高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的压力和温度场数值模拟与试验
邵运果,苏工兵,邹舒畅,孟秀萍
(武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院,武汉 430073)
高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的压力和温度场数值模拟与试验
邵运果,苏工兵※,邹舒畅,孟秀萍
(武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院,武汉 430073)
为了研究苎麻纤维残留胶质的射流冲击分纤脱胶机理,设计试制了高温射流冲洗试验装置,开展了单喷嘴和双喷嘴开纤脱胶试验,数值模拟了单喷嘴和双喷嘴射流冲击壁面的表面温度场、压力场分布及有效的作用区域。结果表明,当喷嘴直径为2.0 mm,进口温度为373 K时,单喷嘴射流冲击试验的较佳组合参数喷距为30 mm,进口压强为1.2 MPa,时间为16 min,测得残胶率为3.1%;以单喷嘴相同设定参数模拟了双喷嘴较佳喷嘴间距为30 mm,冲击压力范围为0.2~0.3 MPa,温度范围为320~334 K,该试验测试的喷嘴间距与数值模拟相符合,测试残胶率为3.1%,单纤维断裂强力为51.71 cN。该技术为开发新型苎麻纤维分纤洗脱设备提供技术参数。
纤维;温度;压力;射流冲击;苎麻;数值模拟;开纤;脱胶
邵运果,苏工兵,邹舒畅,孟秀萍. 高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的压力和温度场数值模拟与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(10):302-309. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.040 http://www.tcsae.org
Shao Yunguo, Su Gongbing, Zou Shuchang, Meng Xiuping. Numerical simulation and experiment of pressure and temperature field for jet impinging ramie fiber separation and degumming[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(10): 302-309. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.040 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
近年来,国内外在麻类纤维制备方面的技术研究主要侧重于以生物脱胶或其他脱胶工艺取代或部分取代传统化学脱胶的煮练工序,并已取得重大成就[1-5]。但对煮练后开纤脱胶的整理技术仍沿用传统的圆盘式敲麻机机械式分纤、漂洗等分段工序,许多研究者开展了相关的新技术和设备的研究。张勇[6]等介绍了一种基于物理机械力的苎麻脱胶新技术,该技术是对经低浴比浸渍预处理的苎麻软湿麻施以物理方法为主的机械力开纤脱胶和整理;陈朝武[7]等介绍了旋锤式苎麻水麻开纤机技术,该技术是通过利用旋锤的连续锤打,在旋锤和辊轮的拉力和牵伸力共同作用下,对苎麻进行开纤和去除胶质杂物。机械式分纤存在纤维噪声大、麻束凌乱、均匀性差、麻纤维表面损伤等[8-11]问题。周万阳[12]等介绍了高压水射流清洗地铁隧道壁面的CFD数值模拟方法,分析了壁面打击力和径向动压分布;叶建友[13]等介绍了基于 FLUENT的清洗用扇形喷嘴清洗参数研究,分析了不同出口直径扇形喷嘴在不同压力下的打击力和动压分布。通过以上研究分析,提出了高温(373 K)射流水冲击脱胶后苎麻纤维开纤脱胶的研究,该技术通过射流水对苎麻纤维的冲击和清洗作用实现纤维开纤和将残留胶质洗脱,一次性完成传统机械敲击开纤、漂洗等分段工序的功能。
为了研究苎麻纤维残留胶质的射流冲击开纤脱胶机理和效果,设计试制了高温(373K)射流水冲洗苎麻纤维试验装置,并进行了高温射流苎麻分纤脱胶试验和数值模拟。此技术工艺不仅能将现有分纤洗脱工艺中开纤、漂洗等工序相结合,也为研制开发苎麻分纤洗脱设备提供了新的技术参数。
1 高温(373 K)射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶试验
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 取样
苎麻原麻采用华苎 4号,试验时采用整根原麻,原麻的残胶率按照国标GB/T5889-1986测定为28%。
1.1.2 样本制备
通过采用NaOH浓度为6 g/L,浴比为1:10的碱溶液对原麻常压(101.325 kPa)碱煮4 h,按照GB/T5889-1986测定了碱煮后的残胶率平均值为10.8 %。将煮好的整根原麻从端到尾各截取20 cm,质量20 g为样本试样。
1.2 试验方法
工艺流程:苎麻原麻—常压碱煮—高温压力水冲洗—烘干—精干麻—测试。首先,在该冲洗装置上以喷距、进口压强和时间为因素,洗脱后残胶率为评价指标,开展了单喷嘴射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶三因素三水平试验,分析影响射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的主要因素;其次,以单喷嘴射流冲击试验参数为基础,运用FLUENT软件模拟单喷嘴不同喷距射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面温度场、压力场分布以及有效的作用区域,获取较佳喷距并与单喷嘴正交试验进行了比较分析;同时以单喷嘴较佳喷距为基础,模拟双喷嘴不同喷嘴间距射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面温度场、压力场分布以及有效的作用区域,获取了双喷嘴间的较佳间距;最后,以残胶率和纤维断裂强力为苎麻纤维洗脱后的品质评判主要技术指标,确定双喷嘴间的最佳间距。结合单喷嘴试验和数值分析的结果,在冲洗装置开展双喷嘴较佳间距不同喷距试验。从而获取了双喷嘴射流水冲击苎麻纤维的进口压强,喷嘴直径,进口温度,喷距和喷嘴间距等较佳参数组合。
1.3 试验装置的设计
为了研究射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶作用的影响因素,以进口压强,喷嘴直径,进口温度,喷距和喷嘴间距等参数为可控变量,设计试制了高温(373 K)射流单喷嘴冲击冲洗装置。根据理论计算和经验选用喷嘴出口直径D=2 mm。同时由于高温条件下有利于苎麻纤维中半纤维素和木质素的化学键水解[14],选取喷嘴进口温度373 K,以进口压强,喷距,作用时间为调节变量开展了单喷嘴下纤维分纤洗脱正交试验。试验装置中选取了型号为20NPD22Z的涡流泵(最大压力为1.6 MPa),电机功率为2.2 kW,装置管道直径为25 mm和调压阀。喷嘴的进口压强通过装置的调压阀进行调节,装置的原理图如图1所示。

图1 冲洗装置原理图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of flushing device
1.4 单喷嘴下纤维开纤脱胶试验
为了分析喷距、进口压强和时间三因素共同作用的最佳组合方案以及主要的影响因素,选择水温度为373 K条件下,不考虑因素间的交互作用,设计了三因素三水平表如表 1所示;冲洗后的试验样本残胶率按照国标GB/T5889-1986测定,试验结果与分析结果见表2。
由表2可知,各因素间的最佳组合为A2B3C3,即喷距为30 mm,进口压强为1.2 MPa,时间为16 min,该条件下进行了冲洗试验,测得残胶率为3.1 %。
通过极差R值可以看出,本试验因素主次关系为A>B>C,即影响射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的最主要因素为喷距,其次是进口压强、时间。
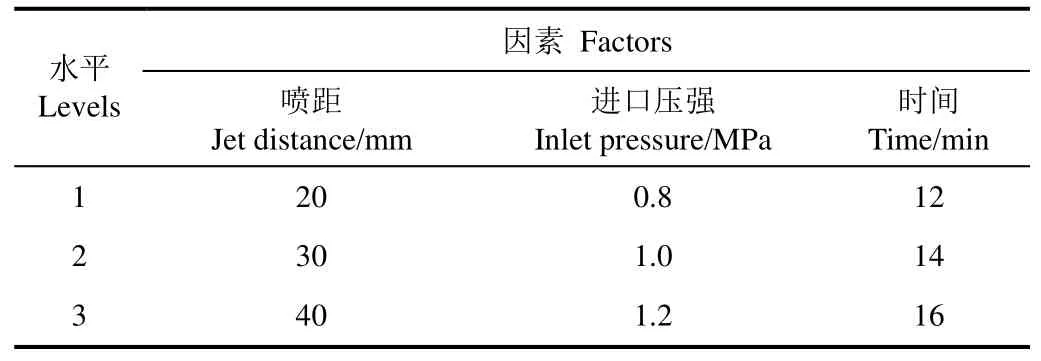
表1 正交试验因素水平表Table 1 Table of factors and levels of orthogonal experiment
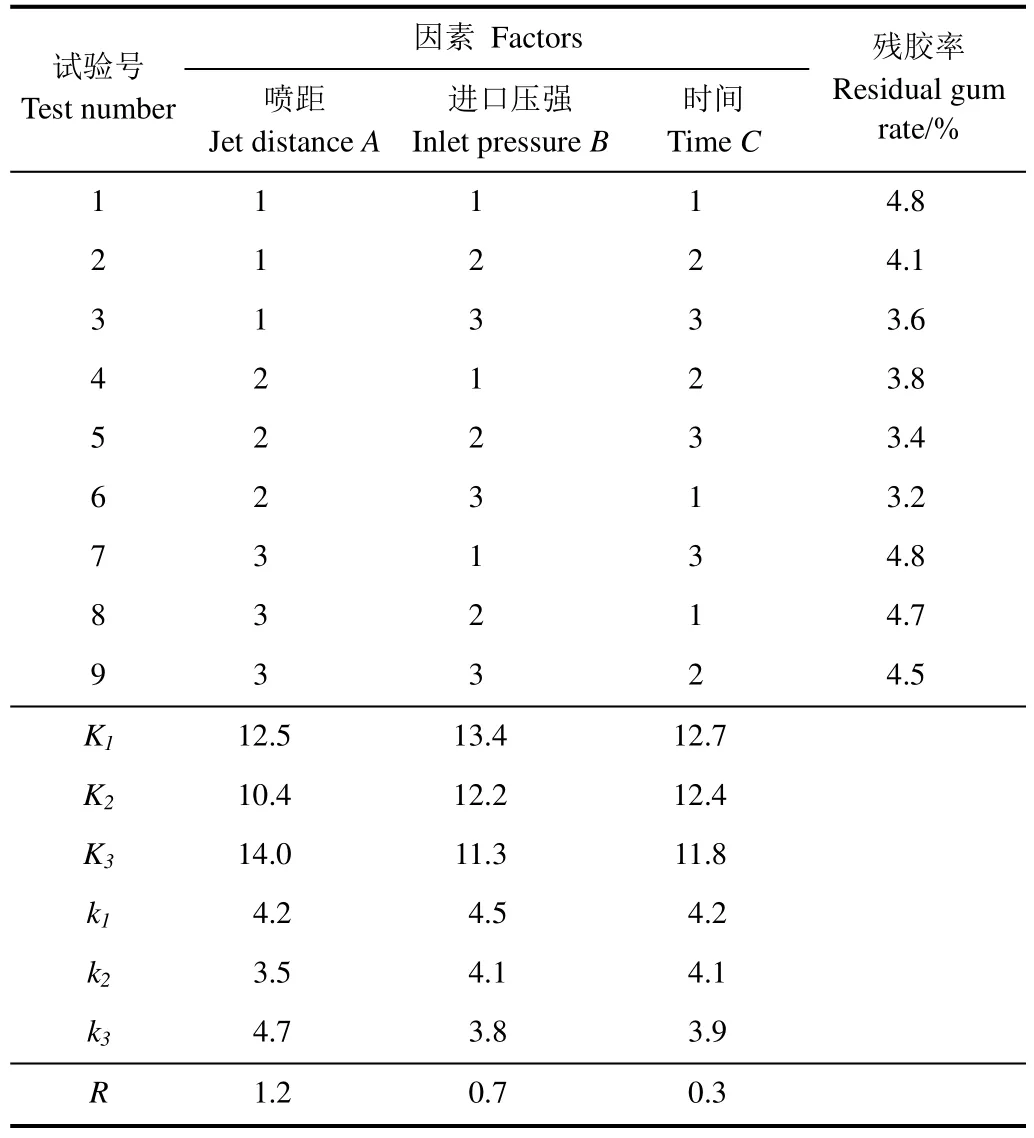
表2 正交表与试验结果Table 2 Orthogonal table and test results
通过正交试验分析可知,喷距是射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的主要影响因素,同时喷距的改变影响着压强和温度在苎麻纤维表面的分布。为了揭示不同喷距下高温射流冲击对纤维开纤和脱胶的作用机理,进行了单喷嘴不同喷距和双喷嘴不同喷嘴间距下高温射流冲击苎麻纤维开纤脱胶数值模拟,模拟了单喷嘴在不同喷距射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面温度场、压力场分布以及有效的作用区域。
2 高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶数值模拟
根据高温单喷嘴射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶试验,以最佳进口压强为1.2 MPa、喷嘴出口直径D=2 mm、喷嘴进口温度为373 K为不变量,采用欧拉多相流模型中的VOF模型、传热模型以及RNGk- 模型,运用FLUENT软件建立了单喷嘴和双喷嘴与冲击壁面的有限元模型,数值模拟了单喷嘴不同喷距和双喷嘴不同喷嘴间距射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面温度场和压力场分布以及有效的作用区域。
2.1 单喷嘴下高温射流冲击有限元模型建立
通过FLUENT软件内置前处理DM模块建立单喷嘴与射流垂直冲击壁面的内外部流场的3D模型,包括喷嘴内部流体区域、V型切槽及外部流场区域;根据需要设定喷嘴出口到壁面的区域高度(喷距),其中冲击壁面长为100 mm,宽为50 mm;网格划分采用六面体网格与四面体网格相结合的方式,喷嘴和V型切槽部位采用四面体网格并进行加密处理,外部流场区域采用六面体网格[15-16],如图2所示。

图2 单喷嘴网格模型Fig.2 Mesh model of single nozzle
2.2 求解设置
该数值模拟主要针对非淹没射流下喷嘴的流动状态,喷嘴内外部流场涉及到气液二相流[17-19]和传热。
1)在FLUENT软件计算模型中选择欧拉多相流模型中的VOF模型、传热模型以及RNGk- 模型。
2)将液相(水)设置为主相,气相设置为次相;入口边界条件为压力入口为1.2 MPa,在保证出口液体不汽化的条件下,入口温度选用373 K,以Y轴负方向为流体射入方向;出口边界条件设置为压力出口为0;湍流参数选择为湍流强度,其值为按默认值设置和水力直径,其值为0.002 m。
3)壁面设置为无滑移标准壁面,将外流场尽头设置为冲击壁面,使流体冲击该壁面。
4)采用隐式方案求解,并采用求解计算方式—SIMPLE算法。
2.3 结果与分析
2.3.1 喷距H的影响
进口压强为1.2 MPa、时间为16 min、喷嘴出口直径D=2 mm和喷嘴进口温度为373 K为不变量,分别选取喷距H=20、30、40和50 mm数值模拟了射流垂直方向和冲击壁面上的温度场和压力场的分布。
1)不同喷距下垂直方向的温度场和压力场分布
从数值模拟的结果中提取了温度场和压力场沿垂直方向的分布云图,如图3所示。
由图3a~d可知,当喷嘴出口的温度均为373 K时,随着喷距的增加,温度沿垂直方向逐渐降低,喷嘴出口到冲击壁面中心位置处的温差逐渐增大。其中喷距为20 mm和30 mm温差比喷距为40 mm和50 mm变化较小。随着喷距增加,在射流运动过程中发生扇面混掺扩散现象较严重,与空气热对流交换增大,导致温度降低。
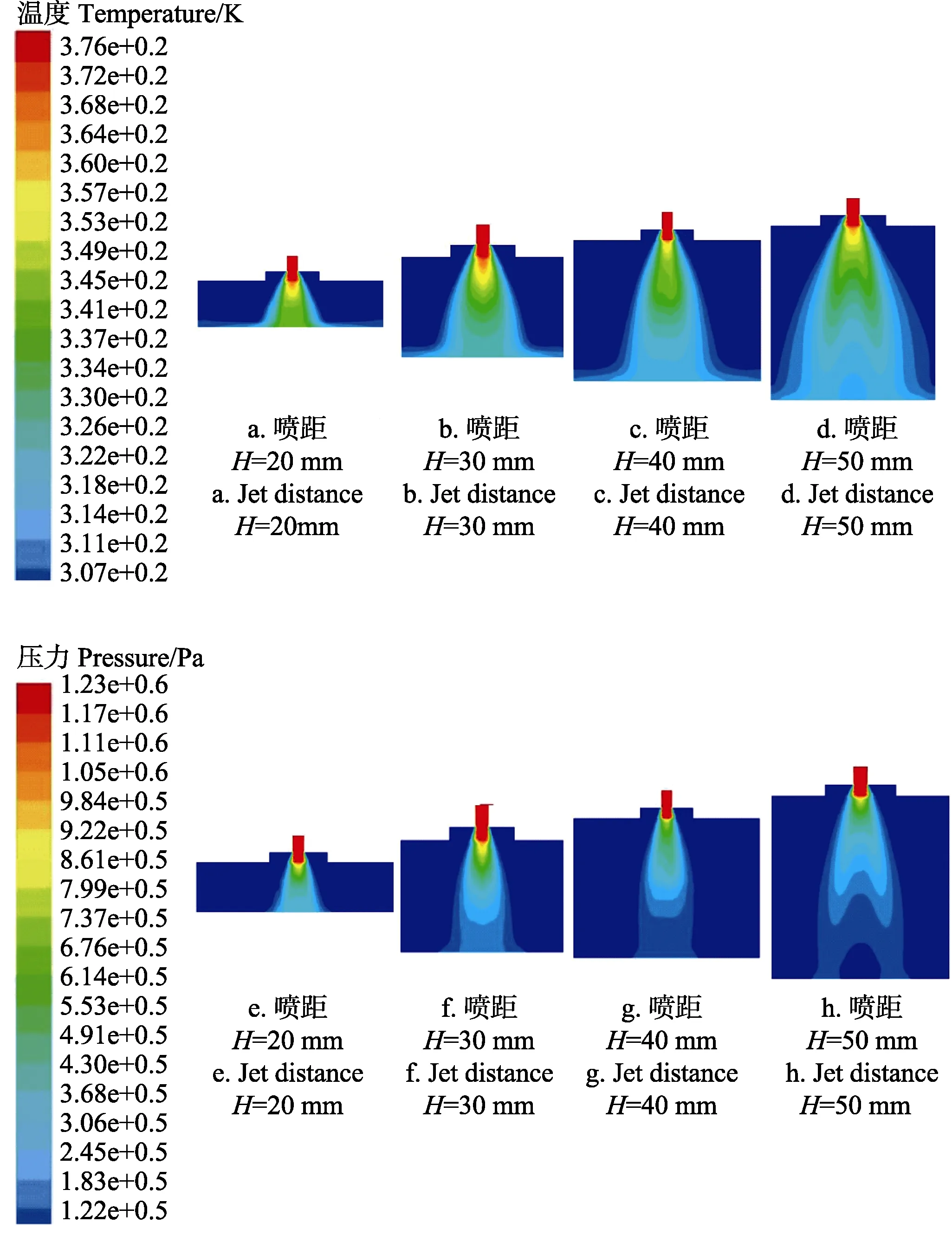
图3 冲击流沿垂直方向的温度场和压力场分布云图Fig.3 Cloud charts of temperature and pressure distribution along vertical direction of impact flow
由图3e~h可知,随着喷距的增加,压力沿垂直方向逐渐降低。喷距为20和30 mm时,到达冲击壁面的中心位置处压力较高,而喷距为40和50 mm时,冲击壁面的中心位置处压力较小。在射流运动过程中,喷距的增大,发生能量传递、动量输送和混掺扩散等现象,动能逐渐降低,速度逐渐减小,射流在壁面的扩散程度增大,冲击力损失变大[20],压力变小。
2)不同喷距下温度和压力在冲击壁面上区域分布
从数值模拟的结果提取了温度和压力在冲击壁面上的区域分布云图,如图4所示。
由图4a~d可知,在不同喷距下冲击壁面温度场均从最高温度中心位置向区域四周扩散,温度逐渐降低。随着喷距的增加,中心位置温度降低,冲击壁面区域变大。喷距为20和30 mm时,温度分布在冲击壁面区域比喷距为40和50 mm要小,但中心位置向冲击壁面区域边界的温度变化范围较小。主要由于液体沿V型槽开口方呈现为一个扇形,当扇形液面到达壁面时,液面发生卷吸,能量消耗,温度场沿冲击壁面区域方向的铺展时,温度逐渐降低。
由图4e~h可知,在不同喷距下冲击壁面压力场均从最高压力中心位置向区域四周扩散,压力逐渐降低。喷距较小时覆盖区域较大,区域内压力变化较明显;喷距较大时,压力在冲击壁面上覆盖范围较小。其中喷距为20 mm和30 mm时,覆盖区域内压力变化梯度比喷距为40 mm和50 mm时要大。扇形液面到达壁面时,压力会沿扇形液面的垂直方向出现壁面切应力,向两边扩散,同时由于液面会发生水楔的冲蚀卷吸[21-22]等现象,导致压力降低。
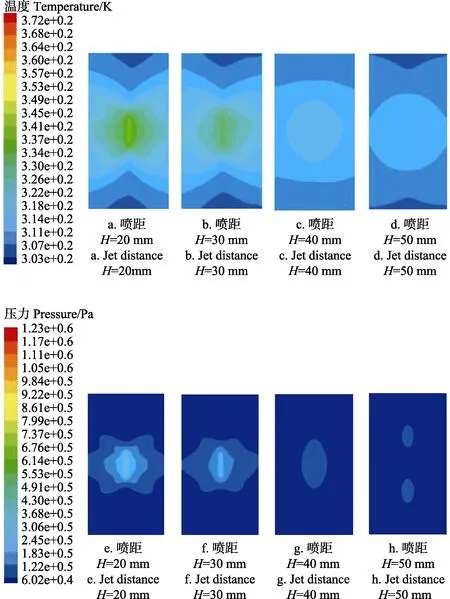
图4 冲击壁面的温度场和压力场分布云图Fig. 4 Cloud charts of temperature and pressure distribution of impact wall
从上述数值模拟结果分析可知,随着喷距增大,温度和压力在垂直方向上逐渐降低。在冲击壁面喷距较小时,温度分布区域比喷距较大要小,但中心位置向冲击壁面区域边界的温度梯度要高。冲击壁面区域喷距小的压力梯度大于喷距大的。随着喷距继续增大,射流未达到壁面区域,压力变为 0但有温度分布。这是由于热量在射流冲击速度作用下被传递到冲击壁面区域。为了避免壁面射流区[23]由于过大的冲击流在壁面产生切速度使苎麻纤维向四周扩散,导致苎麻纤维压力分布不均匀以及水楔的冲蚀卷吸作用不能更好地利用。根据单喷嘴正交试验以及数值模拟结果可得,当进口压强为1.2 MPa、喷嘴出口直径D=2 mm、喷嘴进口温度为373 K,喷距为30 mm时,数值模拟作用于苎麻纤维表面的冲击压力范围为0.16~0.3 MPa,此为高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的较佳有效喷距。
2.4 双喷嘴下高温射流冲击开纤脱胶数值模拟
为了研究多喷嘴下高温射流冲击开纤脱胶的机理,以单喷嘴下高温射流冲击试验和数值模拟的参数为依据,选择双喷嘴数值模拟了不同喷嘴间距下的冲击壁面上的温度场和压力场的分布和有效作用区域,以期获得最佳喷嘴间距。
当喷嘴直径和额定流量不变时,增加喷嘴数目,喷嘴的出口压强变化不大,因此以喷嘴进口压强1.2 MPa,喷嘴出口直径D=2.0 mm,进口温度为373 K和喷距H=30 mm(喷嘴出口到壁面的区域高度)等参数为不变量,分别选取两喷嘴间距为S=20 mm、30 mm和40 mm,其中冲击壁面宽为50 mm,长为120 mm,利用FLUENT软件内置前处理 DM模块建立双喷嘴和射流垂直冲击壁面的内外部流场的3D模型。网格划分方式同单喷嘴数值模拟相似,求解设置同单喷嘴数值模拟相似,如图 5所示,模拟结果分别如图6所示。
图5 双喷嘴网格模型Fig.5 Grid model of double nozzles
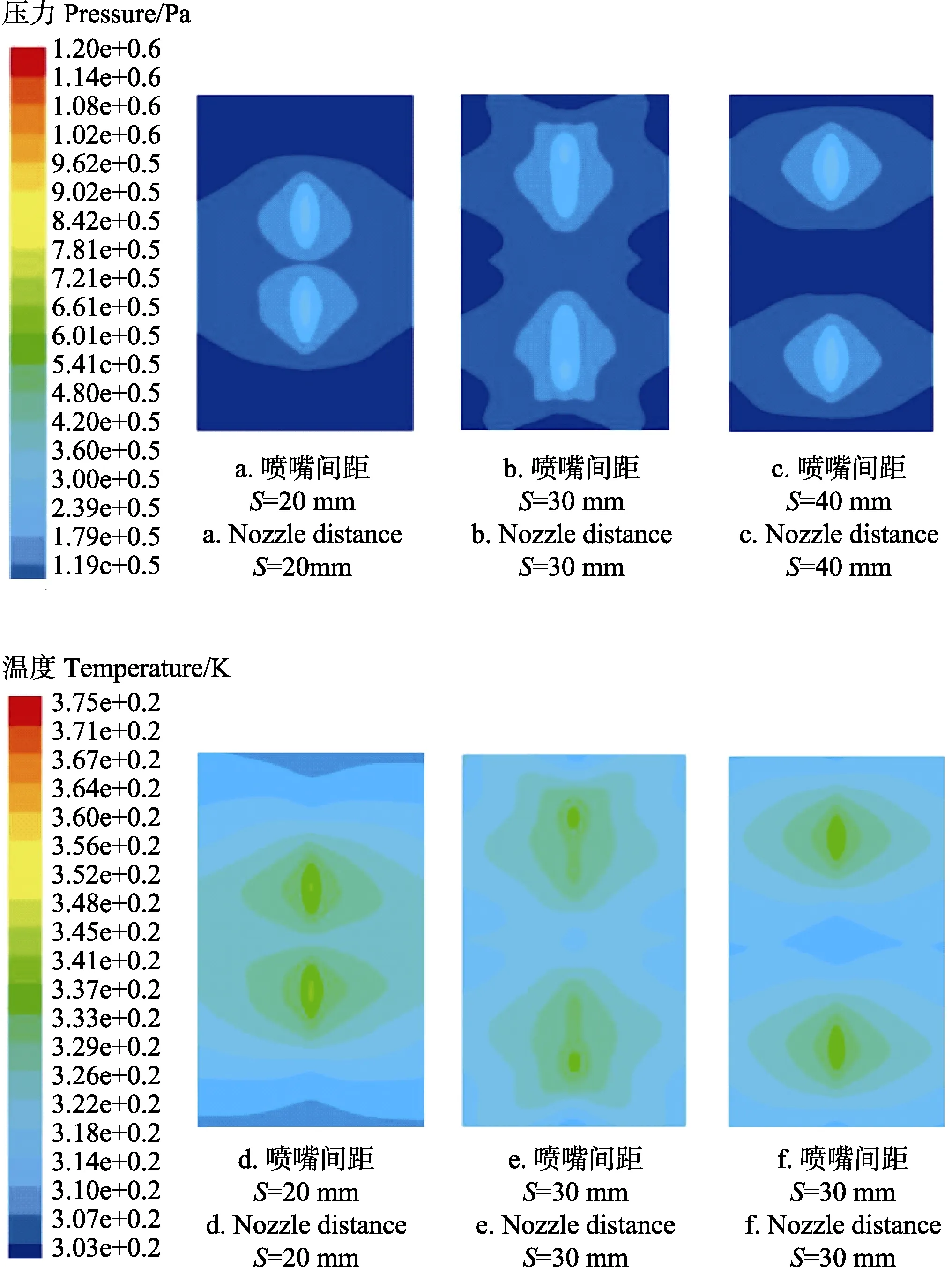
图6 冲击壁面的压力和温度分布云图Fig.6 Cloud charts of pressure and temperature distribution of impact wall
由图6a~c可知,当两喷嘴间距为20 mm时,冲击壁面的压力场区域交叠较多,但覆盖范围区域范围较小;两喷嘴间距为30 mm时,冲击壁面的压力场区域交叠较少,覆盖范围区域范围较大;两喷嘴间距为40 mm时,虽然覆盖范围区域更大,但无区域交叠。
由图6d~f温度场的覆盖范围可知,出现与压力分布相似的变化。其中,当两喷嘴间距为30 mm时,喷嘴垂直于冲击壁面相交处的温度为320 K,压力为0.2 MPa,此时数值模拟作用于苎麻纤维表面的冲击压力范围为 0.2~0.3 MPa,温度范围为320~334 K。
3 双喷嘴下高温射流冲击苎麻纤维开纤脱胶试验
从双喷嘴不同喷距间的数值模拟结果,获取了较佳双喷嘴间距S=30 mm;而从数值模拟和单喷嘴试验结果表明,喷距是影响射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的主要因素,因此,开展了较佳双喷嘴下不同喷距射流冲洗苎麻开纤脱胶试验。
以单喷嘴试验获取的进口压强1.2 MPa、喷嘴出口直径D=2.0 mm和进口温度为373 K等参数为基准,以双喷嘴数值模拟获得的最佳双喷嘴间距S=30 mm为依据,分别选择喷距为20、30、40和50 mm以及冲洗时间为12、14、16、和 18 min,在冲洗装置中开展多组样本试验。以残胶率和纤维断裂强力作为苎麻纤维洗脱后的品质评判主要技术指标,冲洗试验后的样本按照 GB/T5889-1986测定残胶率,按照GB/T5886-1986测定单纤维断裂强力,测试结果如表3所示。
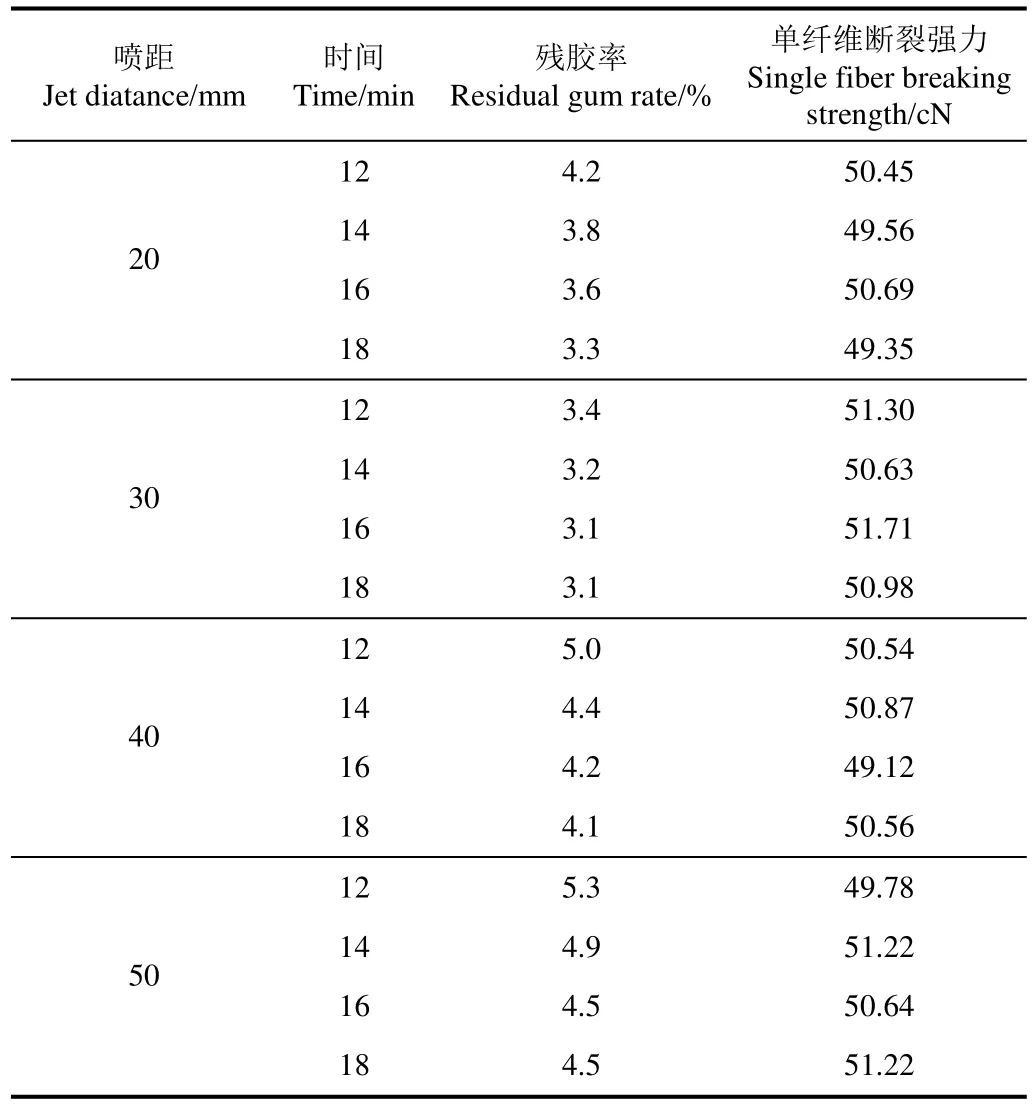
表3 双喷嘴下的试验测试结果Table 3 Test results of double nozzles
由表 3可以看出,相同的冲洗时间,随着喷距的增加,试验测试的残胶率较高;相同的喷距,增加冲洗时间,试验测试的残胶率较低。喷距为20 mm和30 mm时,对应时间段测定的残胶率低于喷距为40 mm和50 mm时的残胶率。但喷距为20 mm时试验测试的残胶率略高于喷距30 mm的残胶率。从数值模拟结果和试验观察可知,主要由于喷距较小时,冲击壁面上的中心位置处压力较大,压力区域内的有较大的压力梯度,射流冲击时麻纤维容易向四周扩散,射流冲击力作用于麻面的范围较小,水流冲洗纤维不均匀,致使残胶率较高。同时较小的喷距,致使喷射的区域较小,需安装更多的喷嘴。而喷距为40 mm和50 mm时,射流冲击壁面的压力场和温度场分布区域较小,且冲击力作用于纤维表面小且不均匀,只是利用了水流冲洗的作用,使黏附在纤维上的胶质不能有效分离,残胶率较高。
由表 3可以看出,当喷距H=30 mm、冲洗时间为16 min,试验结果测得的残胶率为3.1 %,单纤维断裂强力为51.71 cN,效果较明显,试验后的苎麻开纤脱胶效果如图7所示。

图7 冲洗后和烘干后的效果Fig.7 Effect after flushing and drying
图7可以看出,高温射流冲洗苎麻纤维表面较均匀,纤维较松散,其中纤维并丝和硬条情况较少;烘干后苎麻纤维色泽和纤维柔软度较好。其原因为经过碱煮预处理后,麻纤维中果胶、木质素、半纤维素以及少量的脂腊质和灰分等胶杂成分[24-27]大部分被溶解,其中一部分吸附在纤维上,另一部分胶质分子水解但没有完全分离[28]。短时间内温度射流水冲洗,通过水的冲击力以及水楔的冲蚀卷吸作用,洗脱掉了吸附在纤维上面的胶质成分,同时在压力和温度的共同作用下,高温冲击水进一步渗透到苎麻纤维内部,促使半纤维素等胶质成分进一步热降解和产生水合等化反应[29-30],水解了没有完全从苎麻纤维分离的胶质成分,开纤脱胶效果明显。
4 结 论
1)单喷嘴下高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶正交试验表明,当喷嘴直径为2.0 mm,进口温度为373 K时,喷距是射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的主要影响因素,得到的较佳组合参数喷距为 30 mm,进口压强为 1.2 MPa,时间为16 min,该条件下测得的残胶率为3.1%。
2)以较佳进口压强为 1.2 MPa、喷嘴出口直径D=2 mm、喷嘴进口温度为373 K为不变量,数值模拟了单喷嘴射流冲击在喷距H=20 mm、30 mm、40 mm和50 mm射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面温度场、压力场分布以及有效的作用区域。当喷距为30 mm时,数值模拟作用于苎麻纤维表面的冲击压力范围为0.16~0.3 MPa。说明喷距H=30 mm是高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶的最佳有效喷距。
3)以喷嘴进口压强 1.2 MPa,喷嘴出口直径D=2.0 mm,进口温度为373 K和喷距H=30 mm等参量不变,数值模拟了双喷嘴间距S=20 mm、30 mm和40 mm,射流冲击壁面的麻纤维表面有效的作用区域,喷嘴间距较佳值为S=30 mm,此时数值模拟作用于苎麻纤维表面的冲击压力范围为0.2~0.3 MPa,温度范围为320~334 K。冲击壁面的压力场区域有较好的交叠,覆盖范围区域范围最大。以双喷嘴数值模拟相对应的喷嘴间距,进行了双喷嘴射流冲击试验,从测试结果可知,喷嘴间距最佳值为30 mm,冲洗时间为16 min,试验测试苎麻残胶率为 3.1 %,单纤维断裂强力为 51.71 cN。表明数值模拟喷嘴最佳间距与射流冲击冲洗试验的喷嘴最佳间距相符合。
通过高温射流冲击苎麻开纤脱胶数值模拟和试验装置的试验结果表明,采用高温射流水冲击的作用能一次性能完成苎麻脱胶后苎麻纤维开纤脱胶,而在一定压力范围内射流冲击水的柔性作用减少了对苎麻纤维的损伤,该技术工艺为研制苎麻纤维开纤和漂洗等处理技术设备提供了新的技术基础。
[1]谢莉敏,陈桂华,吴晓玉,等. 苎麻脱胶工艺的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学,2012,40(2):226-228.Xie Limin, Chen Guihua, Wu Xiaoyu, et al. Research progress of ramie degumming technology[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(2): 226-228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2]张合飞,张元明,郁崇文,等. 苎麻生物脱胶精干麻的纺纱性能研究[J]. 上海纺织科技,2013,39(3):24-26.Zhang Hanfei, Zhang Yuanming, Yu Chongwen, et al. Study on spinning performance of ramie fibers degummed by biological treatment[J]. Shanghai Textile Science &Technology, 2013, 39(3): 24-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3]陈景浩,卢必涛,王天佑,等. 苎麻微生物脱胶菌株的最佳脱胶条件[J]. 纺织学报,2014,35(12):94-95.Chen Jinghao, Lu Bitao, Wang Tianyou, et al. Optimal degumming conditions of strains for microbial degumming of ramie[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2014, 35(12): 94-95.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4]李立恒,谢达平,揭雨成,等. 苎麻酶-化学联合脱胶工艺优化[J]. 纺织学报,2010,31(2):60-63.Li Liheng, Xie Daping, Jie Yucheng, et al. Optimizing enzymatic-chemical degumming of ramie[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2010, 31(2): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5]杜兆芳,黄芙蓉. 苎麻复合微生物脱胶工艺优化[J]. 纺织学报,2012,33(5):56-61.Du Zhaofang, Huang Furong. Process optimization of composite microorganism degumming of ramie[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2012, 33(5): 56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6]张勇,陈祥平,谭天福,等. 基于物理机械力的苎麻脱胶新技术[J]. 纺织科技进展,2012 (3):65-67.Zhang Yong, Chen Xiangping, Tan Tianfu, et al. New technology for ramie degumming based on mechanical force[J]. Progress in Textile Science&Technology, 2012(3):65-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7]陈朝武,陈定俊. 旋锤式苎麻水麻开纤机的原理及应用[J].纺织科技进展,2008 (4):65-66.Chen Chaowu, Chen Dingjun. Principle and application of rotary hammer type fiber opening machine of ramie[J].Progress in Textile Science & Technology, 2008 (4): 65-66.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[8]陈祥平,方佳,李乔兰,等. 苎麻机械连续化脱胶后整理技术研究[J]. 中国麻业科学,2014,36(5):248-251.Chen Xiangping, Fang Jia, Li Qiaolan, et al. Continuous mechanical processing on degummed ramie fiber[J]. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 2014, 36(5): 248-251. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9]陈静,薛建设,李朝康,等.一种带状精干麻自动化连续生产装置[J]. 山东纺织科技,2013,54(2):19-22.Chen Jing, Xue Jianshe, Li Zhaokang, et al. A strip ramie production equipment with characters of automation and continuation[J]. Shandong Textile Science & Technology,2013, 54(2): 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10]王君平. 带状麻复式开纤设备的研究[J]. 纺织科技进展,1995(1):2-8.Wang Junping. Study on fiber compound splitting equipment[J]. Progress in Textile Science&Technology, 1995(1): 2-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11]费楷,赵坤伟,彭建新. 苎麻带状麻开纤技术原理浅析[J].纺织科技进展,2009 (4):52-53.Fei Kai, Zhao Kunwei, Peng Jianxin. Analysis of ramie zonal splitting principle[J]. Progress in Textile Science &Technology, 2009(4): 52-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12]周万阳,于兰英,邓斌,等. 基于CFD的地铁隧道壁面冲洗扇形喷嘴的参数优选[J]. 液压气动与密封,2015,35(9):78-80.Zhou Wanyang, Yu Lanying, Deng Bin, et al. Parameters optimization of flat fan nozzle for subway tunnel wall cleaning based on CFD[J]. Hydraulics Pneumatics & Seals,2015, 35(9): 78-80. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13]叶建友,吕彦明. 水射流冲击压力最佳喷距数值仿真及试验研究[J]. 电加工与模具,2014(5):34-36.Ye Jianyou, Lü Yanming. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Research on the Best Jet Distances of Water Jet Impact Force[J]. Electromachining & Mould, 2014(5): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14]陈洪章,刘丽英. 蒸汽爆碎技术原理及应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2007:2-11.
[15]林翔,刘恒龙,王国志,等. 扇形喷嘴的低压射流特性研究[J]. 机床与液压,2015,43(2):164-167.Lin Xiang, Liu Huanlong, Wang Guozhi, et al. Study of low-pressure jet characteristic of fan nozzle[J]. Machine Tool&Hydraulics, 2015, 43(2): 164-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16]于兰英,周万阳,邓斌,等. 基于CFD的清洗用扇形喷嘴清洗参数研究[J]. 机床与液压2016,44(13):164-167.Yu Lanying, Zhou Wanyang, Deng Bin, et al. Study in cleaning parameters of flat fan nozzle used in cleaning based on CFD[J]. Machine Tool&Hydraulics, 2016, 44(13): 164-167. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17]刘建瑞,文海罡,高振军,等. 射流喷嘴几何参数对喷灌泵自吸性能的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(24):47-54.Liu Jianrui, Wen Haigang, Gao Zhenjun, et al. Effects of geometric parameters for jet nozzle on self-priming performance of spray pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(24): 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18]李俊,张庆,周一睁. 喷嘴结构对水射流性能影响的分析[J]. 机械制造与自动化,2015(5):102-104.Li Jun, Zhangh Qing, Zhou Yizheng. Analysis of influence of nozzle convergence on water-jet capacity[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2015(5): 102-104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19]袁丹青,王冠军,乌骏,等. 多喷嘴射流泵数值模拟及试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(10):95-99.Yuan Danqing, Wang Guanjun, Wu Jun, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment study on multi-nozzle jet pump[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(10): 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20]李喆,王国志,邓颖海,等. 扇形喷嘴的射流特性研究[J].机床与液压,2016,44(1):104-107.Li Zhe, Wang Guozhi, Deng Yinghai, et al. Study on the characteristics of jet fan nozzles[J]. Machine Tool &Hydraulics, 2016, 44(1): 104-107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21]董鹏,孙立源,梁创记.高压水清洗喷嘴、喷头的选用[J].清洗世界,2013,29(3):6-10.Dong Peng, Sun Liyuan, Liang Chuangji. Nozzles selection of high pressure water cleaning[J]. Cleaning World, 2013, 29(3):6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22]吴占芳,刘丽伟,鲁传林,等. 高压水清洗钢板系统参数系统分析与研究[J]. 冶金设备,2009(3):60-63.Wu Zhanfang, Liu Liwei, Lu Chuanlin, et al. Analysis and study of parameters in high pressure water jet cleaning steel plate system[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2009(3): 60-63.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[23]董志勇. 射流力学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2005:23-50.
[24]姜伟,韩光亭,张元明,等. 基于近红外技术的苎麻纤维素及胶质含量快速测定[J]. 纺织学报,2012,33(1):6-10.Jiang Wei, Han Guangting, Zhang Yuanmmg, et al. Fast quantitative analysis of cellulose and gum content in ramie based on near-infrared technique[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2012, 33(1): 6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25]A.I.S. Brigida. Effect of chemical treatments on properties of green coconut fiber[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2010, 7(9):832-838.
[26]冷鹃,肖爱平,廖丽萍,等. 自动苎麻化学脱胶试验仪的研制[J]. 中国麻业科学,2016,38(2):79-84.Leng Juan, Xiao Aiping, Liao Liping, et al. Development of automatic ramie chemical degumming tester[J]. Plant Fibers and Products. 2016, 38(2): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27]李振华,董欣. 苎麻快速化学脱胶技术研究[J]. 成都纺织高等专科学校学报,2000,17(4):5-8.Li Zhenghua, Dong xin. A study on the technique of rapid chemical deguming of ramie[J]. Journal of Chengdu Textile College, 2000, 17(4): 5-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28]刘德桃,李军,孙勇,等. 蒸汽喷射处理植物纤维成形体的降解液物理化学特性研究[J]. 林产化学与工业,2008,28(6):61-66.Liu Detao, Li Jun, Sun Yong, et al. Research on physicochemical characteristics of degradated products from cellulose-based composites by steam injection[J]. Chemistry& Industry of Forest Products, 2008, 28(6): 61-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29]闫军,冯连勋. 蒸汽爆破技术的研究[J].现代农业科技,2009(11):278-280.Yan Jun, Feng Lianxun. Study on steam exploded technolog[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2009(11): 278-280. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30]蔡侠,熊和平,严理,等. 大麻微生物-蒸汽爆破联合脱胶技术[J]. 纺织学报,2011,32(7):75-79.Cai Xia, Xiong Heping, Yan Li, et al. Microbial and steam explosion united technique in hemp degumming[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2011, 32(7): 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Numerical simulation and experiment of pressure and temperature field for jet impinging ramie fiber separation and degumming
Shao Yunguo, Su Gongbing※, Zou Shuchang, Meng Xiuping
(School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Wuhan Textile University,Wuhan 430073, China)
In order to research and develop a new technology of ramie fiber splitting and residual gum removal, ramie fibers treated by alkali scouring with 10.8% residual gum content were selected as the research object. A hydraulic dynamic device was trial-manufactured for investigating the ramie fiber splitting and residual gum removal. According to the trial results, an equipment with a high temperature (373 K) water-jet function was designed and manufactured. Firstly, without consideration of interaction among factors, orthogonal experiments with 3 factors and 3 levels were carried out using the equipment with single nozzle to inspect the influence of jet distance, inlet pressure, and treating time on the residual gum content. The results showed that the optimal combination was 30 mm jet distance, 1.2 MPa inlet pressure, and 16 min treating time, and the jet distance was the primary factor. Under the optimal conditions, residual gum rate was 3.1%. Secondly, under the conditions of the inlet pressure of 1.2 MPa, the outlet diameter of 2.0 mm, and the temperature of 373 K, the distribution of both temperature field and pressure field, and the effective area on ramie fiber surface by the treatment of water-jet impact with single nozzle were simulated using the FLUENT software, with different jet distance of 20, 30, 40 and 50 mm. The numerical simulation results indicated that with 30 mm jet distance, the pressure field on ramie fiber surface was in a range from 0.16 to 0.30 MPa,which was consistent with the outcomes of hydraulic dynamic impact experiment as well as the orthogonal experiments. Thus,it hinted that the jet distance at 30 mm was the most effective condition for the ramie fiber splitting and residual gum removal.Meanwhile, the inlet pressure at 1.2 MPa, the outlet diameter of 2.0 mm, the temperature at 373 K, the jet distance at 30 mm,and the internal space between nozzles ranging from 20, 30 to 40 mm were set to simulate the effective area on ramie fiber surface by the treatment of water-jet impact with double nozzles. The numerical simulation results suggested that the optimal internal space between nozzles was 30 mm, and the pressure field and temperature field on ramie fiber surface were from 0.2 to 0.3 MPa and from 320 to 334 K respectively. Under the optimal conditions, it had a better overlap area and a maximum coverage of pressure field. Eventually, the residual gum content and fiber breaking force were applied to assess the fiber quality after treatment. Based on the single nozzle trial results and the data analyses, jet distance was the most impactful factor.According to the optimal internal space between nozzles of 30 mm, multi tests were carried out with jet distance of 20, 30, 40 and 50 mm and treating time of 12, 14, 16 and 18 min. The results stated that the optimal internal space was 30 mm and the optimal treating time was 16 min, which acquired 3.1% residual gum content and 51.71 cN singe-fiber breaking force.According to the results of numerical simulation and equipment practices, it suggested that the fiber splitting and residual gum removal of the pre-degumming ramie fiber were satisfactorily achieved at one time, without fiber damage ascribed to the flexible property of water within a certain pressure extent. This technology not only can combine the stages of fiber splitting,bleaching, and rinsing in the existing process, but also provides a novel technology for researching and developing equipment for ramie fiber splitting and gum removal.
fiber; temperature; pressure; jet impingement; ramie; numerical simulation; splitting; degumming
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.040
TS122.1
A
1002-6819(2017)-10-0302-08
2016-10-25
2017-04-08
国家自然科学基金项目(51375351)
邵运果,男,山东菏泽人,主要从事机械设计及优化仿真方面的研究。武汉 武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院,430073,
Email:978327769@qq.com
※通信作者:苏工兵,男,湖北天门人,教授,主要从事机械系统仿真与有限元数值方面的研究。武汉 武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院,430073,
Email:sgb6710@163.com

