表现为播散性丘疹型的皮肤型窦组织细胞增生症一例
赵丽萍,王良明,史晓蔚,张圆程,李树良,王艳红,张士发
表现为播散性丘疹型的皮肤型窦组织细胞增生症一例
赵丽萍,王良明,史晓蔚,张圆程,李树良,王艳红,张士发
患者男,54岁,全身红色丘疹、结节及斑块4个月。皮损初发于双下肢,渐波散至全身。查体示全身密集分布的红色丘疹、结节,孤立或呈环形、条带状分布,直径0.3~2.5 cm,质地较硬,略有压痛,有浸润感;皮损大致对称分布,以四肢伸侧、面颊部为著。组织病理示真皮内弥漫性组织细胞浸润,多个具有分枝的肥大的组织细胞及多核巨细胞浸润,灶性浆细胞、淋巴细胞、中性粒细胞浸润,少许嗜酸粒细胞浸润,有细胞伸入现象。免疫组化检查示肥大的组织细胞及多核巨细胞CD68、CD163、S-100蛋白均阳性,CD1a阴性。诊断:皮肤型窦组织细胞增多症。给予复方甘草酸苷口服及卡介菌多糖核酸肌内注射1个月,皮损部分消退。
窦组织细胞增生症,皮肤型
[J Pract Dermatol, 2017, 10(3):180-182]
临床资料
患者,男,54岁。因全身红色丘疹、结节及斑块4个月,于2016年7月11日就诊。4个月前,无诱因患者双下肢出现较多散在分布的红色丘疹,于当地医院诊断为多形红斑,药物(不详)治疗无效,丘疹继续增多,迅速融合成斑块,扩散至全身,以双下肢为著。在北京多家医院按结节病、淋巴瘤、淋巴瘤样丘疹病诊治,治疗数月均无效。既往史、过敏史及家族史无特殊。系统查体未见明显异常,浅表淋巴结未扪及增大。皮肤科情况:全身对称性分布密集的边界清楚的红色丘疹、结节,直径0.3~2.5 cm,孤立或融合呈环形、条带状,表面不规则隆起,部分丘疹顶端呈黄色或灰白色,无鳞屑及结痂;质地较硬,较大的结节或斑块坚实,略有压痛,基底部有浸润感;皮损以四肢伸侧、面颊部为著(图1)。实验室及辅助检查:抗单纯疱疹病毒1-IgG(+),抗EB病毒核心抗体(+),血生化检测、血免疫功能、自身免疫抗体、肿瘤系列等检测均正常;T淋巴细胞及B淋巴细胞计数均正常。胸部X线检查及腹部超声多谱勒检查无明显异常。取躯干、四肢不同类型的4处皮损(红色丘疹、黄红色丘疹、灰褐色疣状丘疹结节、较大灰红色斑块)行组织病理检查,病理表现基本一致:皮损顶端表皮挤压变薄,皮突缩小或变平;真皮增厚,皮下组织间隔增宽,皮脂腺小叶明显缩小;真皮及皮下组织内大量的肥大的分枝状组织细胞浸润,灶性密集的淋巴细胞、浆细胞浸润,少许嗜酸粒细胞及中性粒细胞浸润,部分组织细胞胞质内可见少许淋巴细胞,即细胞吞入现象阳性;完整的毛囊皮脂腺结构缺失(图2a-2d)。抗酸染色、阿辛蓝染色均阴性。免疫组化:肥大的组织细胞及多核巨细胞CD163(+)、CD68(+)、S-100蛋白(+),CD1a(-)(图3a-3d)。诊断:皮肤型窦性组织细胞增生症。治疗:复方甘草酸苷3片每日3次口服,卡介菌多糖核酸注射液0.7 mg每周2次肌内注射。治疗1个月后,皮损范围缩小,丘疹、斑块变平,少部分消退。后失访。
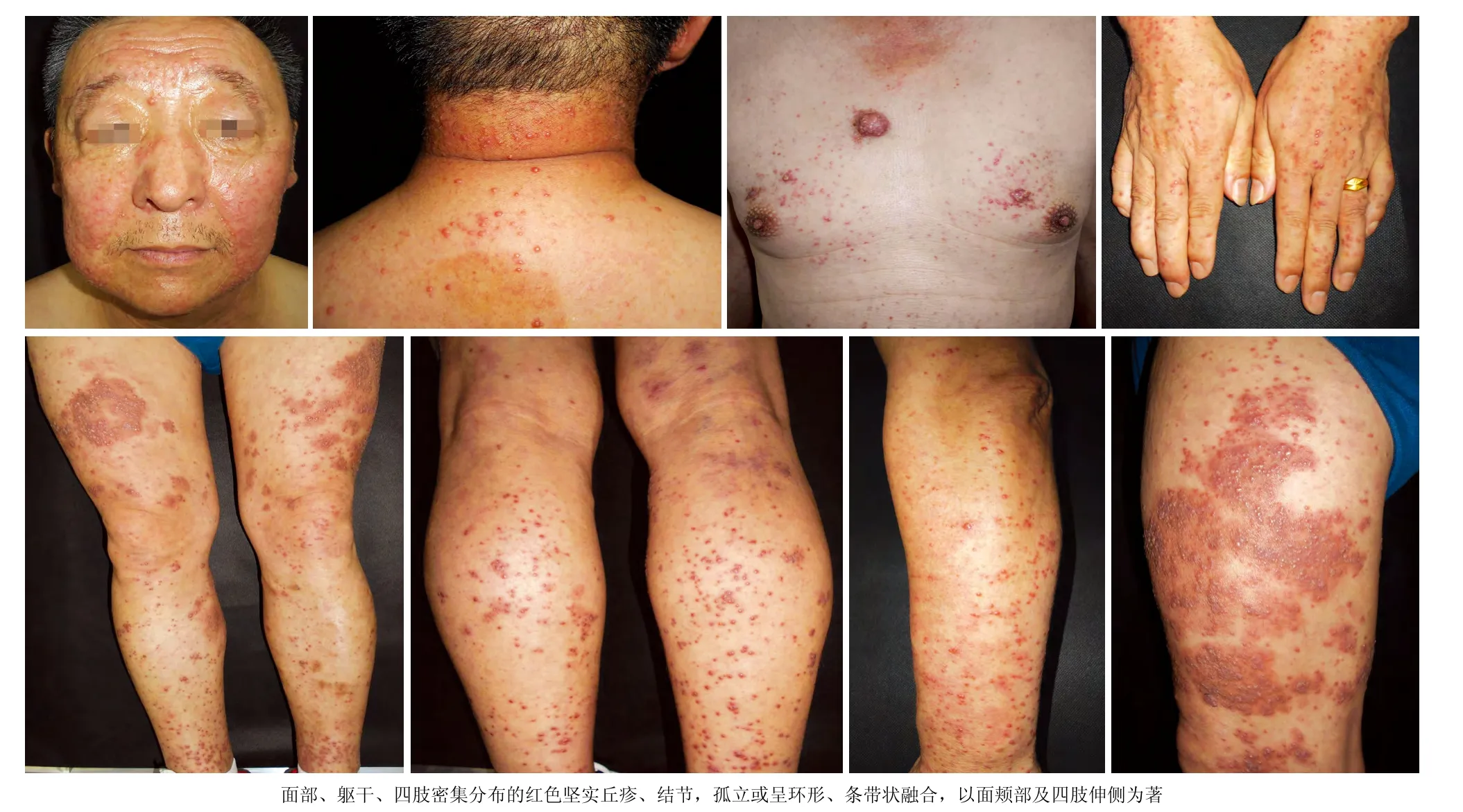
图1 皮肤型窦性组织细胞增生症患者临床表现
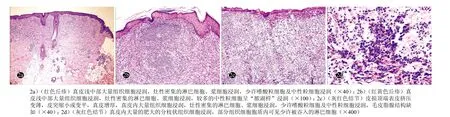
图2 皮肤型窦性组织细胞增生症患者皮损组织病理(HE染色)
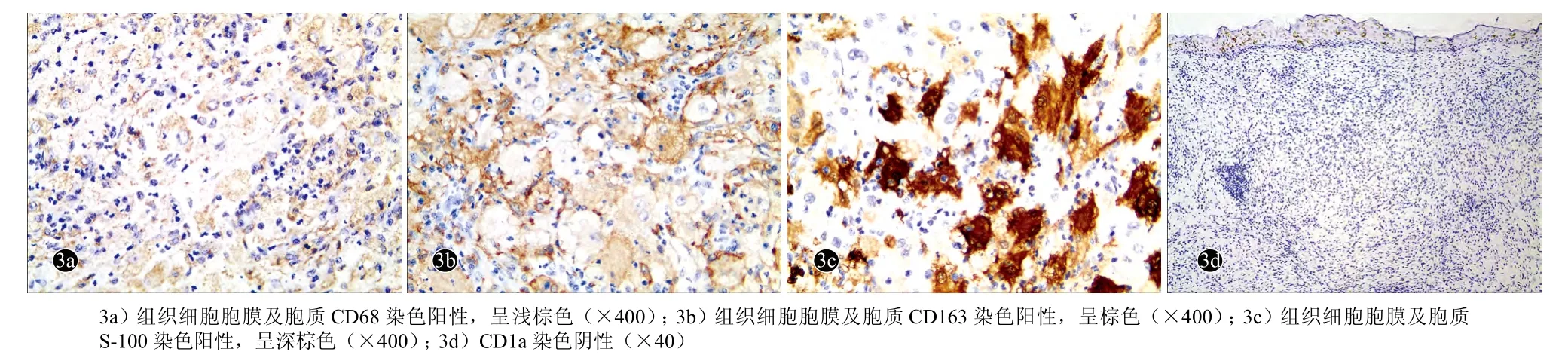
图3 皮肤型窦性组织细胞增生症患者皮损免疫组化组织病理(ABC法)
讨论
经典的窦性组织细胞增生症全称为伴有巨大淋巴结病的窦性组织细胞增生症(sinus histiocytosis with massive lympha-denopathy,SHML),首先由Rosai和Dorfman(1969)描述。皮肤是最常见的结外受累区域。仅有皮肤损害,而无淋巴结及内脏损害的病变,称为皮肤型窦性组织细胞增生症(cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease,CRDD),较少见[1-3],仅占报道患者的3%[4]。目前尚未发现皮损泛发全身的CRDD个例报道。
CRDD病因不清,可能与病毒感染等有关,机体免疫功能障碍被认为是导致发病的因素之一。临床上CRDD多发于中年女性,累及四肢、躯干及面部[5,6],皮损缓慢增大。最常见皮损为丘疹结节型,其次为硬结斑块型及肿瘤型。本病多数呈良性临床表现,可持续多年,或自发消退。病变主要累及真皮,可侵入皮下组织;有较多的组织细胞增生,较多的淋巴细胞、浆细胞灶状浸润,可伴有中性粒细胞浸润;特征性的表现是组织细胞胞质内有完整的炎性细胞即细胞伸入运动;分枝状肥大的组织细胞呈S-100蛋白、CD68、CD163阳性,CD1a阴性。
本例临床特征为老年男性,皮损分布广泛,遍及全身;皮损多形,主要表现为红色、黄红色、红白色、红褐色、褐色和褐灰色的丘疹、结节及斑块;组织病理表现典型,有典型的细胞伸入现象;无其他器官受累,病毒检测显示曾有EB病毒及单纯疱疹病毒(HSV)感染。分析本例患者的发病原因,可能与病毒感染有一定关联性。CRDD临床表现应与下列皮肤病鉴别:黄色肉芽肿、黄瘤病、朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症、结节病、多中心网状组织细胞增生症和麻风病等。但由于其组织病理有特征性改变,因此通过组织病理检查可以鉴别。
CRDD 预后较好,一般很少发生系统累及,多数患者经数月至数年后皮损可缓慢自行消退。本病无特效的治疗办法,可选用维A酸类药、糖皮质激素、沙利度胺、甲氨蝶呤、雷公藤等药物,限局性病变亦可手术切除治疗[7-11]。目前对本病主张避免过度医疗。本例患者仅给予复方甘草酸苷、卡介菌多糖核酸等治疗1个月,皮损即有所好转,可能因该治疗方法可在一定程度上调节免疫水平和抗炎作用等有关。
[1] Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: a newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity [J]. Arch Pathol, 1969, 87 (1):63-70.
[2] Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity [J]. Semin Diagn Pathol, 1990, (1):19-73.
[3] Brenn T, Calonje E, Granter SR, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease is a distinct clinical entity [J]. Am J Dermatopathol, 2002, 24(5):385-391.
[4] Chu P, LeBoit PE. Histologic features of cutaneous sinus histiocytosis (Rosai-Dorfman disease): study of cases both with and without systemic involvement [J]. J Cutan Pathol, 1992, 3(19):201-206.
[5] Frater JL, Maddox JS, Obadiah JM, et al. Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease: comprehensive review of cases reported in the medical literature since 1990 and presentation of an illustrative case [J]. J Cutan Med Surg, 2006, 10(6):281-290.
[6] Kong YY, Kong JC, Shi DR, et al. Cutaneous Rosai- Dorfman disease: a clinical and histopathologic study of 25 cases in China [J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2007, 31(3):341-350.
[7] Lu C-I, Kuo T, Wong W-R et al. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease in Taiwan [J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2004, 6(51):931-939.
[8] Chang L-Y, Kuo T, Chan-L. Extranodal Rosai- Dorfman disease with cutaneous, opthalmic and laryngeal involvement: report of a case treated with isotretinoin [J]. Int J Dermatol, 2002, 12(41):888-891.
[9] Bens G, Kerdraon R, De Kyvon JJ, et al. Indolent firmreddish papules cutaneous Rosaidorfman disease [J]. Hautarzt, 2011, 62(5):384-387.
[10] Fening K, Bechtel M, Peters S, et al. Cutaneous rosai- dorfman disease persisting after surgical excision: report of a case treated with acitretin [J]. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol, 2010, 3(9):34-46.
[11] 马锦媛, 康宏霞, 何勤, 等. 皮肤窦组织细胞增生症一例 [J]. 实用皮肤病学杂志, 2013, 6(6):371-374.
A case of disseminated papular cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease
ZHAO Li-ping,WANG Liang-ming,SHI Xiao-wei,et al
Department of Dermatology, the General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Shenyang 110016, China
A 54-year-old male patient presented with multiple red papules, nodules and plaques over the whole body for 4 months. The lesions occurred firstly in the lower limbs and gradually scattered to the whole body. Dermatological examination showed dense deep red papules and nodules arranging in solitary, circular, or strip shape line, about 0.3~2.5cm in diameter, with a hard texture, slight tenderness, and the base of lesions were slightly infiltrative. The lesions were more severe on the extensor of the extremities and cheek, and roughly symmetric. Pathological examination showed diffuse histiocytic infiltration in the dermis, with multiple branched hypertrophic histiocytes and multinucleated giant cells, and focal infiltrate of plasma cells, lymphocytes, neutrophils and a little of eosinophils, with the phenomenon of emperipolesis. Immunohistochemical examination showed that hypertrophic cells and multinucleated giant cells were stained positive for CD68, CD163, S100, and negative for CD1a. The diagnosis was cutaneous sinus histiocytosis. The patient was treated with oral compound glycyrrhizin tablets and intramuscular injection of BCG polysaccharide and nucleic acid injection for 1 month, and the lesions subsided partly.
Sinus histiocytosis,Rosai-Dorfman disease,cutaneous
R758.4
A
1674-1293(2017)03-0180-03
2016-11-16
2017-02-08)
(本文编辑 祝贺)
10.11786/sypfbxzz.1674-1293.20170316
110016 沈阳,沈阳军区总医院皮肤科(赵丽萍,王良明,史晓蔚,张圆程,李树良,王艳红,张士发)
赵丽萍,女,主治医师,主要从事皮肤性病科临床及皮肤病理诊断,E-mail: zhaolp1@163.com

