雪胆素甲诱导非小细胞肺癌系NCI-H460和A549的凋亡效应及其作用机制初探
陈育林,咸 婧,肖 翠,钟月玲,苏小妹,徐 丽,罗巧丽,程 朋,王 涛,刘 进,张 涛,阳 泰,邹 强,李 华
(1.西南交通大学生命科学与工程学院,四川 成都 610031;2.成都医学院科研实验中心,四川 成都 610500;3.成都军区总医院肿瘤诊治中心肿瘤科,四川 成都 610083;4.川北医学院临床医学系,四川 南充 637000)
雪胆素甲诱导非小细胞肺癌系NCI-H460和A549的凋亡效应及其作用机制初探
陈育林1,咸 婧3,肖 翠2,钟月玲2,苏小妹3,徐 丽4,罗巧丽3,程 朋3,王 涛3,刘 进2,张 涛3,阳 泰2,邹 强2,李 华3
(1.西南交通大学生命科学与工程学院,四川 成都 610031;2.成都医学院科研实验中心,四川 成都 610500;3.成都军区总医院肿瘤诊治中心肿瘤科,四川 成都 610083;4.川北医学院临床医学系,四川 南充 637000)
目的 雪胆素甲(CuⅡa)诱导肺癌NCI-H460和A549的凋亡效应及其作用机制初探。方法 利用CCK-8检测CuⅡa对肿瘤细胞抑制活性;流式细胞术检测CuⅡa对肿瘤细胞凋亡以及周期的影响;Western blot检测CuⅡa对Aurora A、STAT3以及Cofilin蛋白磷酸化的影响。结果 CuⅡa对肺癌细胞NCI-H460和A549具有明显抑制作用,其IC50分别为224.9和108.3 nmol·L-1;CuⅡa能诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,并阻滞细胞周期于G2/M期;Western blot实验结果显示CuⅡa对STAT3和Cofilin的磷酸化具有抑制作用,且呈现剂量依赖性,CuⅡa能抑制Aurora A磷酸化,符合Aurora A激酶抑制剂抗肿瘤效应重要特征—阻滞细胞于G2/M期。结论 CuⅡa对非小细胞肺癌细胞系NCI-H460和A549具有明显的抑制作用,CuⅡa可作为抗非小细胞肺癌的先导化合物进行下一步研究。
雪胆素甲;非小细胞肺癌;凋亡;Aurora A;Cofilin;STAT3
雪胆素甲(cucurbitacin Ⅱa,CuⅡa) 是葫芦科雪胆属所提取的一种四环三萜类天然化合物,是雪胆属植物的主要活性成分。其化学名称为 23,24-双氢葫芦素 F-25-乙酸酯(23,24-dihydroxycucurbitacin F-25-acetate)。近年来,CuⅡa抗肿瘤活性相继报道。例如:CuⅡa能明显抑制人前列腺癌细胞系PC3以及CWR22Rv1增殖,其主要机制可能是通过诱导肌动蛋白聚集,破坏微丝骨架,阻滞细胞周期的进程于G2/M期[1,2]。CuⅡa对人肺癌细胞株A549也有抑制作用,可阻滞细胞周期于G2/M期[3],其作用机制值得深入研究。本研究拟通过人肺癌细胞株A549以及人大细胞肺腺癌细胞株NCI-H460为人肺腺癌细胞模型,探讨CuⅡa的作用机制,为进一步丰富CuⅡa抗肿瘤效应及其作用机制提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 CuⅡa(纯度>99%)购自成都曼思特生物科技有限公司;胎牛血清(FBS)、RIP细胞裂解液、PVDF膜和ECL化学发光试剂购自Millipore公司;培养基高糖DMEM及双抗(青霉素和硫酸链霉素)购自Hyclone;CCK-8试剂盒购自日本DoJindo公司;细胞凋亡试剂盒Annexin V-PE/7-ADD购自BD公司;细胞周期试剂盒PI染色购自碧云天公司;兔抗人p-STAT3(Tyr705)、STAT3、Cleaved-PARP、p-Cofilin(Ser3)以及Cofilin购自Cell Signaling公司;兔抗人p-Aurora A(Phospho T288),Aurora A购自Abcam公司;兔抗人GAPDH购自杭州华安生物公司;辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗兔二抗购自CST公司; CuⅡa用DMSO溶解,浓度为20 mmol·L-1,冻存于-20℃,使用时用培养基DMEM稀释。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养 DMEM培养基含双抗(100 U·L-1青霉素和100 μg·L-1硫酸链霉素)和10% FBS,细胞培养于37℃ CO2培养箱,CO2浓度为5%。取对数生长期细胞进行实验。
1.2.2 细胞活性实验 取对数生长期细胞接种96孔板,细胞密度为5 000个细胞/孔。细胞培养12 h,贴壁后加入不同浓度CuⅡa(32~50 000 nmol·L-1)。药物作用48 h后加入CCK-8,作用4h,使用酶标仪测定450 nm波长光吸收值。药物对肿瘤细胞生长抑制率按照美国国家癌症研究所标准计算:当Ti大于Tz时,肿瘤细胞存活率/%=[(Ti-Tz)/(C-Tz)]×100;当Ti小于Tz时,肿瘤细胞存活率/%=[(Ti-Tz)/Tz]×100(Ti为药物组培养48 h后,测定的OD值;Tz为不含药物组起始培养测定的OD值;C为不含药物组培养48 h后测定的OD值)。
1.2.3 克隆形成实验 取对数生长期细胞接种6孔板,细胞密度为200个细胞/孔,细胞培养12 h,贴壁后加入不同浓度CuⅡa。药物作用细胞24 h后,换新鲜含血清培养基培养,每2~3 d换1次培养基。培养14 d,用甲醇固定10 min,用结晶紫进行染色10 min,计算克隆群落。
1.2.4 细胞凋亡实验 取对数生长期细胞接种于24孔板,细胞密度为5×104个细胞/孔,细胞培养12 h贴壁后,加入不同浓度CuⅡa(400~1 600 nmol·L-1)。药物作用12 h,收集细胞,按照凋亡试剂盒Annexin V-PE/7-ADD(BD公司)说明书进行操作,避光染色30 min,用BD公司Accuri C6流式细胞仪进行检测。
1.2.5 细胞周期实验 取对数生长期细胞铺板于6孔板中,细胞密度为5×105个细胞/孔,细胞培养12 h贴壁后,加入不同浓度CuⅡa(400~1 600 nmol·L-1)。药物作用48 h,收集细胞。按照周期试剂盒PI染色(碧云天)说明书进行操作,37℃避光染色30 min,用BD公司Accuri C6流式细胞仪进行检测。
1.2.6 Western blot实验 取对数生长期细胞至培养皿中,细胞密度为5×105个细胞/孔,细胞培养12 h贴壁后,加入不同浓度CuⅡa(400~3 200 nmol·L-1)。药物作用12 h,收集蛋白样品,采用BCA法测定蛋白浓度,蛋白(80~100 )μg上样,进行SDS-PAGE电泳后,在恒流(250~350 mA)条件下电转60 min,用5%的脱脂奶粉进行封闭(1~2 h),4℃摇床过夜孵育一抗,用TBST清洗3次,每次5~10 min,用辣根过氧化物酶供价的二抗37℃孵育2 h,TBST洗膜3~5次,每次5~10 min,加入化学发光液,凝胶图像处理系统观察并分析结果。
2 结果
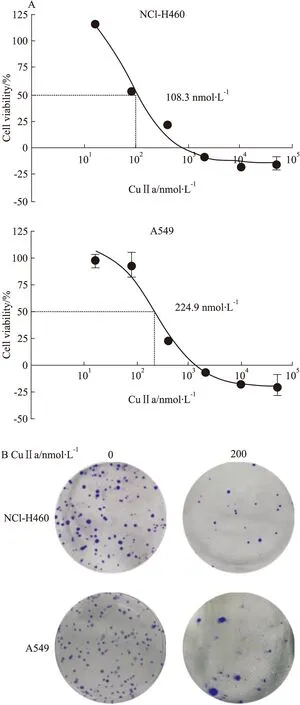
Fig 1 Effect of CuⅡa on NCI-H460 and A549cell proliferation and clone formation
A: Cell counting Kit-8 assay of non-small cell lung cancer lines treated with different dose of CuⅡa; B: Clone formation rate of NCI-H460 and A549 cell treated or untreated with CuⅡa at 200 nmol·L-1concentration
2.1 CuⅡa对NCI-H460和A549肿瘤细胞增殖的影响 CCK-8结果表明:CuⅡa处理NCI-H460和A549细胞48 h后,两种细胞株的增殖均受到明显抑制,且呈现剂量依赖性关系(Fig 1A)。CuⅡa对肺癌细胞系NCI-H460和A549的IC50分别为:108.3、224.9 nmol·L-1。用100、200 nmol·L-1分别处理NCI-H460和A549细胞24 h(Fig 1B),克隆形成率分别为(10.1±2.5)%和(6.7±2.4)%,与空白组对照差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明CuⅡa能明显抑制NCI-H460和A549肿瘤细胞增殖。
2.2 CuⅡa诱导肺癌细胞NCI-H460和A549凋亡 不同浓度CuⅡa作用NCI-H460和A549肺癌细胞株12 h后, Annexin V-PE/7-ADD双染标记,经细胞流式仪检测。随着CuⅡa浓度的增加,细胞凋亡比例明显增加,NCI-H460的凋亡比例由4.3%增长到30.3%,而A549的凋亡比例由2.4%增加到24.6%(Fig 2A)。Western blot检测CuⅡa检测相关蛋白,随着CuⅡa浓度的增加,凋亡活化标志片段Cleaved-PARP的表达量明显增加(Fig 2B),说明CuⅡa能诱导肺癌细胞系NCI-H460和A549凋亡。
2.3 CuⅡa阻滞细胞周期于G2/M期并抑制Aurora A磷酸化 肺癌细胞NCI-H460和A549经不同浓度CuⅡa处理后检测其对细胞周期的影响。随着CuⅡa作用浓度增加,G2/M期细胞比例不断增加,NCI-H460细胞G2/M期比例由22.2%增加到45.3%,而A549细胞G2/M期比例由26.5%增加到51.2%(Fig 3A)。Western blot结果显示CuⅡa抑制AuroraA磷酸化(Fig 3B),且呈现剂量依赖性,s2770作为阳性对照。
2.4 CuⅡa抑制STAT3及Cofilin磷酸化 Western blot结果表明(Fig 4),CuⅡa能抑制STAT3(Fig 4A)和Cofilin(Fig 4B)磷酸化,而STAT3和Cofilin的表达量并无明显变化。随着CuⅡa浓度增大,其抑制STAT3和Cofilin蛋白磷酸化越明显,呈现出剂量依赖性,Ruxolitinib作为STAT3抑制剂对照。
3 讨论
本实验以CuⅡa为研究对象,探究CuⅡa对人肺癌细胞株A549和NCI-H460增殖的影响及其作用机制。结果显示CuⅡa能明显抑制肺癌细胞系NCI-H460和A549增殖,且呈现剂量依赖性。一方面,CuⅡa诱导凋亡活化标志片段Cleaved-PARP的表达,促进细胞凋亡,另一方面抑制Aurora A、STAT3以及Cofilin磷酸化,使细胞滞留于G2/M期。
已知蛋白激酶信号通路介导多种重要细胞生理反应,是人体一系列疾病重要发生机制[4]。STAT3作为转录因子的重要成员之一,广泛表达于多种组织和各类细胞[5],可被JAK激酶激活发生酪氨酸磷酸化,广泛参与了肿瘤细胞增殖,并且对非小细胞肺癌的化疗耐受起到了关键作用,阻断JAK/STAT3通路是抑制肿瘤细胞增殖的重要策略[6]。Zheng等[7]通过加入选择性JSI-124抑制JAK/STAT3信号通路,抑制了肺癌细胞系A549的增殖并诱导凋亡。Jiang等[8]采用青藤碱,可抑制STAT3磷酸化进而抑制肺癌细胞侵袭。本研究在小分子单体CuⅡa抑制肺癌细胞NCI-H460和A549的结果基础上,进一步发现CuⅡa能够抑制STAT3的磷酸化,这可能是CuⅡa抑制肺癌细胞增殖的重要机制之一。
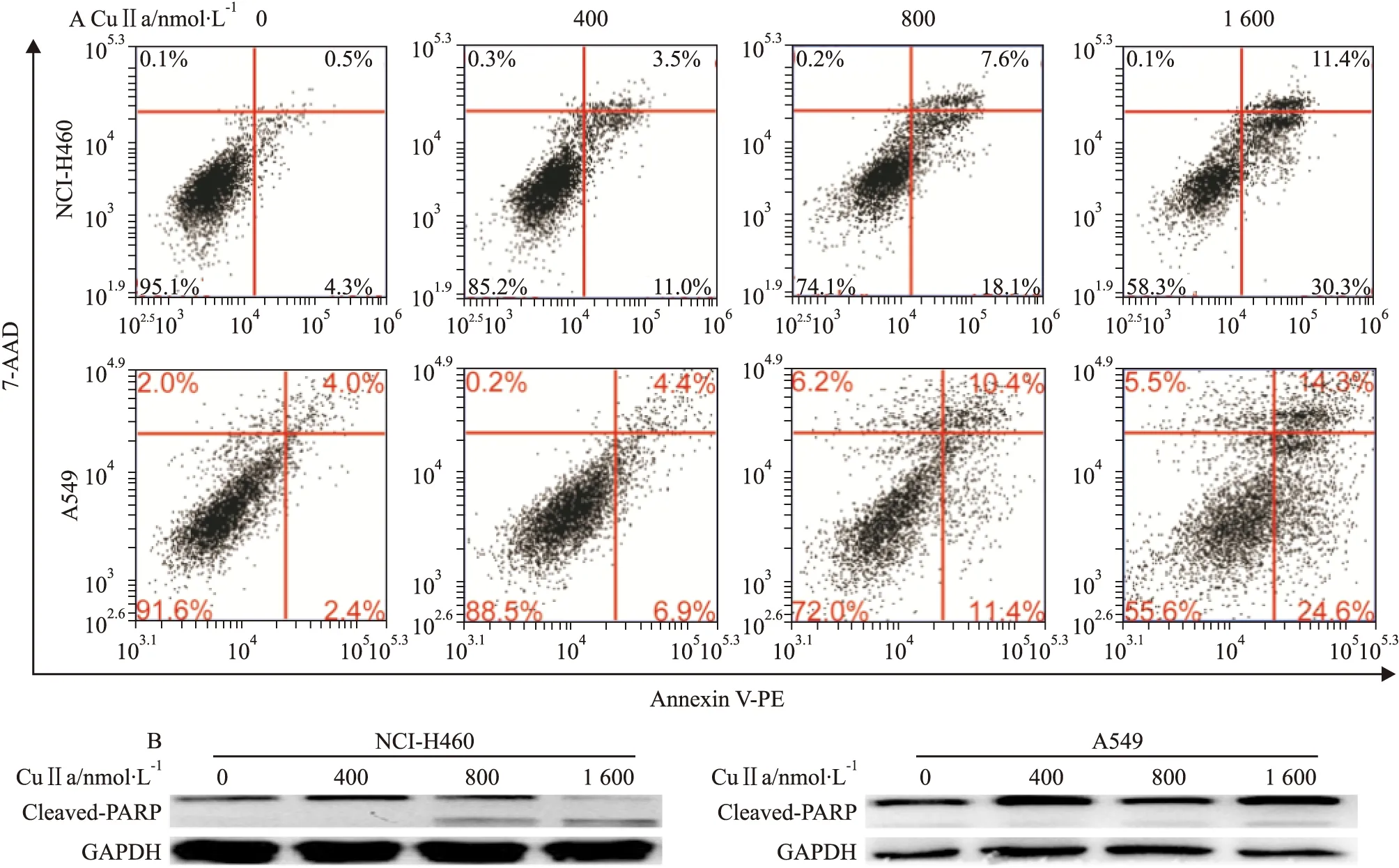
Fig 2 Apoptosis of lung cancer cell lines NCI-H460 and A549 treated with CuⅡa and the expression of Cleaved-PARP
A:Flow cytometric analysis of cell lines apoptosis induced by different dose of CuⅡa; B: The expression of cleaved-PARP in the NCI-H460 and A549 cells treated with different dose of CuⅡa was determined by Western blot
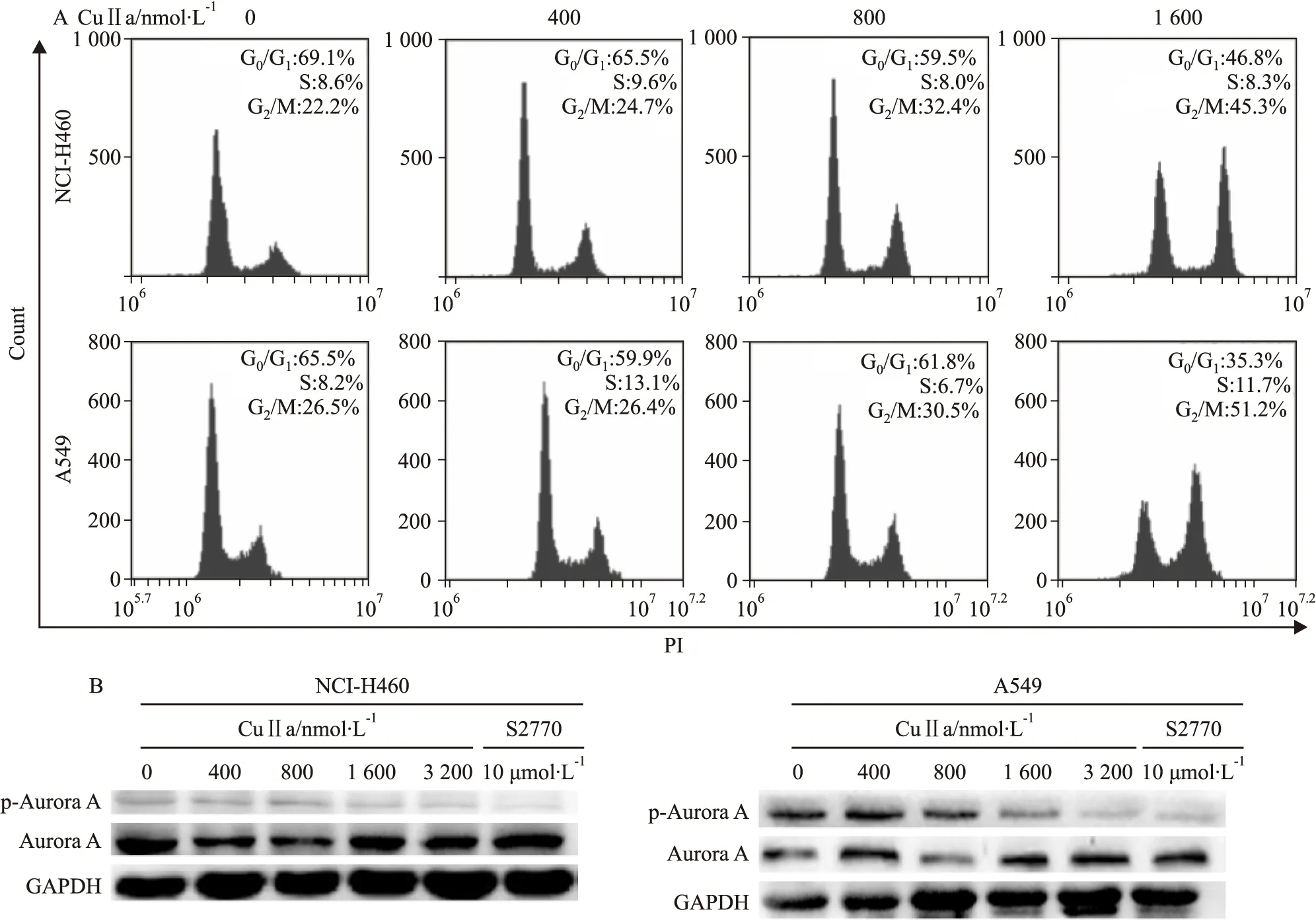
Fig 3 CuⅡa treatment caused G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and inhibit Aurora phosphorylation in NCI-H460 and A549 cells
A: CuⅡa caused G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in NCI-H460 and A549 cells at in a dose-dependent manner; B: CuⅡa inhibited Aurora A phosphorylation in a dose -dependent manner

Fig 4 CuⅡa inhibited dephosphorization of STAT3 and Cofilin
A: CuⅡa inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner in NCI-H460 and A549 cells pretreated with CuⅡa; B: CuⅡa caused Cofilin dephosphorylation in NCI-H460 and A549 cells
已知CuⅡa诱导肺癌细胞凋亡并阻滞细胞周期于G2/M期,但其机制尚未见报道。与细胞周期调控密切相关的Aurora A激酶参与了细胞分裂的多个生理过程,如中心粒的成熟和分离,纺锤体的形成,染色体的分离和胞质分裂等[9]。已有一些Aurora A激酶抑制剂被发现,例如:Chinn等[10]用Aurora A抑制剂MK-5108处理多种非小细胞肺癌细胞株,抑制细胞增殖并滞留细胞于G2/M期。另外,通过下调或抑制Aurora A基因表达,也能抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并诱导G2/M期阻滞[11-12]。本研究证实CuⅡa明显抑制Aurora A激酶蛋白磷酸化,导致其活性受到抑制,进而影响细胞分裂过程,阻滞肿瘤细胞于G2/M期,发挥抗肿瘤效应。
研究同时还发现CuⅡa与葫芦素B等传统葫芦素类似物一样,能够抑制Cofilin磷酸化。Cofilin作为Cofilin家族一员,在调节肌动蛋白的动力学[13],维持细胞形态以及细胞分裂起到重要作用[14-15],其磷酸化被抑制导致肌动蛋白聚集、细胞形态及分裂异常。推测CuⅡa抑制Cofilin磷酸化是诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡重要机制。
综上所述,CuⅡa能明显抑制人肺癌细胞系NCI-H460和A549增殖并诱导凋亡,其效应机制可能是抑制Aurora A、STAT3以及Cofilin多种信号通路的结果。CuⅡa能抑制与肿瘤异常增殖多种信号通路,其多靶点协同抗肿瘤效应机制为该重要天然产物后续研究提供了理论依据。
(致谢:本实验在成都医学院科研实验中心完成的,感谢各位老师和同学对本实验提供的帮助和支持。)
[1] Boykin C, Zhang G, Chen Y H, et al.Cucurbitacin IIa: a novel class of anti-cancer drug inducing non-reversible actin aggregation and inhibiting survivin independent of JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation[J].BrJCancer, 2011, 104(5): 781-9.
[2] 任 帅, 徐丽慧, 曾龙辉,等.雪胆素乙通过破坏微丝结构和促进p21~(Cip1)表达抑制前列腺癌PC-3细胞的增殖[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2012,26(6): 835-41.
[2] Ren S, Xu L H, Zeng L H, et al. Inhibitory effect of CucurbitacinⅡb on proliferation of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells through disruption of microfilaments and upregulation of p21 Cip1 expression[J].ChinJPharmacolToxicol, 2012,26(6): 835-41.
[3] 高 申, 于孟可, 魏佳慧,等.雪胆甲素对人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志, 2012,25(1): 69-71.
[3]Gao S, Yu M K, Wei J H, et al. Inhibitory effect of cucurbitacinⅡa on proliferation of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells[J].ChinJBiol, 2012, 25(1): 69-71.
[4] Suo S B, Qiu J D, Shi S P, et al.PSEA: Kinase-specific prediction and analysis of human phosphorylation substrates[J].SciRep, 2014, 4:4524.
[5] Xiong A, Yang Z, Shen Y, et al.Transcription factor STAT3 as a novel molecular target for cancer prevention[J].Cancers(Basel),2014,6(2): 926-57.
[6] Cuyas E, Perez-Sanchez A, Micol V, et al.STAT3-targeted treatment with silibinin overcomes the acquired resistance to crizotinib in ALK-rearranged lung cancer[J].CellCycle, 2016,15(24): 1-06.
[7] Zheng X J, Yang Z X, Dong Y J, et al.Downregulation of leptin inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells via the Notch and JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways[J].BiolOpen, 2016, 5(6): 794-800.
[8] Jiang S, Gao Y, Hou W, et al.Sinomenine inhibits A549 human lung cancer cell invasion by mediating the STAT3 signaling pathway[J].OncolLett, 2016, 12(2): 1380-6.
[9] 朱海静, 焦 宇.Aurora激酶及其抑制剂的研究进展[J].中国现代应用药学, 2014,31(10): 1288-96.
[9] Zhu H J, Jiao Y. Progress of aurora kinase and its inhibitors[J].ChinJModApplPharm, 2014,31(10): 1288-96.
[10]Chinn D C, Holland W S, Mack P C. Anticancer activity of the Aurora A kinase inhibitor MK-5108 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in vitro as monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapies[J].JCancerResClinOncol, 2014, 140(7): 1137-9.
[11]Lu Y, Liu Y, Jiang J, et al.Knocking down the expression of Aurora-A gene inhibits cell proliferation and induces G2/M phase arrest in human small cell lung cancer cells[J].OncolRep, 2014, 32(1): 243-9.
[12]Lee S Y, Lee G R, Woo D H, et al.Depletion of Aurora A leads to upregulation of FoxO1 to induce cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J].CellCycle, 2013, 12(1): 67-75.
[13]Blanchoin L, Boujemaa-Paterski R, Sykes C, et al.Actin dynamics, architecture, and mechanics in cell motility[J].PhysiolRev, 2014, 94(1): 235-63.
[14]Wang F, Liu D Z, Xu H, et al.Thapsigargin induces apoptosis by impairing cytoskeleton dynamics in human lung adenocarcinoma cells[J].ScientificWorldJ, 2014, 2014: 619050.
[15]雷艳萍, 何 洁, 苏 琦.Cofilin与分化的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报, 2014,30(2): 164-7.
[15]Lei Y P, He J, Su Q. Research development of Cofilin and differentiation[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2014,30(2):164-7.
Effects of cucurbitacin Ⅱa on apoptosis of human lung cancer cell lines NCI-H460 and A549 and its mechanism
CHEN Yu-lin1,XIAN Qing3,XIAO Cui2,ZHONG Yue-ling2,SU Xiao-mei3,XU Li4,LUO Qiao-li3,CHENG Peng3,WANG Tao3,LIU Jin2,ZHANG Tao3,YANG Tai2,ZOU Qiang2,LI Hua3
(1.SchoolofLifeScienceandEngineering,SouthwestJiaotongUniversity,Chengdu610031,China;2.ChengduMedicalCollege,Chengdu610500,China;3.CancerCenter,ChengduMilitaryGeneralHospital,Chengdu610083,China;4.DeptofClinicalMedicine,NorthSichuanMedicalCollege,NanchongSichuan637000,China)
Aim To study the apoptosis effect of cucurbitacin Ⅱa on non-small cell lung cancer cell lines NCI-H460 and A549 and its underlying mechanism.Methods Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 assay. The apoptosis effect and cell cycle arrest were detected by Flow cytometry. Western blot was employed to detect the related protein.Results The proliferation of lung cancer cell lines NCI-H460 and A549 was inhibited by CuⅡa, which showed cytotoxic activity with IC50values of 224.9 nmol·L-1and 108.3 nmol·L-1against NCI-H460 and A549 respectively. CuⅡa induced the cells apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. The results of Western blot showed CuⅡa inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3 and Cofilin in a dose-dependent manner. Further, CuⅡa inhibited the phosphorylation of Aurora A, in line with the important characteristics of anti-tumor effect of Aurora A kinase inhibitor with blocking cells in the G2/M phase.Conclusion CuⅡa has obvious anti-tumor effect against non-small cell lung cancer, which suggests its value as a lead compound for lung cell carcinoma.
curcerbitacin Ⅱa;non-small-cell lung cancer;apoptosis;Aurora A;Cofilin;STAT3
2017-01-20,
2017-03-08
国家自然科学基金面上项目(No 81273530);成都军区十二五重大项目(No B14005);医院研究型课题重大项目(No 2013YG-A004)
陈育林(1990-),男,硕士生,研究方向:肿瘤免疫及药物小分子,E-mail:1015062445@qq.com; 邹 强(1971-),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:自身免疫性疾病发病机制与治疗药物筛选,通讯作者,E-mail:qiangzou99@gmail.com; 李 华(1971-),女,博士,教授,硕士生导师,研究方向:疾病基因组学与肿瘤免疫,通讯作者,E-mail:huali99@gmail.com
时间:2017-6-7 19:04 网络出版地址:http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20170607.1904.016.html
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2017.07.008
A
1001-1978(2017)07-0922-06
R284.1;R329.25;R329.28;R734.202.2;R979.1

