自适应奇异值分解的随机共振提取微弱故障特征
李志星,石博强
(1. 北京科技大学机械工程学院,北京 100083; 2. 内蒙古科技大学机械工程学院,包头 014000)
自适应奇异值分解的随机共振提取微弱故障特征
李志星1,2,石博强1※
(1. 北京科技大学机械工程学院,北京 100083; 2. 内蒙古科技大学机械工程学院,包头 014000)
针对农业机械设备在强背景噪声下微弱故障特征难以提取的问题,提出一种基于自适应奇异值分解的随机共振微弱故障特征提取方法。首先,将原始信号奇异值分解并重构得到分量信号,构建互信息差分谱,权衡各分量信号对原始信号的贡献率,自适应选取有效奇异值个数,以克服已有方法人为主观选择或仅考虑奇异值大小等不足;其次,对选取的有效奇异值对应的分量信号自适应随机共振,使其微弱故障特征增强;最后,对增强的分量信号统计学平均以提取微弱故障特征。仿真和轴承外圈故障试验结果表明,该方法不仅克服了强背景噪声下有效奇异值的选取困难,而且结合自适应随机共振,有效提取出仿真信号100 Hz和轴承外圈 155.5 Hz的故障特征频率,因此,所提方法不仅能够更好的增强微弱故障特征,而且分析结果优于单纯的奇异值分解和随机共振方法。该文提出的方法不仅可适用于强噪声背景下轴承的故障诊断,同时为农业机械设备的轴承故障诊断提供参考。
振动;农业机械;故障检测;奇异值分解;互信息差分谱;微弱特征
0 引 言
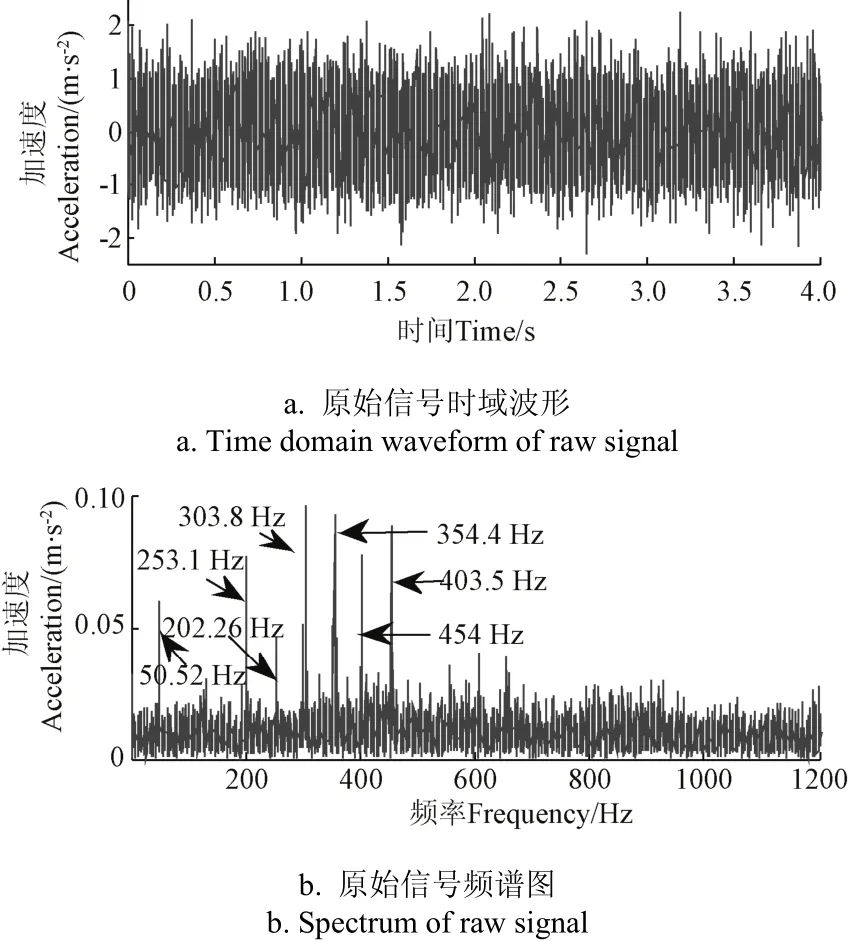
近年来,随着农业科学技术的发展,农业机械设备不断向大功率、大型化、高速化方向发展,而轴承是农业机械设备的重要部件之一,其故障严重危害设备的健康运行,严重情况下可能导致机毁人亡,因此,农业机械设备的故障诊断越来越受到重视[1-3]。对其进行故障诊断时,利用振动信号提取故障特征是最常用的方法,但对于强背景噪声干扰下的微弱故障特征往往难以提取[4-5],因此,提取强背景噪声下极低信噪比的微弱故障特征成为农业机械轴承故障诊断的关键。
针对强背景噪声下的微弱故障特征提取一般有2种方法。一种方法是从抑制或消除噪声的角度提取微弱故障特征,如小波分析[6-8],奇异值分解(singular value decomposition, SVD)[9-10]及总体平均经验模态分解[11-13]等,其中SVD在轴承故障诊断中具有优异的降噪特性[14-15],尤其是脉冲信号。赵学智等[16]提出奇异值分解与小波变换具有相似性并研究了奇异值分解的机理,何田等[17]用奇异值分解方法检测信号中的突变信息,Kang等[18]利用奇异值分解对感应电机提取故障,并利用支持向量机对故障分类,郑安总等[19]通过奇异值分解寻找特征信号分量与噪声强度相匹配的分量信号,以获取强噪声背景下的特征信号,以上研究均根据奇异值曲线选取k个奇异值,其余奇异值置0,奇异值的个数选择取决于人为设定,奇异值选择过多,会使有用信号混入过多噪声,选择过少,则使有用信号丢失,因此有必要研究一种有效奇异值的选择方法。杨文献等[20]利用奇异值熵增量选择有效奇异值,需人为经验才能确定奇异值个数,赵学智等[21]通过构造奇异值差分谱实现了自适应选择,但仅考虑奇异值的大小,容易使隐藏在强背景噪声下的有用信号被移除,影响微弱故障的检测结果,因此,有效奇异值选择问题并未从根本上解决[22]。
另一种方法不是消除噪声而是利用噪声提高信噪比以提取微弱故障特征,主要是随机共振理论。随机共振最早由Benzi等[23]在研究古气象冰川问题时提出,它与传统降噪方法相比,反其道而行之,利用噪声能量向微弱信号转移,在增强微弱故障特征的同时削弱部分噪声,由于随机共振在强背景噪声中提取微弱故障特征的优良特性,成为近年众多学者研究的热点[24]。Li等[25]提出一种变步长随机共振用于轴承的故障诊断,雷亚国等[26-28]利用蚁群算法优化随机共振参数,使随机共振效果达到最优,以上研究为检测大参数信号[29-30](不满足信号幅值A<<1,噪声强度D<<1,信号频率f<<1的信号)及随机共振参数优化提供了理论依据,尤其对提取强背景噪声下的微弱故障特征具有重要意义。
结合SVD降噪和随机共振各自的优势,本文提出自适应奇异值分解的随机共振微弱故障特征提取方法。首先对含噪信号奇异值分解并重构得到k个分量信号,然后构造互信息差分谱,选取有效奇异值,对选取的有效分量自适应随机共振,通过有效分量信号合成并统计学平均,以期提取出强背景噪声下的微弱故障特征。
1 SVD降噪原理
对于实矩阵A∈Rm×n(假设m>n),其奇异值分解存在正交矩阵U∈Rm×n和V∈Rm×n,以及矩阵,使得

式中σ1≥σ2≥σ3…σq>0称为矩阵A的奇异值。其中q≤min(m, n),U、V分别称为矩阵A的左、右奇异矩阵。
对于实测信号X=[x(1), x(2), …, x(N)],利用此信号构造Hankel矩阵如下:

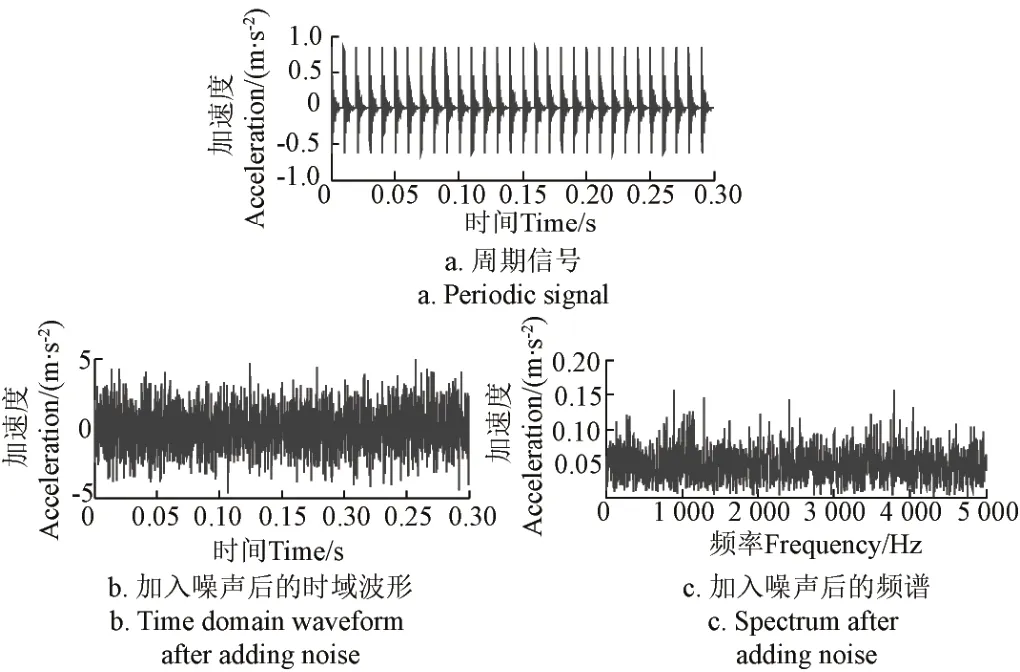
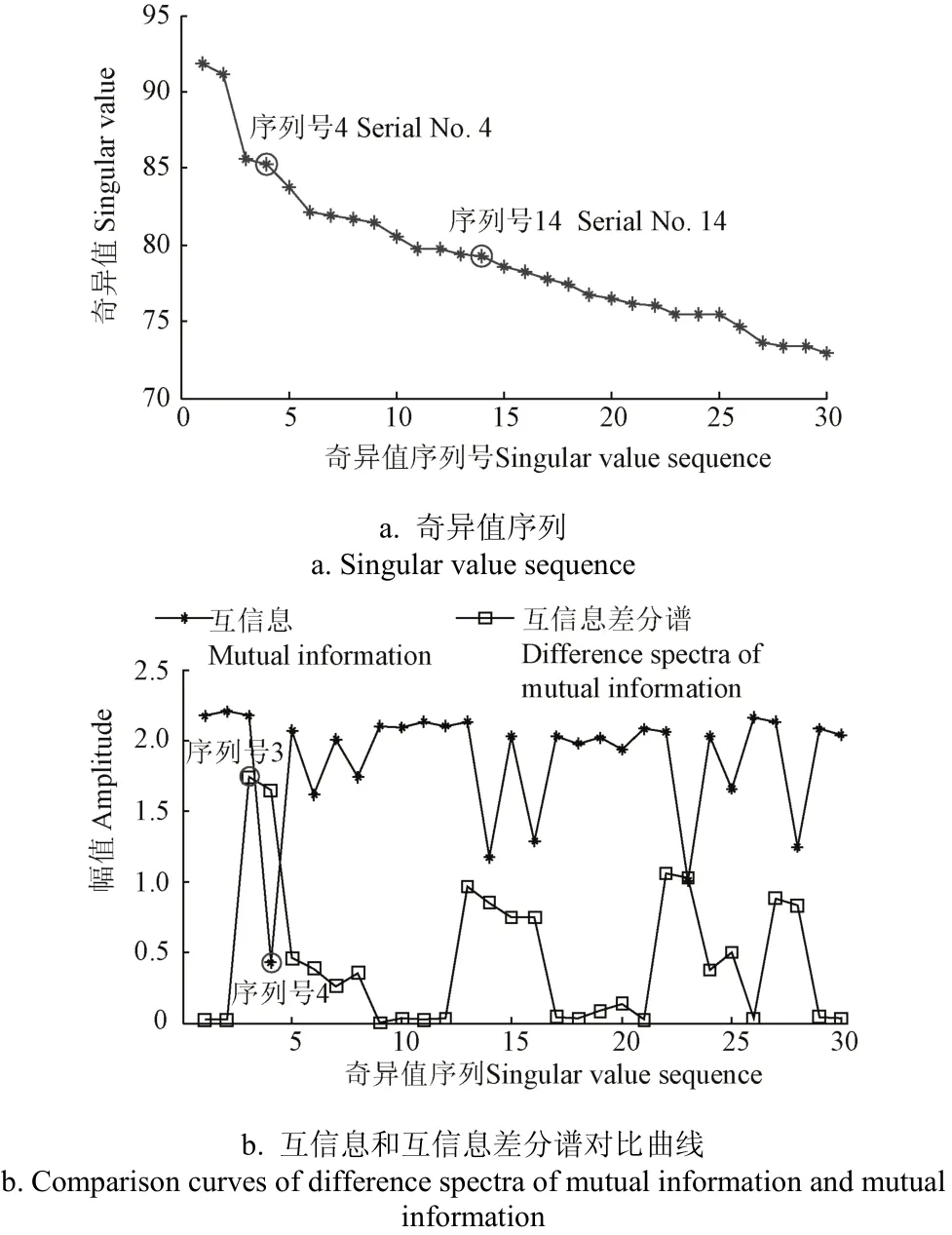
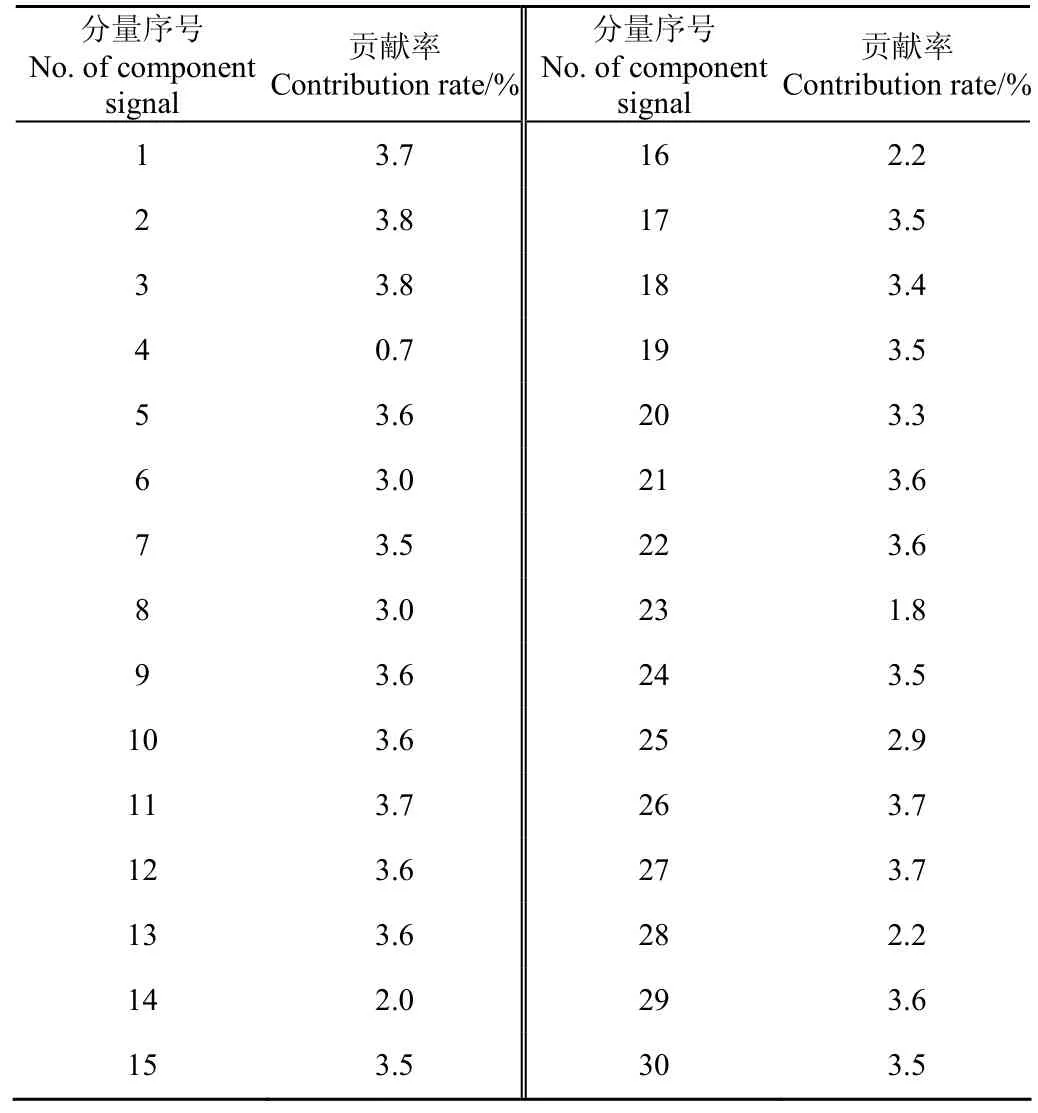
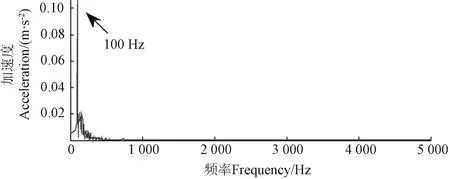
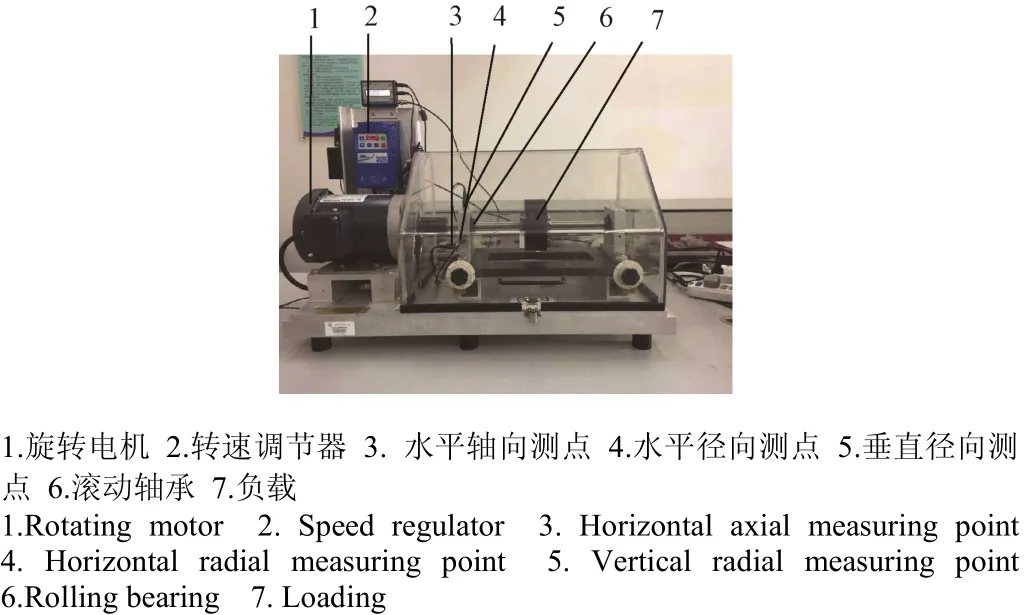
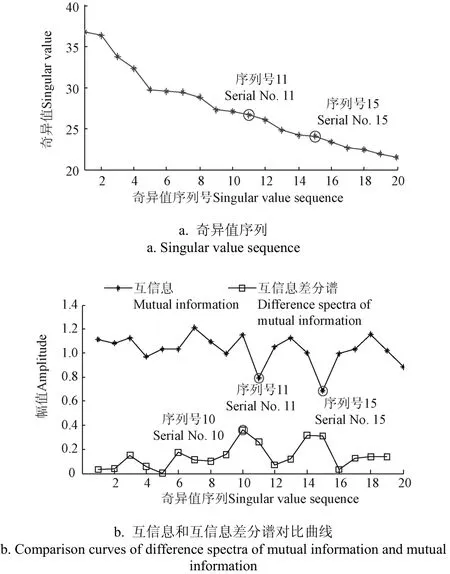
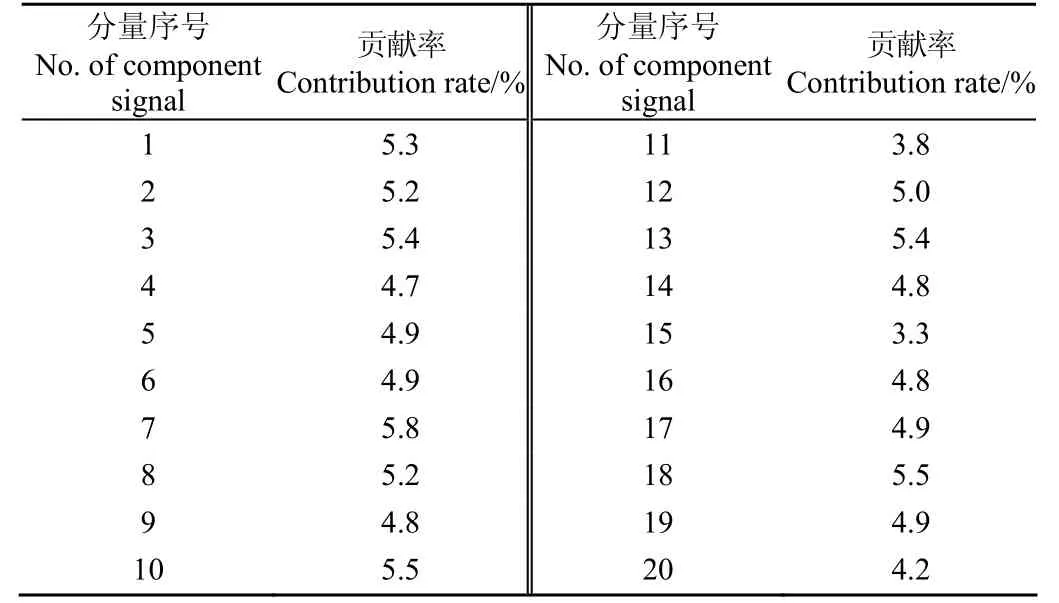
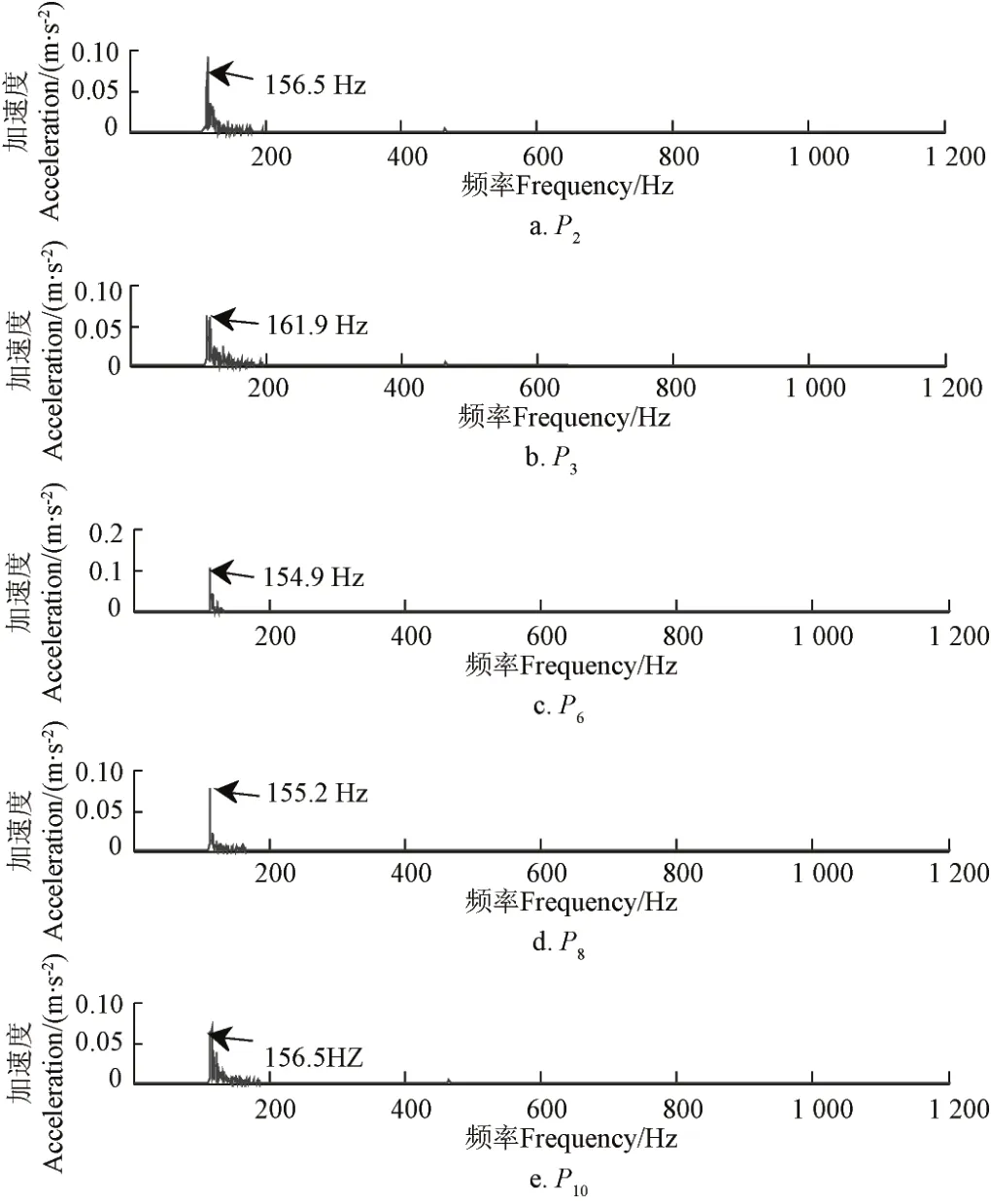
式中1 式中ui∈Rm×1,vi∈Rn×1,i=1,2,··,q, q=min(m, n)。设Ai的第一个行矢量用Pi,n表示,而Hi,n是Ai最后一个列矢量减去第一个元素后的子列矢量,将Pi,1和Hi,n的转置首尾相接构成一个分量信号Pi,写成矢量形式: 其中,Pi,1∈R1×n,Hi,1∈R(m-1)×1,所有分量信号Pi的线性叠加构成了原始信号X的分解,即: 随机共振系统一般包括非线性系统、周期信号及噪声,当三者达到最佳匹配时共振现象最为明显。常用的随机共振模型是双稳系统,用Langevin方程可表示为: 式中a>0,b>0为系统参数,s(t)为周期信号,n(t)是零均值的高斯白噪声,双稳系统的势函数为: 3.1 构建互信息差分谱 互信息(mutual information,MI)是信息理论中的基本概念,通常用于描述系统之间的相关性。根据奇异值分解理论可知,原始信号可分解成一组分量信号。分量信号A与原始信号B的互信息用公式表示为: QA(a)、QB(b)分别为分量信号与原始信号的边缘概率分布,其公式: QAB(a,b)是分量信号与原始信号的联合概率分布,用2个信号重叠区域的归一化联合直方图表示。 各分量信号的互信息不仅体现对原始信号的贡献率,而且包含强背景噪声下的全部故障信息,原始信号各分量的互信息所形成的序列S=[MI1,MI2,··MIq],为了描述互信息之间突变信息,引入互信息差分谱的概念: 其中i=1,2,··,q+1,所有λi形成的序列C=[λ1, λ2,··,λq-1]称为互信息差分谱(difference spectrum of mutual information,DSMI)。文中将奇异值重构得到分量信号,各分量信号中都有可能包含有用信号与噪声成分,采用互信息差分谱选取有效奇异值,重点考虑各分量信号对原始信号的互信息,通过互信息突变选取有效奇异值。当相邻互信息差别较大时,互信息差分谱发生突变,即相邻两分量信号对原始信号的贡献率发生突变,在整个差分谱序列中必有一个最大突变峰值ki,它不仅反映了分量信号与原始信号的贡献率变化达到极大值,而且说明信号在性质上发生了根本性变化,也就是有用信号与噪声信号之间发生转变的自然反映,即前k个分量信号为有用信号(对应k个奇异值),其余为噪声信号。 3.2 自适应随机共振 由于随机共振仅适用于幅值、噪声强度和频率远远小于1的情形,为满足小参数要求,首先将选取的k个有效分量信号(对应k个奇异值)移频变尺度处理,即设计一个频率压缩尺度R,将信号频率压缩,然后利用蚁群算法自适应优化系统参数a和b,在0 本文方法具体步骤如下:1)原始信号X重构得到Hankel矩阵,求出N个奇异值σi;2)对每个奇异值σi重构得到N个分量信号Pi;3)计算分量信号Pi与原始信号X的边缘概率分布及联合概率分布,得出各分量信号的互信息,并求取各分量信号对原始信号的贡献率;4)计算各分量信号Pi的互信息差分谱,根据最大突变峰值ki选取有效分量,即选取有效奇异值个数;5)将选取的k个有效奇异值σi对应的分量信号Pi移频变尺度处理,使其满足小参数要求;6)将移频变尺度处理后的分量信号Pi输入到随机共振系统,利用蚁群算法自适应优化随机共振的2个参数a和b,得到k个被增强的有效分量信号;7)计算k个有效分量信号的均值,最终提取微弱故障特征。 为了验证所提方法的有效性,仿真一个周期信号[31],采样频率为10 KHz,特征频率是100 Hz,采样时间是0.3 s,如图1a所示。为了模仿强背景噪声下的轴承故障信号,向周期信号加入标准差为0.5的高斯白噪声,如图1b所示。 图1 仿真信号时域波形和频谱图Fig.1 Time domain waveform and spectrum of simulation signal 由于周期信号被强噪声所淹没,在图1c频谱中不能获取周期信号的特征频率,因此,采用奇异值分解降噪,构建行列式为1 700×30的Hankel矩阵,得到30个从大到小依次排列的奇异值,如图2a所示。为了获取强噪声背景下的有效奇异值,将所有奇异值重构得到30个分量信号,根据式(8)得出30个分量信号的互信息,如图2b所示。从图2b中可知,每个分量信号互信息不同,而各分量信号互信息与所有分量信号互信息的百分比以贡献率衡量,由此得出各分量信号对原始信号的贡献率,如表1所示。 图2 互信息差分谱选取的有效奇异值Fig.2 Difference spectra of mutual information select effective singular value 表1 奇异值重构的分量信号对原始信号的贡献率Table 1 Contribution rate of singular value reconstruction component signal to raw signal 由图2a可知,序列号4具有较大奇异值,但对原始信号的贡献率最小仅为0.7%;同理,序列号14也具有较大奇异值,但对原始信号的贡献率为2.0%,与其他奇异值对原始信号的贡献率相比数值较小,根据互信息差分谱选取有效奇异值的方法,在序列号3处突变最大,因此选取前3个奇异值为有用信号,即得到3个有效奇异值,说明序列号4和14虽然具有较大奇异值,但并非有用信号,即奇异值大不一定包含有用信息,在强噪声背景下可能为噪声干扰。根据选取的前3个奇异值分别重构分量信号,每个分量信号的频谱图,如图3a所示。 图3 自适应选取的分量信号频谱Fig.3 Spectrum of adaptive selected component signal 由图3a可知,分量信号P1和P2高频段频率比较明显,但特征频率不在其范围内,而分量信号P3在低频段有明显频率,但无法识别目标频率,说明对于强背景噪声下的微弱故障特征,仅SVD降噪难以提取出特征频率,因此,将3个有效分量信号分别输入到随机共振,首先采用移频变尺度处理,由于目标频率是100 Hz,载波频率是1 000 Hz,因此设定高通滤波器的通过频率和截止频率是分别是90和85 Hz,调制频率为85 Hz,变尺度压缩率是400,则预处理后的目标频率被压缩为0.0751,满足小参数要求,利用蚁群算法在0<α<10,0 从图3b可知,有效分量信号自适应随机共振处理后,强背景噪声下的周期信号特征频率被明显增强,但每个有效分量随机共振的最大谱峰频率不同,P1、P2分量信号的最大谱峰频率为100 Hz,P3分量信号的最大谱峰频率为96.67 Hz,由于故障特征频率被载波信号所调制,在频谱中表现为以载波频率为中心,以故障特征频率为边带的一个共振频带,因此不能根据P1和P2判断故障频率,只能判断是否存在共振频带,另外,有效分量信号的最大谱峰频率并不都是目标频率,因此,将3个有效分量信号统计学平均得出最终频谱图,如图4所示。 图4 统计学平均的频谱图Fig.4 Spectra of statistical average 由图4可知,通过统计学平均后部分噪声被过滤,噪声减少意味着干扰减少,从而要提取的故障特征频率100 Hz被明显凸显出来,幅值为0.106 9,与周期信号的特征频率完全相同,从而验证了所提方法的有效性。 试验中采用Spectra Quest公司生产的机械设备故障综合试验台,如图5所示。信号则由IOtech公司生产的Zonic Book/618E 型数据动态系统采集,该设备由8个信号输出通道,幅值精度可达±0.5 dB,试验中采用ER-10k滚动轴承作为故障轴承,其几何尺寸D=33.5,d=7.939 5 mm,α=0°, Z=8,采样频率为2 560 Hz,转速为3 060 r/min,根据振动理论分析可知,轴承外圈的特征频率是155.664 Hz,原始信号的时域和频谱图如图6所示。 图5 机械设备综合故障试验台Fig.5 Comprehensive failure test of mechanical equipment 由图6a原始信号时域波形可知,由于轴承外圈故障频率被强背景噪声所淹没信噪比极低,看不出任何故障特征,而在频谱图6b中有明显的转频50.52 Hz以及转频的4~9倍频,但无法看到155.664 Hz的故障频率,为了提取微弱故障特征,利用本文所提出的方法检测轴承外圈故障,将原始信号构建行列式为1 700×20的Hankel矩阵,得出20个奇异值序列,如图7a所示。 图6 原始信号的时域波形和频谱Fig.6 Time domain waveform and spectrum of raw signal 图7 互信息差分谱选取有效奇异值Fig.7 Difference spectra of mutual information selecting effective singular value 通过重构奇异值获取20个分量信号,利用式(8)求取各分量信号的互信息,如图7b所示。由图7b可知,每个分量信号互信息不同,序列号11和15具有相对较大的奇异值,但贡献率较小,由表2可知,其值分别为3.8%和3.3%,且序列号15的互信息达到最小,而根据互信息差分谱选取有效奇异值的方法,在序列号10处出现最大突变,因此选取前10个分量信号为有效分量,即选取前10个奇异值为有效奇异值,而序列号11和15并非有效奇异值,从而通过试验验证奇异值较大不一定为有效奇异值,有可能为噪声信息。根据选取的前10个有效奇异值重构得到分量信号,随机选取不同贡献率的分量信号,即序号为2、3、6、8和10的分量信号作为分析样本,对其频谱分析,如图8所示。 表2 轴承外圈信号奇异值重构的分量信号对原始信号的贡献率Table 2 Contribution rate of component signal by singular value reconstruction to raw signal for bearing inner ring 图8 P2,P3,P6,P8,P10分量信号频谱图Fig.8 Spectrum of P2, P3, P6, P8, P10component signal 由图8可知,各分量信号噪声有所降低,但仍难以提取故障特征,同样说明在信噪比极低情况下仅奇异值分解无法提取故障特征,因此将选取的5个有效分量样本信号自适应随机共振。由于轴承外圈的故障特征频率是155.664 Hz,首先采用移频变尺度处理,设定高通滤波器的通过频率和截止频率分别是是154和150 Hz,调制频率为150 Hz,变尺度压缩率是400,则预处理后的目标频率被压缩为0.014 16,满足小参数要求,利用蚁群算法在0<α<10,0 图9 P2,P3,P6,P8,P10分量信号自适应随机共振频谱图Fig.9 Spectra of P2, P3, P6, P8, P10component signal adaptive stochastic resonance 由图9可知,强背景噪声中的微弱故障特征被明显增强, P2,P6,P8,P10分量信号自适应随机共振的最大谱峰频率接近于故障频率155.664 Hz,但最大谱峰频率大小不同,P3分量信号自适应随机共振的最大谱峰频率为161.9 Hz,与特征频率155.664 Hz相差较大,不能真实反映轴承的外圈故障,因此将各有效分量信号合成并统计学平均得出最终的频谱图,如图10所示。 图10 统计学平均频域图Fig.10 Spectra of statistical average 由图10可知,最大谱峰频率是155.5 Hz,与随机选取分量信号自适应随机共振的最大谱峰频率相比,统计学平均的最大谱峰频率辨识度更高,更接近于轴承外圈故障频率155.664 Hz,因此,利用统计学平均随机共振比单个分量信号的随机共振效果更优,更接近于特征频率,从而通过试验再次验证了所提方法的有效性。 提出了自适应奇异值分解的随机共振微弱故障特征提取方法,可有效提取强背景噪声下的微弱故障特征。 1)通过构造互信息差分谱,提出了一种有效奇异值选择方法。该方法考虑分量信号与原始信号的贡献率,一方面防止了有用信号的剔除;另一方面实现了自适应选取,有效避免人为选择的主观性。另外,利用互信息差分谱,在仿真和轴承外圈信号中分别得出在序列号3和序列号10发生突变,因此,可分别选取3个和10个有效奇异值。 2)由于强背景噪声的存在,较大的奇异值可能有较小的互信息,但并非是有效奇异值,说明奇异值较大不一定包含有用信息,有可能是噪声干扰,因此有效奇异值的选择不应以奇异值的大小作为判定依据。 3)由于强背景噪声下信噪比极低,仅通过奇异值分解不能提取微弱故障特征,而利用随机共振提取分量信号的故障特征,最大谱峰频率大小不同,本文将两者结合,不仅克服了强背景噪声下有效奇异值的选取困难,而且能够更好的增强微弱故障特征,通过仿真和轴承外圈试验有效提取出100和155.5 Hz的微弱故障特征,从而得出该方法提取效果优于单纯的奇异值分解和随机共振方法。 该研究可广泛应用于强噪声背景下的轴承故障诊断,可对农业机械及大功率、高转速设备的轴承故障诊断提供参考。 [1] 钟成义,王素珍,常春. 农业机械故障诊断技术研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农机化学报,2014,35(2):29-31. Zhong Chengyi, Wang Suzhen, Chang Chun. Review on research status for agricultural machinery fault diagnosis technology[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2014, 35(2): 29-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] Dhekale R B, Jadhav B D, Patil P M. Satellite image (multispectral) enhancement techniques in wavelet domain: An overview[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2015, 112(11): 16-20. [3] Randall R B, Antoni J. Rolling element bearing diagnostics: A tutorial[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(2): 485-520. [4] Wong M L D, Zhang M, Nandi A K. Effects of compressed sensing on classification of bearing faults with entropic features[C]//Signal Processing Conference, 2015: 2256-2260. [5] Abboud D, Antoni J, Sieg Zieba S, et al. Envelope analysis of rotating machine vibrations in variable speed conditions: A comprehensive treatment[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 84: 200-226. [6] Gryllias K C, Antoniadis I A. Estimation of the instantaneous rotation speed using complex shifted Monet wavelets[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 38(1): 78-95. [7] 胥永刚,孟志鹏,赵国亮,等. 基于双树复小波包变换能量泄漏特性分析的齿轮故障诊断[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(2):72-77. Xu Yonggang, Meng Zhipeng, Zhao Guoliang, et al. Analysis of energy leakage characteristics of dual-tree complex wavelet packet transform and its application on gear fault diagnosis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(2): 72-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 胡振邦,许睦旬,姜歌东,等. 基于小波降噪和短时傅里叶变换的主轴突加不平衡非平稳信号分析[J]. 振动与冲击,2014,33(5):20-23. Hu Zhenbang, Xu Muxun, Jiang Gedong, et al. Analysis of non-stationary signal of a sudden unbalanced spindle based on wavelet noise reduction and short-time Fourier transformation[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(5): 20-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 孟宗,王亚超. 基于微分局部均值分解的旋转机械故障诊断方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2014,50(11):101-107. Meng Zong, Wang Yachao. Rotating machinery fault diagnosis method based on the differential local mean decomposition[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(11): 101-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 王建国,李健,万旭东. 基于奇异值分解和局域均值分解的滚动轴承故障特征提取方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(3):104-110. Wang Jianguo, Li Jian, Wan Xudong. Fault feature extraction method of rolling bearings based on singular value decomposition and local mean decomposition[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 51(3): 104-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] Li Z X, Shi B Q. Research of fault diagnosis based on sensitive intrinsic mode function selection of EEMD and adaptive stochastic resonance[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2016(11): 1-12. [12] 周智,朱永生,张优云,等. 基于EEMD和共振解调的滚动轴承自适应故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,33(2):76-80. Zhou Zhi, Zhu Yongsheng, Zhang Youyun, et al. Adaptive fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on EEMD and demodulated resonance[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 33(2): 76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] Georgoulas G, Tsoumas I P, Antonino Daviu J A, et al. Automatic pattern identification based on the complex empirical mode decomposition of the startup current for the diagnosis of rotor asymmetries in asynchronous machines[J]. IEEE Trans on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(9): 4937-4946. [14] Pan Zhengrong, Qiao Zijian. Feature extraction based on improved SVD denoising and spectral kurtosis in early fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Test Automation and Instrumentation, 2014, 1(10): 123-133. [15] 赵学智,聂振国,叶艳邦,等. 信号有效奇异值的数量规律及其在特征提取中的应用[J]. 振动工程学报,2016,3(29):532-541. Zhao Xuezhi, Nie Zhenguo, Ye Yanbang, et al. Number law of effective singular values of signal and its application to feature extraction[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2016, 3(29): 532-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 赵学智,叶彦邦. SVD和小波变换的信号处理效果相似性及其机理分析[J]. 电子学报,2008,36(8):1582-1589. Zhao Xuezhi, Ye Bangyan. The similarity of signal processing effect between SVD and wavelet transform and its mechanism analysis[J]. Journal of Electronic, 2008, 36(8): 1582-1589. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 何田,刘献栋,李其汉. 噪声背景下检测突变信息的奇异值分解技术[J]. 振动工程学报,2006,19(3):399-403. He Tian, Liu Xiandong, Li Qihan. An improved method of detecting abrupt information based on singular value decomposition in noise background[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2006, 19(3): 399-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] Kang Myeongsu, Kim Jongmyon. Singular value decomposition based feature extraction approaches for classifying faults of induction motors[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 41(1): 348-356. [19] 郑安总,冷永刚,范胜波. 基于奇异值分解的随机共振特征提取研究[J]. 物理学报,2012,21(16):210503. Zhang Anzong, Leng Yongang, Fan Shengbo. Features extraction based on singular value decomposition and stochastic resonance[J]. Journal of Physics, 2012, 21(16): 210503. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 杨文献,姜节胜. 机械信号奇异熵研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2000,36(12):9-13. Yang Wenxian, Jiang Jiesheng. Study on the singular entropy of mechanical signal[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2000, 36(12): 9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 赵学智,叶邦彦,陈统坚. 奇异值差分谱理论及其在车床主轴箱故障诊断中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报,2010,46(1):100-108. Zhao Xuezhi, Ye Yanbang, Chen Tongjian. Difference spectrum theory of singular value and its application to the fault diagnosis of headstock of lathe[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(1): 100-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] Qiao Zijian, Pan Zhengrong. SVD principle analysis and fault diagnosis for bearings based on the correlation coefficient[J]. Measurement Science and Technology. 2015, 26(8): 085014. [23] Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A. Mechanism of stochastic resonance[J]. Physical A, 1981, 14(11): L453-L457. [24] 谢有浩,刘晓乐,刘后广,等. 基于改进移频变尺度随机共振的齿轮故障诊断[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(8):70-76. Xie Youhao, Liu Xiaole, Liu Houguang, et al. Improved frequency-shifted and re-scaling stochastic resonance for gear fault diagnosis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(8): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] Li Qiang, Wang Taiyong, Leng Yonggang, et al. Engineering signal processing based on adaptive step-changed stochastic resonance[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2007, 21(5): 2267-2279. [26] 雷亚国,韩冬,林京,等. 自适应随机共振新方法及其在故障诊断中的应用[J]. 机械工程学报,2012,48(7):62-67. Lei Yaguo, Han Dong, Lin Jing, et al. New adaptivestochastic resonance method and its application to fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(7): 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] Lei YG, Qiao Z J, Xu X, et al. An underdamped stochastic resonance method with stable-state matching for incipient fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 94: 148-164. [28] Qiao Z J, Lei Y G, Lin J, et al. An adaptive unsaturated bistable stochastic resonance method and its application in mechanical fault diagnosis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2017, 84: 731-746. [29] Mcnamara B, Wiesenfeld K. Theory of stochastic resonance[J]. Physical Review A, 1989, 39(9): 4854-4869. [30] Tan Jiyong, Chen Xuefeng, Wang Junying, et al. Study of frequency-shifted and re-scaling stochastic resonance and its application to fault diagnosis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 23(3): 811-822. [31] Robert Benzi, Randall, Antonib Jérôme. Rolling element bearing diagnostics-a tutorial[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(2): 485-520. Extracting weak fault characteristics with adaptive singular value decomposition and stochastic resonance Li Zhixing1,2, Shi Boqiang1※ Bearings are the important component of agricultural machinery and equipment, whose failure may seriously endanger the healthy operation of equipment and even lead to bodily injury. So the fault diagnosis of agricultural machinery and equipment gains more and more attention. Using the vibration signal to extract the fault characteristics is the most common method, but it is difficult to extract the weak fault characteristics in strong background noise. Therefore, the extraction of weak fault characteristics with very low SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) under strong background noise becomes the key to the fault diagnosis of agricultural machinery bearings. There are 2 general methods for weak feature extraction under weak background noise. One method is to extract weak faults from the perspective of suppressing or eliminating noise. The other one is not to eliminate noise but using noise to improve the SNR to extract the weak fault characteristics, such as stochastic resonance (SR) theory. Compared to the traditional noise reduction method, SR makes use of noise energy transfer to weak signal, so the weak fault characteristics are enhanced while some of the noises are weakened. Because of the excellent features of extracting weak fault characteristics in strong background noise, SR has become a hot topic for many scholars in recent years. In this paper, the weak fault characteristics extraction method of SR based on adaptive SVD (singular value decomposition) was proposed. In the method, firstly, the original signal was decomposed by singular value and reconstructed to obtain the component signal; the difference spectrum of mutual information was constructed, the mutual information of each component signal and the original signal was weighed, and the number of valid singular values was selected adaptively, in order to overcome the problem of existing methods including human subjective choice or only considering the size of singular values and other deficiencies. Using the mutual information difference spectrum, 3 and 10 effective singular values were obtained in the simulation signal and bearing outer ring signal, respectively. Secondly, the adaptive SR was performed for the component signal corresponding to the selected effective singular value which enhances weak fault characteristics. Finally, the enhanced component signals were statistically averaged to extract the weak fault characteristics. In this paper, constructing the mutual information differential spectrum, and considering the mutual information of the component signal and the original signal, on the one hand, it avoids the elimination of the useful signals; on the other hand, the adaptive selection is realized which avoids the subjectivity of the artificial selection. In addition, due to the presence of strong background noise, the larger singular value may have smaller mutual information, but it is not valid singular value. It indicates that large singular value does not necessarily contain useful information, and there may be noise interference. Hence, the selection of effective singular values should not be based on the size of the singular value. The above analysis shows that it is difficult to extract the weak fault characteristics by SVD in strong background noise. We combine the 2 methods to process the effective component signal selected by mutual information difference spectrum in SR, and the maximum spectral frequency of each component is obtained. The statistical average is used to achieve noise filtering in order to highlight the characteristics of weak fault frequency. The results of simulation and bearing outer ring test show that, the proposed method is superior to the SVD and SR method. The method can effectively extract 100 and 155.5 Hz weak fault characteristics respectively for simulation signal and bearing outer ring signal. The proposed method can be applied not only to the fault diagnosis of bearing in strong noise background, but also to provide reference for bearing fault diagnosis of agricultural machinery and equipment. vibrations; agricultural machinery; fault detection; singular value decomposition; difference spectrum of mutual information; weak characteristic 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.008 TN911.72 A 1002-6819(2017)-11-0060-08 李志星,石博强. 自适应奇异值分解的随机共振提取微弱故障特征[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(11):60-67. 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.008 http://www.tcsae.org Li Zhixing, Shi Boqiang. Extracting weak fault characteristics with adaptive singular value decomposition and stochastic resonance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(11): 60-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.008 http://www.tcsae.org 2016-12-13 2017-05-10 国家自然科学基金资助项目(51075029) 李志星,男(汉族),河北衡水人,博士生,讲师,主要从事机械设备故障诊断的研究。北京 北京科技大学机械工程学院,100083。 Email:onyxlzx@126.com ※通信作者:石博强,男(汉族),河北唐山人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事机械设备故障诊断、机械可靠性研究。北京 北京科技大学机械工程学院,100083。Email:shiboqiang@ustb.edu.cn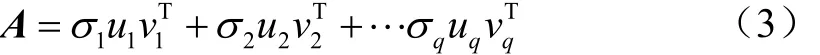

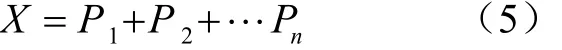
2 随机共振理论

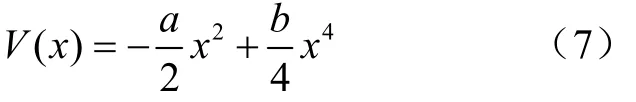
3 有效奇异值选择和随机共振方法的提出




4 自适应选取仿真信号的奇异值及特征提取

5 试验验证


6 结 论
(1. School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science & Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China; 2. School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science & Technology Inner Mongolia, Baotou 014000, China)

