‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因的克隆及在花粉发育过程中的表达分析
吴莹莹,张 迟,陈高峰,孙靳俭,朱咪咪,张 敏
(浙江农林大学 省部共建亚热带森林培育国家重点实验室,浙江 临安 311300)
‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因的克隆及在花粉发育过程中的表达分析
吴莹莹,张 迟,陈高峰,孙靳俭,朱咪咪,张 敏
(浙江农林大学 省部共建亚热带森林培育国家重点实验室,浙江 临安 311300)
‘无籽瓯柑’的雄性不育主要表现为花粉败育,起始于小孢子母细胞减数分裂时期。本研究克隆了‘无籽瓯柑’减数分裂相关基因CsRAD51,并采用荧光定量PCR检测其在瓯柑及‘无籽瓯柑’中的表达差异。结果显示,CsRAD51基因的cDNA全长1210 bp,含有一个1029 bp的ORF区;其编码的蛋白质属于疏水性蛋白,分子量45740.1D,氨基酸数388,原子总数6 555,等电点10.20。同源性比对发现,‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51的氨基酸序列与甜橙、麻疯树、油棕、黄瓜、黑杨等的RAD51蛋白高度同源,分别达99%,98%,98%,98%,98%。RT-PCR结果显示‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51在小孢子母细胞、四分体以及单核花粉粒时期的相对表达量显著高于瓯柑。CsRAD51的过量表达可能影响了DSBs的同源重组修复,致使‘无籽瓯柑’小孢子母细胞时期减数分裂异常。
柑橘;雄性不育;减数分裂;CsRAD51;实时荧光定量PCR.
‘无籽瓯柑’Citrus suavissima‘Wuzi Ougan’ 是瓯柑C. suavissima的无核突变体,2004年2月通过浙江省林木良种审定委员会的良种认定并命名[1-2]。‘无籽瓯柑’的雄性不育主要表现为花粉败育,败育起始于小孢子母细胞减数分裂至四分体时期[3]。
RAD51基因在减数分裂过程中起着十分重要的作用,能够编码一种重组酶,在DNA单链入侵完整双链过程中起作用[4]。RAD51基因家族是真核生物中广泛存在的一个高度保守的基因家族,它编码的蛋白与原核生物中的RecA蛋白高度同源。在植物中,RAD51基因家族由于基因重复和基因水平转移而形成RAD51,DMC1,RAD51B,RAD51C,RAD51D,XRCC2,XRCC3,RecA等多个成员,它们大都在减数分裂过程中起重要作用[5]。Kou等[6]研究了RAD51基因对水稻雌雄配子体发育的作用,敲除RAD51C基因后得到的不育植株伴随有大孢子母细胞和花粉母细胞早期减数分裂过程异常,花粉母细胞粗线期染色体异常,最终产生不育花粉和异常胚囊,但花药壁发育正常,对基因敲除后的不育植株重新转入RAD51C基因,以转入空载体为对照,结果发现前者育性恢复,说明该基因主要是调节减数分裂。Li和Wang等[7-8]研究发现,拟南芥突变基因AHP2和AtRAD51C的功能分别是参与同源染色体的联会和着丝点结构的形成,在拟南芥中利用RNA干扰技术分别沉默该两基因,产生的转基因植物中,50%以上的花粉无育性。在高等真核生物中,RAD51是DNA双链断裂(Double-strand breaks简称DSB)与同源重组修复过程中的重要蛋白,在这些过程中,RAD51催化单链DNA和双链DNA之间的同源配对。RAD51参与有丝分裂和减数分裂的同源重组[9],在同源重组期间,RAD51促进ATP依赖的同源配对,通过该单链DNA(ssDNA)与同源双链DNA(dsDNA)的互补链形成新的Watson-Crick碱基对(异源)[10-14]。
研究‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因的功能与特性,根据已完成的瓯柑花药转录组测序所得基因序列,克隆并获得‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因的全长cDNA序列并对其进行生物信息学分析,通过实时荧光定量PCR技术对目标基因mRNA在花粉发育不同时期的表达量进行实时定量分析。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料及试剂仪器
‘无籽瓯柑’和瓯柑的花药均采自浙江省瑞安市金潮港农场,根据不同直径的花蕾切片和显微观察结果[15],分别采集小孢子母细胞时期(2.0 ~ 2.4 mm)I、四分体时期(2.8 ~ 3.1 mm)II、单核花粉粒时期(3.5 ~ 4.5 mm)III、双核花粉粒时期(4.5 ~ 6.5 mm)IV、成熟花粉粒时期V(6.5 ~ 7.1 mm)的花药,保存于-70℃超低温冰箱备用。
试验试剂包括:Trizol总RNA提取试剂盒、5'RACE试剂盒等(Invitrogen公司),胶回收试剂盒(TaKaRa公司)、Taq酶、LA Taq酶、Ribonuclease Inhibitor、DNaseⅠ(RNase Free)、X-gal(TaKaRa公司)等,SMART MMLV 反转录酶(Clontech公司),Amp、IPTG(上海申能博彩生物科技有限公司),普通生化试剂(生工生物工程(上海)有限公司)。
克隆用菌种为大肠杆菌DH 5α,由本实验室保存;克隆载体为Pmd18-T载体,购自TaKaRa公司。
主要仪器设备:荧光定量PCR仪(CFX96TM Real-Time PCR Detection System/Bio-Rad)、微量分光光度计(NanoDrop® ND-1000 UV Spectrophotometer)、凝胶成像分析系统(AlphaImager® HP)、梯度PCR仪( Eppendorf Mastercycler pro)、紫外分析仪(WD-9403C型)、DNA浓缩仪(DNA120 SpeedVac®)、超净工作台、通风柜、电子天平等。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 总RNA提取 以‘无籽瓯柑’和瓯柑花药为试材,参照改良的Trizol法,用Trizol总RNA提取试剂盒(Invitrogen)分别提取5个时期花药的RNA,并对各样品的RNA进行电泳检测,再测其OD值,检测样品RNA的质量。
1.2.2 荧光定量PCR cDNA的合成参照反转录试剂盒PrimeScript RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time)的指导说明。根据前期转录组测序所得序列,利用Primer 5.0设计CsRAD51基因克隆和荧光定量的特异性引物(表1),引物序列交由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。以反转录后的cDNA为模板,对所

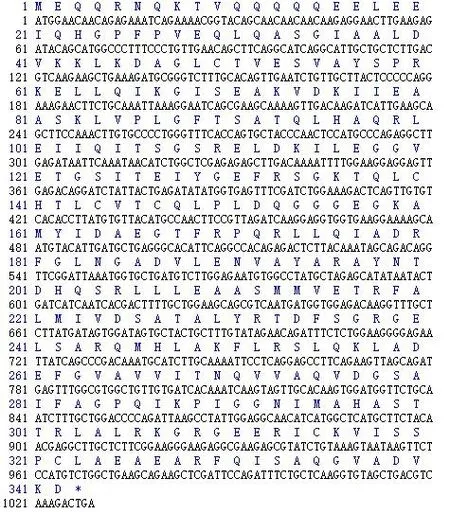
图2 CsRAD51基因的核苷酸序列及所编码的氨基酸序列Figure 2 Nucleotide sequence of CsRAD51 and the corresponding amino acid sequence
使用在线工具ProtParam分析蛋白质的理化性质,CsRAD51基因编码蛋白质分子量为45 740.1,氨基酸数为388,原子总数为6 555,等电点为10.20;所有氨基酸组成中亮氨酸(Leu)所占比例最高,为18.8%,其次为丝氨酸(Ser),所占比例为10.1%;总的带负电荷残基Asp和Glu为27个,总的带正电荷残基Arg和Lys为60个;蛋白质不稳定指数为 51.45%,这种分类的蛋白质是不稳定的。用ProtScale工具分析蛋白的疏水性和亲水性,总平均亲水性(Grand average of hydropathicity)为-0.150,第247位异亮氨酸(Ile)亲水性最强(Score:3.400),第42位和第43位天冬酰胺(Asn)疏水性最强(Score:-3.267),蛋白的疏水区明显多于亲水区,表明‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因编码的蛋白质是一种疏水性蛋白(图3)。用SOPMA方法对CsRAD51基因编码的蛋白质的二级结构进行预测,其结构主要以α螺旋(50.26%)和无规则卷曲(22.94%)为主,此外还有β片层(17.01%)和未知区域(9.79%)(图 4)。

图3 CsRAD51基因编码蛋白疏水性和亲水性分析Figure 3 Analysis of hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of protein encoded by CsRAD51
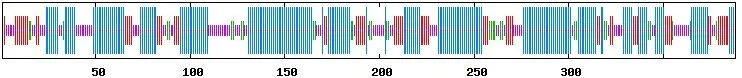
图 4 CsRAD51基因编码蛋白二级结构预测Figure 4 The secondary structure prediction of CsRAD51

图5 ‘无籽瓯柑’与其它植物RAD51氨基酸序列比对Figure 5 Amino acid sequence alignment of RAD51 ofC. suavissima ‘Wuzi Ougan’ with that of other plants
Blastx分析‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因编码的氨基酸序列与CsRAD51(甜橙C. sinensis),JcRAD51(麻疯树Jatropha curcas),EgRAD51(油棕Elaeis guineensis),CsRAD51(黄瓜Cucumis sativus),PnRAD51(黑杨Populus nigra),SiRAD51(芝麻Sesamum indicum),ZjRAD51(枣Ziziphus jujuba),VvRAD51(葡萄Vitis vinifera),NnRAD51(莲Nelumbo nucifera),PeRAD51(胡杨Populus euphratica)和PdRAD51(海枣Phoenix dactylifera)的同源性,分别达到99%,98%,98%,98%,98%,97%,97%,97%,97%,97%,97%(图5)。使用MEGA5构建同源基因的系统进化树,采用Neighbor-joining法,设置Bootstrap value数值为1 000,分析物种间的亲缘关系[16]。结果显示,‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因与甜橙、黑杨、胡杨的距离最近(见图6)。


4 结论
实验结果表明,‘无籽瓯柑’的CsRAD51基因编码的蛋白质属于疏水性蛋白且该蛋白质不稳定,同时该基因与甜橙、麻疯树、油棕、黄瓜、黑杨、芝麻、枣、葡萄、莲、胡杨和海枣等具有很高的同源性,由此可知RAD51基因在遗传上较稳定。小孢子母细胞时期、四分体时期和单核花粉粒时期‘无籽瓯柑’CsRAD51基因在花药中的相对表达量极显著高于瓯柑,说明CsRAD51的过量表达可能影响了‘无籽瓯柑’DSBs的同源重组修复,使细胞内积累了未被修复的DSBs,造成减数分裂异常。
[1] 张 敏,刘志辉,宋雪恩,等.‘无籽’瓯柑CsLTP和CsLOX基因的克隆与表达分析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报,2014,31(6):823-830.
[2] 徐象华,颜福花,叶荣华,等. 瓯柑研究进展[J]. 浙江林业科技,2008,03:75-77.
[3] 张迟,张敏,朱铨,等. ‘瓯柑’及其无子突变体花粉发育的细胞学观察[J]. 果树学报,2014,31(2):265-269,345.
[4] 张峰. 拟南芥减数分裂重组相关基因RAD51、PTD功能分析[D]. 上海:上海师范大学,2013.
[5] Lin Z G,Kong H Z,Nei M,et al. Origins and evolution of the recA/RAD51 gene family: evidence for ancient gene duplication and endosymbiotic gene transfer[J]. PNAS,2006,103(27):10328-10333.
[6] Kou Y J,Chang Y X,Li X H,et al. The rice RAD51C gene is required for the meiosis of both female and male gametocytes and the DNA repair of somatic cells[J]. J Exp Bot,2012,63(14):5323-5335.
[7] Li W,Yang X,Lin Z,et al. The AtRAD51C gene is required for normal meiotic chromosome syapsis and double-stranded break repair in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiol,2005,138(2):965-976.
[8] Wang X,Singer S D,Liu Z. Silencing of meiosis-critical genes for engineering male sterility in plants[J]. Plant cell Rep,2012,31(4):747-756.
[9] Shinohara A,Ogawa H,Ogawa A T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein[J]. Cell,1992,69(3):457.
[10] Sung P. Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein[J]. Science,1994,265(5176):1241.
[11] Sung P,Robberson D L. DNA strand exchange mediated by a RAD51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament with polarity opposite to that of RecA[J]. Cell,1995,82(3):453-461.
[12] Baumann P,Benson F E,West S C. Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro[J]. Cell,87(4):757.
[13] Maeshima K,Morimatsu K,Horii T. Purification and characterization of XRad51.1 protein, Xenopus RAD51 homologue: recombinant XRad51.1 promotes strand exchange reaction[J]. Gene Cells,1997,1(12):1057-1068.
[14] Gupta R C,Bazemore L R,Golub E I,et al. Activities of human recombination protein Rad51[J]. PNAS,1997,94(2):463-468.
[15] 朱咪咪. ‘无籽瓯柑’小孢子母细胞减数分裂异常的分子机理研究[D]. 临安:浙江农林大学,2016.
[16] Clough S J,Bent A F. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant J,1998,16(6):735-743.
[17] Sheridan S D,Yu X,Roth R,et al. A comparative analysis of Dmc1 and RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments[J]. Nucl Acid Res,2008,36(12):4057-4066.
[18] Masson J Y,West S C. The Rad51 and Dmc1 recombinases: a non-identical twin relationship[J]. Trend Biochem Sci,2001,26(2):131.
[19] Hong E L,Shinohara A, Bishop D K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dmc1 protein promotes renaturation of single-strand DNA(ssDNA) and assimilation of ssDNA into homologous super-coiled duplex DNA[J]. J Biol Chem,2001,276(45):41906.
[20] Li Z,Golub E I,Gupta R,et al. Recombination activities of HsDmc1 protein, the meiotic human homolog of RecA protein[J]. PNAS,1997,94(21):11221-11226.
[21] Sung P. Catalysis of ATP-dependent homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange by yeast RAD51 protein[J]. Science,1994,265(5176):1241.
[22] Bishop D K,Park D,Xu L Z,et al. DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression[J]. Cell,1992,69(3):439-456.
[23] Neale M J,Keeney S. Clarifying the mechanics of DNA strand exchange in meiotic recombination[J]. Nature,2006,442(7099):153–158.
[24] Shinohara A,Ogawa H,Ogawa A T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein[J]. Cell,1992,69(3):457.
[25] Aboussekhra A,Chanet R,Adjiri A,et al. Semidominant suppressors of Srs2 helicase mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae map in the RAD51 gene, whose sequence predicts a protein with similarities to prokaryotic RecA proteins[J]. Mol Cell Biol,1992,12(7):3224-3234.
[26] 李亚非,程祝宽. 植物减数分裂同源染色体重组的分子机理[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2015,06:537-543.
[27] Li W,Chen C,Markmann-Mulisch U,et al. The Arabidopsis AtRAD51 gene is dispensable for vegetative development but required for meiosis[J]. PNAS,2004,101(29):10596-10600.
[28] 周锦. 油菜雄性不育相关基因的表达差异及克隆与序列分析[D]. 武汉:中南民族大学,2008.
[29] Li J,Harper L C,Golubovskaya I,et al. Functional Analysis of Maize RAD51 in Meiosis and Double-Strand Break Repair[J]. Genetics,2007,176(3):1469-1482.
[30] Ding T,Miao C,Li Y,et al. OsRAD51C is essential for double-strand break repair in rice meiosis[J]. Front Plant Sci,2014,5(2):167.
[31] Vispé S,Cazaux C,Lesca C,et al. Over expression of Rad51 protein stimulates homologous recombination and increases resistance of mammalian cells to ionizing radiation[J].Nucl Acid Res,1998,26(12):2859.
[32] Richardson C,Stark J M,Ommundsen M,et al. Rad51 over-expression promotes alternative double-strand break repair pathways and genome instability[J].Oncogene,2004,23(2):546.
[33] Paffett K S,Clikeman J A,Palmer S,et al. Over expression of Rad51 inhibits double-strand break-induced homologous recombination but does not affect gene conversion tract lengths[J]. DNA Repair(Amst),2005,4(6):687-698.
Cloning and Expression of CsRAD51 Gene of Citrus suavissima 'Wuzi Ougan'
WU Ying-ying,ZHANG Chi,CHEN Gao-feng,SUN Jin-jian,ZHU Mi-mi,ZHANG Min
(State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Silviculture, Zhejiang A & F University, Lin’an 311300, China)
Citrus suavissima‘Wuzi Ougan’ is a seedless bud variation ofC. suavissimawith male sterility and pollen abortion from the tetrad stage. RNA ofC. suavissimaandC. suavissima‘Wuzi Ougan’ was extracted and the full-length cDNA was cloned and bioinformatics analysis of amino acid sequences was conducted. The results showed that the sequence length of CsRAD51 was 1210bp, containing an ORF of 1029bp. The deduced protein was hydrophobic one, encoded 388 amino acids. Its molecular weight was 45740.1D, with atom number of 6555 and isoelectric point of 10.20. Homologous alignment demonstrated the homology coefficient ofC. suavissima‘Wuzi Ougan’ withC. sinensis,Jatropha curcas,Elaeis guineensis,Cucumis sativusandPopulus nigrawas 99%,98%,98%,98%,98% respectively. The Real-time PCR results showed that the relative expression of CsRAD51 inC. suavissima‘Wuzi Ougan’ was significantly higher thanC. suavissimaat microsporocyte stage, tetrad stage and uninucleus microspore stage, indicating that overexpression of CsRAD51 inhibited double-strand break-induced homologous recombination and led to DNA damage and abnormal meiosis.
Citrus; male sterility; meiosis; CsRAD51; Real-time PCR.
S666.1
A
1001-3776(2017)02-0001-09
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3776.2017.02.001
2016-11-21 ;
2017-02-28
浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划项目(2016R412003),国家自然科学基金资助项目(31000897),浙江省团队科技特派员服务计划项目(浙科发农[2013]215-122)
吴莹莹,本科生,从事经济林栽培与利用研究;E-mail:1009069852@qq.com。通信作者:张敏,副教授,博士,从事经济林遗传育种研究;E-mail:mzhang@zafu.edu.cn。
——紫 苏

