炎症反应、活性氧释放、谷氨酸毒性及线粒体功能障碍等[8-9]。目前,肺爆震伤患者只能接受常规抗炎与机械辅助治疗[10],无针对性治疗与保护类药物,死亡率居高不下。因此,研究爆震伤致ALI的发病机制与救治方法具有重要意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物 选取沈阳军区总医院实验动物科的健康清洁级SD大鼠40只,体质量(200±22)g,随机分成4组(对照组,6 h组、12 h组、24 h组),每组各10只。清洁级动物房常规饲养,适应性喂养3 d。
1.2 实验试剂 ELISA、Trizol reagent、SYBR Green PCR试剂盒、逆转录试剂盒均购自日本TAKALA公司,蛋白提取试剂盒、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒均购自南京Vazyme公司,ECL显色试剂盒购自美国BIO-RAD公司,二抗、高迁移率族蛋白(high mobility group box protein,HMGB)-1抗体、糖基化终产物受体(receptor for advanced glycation end-products,RAGE)抗体、Toll样受体(toll-like family of receptors,TLR)-4抗体、两面神激酶(Janus kinase,JAK)-2抗体、信号传导及转录激活因子(signal transducers and activators of transcription,STAT)-3抗体均购自英国Abcam公司,白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-1α抗体、IL-8抗体、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPK)抗体、β-actin抗体均购自美国Santa公司。
1.3 动物模型建立 采用自主设计研发的高仿真爆震伤模拟装置,建立爆震伤致大鼠ALI模型。装置设计如下:下方为空气压缩装置,长度约100.0 cm,周径约30.0 cm,将16层厚度约0.8 μm的铝薄置于中间层。通过空气压缩装置压缩空气,当达到一定压力时,铝膜破裂产生冲击波。大鼠称质量后进行麻醉,将麻醉后的大鼠置于保护罩内,保护大鼠其他部位,只显露胸部,随后将大鼠固定于装置的网状部位。通电后记录铝膜爆破的时间、下方空气压缩装置内压力及上方压力传感器所记录的超压波压力。
1.4 ELISA 取各组大鼠血液,分离血清后,通过ELISA试剂盒检测HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8的浓度。具体步骤见试剂盒说明书。
1.5 Real Time PCR Trizol reagent提取大鼠肺组织总RNA。取4.0 μg总RNA,65℃变性5 min,逆转录酶42℃逆转录30 min,合成cDNA。采用SYBR荧光染料,Smart Cycler System软件进行分析。反应体系如下:cDNA 2.0 μl,ddH2O 6.4 μl,上下游引物各0.8 μl,SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ 10.0 μl。扩增条件:56℃退火30 s,72℃延伸30 s,45个循环。根据GenBank HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8、RAGE、TLR-4、p38 MAPK、JAK-2、STAT-3及β-actin cDNA序列,Primer 5引物软件设计特异性引物(表1)。
1.6 Western Blot 取大鼠肺组织,加入蛋白裂解液,匀浆机制成匀浆,12 000 r/min离心5 min,吸取上清蛋白液,BCA蛋白定量试剂盒与酶标仪测定蛋白浓度。实验蛋白样品配平后,加入相应比例的6×Loading Buffer,煮沸变性5 min,SDS-PAGE电泳后,转膜,5%脱脂奶粉PBST缓冲液室温封闭2 h,PBST洗膜3次。加入一抗HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8、RAGE、TLR-4、p38 MAPK、JAK-2、STAT-3及β-actin 4℃孵育过夜。PBST洗膜3次,每次10 min,辣根过氧化物酶标记二抗,室温孵育1.5 h。洗膜3次,ECL显影。1.7 免疫荧光 石蜡切片脱蜡与水化,3% H2O2室温孵育10 min以消除内源性过氧化物酶的活性。浸泡3次,每次5 min。抗原修复:高压锅中加入0.01 mol/L柠檬酸钠缓冲液,放入组织芯片,加热,保压100 s后,冷却至室温。PBS浸泡2次,每次5 min。正常山羊血清封闭,室温孵育30 min,倒去血清,滴加一抗工作液,4℃过夜。PBS浸泡3次,每次5 min,滴加适量荧光二抗,室温孵育1 h,PBS浸泡3次,每次5 min。滴加适量的DAPI,室温孵育10 min,PBS浸泡3次,每次5 min,封片镜检。

2 结果
2.1 ELISA检测大鼠血清炎症因子HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8 与对照组比较,12 h组、24 h组HMGB-1与IL-1α表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组IL-8表达增高,12 h组表达量最高(P<0.05)。见表2。
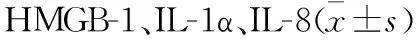
表2 ELISA检测大鼠血清炎症因子
注:与对照组比较,①P<0.05
2.2 Real Time PCR、Western Blot及免疫荧光检测大鼠肺组织炎症因子HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8 与对照组比较,12 h组、24 h组HMGB-1与IL-1α表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组IL-8表达增高,12 h组表达量最高(P<0.05)。见图1、2。
2.3 Real Time PCR、Western Blot及免疫荧光检测通路相关蛋白 RAGE、TLR-4、p38 MAPK、JAK-2、STAT-3与对照组比较,12 h组RAGE表达增高;12 h组、24 h组TLR-4、p38 MAPK表达增高,12 h组表达量最高;6 h组、12 h组、24 h组JAK-2、STAT-3表达增高,12 h组表达量最高(P<0.05)。见图3、4。
3 讨论
爆震伤致ALI患者病情严重、救治困难,易早期死亡[11]。肺组织的原发性损伤是由爆炸时瞬间产生的冲击波与高能碎片冲击所致,之后,肺组织细胞的损伤坏死诱导内源性炎症介质的表达与释放,引起继发性损伤[12]。
HMGB-1是一种非组蛋白染色体结合蛋白,当机体处于稳态、无外界刺激时,HMGB-1主要存在于细胞核中[13-15];当外界信号刺激细胞时,细胞应激,HMGB-1赖氨酸残基被乙酰化后,释放到细胞外,诱导局部组织或全身性炎症反应,细胞破损或坏死亦可导致HMGB-1的释放增加[16-17]。HMGB-1可刺激巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞及单核细胞,使肿瘤坏死因子、IL-1α、IL -1β、IL -6、IL-8、巨噬细胞炎性蛋白-1α等分泌量增加[16,18-22]。HMGB-1激活炎症反应主要通过结合晚期RAGE实现[23]。RAGE是广泛存在于不同细胞表面的免疫球蛋白超家族跨膜蛋白,在正常组织细胞中的表达水平很低,其配体聚集时可诱导其表达增加[24-25]。HMGB-1与RAGE受体结合后,激活JAK/STAT信号转导通路,活化NF-κB,促进炎症因子表达,反馈调节HMGB-1。另外,HMGB-1可激活p38 MAPK通路,调节炎症反应[26-27]。本研究结果中,爆震伤致大鼠ALI诱导了HMGB-1的释放,促进了RAGE、p38 MAPK、JAK-2、STAT-3的表达。这说明,爆震伤致ALI引起的细胞应激与损伤坏死可促进HMGB-1释放,增加HMGB-1与RAGE受体结合,激活p38 MAPK与JAK/STAT通路,促进IL-1、IL-8等炎症因子释放,诱导炎症反应。
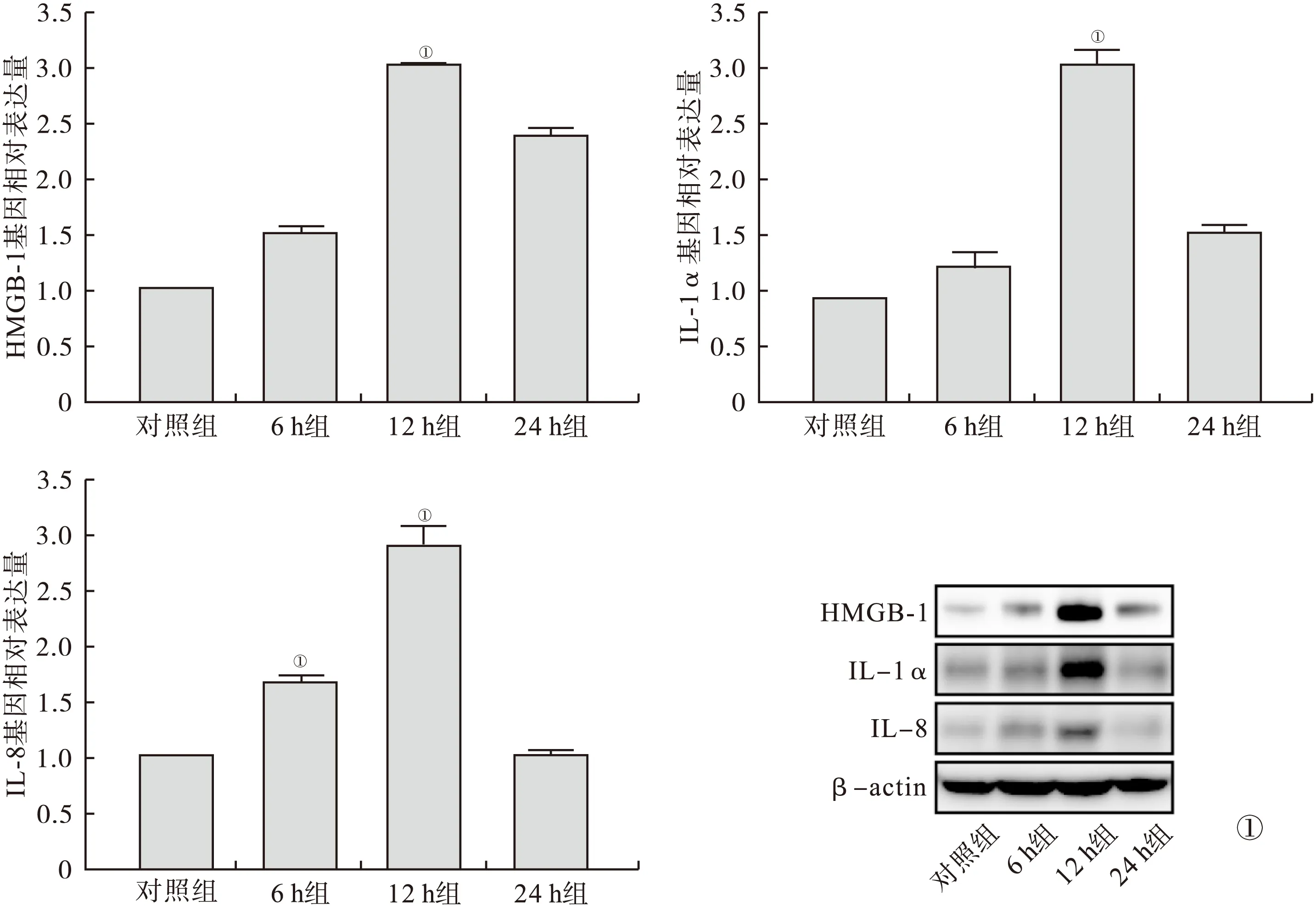
图1 Real Time PCR与Western Blot检测大鼠肺组织炎症因子HMGB-1、IL-1α、IL-8(与对照组比较,①P<0.05)

图2 免疫荧光检测大鼠肺组织炎症因子HMGB-1(400倍)
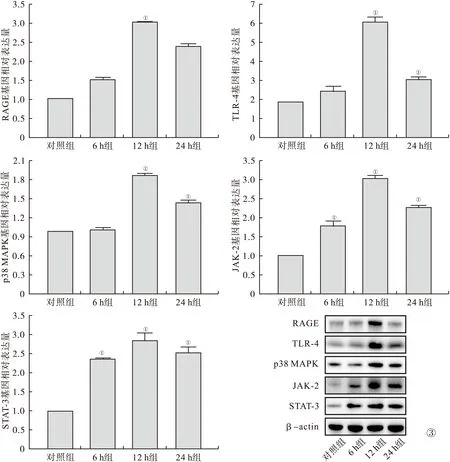
图3 Real Time PCR与Western Blot检测通路相关蛋白RAGE、TLR-4、p38 MAPK、JAK-2、STAT-3(与对照组比较,①P<0.05)
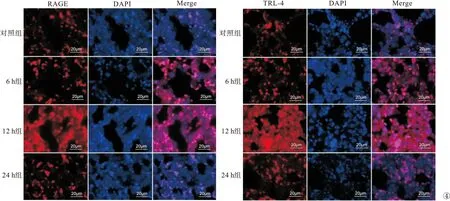
图4 免疫荧光检测通路相关蛋白RAGE、TLR-4(400倍)
研究发现,通过阻断抗体或基因沉默敲除RAGE并不能完全抑制HMGB-1诱导的炎症反应,Toll样受体家族中的TLR-2与TLR-4受体也可与HMGB-1结合,活化NF-κB,诱导炎症反应发生[28-29]。HMGB-1介导的TLR-4可激活IKK-α与IKK-β,而RAGE仅可激活IKK-β[30-31]。TLR-4还可激活p38 MAPK通路[32-33]。本研究结果中,爆震伤致大鼠ALI诱导了HMGB-1的释放,促进了TLR-4、p38 MAPK的表达。这说明,爆震伤致ALI引起的细胞应激与损伤坏死可促进HMGB-1释放,除结合RAGE受体外,还可结合TLR-4受体并激活p38 MAPK通路,促进IL-1、IL-8等炎症因子释放,诱导炎症反应。
综上所述,爆震伤致大鼠急性肺损伤诱导HMGB-1释放,结合RAGE与TLR-4受体,激活p38 MAPK与JAK/STAT通路,促进炎症因子IL-1α、IL-8作用,调节炎症反应。
[1] W Brad H,Shaylen G,Carly N,et al.Distinguishing the unique neuropathological profile of blast polytrauma[J].Oxid Med Cell Longev,2017,2017:5175249.
[2] Brandon PL,Ryan CT,Aric FL,et al.Blast scaling parameters:transitioning from lung to skull base metrics[J].J Surg Emerg Med,2017,1(1):3.
[3] Scott TE,Kirkman E,Haque M,et al.Primary blast lung injury-a review[J].Br J Anaesth,2017,118(3):311.
[4] Barnettvanes A,Sharrock A,Eftaxiopoulou T,et al.CD43Lo classical monocytes participate in the cellular immune response to isolated primary blast lung injury[J].J Trauma Acute Care Surg,2016,81:1.
[5] Scott T,Hulse E,Haque M,et al.Modelling primary blast lung injury:current capability and future direction[J].J R Army Med Corps,2016:jramc-2016-000678.
[6] Hu PJ,Pittet JF,Kerby JD,et al.Acute brain trauma,lung injury,and pneumonia:more than just altered mental status and decreased airway protection[J].Am J Pathol,2017:ajplung-00485-2016.
[7] Deng B,Deng C,Cheng Z.Chinese herbal extractions for relieving radiation induced lung injury:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2017,2017:2141645.
[8] Gill SE,Yamashita CM,Veldhuizen RA.Lung remodeling associated with recovery from acute lung injury[J].Cell Tissue Res,2017,367(3):495-509.
[9] Liu WW,Han CH,Zhang PX,et al.Nitric oxide and hyperoxic acute lung injury[J].Med Gas Res,2016,6(2):85-95.
[10] Schmidt GA.Managing acute lung injury[J].Clin Chest Med,2016,37(4):647-658.
[11] Singleton JA,Gibb IE,Bull AM,et al.Primary blast lung injury prevalence and fatal injuries from explosions:insights from postmortem computed tomographic analysis of 121 improvised explosive device fatalities[J].J Trauma Acute Care Surg,2013,75(Suppl 2):S269.
[12] Chai JK,Cai JH,Deng HP,et al.Role of neutrophil elastase in lung injury induced by burn-blast combined injury in rats[J].Burns,2013,39(4):745.
[13] Di Candia L,Gomez E,Venereau E,et al.HMGB-1 is upregulated in the airways in asthma and potentiates airway smooth muscle contraction via TLR-4[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol,2017.
[14] Lim HA,Lee EK,Kim JM,et al.PPARγ activation by baicalin suppresses NF-κB-mediated inflammation in aged rat kidney[J].Biogerontology,2012,13(2):133-145.
[15] Yang R,Zou X,Tenhunen J,et al.HMGB-1 and extracellular histones significantly contribute to systemic inflammation and multiple organ failure in acute liver failure[J].Mediators Inflamm,2017,2017:5928078.
[16] Gil M,Kim YK,Hong SB,et al.Naringin decreases TNF-alpha and HMGB-1 release from Lps-stimulated macrophages and improves survival in a clp-induced sepsis mice[J].PLoS One,2016,11(10):e0164186.
[17] Cheng Y,Wang D,Wang B,et al.HMGB-1 translocation and release mediate cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation in mice through a TLR-4/Myd88-dependent signaling pathway[J].Mol Biol Cell,2016,28(1):201-209.
[18] Saidi H,Bras M,Formaglio P,et al.HMGB-1 is involved in IFN-Alpha production and trail expression by HIV-1-exposed plasmacytoid dendritic cells:impact of the crosstalk with Nk cells[J].PLoS Pathog,12(2016),e1005407.
[19] Chung HW,Lim JB.High-mobility group box-1 contributes tumor angiogenesis under interleukin-8 mediation during gastric cancer progression[J].Cancer Sci,2017.
[20] Li N,Wang BM,Cai S,et al.The Role of serum high mobility group box-1 and interleukin-6 levels in acute pancreatitis:a meta-analysis[J].J Cell Biochem,2017.
[21] Fu Y,Lei J,Zhuang Y,et al.Overexpression of HMGB-1 a-box reduced Ll-1beta-induced mmp expression and the production of inflammatory mediators in human chondrocytes[J].Exp Cell Res,2016,349(1):184-190.
[22] Gao XJ,Qu YY,Liu XW,et al.Immune complexes induce TNF-alpha and baff production from U937 cells by HMGB-1 and rage[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2017,21(8):1810.
[23] Imbalzano E,Quartuccio S,Di Salvo E,et al.Association between HMGB-1 and asthma:a literature review[J].Clin Mol Allergy,2017,15(1):12.
[24] Saleh A,Smith DR,Tessler L,et al.Receptor for advanced glycation end-products(rage)activates divergent signaling pathways to augment neurite outgrowth of adult sensory neurons[J].Exp Neurol,2013,249(5):149-159.
[25] Huang JS,Lee YH,Chuan LY,et al.Cinnamaldehyde and nitric oxide attenuate advanced glycation end products-induced the Jak/Stat signaling in human renal tubular cells[J].J Cell Biochem,2015,116(6):1028-1038.
[26] Sun Y,Kang L,Li J,et al.Advanced glycation end products impair the functions of saphenous vein but not thoracic artery smooth muscle cells through Rage/Mapk signalling pathway in diabetes[J].J Cell Mol Med,2016,20(10):1945.
[27] Chen Y,Wu Y,Gan X,et al.Iridoid glycoside from cornus officinalis ameliorated diabetes mellitus-induced testicular damage in male rats:involvement of suppression of the Ages/Rage/P38 Mapk signaling pathway[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2016,194:850.
[28] Song E,Jahng JW,Chong LP,et al.Lipocalin-2 induces Nlrp3 inflammasome activation via HMGB-1 induced TLR-4 signaling in heart tissue of mice under pressure overload challenge[J].Am J Transl Res,2017,9(6):2723.
[29] Li C,Peng S,Liu X,et al.Glycyrrhizin,a direct HMGB-1 antagonist,ameliorates inflammatory infiltration in a model of autoimmune thyroiditis via inhibition of Tlr2-HMGB-1 signaling[J].Thyroid,2017.
[30] Tao L,Cao F,Xu G,et al.Mogroside Iiie attenuates Lps-induced acute lung injury in mice partly through regulation of the TLR-4/Mapk/Nf-Kappab axis via ampk activation[J].Phytother Res,2017.
[31] Liu AH,Wu YT,Wang YP.Microrna-129-5p inhibits the development of autoimmune encephalomyelitis-related epilepsy by targeting HMGB-1 through the TLR-4/Nf-Kb signaling pathway[J].Brain Res Bull,2017.
[32] Nicolls MR,Laubach VE.Traumatic brain injury:lungs in a rage[J].Sci Transl Med,2014,6(252):4531-4536.
[33] Yang W,Li J,Shang Y,et al.HMGB-1,TLR-4 axis plays a regulatory role in the pathogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy in immature rat model and children via the P38mapk signaling pathway[J].Neurochem Res,2017.
Effects of HMGB-1,RAGE and TLR-4 pathway on acute lung injury induced by blast in rats
TONG Chang-ci,LIU Yun-en,ZHANG Yu-biao,SHI Lin,CONG Pei-fang,LIU Ying,SHI Xiu-yun,JIN Hong-xu,HOU Ming-xiao
(Emergency Medicine Department of General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Laboratory of Rescue Center of Severe Wound and Trauma PLA, Severe Trauma and Organ Protection key Laboratory of Liaoning Province,Shenyang 110016, China)
Objective To investigate the mechanism of high mobility group protein-1(HMGB-1),receptor for advanced glycation end products(RAGE)and Toll-like receptor-4(TLR-4)pathway on acute lung injury induced by blast in rats.Methods There were 40 SD rats were selected,10 rats were divided into the control group;the other 30 rats were divided into the 6 hours group,12 hours group and 24 hours group after the establishment of rat model with acute lung injury induced by blast.The levels of serum HMGB-1,IL-1α and IL-8 were detected by ELISA.The expression of HMGB-1,IL-1α,IL-8,RAGE,TLR-4,p38 MAPK,JAK-2 and STAT-3 in lung tissue were detected by Western Blot,Real Time PCR and immunofluorescence.Results The result of ELISA showed that,compared with the control group,the expression of HMGB-1 and IL-1α in 12 hours group and 24 hours group both increased,and the level reached the highest in 12 hours group;the expression of IL-8 in 6 hours group and 12 hours group increased,and the level reached the higher in 12 hours group(P<0.05).The results of Western Blot,Real Time PCR and immunofluorescence showed that,compared with the control group,the expression of HMGB-1 and IL-1αin 12 hours group and 24 hours group increased,and the level reached the highest in 12 hours group;the expression of IL-8 in 6 hours and 12 hours increased,and the level reached the highest in 12 hours group;the expression of RAGE in 12 hours group increased;the expression of TLR-4 and p38 MAPK in 12 hours group and 24 hours group increased,and the level reached the highest in 12 hours group;the expression of JAK-2 and STAT-3 in 6 hours,12 hours and 24 hours groups increased,and the level reached the highest in 12 hours group(P<0.05).Conclusion The acute lung injury induced by blast injury in rats can promote the release of inflammatory factors and promote the inflammatory response by promoting the release of HMGB-1,binding to RAGE and TLR-4,activating p38 MAPK and JAK/STAT pathway.
Blast injury; Acute lung injury; Rats; High mobility group protein; Receptor for advanced glycation end products; Toll-like receptor
佟昌慈(1988-),女,辽宁抚顺人,技士,硕士
侯明晓,E-mail:houmingxiao188@163.com
2095-5561(2017)04-0198-07 DOI∶10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2017.04.02
2017-07-17

