负压式小麦精量排种器参数优化与试验
赵晓顺,于华丽,马跃进,张晋国,桑永英,霍晓静
(河北农业大学机电工程学院,保定 071001)
·农业装备工程与机械化·
负压式小麦精量排种器参数优化与试验
赵晓顺,于华丽,马跃进,张晋国,桑永英,霍晓静
(河北农业大学机电工程学院,保定 071001)
为了改变传统小麦条播作业模式,通过精量播种技术精确控制播种量和均匀性,实现在省种、节肥、节水的条件下保证小麦稳产高产的目的,设计了一种一器多行负压式小麦精量排种器。运用流体计算软件STAR-CCM+仿真分析了排种器结构参数(排种盘直径、吸种缝隙宽度、吸种环槽横截面形状、排种盘气室轴向深度)对气室流场的影响,压力云图、流速矢量图和流线图结果表明排种器具备较理想流场特性的结构参数为:吸种缝隙宽度为0.5 mm,排种盘直径范围为150~200 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm,吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型。在JPS-12排种器试验台上进行了排种均匀性试验,通过试验研究了吸种环槽横截面形状、吸种缝隙宽度、排种盘直径、排种盘气室轴向深度对合格指数、漏播指数、重播指数和合格粒距变异系数的影响规律,确定了排种器较优结构参数为:圆弧型吸种环槽横截面,0.5~0.8 mm的吸种缝隙宽度,170~200 mm的排种盘直径。2.0~3.0 mm的排种盘气室轴向深度。对参数优化后的排种器(0.7 mm的吸种缝隙、180 mm的排种盘直径、2.5 mm的气室轴向深度、圆弧型吸种环槽横截面)进行排种均匀性试验,合格指数为86.66%、漏播指数为5.09%、重播指数为8.25%,合格粒距变异系数为24.50%,满足JB/T 10293-2013《单粒(精密)播种机技术条件》中的参数指标。
机械化;优化;计算机仿真;小麦;排种器
0 引 言
小麦精量播种技术通过精确控制播种量和均匀性使每个植株都获得足够的营养面积和空间,肥水利用率高,有效分蘖多,在减少种子、水肥投入的基础上,保证小麦的稳产高产,可获得巨大经济效益和社会效益[1-2]。为了实现小麦精播技术,精量排种器起到了决定性作用,它制约了小麦精量播种均匀性、整机实用性和推广性[3-4]。
目前,国外气力式排种器是精量播种的常用装置,在玉米、大豆等作物的播种机上得到了广泛应用[5-10]。对于小麦等小粒条播类作物应用较少,成熟的机型有德国雷肯气力式精量播种机Solitair 9系列播种机、马特马克负压式谷物播种机等[11-12],但是机型庞大,价格昂贵,不适合国内市场[13-15]。在国内,何东键等[16-19]曾对组合吸孔式排种器进行过设计、改进、理论分析和试验研究。王瑞雪等[20]基于均匀性设计了一种小麦气吸式精量排种器,并进行了试验研究。杜辉等[21-22]研究制造了两代气吸式小麦精量播种机,并进行了试验。马立等[23-28]研究了一种圆管孔眼式气吸小麦播种机。但是以上文献中提到的排种器结构均为吸孔式,该形式的排种器容易导致堵塞、排种均匀性差等缺陷。因此设计一种排种均匀性好、稳定性高、不易堵塞的小麦精量排种器,以进一步推动小麦精量播种农艺技术的发展,以期为研究适合中国农业生产的小麦精量播种机提供参考。
1 排种器结构与工作原理
1.1 排种器结构
本排种器结构设计获得了两项国家发明专利权[29-30]。排种器主要由排种器外壳、充种高度控制板、挡种块、落种清堵片、负压管轴、动排种盘Ⅰ、动排种盘Ⅱ、静排种盘、固定套筒、控缝连接块、连接螺钉等组成,如图1所示。
动排种盘Ⅱ的两侧内部凹进形成半个负压室,动排种盘Ⅰ与动排种盘Ⅱ相对的一侧内部凹进形成另外半个负压室。动排种盘外缘相对处加工成一个吸种环槽,用于存放被均匀吸附排布的种子,吸种环槽内部是吸种缝隙。动排种盘通过固定套筒与负压管轴连接成一体。负压管轴处于负压室的位置处沿圆周方向加工通孔阵列,使负压室与负压管轴内腔形成一个相通的负压腔。充种高度控制板可对充入排种器外壳内种子的高度进行控制。在排种器外壳底部内的凸台上固定有落种清堵片,用于清落小麦种子。
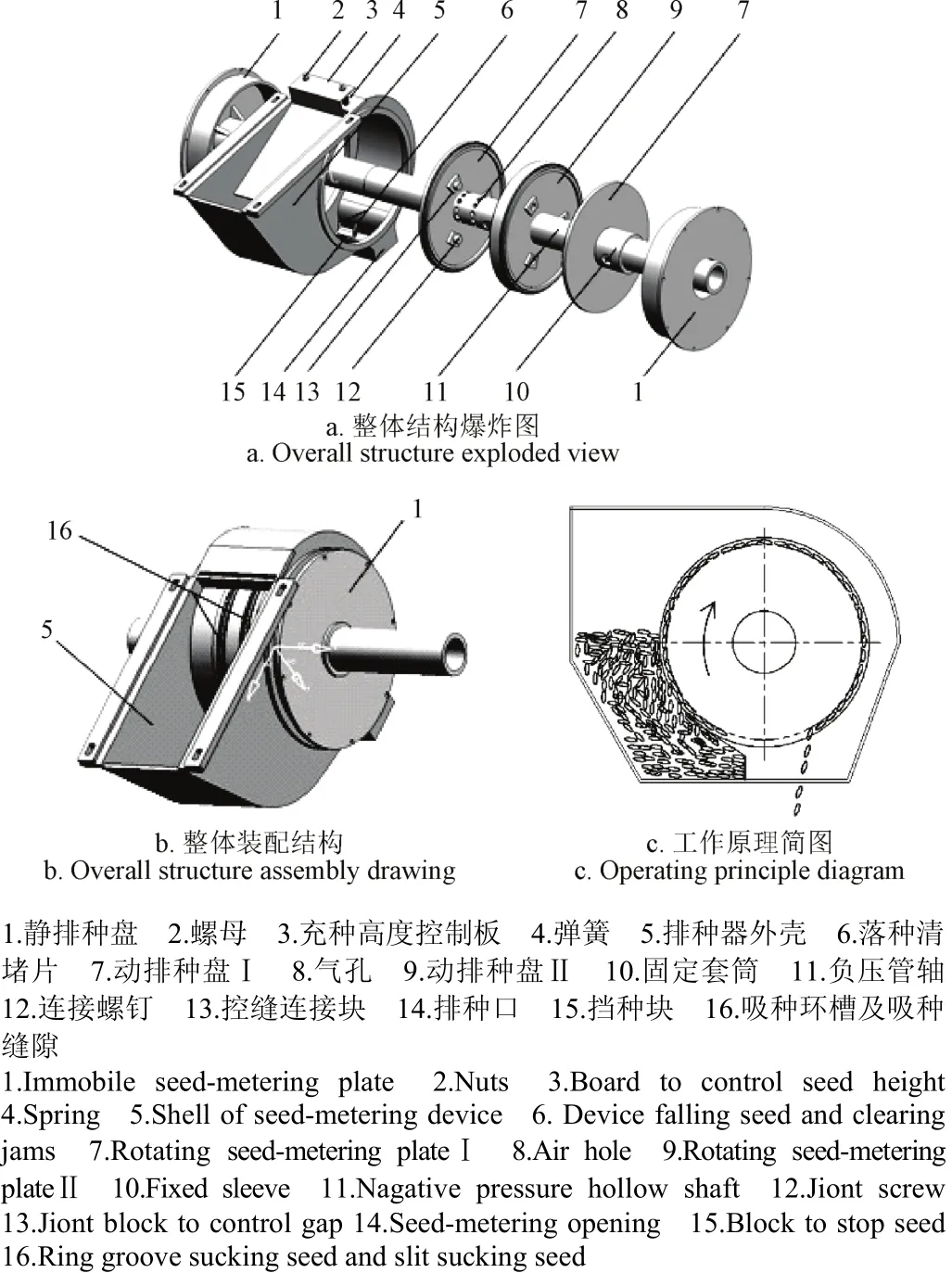
图1 排种器结构示意图Fig.1 Structure diagram of seed-metering device
1.2 排种器工作原理
如图1所示,通过旋转接头将风机连接软管与排种器负压管轴连接,负压管轴在相对的两个动排种盘形成的真空负压型腔位置处沿圆周方向等间距加工阵列圆孔,这样由排种盘外缘大气压到风机形成一个气流通路,气流由排种盘外缘向里流动,在排种盘转动的过程中,麦种沿外圆方向被吸附并形成环形种子带。在非稳定区通过负压吸力将种盒内的麦种吸附在排种盘外圆环形槽带中,旋转通过稳定区,到达落种区,在落种区由落种清堵片提前切断气路或者减小气流吸力,麦种在重力作用下自由落入导种管。落种清堵片动排种盘的吸种缝隙内,用于清落种子的同时,也清除了缝隙内的被吸近的麦种杂质,预防了长期工作后缝隙的堵塞。
此排种器将传统的拥挤在一定宽度上的密集条播麦种分散成一条线的播种带,在节种的同时,克服了小麦籽粒拥挤以及个体之间对肥水和营养的竞争问题,促进了个体健壮生长发育,根系发达,改善了小麦株间的通风透光条件。由于麦种在田间的分布更加合理,能最大限度地汲取肥水及养分,肥水利用率得到了提高,有效分蘖多,在保证小麦稳产情况下节水节肥。
2 排种器结构参数对流场的影响仿真
2.1 分析步骤及边界条件设置
运用SolidWork建立排种器三维立体模型,将排种器模型导入有限元分析软件Star-CCM+中,选择多面体网格类型。进行网格划分,物理模型参数设置为:三维稳态计算模型,分离求解器,流体域为气体,定常密度,标准K-ε湍流模型。边界条件为:设置定常压力进口的压力数值为标准大气压,压力出口的压力数值为−22 kPa(JPS-12排种器试验台提供最大负压值的80%,取整数)。建立旋转模型及参数(转速为80 r/min,排种器设计最大转速),并将其应用到整个流体域模型中,以模拟排种器实际工作旋转场景。
2.2 仿真结果及分析
2.2.1 不同形状吸种环槽横截面对气室流场影响的仿真分析
不同形状吸种环槽横截面对流场稳定性和麦种排列姿态有很大影响,本文对比分析圆弧型、V型、倒梯型,直槽型4种不同吸种环槽横截面(如图2a)对气流场压力分布情况的影响。排种器模型的吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,排种盘直径为170 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。图2b为对比流场压力云图,由图2b可知,吸种环槽横截面为圆弧型、V型、倒梯型的吸种缝隙压力云图较直槽稳定的多,圆弧型和V型相当,但是通过局部放大图可知,圆弧型环槽截面吸种缝隙入口处的压力梯度更加稳定。

图2 不同形状吸种环槽横截面的流场压力云图Fig.2 Cross section pressure nephogram under different shape cross-section of ring groove sucking seed
2.2.2 不同吸种缝隙宽度对气室流场的影响
吸种缝隙的大小对气室流场的真空度、流速稳定性以及风机功率消耗影响较大,通过理论计算及经验参考,初步确定缝隙宽度为0.45~0.54 mm。在计算流体力学仿真分析中适当增加取值范围,以便更加清楚分析影响规律,分别设定了0.3、0.5、0.8、1 mm 4种不同尺寸的缝隙宽度进行模型分析,吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,排种盘直径为170 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。图3a为仿真计算后的不同缝隙宽度排种器模型的流场压力云图,由图3a可知,0.3 mm的缝隙宽度的气室流场缝隙入口处(蓝色区域与红色区域的交界处)的压力非常不稳定,压力突变比较明显,缝隙内(蓝色细长区域)的压力变化也不成梯度渐变,稳定性比较差。同样对比分析图3b可知,随着缝隙宽度的增加,缝隙入口处的压力不稳定区域在增加,尤其是当缝隙宽度增加到1.0 mm时,在远离缝隙的吸种环槽带流场区域也出现了压力不稳定现象。从图3a中数值等值柱可知:缝隙为1.0、0.8、0.5、0.3 mm时最大负压值分别为:−34 310、−42 720、−63 855、−58 728 Pa,0.5 mm吸种缝隙的吸力最大。另外,0.5 mm缝隙内的压力场呈梯度连续平稳变化,较其他缝隙宽度的压力场稳定。

图3 不同吸种缝隙宽度气室压力云图和流速矢量图Fig.3 Cross section of pressure nephogram and velocity vectogram of air chamber with different width of slit sucking seed
图3 b显示了不同缝隙宽度流体域流速情况,缝隙为0.5 mm时流体域中最大流速为310.73 m/s(图3b中的数值等值柱),随着缝隙宽度加大流速在降低。同时,在0.8和1.0 mm的缝隙宽度的流体域中出现了回流现象(图3b中蓝色向上箭头),这将导致麦种的波动进而影响吸种稳定性。综合压力云图和流速矢量图:0.5 mm吸种缝隙宽度的压力场均匀稳定,流速图基本无回流现象,属于较优参数。
2.2.3 排种盘直径对气室流场影响的仿真分析
排种盘直径对排种器排种效率和风机功率消耗有比较大的影响。在保证降低风机功耗的前提下尽量增加排种盘直径,以提高排种作业效率。排种盘的设计直径一般在140~260 mm范围内[31]。本文选择了150、200、250 mm 共3种尺寸的排种盘模型进行流体仿真计算,以分析直径对气室流场真空度的影响趋势。排种器模型的吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。结果如图4所示。从图4a可以看出,随着排种盘直径的增加,吸种缝隙处最大负压值的绝对值(图4a中数值等值柱)呈减小趋势;流体域出口处(轴孔位置)附近区域颜色由黄逐渐变绿,即压力差的绝对值逐渐变大,需要的真空度在增加,也就是在吸种缝隙处要达到同等真空度的情况下风机功率消耗加大。由图4b可知,排种盘直径越大,吸种缝隙内压力差的绝对值越小(图4b中数值等值柱),即真空度越低;同时,250 mm 排种盘流体域中对应吸种环槽区域出现了压力波动现象(图4b中250 mm压力云图右下角与红色不一致区域)。综合考虑工作效率、功耗、加工所用材料的规格等因素,排种盘直径较优参数范围为150~200 mm之间。

图4 不同排种盘直径气室流场压力云图Fig.4 Pressure nephogram of air chamber with different diameters of seed-metering disc
2.2.4 排种盘气室轴向深度对气室流场影响的仿真分析
排种盘气室是衔接风机与吸种缝隙的一个过度腔体,在直径一定的情况下,
其轴向深度及形状直接影响排种器整体流场的压力和流速,进而决定了排种器的充种及排种性能。图5排种器模型的气室轴向深度分别为1.0、2.0、3.0 mm,吸种缝隙宽度为0.5mm,吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,排种盘直径为170 mm。由图5可知:气室轴向深度越大,流体域出口处(轴孔位置)附近区域颜色与气室流体域颜色逐渐趋于一致(由绿色渐变为黄色),说明气室轴向深度越大,压力差的绝对值越小,即气阻越小。同时,气室轴向深度越大,吸种缝隙真空度越大(图5c中数值等值柱最大值蓝色环带,−88 109 Pa)。由此可知,增加排种盘气室轴向深度对减少气阻、增大缝隙真空度是有利的,但是气室轴向深度增加过大时,会导致吸种缝隙宽度与气室横截面相差太大,气流通道由窄变宽剧烈,出现回流现象(图6中蓝色回流箭头),影响排种器的吸种稳定性。综合分析,2.0 mm的排种器气室轴向深度为较优参数值。

图5 不同排种盘气室轴向深度流场压力云图Fig.5 Pressure nephogram under different axial depths of air chamber in seed-metering disc

图6 排种盘气室轴向深度为3.0 mm时的流速矢量图截面图Fig.6 Cross section of velocity vectogram under 3.0 mm axial depth of air chamber in seed-metering disc
2.3 检查验证试验
为了验证流体仿真计算模型及结果的可信性,需要对排种器气室内的压力进行监测。试验验证了0.3、0.5、0.8和1.0 mm共4种不同吸种缝隙宽度的气室流场的稳定性,吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,排种盘直径为170 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。在排种盘吸种缝隙内间隔90°布置了4个测压点,测压探针用φ1.5 mm直径针头制成,测压仪器采用的是宏诚科技的HT-930,精度为±0.3%。对应于模拟数据的压力下,每个测点测取3次压力值,然后取平均值,测试结果见表1。

表1 排种器吸种缝隙测压点实测压力值Table 1 Testing pressure value in slit sucking seed of seed-metering device
由表1可知,0.5和0.8 mm缝隙的测压点压力值要稳定的多,数值模拟值和试验值吻合较好,从而验证了数值模拟方法的可行性。
3 排种器台架试验
3.1 试验材料及试验设备
试验所用小麦种粒材料为石新828:长度平均值6.26 mm、宽度平均值3.53 mm、厚度平均值3.12 mm、千粒质量40.90 g。用尼龙棒加工的不同结构参数的排种器。试验设备是JPS-12计算机视觉排种器试验台,如图7所示。

图7 JPS-12排种器试验台Fig.7 JPS-12 seed-metering device test bench
3.2 试验因素及评价指标
以吸种缝隙宽度、吸种环槽横截面形状、排种圆盘直径、排种盘气室轴向深度4个结构参数作为试验因素,分析各个参数对排种性能的影响,并用于验证计算机流体仿真分析结果。排种器排种性能采用排种均匀性作为评价指标,分析种子在行内纵向分布的均匀程度。JPS-12试验台可以测得符合GB/T6973-2005《单粒(精密)播种机试验方法》[32]中要求的试验数据,可获得排种试验中麦种在种床带上的实时图像(如图8a),也可人工分析小麦种子在种床带上的分布情况(如图8b)。
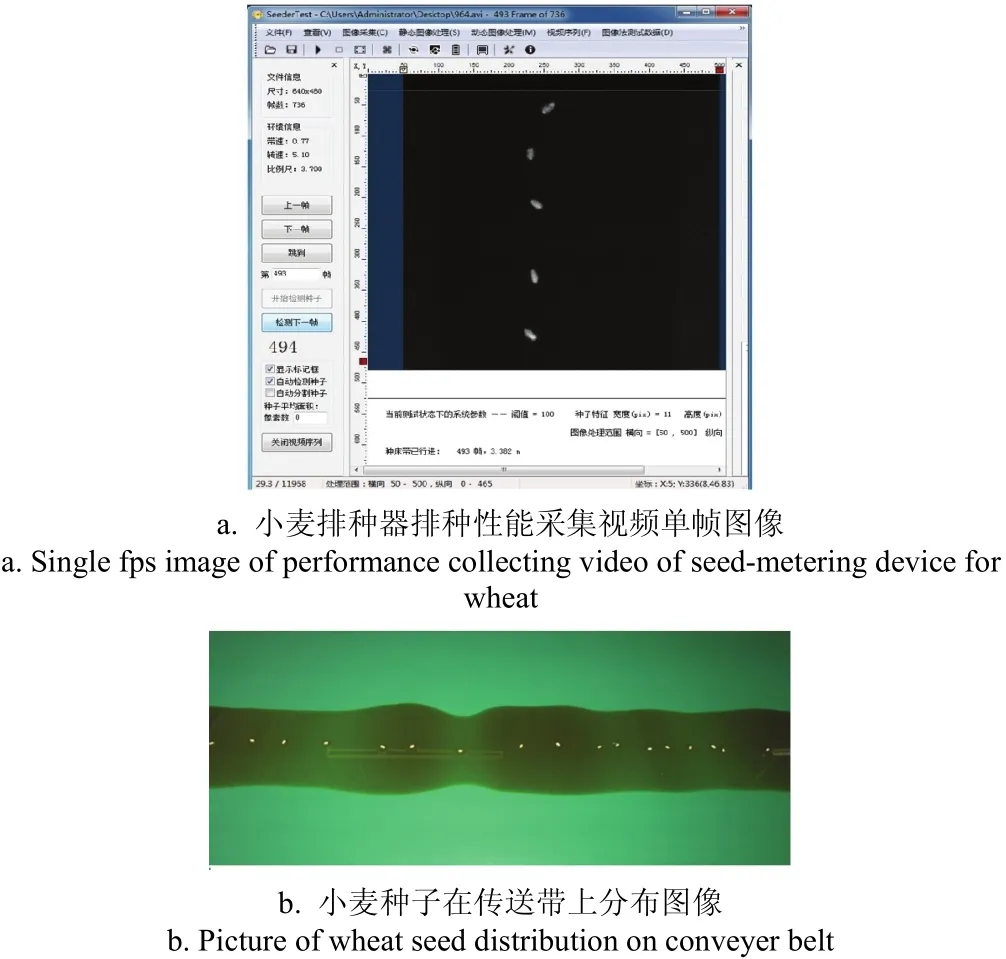
图8 麦种分布及视频采集图Fig.8 Wheat seed distribution and video capturing images
根据国标GB/T 6973-2005《单粒(精播)播种机试验方法》,排种性能指标确定为合格指数A、重播指数D和漏播指数M;排种精确性指标为种子粒距变异系数C。本试验测定区段为500个粒距。试验中,设定排种器转速为10.0 r/min,种床带速度为2.0 km/h,测试负压为−0.9 kPa。在JPS-12试验台上分别测取合格指数A、重播指数D、漏播指数M和合格粒距变异系数C,每组试验重复3次,结果取平均值。
3.3 试验结果及分析
3.3.1 吸种环槽横截面形状对排种均匀性的影响
吸种环槽横截面的形状决定了麦种在排种器上被吸附的排列姿态,也直接影响气室流场的压力场和流速场的稳定性,因此首先通过试验确定此参数,方便后续的进一步试验。在试验中,设计加工了直槽型、V型、倒梯型和圆弧型4种结构的排种器,吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,排种盘直径为170 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。试验结果见表2。对比分析,圆弧型的合格指数最高,其值为86.43%,漏播指数、重播指数和合格粒距变异系数均较低,分别为5.29%、8.29%、21.47%;直槽的合格指数最低,漏播指数最高,分别为69.23%、15.52%。试验结果分析,圆弧型吸种环槽横截面的排种器的吸排种均匀性最理想。试验过程中的排种器实时吸种效果(如图9所示)定性地支撑了此结论。
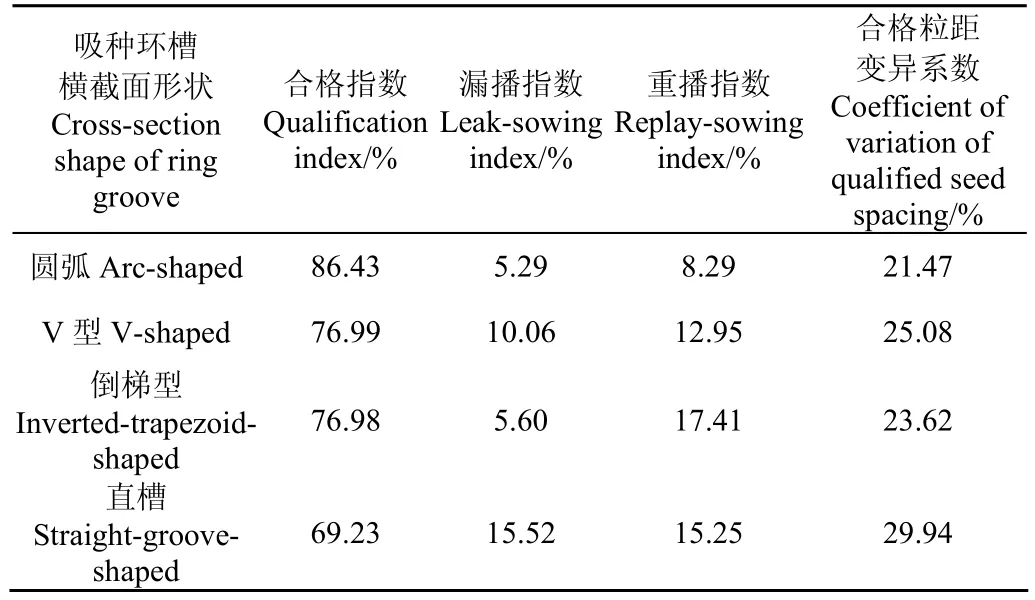
表2 不同吸种环槽横截面形状的排种器均匀性试验数据Table 2 Uniformity test data of seed-metering device with different shapes cross-section of ring groove sucking seed

图9 不同吸种环槽横截面形状的排种器吸种效果图Fig.9 Sucking seed status picture of seed-metering device with different shapes cross-section of ring groove sucking seed
吸种环槽横截面形状对排种均匀性的影响比较明显:圆弧型比V型、倒梯型、直槽结构的合格指数分别高9.44%、9.45%、17.20%,圆弧型吸种环槽与小麦种子外形比较贴合,气流平顺稳定,在排种盘旋转通过麦种群时,有利于充种,漏播指数低(5.29%),而且沿圆盘外缘周向环槽麦种以长径为线首尾顺序排列,重播指数也低(8.29%)。
3.3.2 吸种缝隙宽度对排种均匀性的影响
试验用排种器吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,排种盘直径为170 mm,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm,吸种缝隙宽度分别为0.3、0.5、0.8、1.0 mm。试验数据见表3。通过试验结果可以看出,吸种缝隙在0.5~0.8 mm范围内,吸种效果比较理想。
吸种缝隙对排种均匀性的影响很大,在真空度一定的条件下,吸种缝隙的减小(0.3 mm)会使吸附力不足而影响吸种效果,导致漏播明显增加(漏播指数为21.88%),合格指数也很低(69.79%),甚至麦种不能被稳定吸附而脱落在非稳定区。

表3 不同吸种缝隙宽度的排种器均匀性试验数据Table 3 Uniformity test data of seed-metering device with different widths of slit sucking seed
3.3.3 排种盘直径对排种均匀性的影响
根据前面的理论分析和计算流体仿真分析结果,在本试验中,设计了150、170、200、250 mm 4种不同尺寸排种盘直径的排种器,吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,排种盘气室轴向深度为2.0 mm。试验结果见表4。

表4 不同排种盘直径的排种器均匀性试验数据Table 4 Uniformity test data of seed-metering device with different diameters of seed-metering disc
合格指数呈减小趋势,漏播指数增加趋势明显,重播指数基本呈下降趋势,合格粒距变异系数呈下降趋势,但是250 mm时又明显增加。排种盘直径的改变对排种均匀性的影响是多方面的,随着排种盘直径的增大,吸种缝隙处的压差减小,边缘处的线速度增加,从试验数据可以看出,漏播明显加大。通过试验结果可以发现随着排种盘直径的增加合格指数在降低,漏播指数明显增加。但是实际播种作业时,排种盘直径减小会降低作业效率,在同样播种量、同样拖拉机前进速度的情况下,小直径排种盘的转速必然提高,进而影响充种性能。因此,综合考虑各因素,排种盘选择在170~200 mm较为合适。
排种盘直径在小于200 mm的试验中,对排种均匀性影响不大,满足精播要求,但是当增加到250 mm时,排种质量明显下降,尤其是漏播量明显增加(漏播指数20.94%),原因是排种盘直径增加,气室容积增大,缝隙处吸力减小,同时排种盘外缘的线速度增加,充种性能下降。
3.3.4 排种盘气室轴向深度对排种均匀性影响
计算流体仿真分析的结果显示,排种盘内气室深度在2.0 mm较为合适,因此在本试验中,单侧圆盘气室深度分别设计了1.0、2.0、3.0 mm 3种尺寸参数进行对比试验。吸种环槽横截面形状为圆弧型,吸种缝隙为0.5 mm,排种盘直径为170 mm。试验结果见表5。合格指数呈增加趋势,但是由2.0到3.0 mm增加不显著,漏播指数呈减小趋势,重播指数先明显下降,而后呈略上升趋势,综合分析,2.0~3.0 mm优于1.0 mm,合格粒距变异系数呈现下降趋势,从试验结果来看,排种盘气室轴向深度在2.0~3.0 mm较为合适。
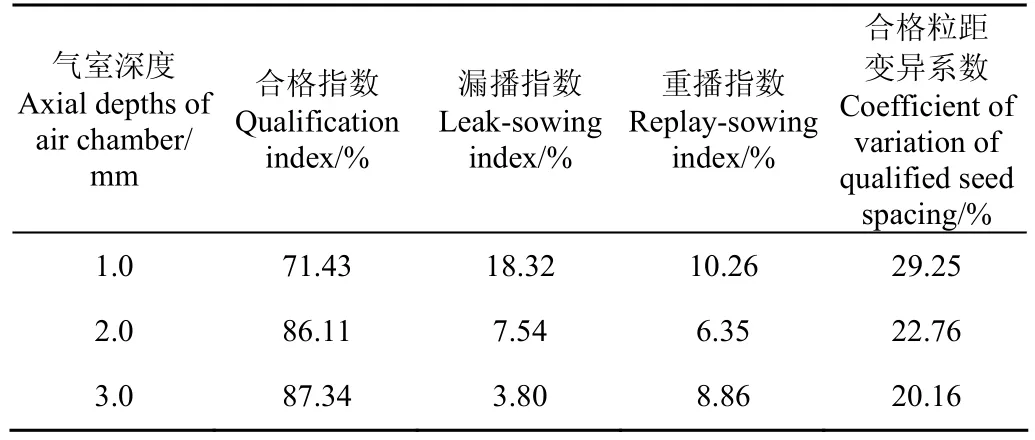
表5 不同气室轴向深度的排种器均匀性试验数据Table 5 Uniformity test data of seed-metering device with different axial depths of air chamber
气室轴向深度小于2.0 mm会由于真空度下降而导致排种器合格指数明显降低,超过2.0 mm后合格指数增加不明显,但是排种器轴向结构尺寸增大,会受到播种机整机结构的限制。
4 优化后排种器排种性能试验
综合仿真分析计算和台架试验结果可以确定排种器较为理想的结构参数范围为圆弧型吸种环槽横截面,0.5~0.8 mm的吸种缝隙,170~200 mm的排种盘直径,2.0~3.0 mm的排种盘内气室深度。在此基础上试制了排种器,结构参数如下:排种盘直径为180 mm,吸种缝隙为0.7 mm,圆弧型吸种环槽横截面,气室轴向深度为2.5 mm。并对该优化定型排种器进行了排种均匀性试验。试验重复进行3次,取平均值,最终试验结果见表6。试验结果满足JB/T 10293-2013《单粒(精密)播种机技术条件》[33]中对精播作业性能要求的指标参数。
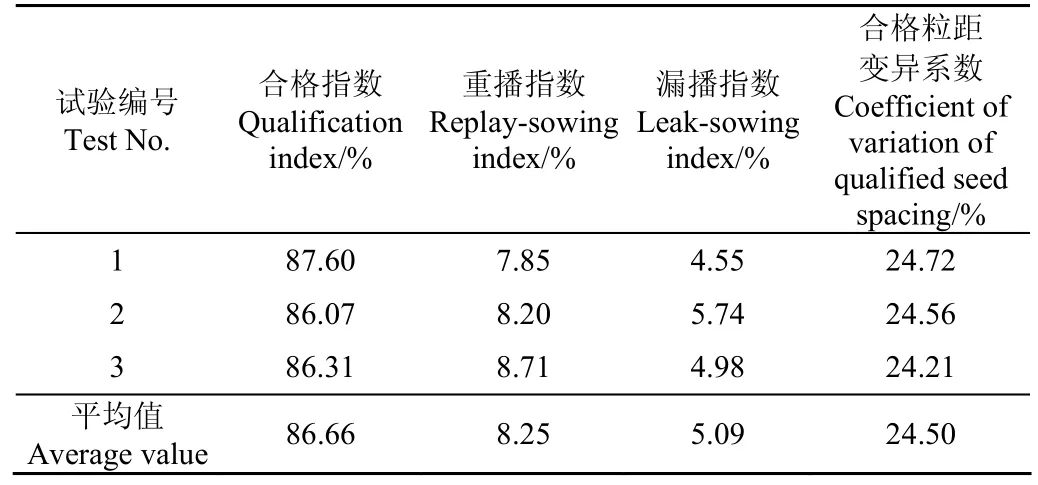
表6 优化后排种器试验性能指标参数Table 6 Test performance indicators of optimised seed-metering device
5 结 论
利用真空负压原理,本文设计了一种小麦精量排种器,可达到一器播种两行小麦的目的,并且改变了传统小麦条播方式:将传统拥挤在一定宽度上的密集条播麦种分散成一条线状播种带,实现小麦精播。
本文运用计算流体力学及排种器台架试验,优化得到了排种器结构参数:圆弧型吸种环槽横截面,0.5~0.8 mm的吸种缝隙,170~200 mm的排种盘直径,2.0~3.0 mm的排种盘气室轴向深度,运用试验台检查试验验证了计算机仿真分析的可行性。对参数优化后的排种器进行排种性能试验,满足JB/T 10293-2013《单粒(精密)播种机技术条件》中的参数指标,达到了小麦精播农艺要求。
[1] 世界小麦种植区域分布分析[EB/OL]. (2013-08-21) [2016-07-21]. http://www.docin.com/p-692152910.html.
[2] 何亮. 小麦精量播种高产栽培技术要点[J]. 北京农业,2015(12):56.
[3] 刘春科. 机械条播小麦不同密度对比试验报告[J]. 农业科技与信息,2010(3):19.
[4] 廖庆喜,杨波,李旭,等. 内充气吹式油菜精量排种器气室流场仿真与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(4):51-54. Liao Qingxi, Yang Bo, Li Xu, et al. Simulation and experiment of inside-filling air-blow precision metering device for rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(4): 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 杨善东,张东兴,刁培松,等. 侧正压玉米排种器的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(增刊1):8-13. Yang Shandong, Zhang Dongxing, Diao Peisong, et al. Design and experiment of side positive pressure seed metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(Supp.1): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 廖庆喜,张朋玲,廖宜涛. 基于EDEM的离心式排种器排种性能数值模拟[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(2):109-114. Liao Qingxi, Zhang Pengling, Liao Yitao, et al. Numerical simulation on seeding performance of centrifugal rape-seed metering device based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(2): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张国忠,罗锡文,臧英,等. 水稻气力式排种器群布吸孔吸种盘吸种精度试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(6):13-20. Zhang Guozhong, Luo Xiwen, Zang Ying, et al. Experiment of sucking precision of sucking plate with group holes on rice pneumatic metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(6): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 石林榕,吴建民,孙伟,等. 基于离散单元法的水平圆盘式精量排种器排种仿真试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(8):40-48. Shi Linrong, Wu Jianmin, Sun Wei, et al. Simulation test for metering process of horizontal disc precision metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 40-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 祁兵,张东兴,崔涛. 中央集排气送式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(18):8-15. Qi Bing, Zhang Dongxing, Cui Tao. Design and experiment of centralized pneumatic seed metering device for maize[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(18): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 丛锦玲,廖庆喜,曹秀英,等. 油菜小麦兼用排种盘的排种器充种性能[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(8):30-39. Cong Jinling, Liao Qingxi, Cao Xiuying, et al. Seed filling performance of dual-purpose seed plate in metering device for both rapeseed & wheat seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 30-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] Arzu Y, Adnan D. Measurement of seed spacing uniformity performance of a precision metering unit as function of the number of holes on vacuum plate[J]. Measurement, 2014(56): 128-135.
[12] Sapkota T B, Majumdar K, Jat M L, et al. Precision nutrient management in conservation agriculture based wheat production of Northwest India: Profitability, nutrient useefficiency and environmental footprint[J]. Field Crops Research, 2014, 155: 233-244.
[13] 田波平,廖庆喜,黄海东,等. 2BFQ-6型油菜精量联合直播机的设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,39(10):211-213. Tian Boping, Liao Qingxi, Huang Haidong, et al. Design of 2BFQ-6 precision jiont direct seeder for rapeseed[J]. Transactions of the CSAM, 2008, 39(10): 211-213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 刘文忠,赵满全,王文明. 气吸式排种装置排种性能分析[J].农机化研究,2008,30(5):45-47. Liu Wenzhong, Zhao Manquan, Wang Wenming. Analysis on the sowing performance of air-suction seed-metering device[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008, 30(5): 45-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 赵湛,李耀明,陈进,等. 气吸滚筒式排种器吸种过程的动力学分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(7):112-116. Zhao Zhan, Li Yaoming, Chen Jin, et al. Dynamic analysis of seeds pick-up process for vacuum-cylinder seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(7): 112-116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 何东健,李增武. 组合吸孔气吸式排种器研究[J]. 农业工程学报,1995,11(4):57-61. He Dongjian, Li Zengwu. A study on planter’s suction seed feed mechanism with combined inhaler[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1995, 11(4): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 封俊,梁素钰,曾爱军,等. 新型组合吸孔式小麦精密排种器运动学与动力学特性的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2000,16(1):63-66. Feng Jun, Liang Suyu, Zeng Aijun, et al. Kinematics and dynamics of a wheat seed in the seed-meter device with combined sucker[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2000, 16(1): 63-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 佟超. ZXJB-4型小区精密播种机的设计[J]. 粮油加工与食品机械,1995(5):3-5.
[19] 梁素钰,封俊,曾爱军,等. 新型组合吸孔式小麦精密排种器性能的试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2001,17(2):84-87. Liang Suyu, Feng Jun, Zeng Aijun, et al. Performance experiments of the seed-meter device with combined sucker[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2001, 17(2): 84-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王瑞雪,仪垂杰,林海波,等. 基于均匀设计的小麦气吸式精密排种器的试验研究[J]. 农机化研究,2009,31(2):141-143. Wang Ruixue, Yi Chuijie, Lin Haibo, et at. Experimental and study of air-suction wheat precision seed metering device based on uniform design[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2009, 31(2): 141-143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 杜辉,王忠举,李汝莘. 气吸式小麦精量播种机的改进研究[J]. 山东农机,2002(6):8-9.
[22] 杜辉. 气吸式小麦精量播种机的改进研究[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学,2003. Du Hui. Study on Improvement of Wheat Pneumatic Precise Seeder[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 马立,张晋国. 圆管孔眼式小麦气吸排种器的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(6):97-100. Ma Li, Zhang Jinguo. The design of the hole-tube air suction wheat seeder[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(6): 97-100. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 马立. 新型缝隙式小麦气吸播种机的研究[D]. 保定:河北农业大学,2010. Ma Li. Study on the New Kind Tube-slit Air-suction Wheat Seeding Machine[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张晋国,马立,史智兴,等. 新型缝隙式小麦气吸排种器的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(4):69-71. Zhang Jinguo, Ma Li, Shi Zhixing, et al. The design of the new slit-style air suction seed-metering device for wheat[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(4): 69-71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 赵晓顺,张晋国,马立. 圆管直缝式小麦气吸排种器性能的试验研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报,2013,36(1):105-108. Zhao Xiaoshun, Zhang Jinguo, Ma Li. Experimentation research of performance of circular tube slit pneumaticprecise wheat seed-metering device[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2013, 36(1): 105-108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 陈凤艳,张晋国,陈凤娟. 槽缝式小麦气吸精密播种机的设计与研究[J]. 农机化研究,2011,33(8):81-84. Chen Fengyan, Zhang Jinguo, Chen Fengjuan. Design and research on suction slot-type precision wheat seeder[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2011, 33(8): 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 陈凤艳. 气吸式小麦精密播种机缝隙式排种器的设计与研究[D]. 保定:河北农业大学,2011. Chen Fengyan. Design and Study on a Slot-type Pneumatic Precision Wheat Feeding Device[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 河北农业大学. 一种负压式精量排种器:2014105515269[P]. 2016-02-03.
[30] 河北农业大学. 一种圆盘气吸式排种装置:2012105070711[P]. 2016-03-16.
[31] 中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册[M]. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2007:355-363.
[32] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T6973-2005,单粒(精密)播种机试验方法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2005.
[33] 全国农业机械标准化技术委员会. JB/T10293-2001,单粒(精密)播种机技术条件[S]. 北京:机械科学研究院,2001.
Parameter optimization and experiment of negative pressure precision seed-metering device for wheat
Zhao Xiaoshun, Yu Huali, Ma Yuejin, Zhang Jinguo, Sang Yongying, Huo Xiaojing
(College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071001, China)
Different from traditional cultivation techniques of sowing in lines for wheat, precision seeding technology ensures the most reasonable distribution of wheat seeds in the field through precisely controlling seeding quantity and uniformity. It makes each grain of wheat seed get enough nutrition area and space, absorb water at the most and possess effective tillering. So it ensures stable and high yield in seed-saving, fertilizer-saving and water-saving conditions. In order to meet the agronomic requirements of precision seeding technology, a negative pressure precision seed-metering device for wheat was designed. The seed-metering device was not a traditional single structure, but multiple seed-metering devices shared a hollow shaft. By the CFD (computational fluid dynamics) software STAR-CCM+, the influences of structural parameters of the seed-metering device on vacuum chamber fluid field were simulated and analyzed. The structural parameters included the diameter of seed-metering disc, the width of suction slit, the cross-section shape of ring groove, and the axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc. The analysis of pressure nephogram, velocity vectogram and streamline graph showed that more ideal structural parameters of seed-metering device are 0.5 mm width of suction slit, 150-200 mm diameter of seed-metering disc, 2.0 mm axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc, and arc-shaped cross-section of ring groove. Seeding uniformity test of the seed-metering device was done on the JPS-12 test-bed. It tested and analyzed the influence of cross-section shape of ring groove, width of suction slit, diameter of seed-metering disc and axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc on the qualified index, multiple index, missing index and coefficient of variation of qualified seed spacing. The qualified index of the seed-metering device with arc-shaped cross-section of ring groove is about 10% higher than the v-shaped and inverted-trapezoid-shaped structure, and about 17% higher than the straight-groove-shaped structure. Meanwhile, its multiple index (8.29%) and missing index (5.29%) are the minimum. The influence of the suction slit width on the seeding uniformity is very visible. In certain vacuum conditions, the decrease of suction slit width causes insufficient suction, which affects the uniformity of suction seed. For example, the missing index and the qualified index of seed-metering device with 0.3 mm suction slit respectively are 21.88% and 69.79%. The seeding uniformity of the seed-metering device with less than 200 mm disc diameter meets precision seeding technology agronomic requirements. The influence of seed-metering disc diameter on the seeding uniformity is very little. But when the disc diameter is larger than 250 mm, the missing index (20.94%) clearly increases. The main reason is that the outer edge of the seed-metering disc with large disc diameter has higher linear speed, which causes the filling seed performance of seed-metering device to reduce. The axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc is not less than 2.0 mm, or its missing index (18.32%) and multiple index (10.26%) significantly increase and its qualified index (71.43%) decreases. The better structural parameters of the seed-metering device were determined as arc-shaped cross-section of ring groove, 0.5-0.8 mm width of suction slit, 170-200 mm diameter of seed-metering disc and 2.0 mm axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc. Based on these, structural parameters of the seed-metering device were optimized: The diameter of seed-metering disc is 180 mm, the width of suction slit is 0.7 mm, the axial depth of gas chamber in the seed-metering disc is 2.5 mm, and the cross-section shape of ring groove is arc-shaped. The optimization seed-metering device was tested on the JPS-12 test-bed. The qualified index is 86.66%, the missing index is 5.09%, the multiple index is 8.25%, and the coefficient of variation of qualified seed spacing is 24.50%. These testing results fully coincide with the standard JB/T 10293-2013 Specifications of single seed drill (precision drill). The seed-metering device meets fully the requirements of wheat precision drilling.
mechanization; optimization; computer simulation; wheat; seed-metering device
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.002
S223.2+2
A
1002-6819(2017)-11-0011-08
赵晓顺,于华丽,马跃进,张晋国,桑永英,霍晓静. 负压式小麦精量排种器参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(11):11-18.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhao Xiaoshun, Yu Huali, Ma Yuejin, Zhang Jinguo, Sang Yongying, Huo Xiaojing. Parameter optimization and experiment of negative pressure precision seed-metering device for wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(11): 11-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.002 http://www.tcsae.org
2016-10-09
2017-04-01
“十二五”国家科技支撑计划:粮食丰产科技工程三期(2013BAD07B05);“十三五”国家科技支撑计划:粮食丰产科技工程(SQ2017YFNC050007)
赵晓顺,男,河北康保人,副教授,博士,研究方向为农业机械与自动化。保定 河北农业大学机电工程学院,071001。
Email:zhao_xsh@126.com

