褪黑素与乳腺癌雌激素受体表达的相关性分析
黄玉钿,陈义忠,周瑞祥,郑 曦,薛玉钦,吴 进福建医科大学附属福州市第一医院病理科,福建 福州 50009;福建医科大学基础医学院免疫学系;人体解剖与组织胚胎学系,福建 福州 50000
褪黑素与乳腺癌雌激素受体表达的相关性分析
黄玉钿1,陈义忠2,周瑞祥3,郑 曦1,薛玉钦1,吴 进11福建医科大学附属福州市第一医院病理科,福建 福州 350009;福建医科大学基础医学院2免疫学系;3人体解剖与组织胚胎学系,福建 福州 350000
目的研究褪黑素对大鼠乳腺癌组织中雌激素受体表达的影响,分析褪黑素在乳腺癌发生发展中的作用。方法选用2月龄清洁级雌性SD大鼠90只,接种大鼠乳腺癌细胞,随机分为注射生理盐水对照组、7.5 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组、15 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组,10 d后乳腺癌大鼠荷瘤模型建立成功并取乳腺癌组织,采用免疫组化法检测乳腺癌中雌激素受体的表达情况。结果注射褪黑素组的大鼠乳腺癌组织雌激素受体表达指数低于注射生理盐水对照组,随着注射褪黑素剂量上升,雌激素受体表达指数进一步下降,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论褪黑素能抑制乳腺癌组织中雌激素受体的表达,可能是褪黑素拮抗乳腺癌发生发展的途径之一。
褪黑素;乳腺癌;雌激素受体
乳腺癌的发生与机体雌激素水平关系密切[1],雌激素分泌上升通过与乳腺上皮细胞的雌激素受体(ER)结合,使细胞过度增殖甚至癌变,是乳腺癌发生的一个重要风险因素[2]。有相关研究表明,长期夜班工作的女性雌激素水平及患乳腺癌风险增高,而体内褪黑素分泌量相对较低[3-4]。褪黑素是否能通过抑制雌激素作用途径而拮抗乳腺癌的发生发展尚未完全明确,本研究通过建立大鼠乳腺癌模型,研究褪黑素与乳腺癌组织中ER表达指数的关系,探讨褪黑素在乳腺癌发生发展中的作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 动物分组和试剂
选用2月龄清洁级雌性SD大鼠90只,体质量200±10 g,标准饲养。随机分成3组,每组30只,分组如下:(1)注射生理盐水对照组;(2)7.5 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组;(3)15 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组。大鼠乳腺癌细胞SHZ-88购自上海生命科学院,褪黑素购自美国Sigma,兔抗大鼠ER多克隆抗体购自英国Biorbyt,免疫组化试剂盒购自福州迈新生物公司。
1.2 建立荷瘤大鼠模型
乳腺癌细胞株于培养瓶中传代培养,细胞处于对数生长期时,制作单细胞悬液,每只大鼠按5×105细胞量在大腿内侧根部皮下接种乳腺癌单细胞悬液1次;自接种日起,每天18:00按照不同分组的干预措施,给予腹腔内注射褪黑素或生理盐水1次,接种后第10天可触及接种处皮下瘤块并处死所有荷乳腺癌大鼠,切除接种处乳腺癌瘤体。
1.3 免疫组化法检测
大鼠乳腺癌以4%中性缓冲甲醛固定,再经酒精脱水、透明浸蜡后,制作石蜡包埋组织块。乳腺癌石蜡包埋组织切片(厚度3~5 μm)以免疫组化两步法检测ER在乳腺癌中的表达,步骤如下:组织切片经脱蜡、水化后,以枸橼酸高压热修复抗原,冷却后加PBS液冲洗,3%H2O2消除内源性过氧化物酶,PBS液冲洗,滴加ER抗体(工作液浓度1∶150),孵育1 h,PBS液冲洗,加聚合物增强剂孵育30 min,PBS液冲洗,加酶标羊抗兔/鼠IgG聚合物孵育30 min,PBS液冲洗,DAB显色,苏木精衬染,梯度酒精脱水干燥,中性树脂封片。以PBS液代替ER作为阴性对照,用已知阳性片作阳性对照。受检组织切片于高倍镜下观察热点区内5个视野,计算每个视野中(ER阳性癌细胞数/癌细胞总数×100%)的比值,以平均比值(%)代表大鼠乳腺癌细胞ER表达指数。
1.4 统计学处理
以均数±标准差表示各组乳腺癌ER表达指数,采用SPSS17.0软件进行统计学分析,不同分组间定量资料的比较采用t检验,P<0.05为组间差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 乳腺癌组织雌激素受体表达差异
ER表达于乳腺癌细胞核上(图1),阳性细胞核呈棕色,注射生理盐水对照组大鼠乳腺癌组织ER表达指数为(28.61±12.52)%,高于注射褪黑素组大鼠乳腺癌组织ER表达指数,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,表1)。
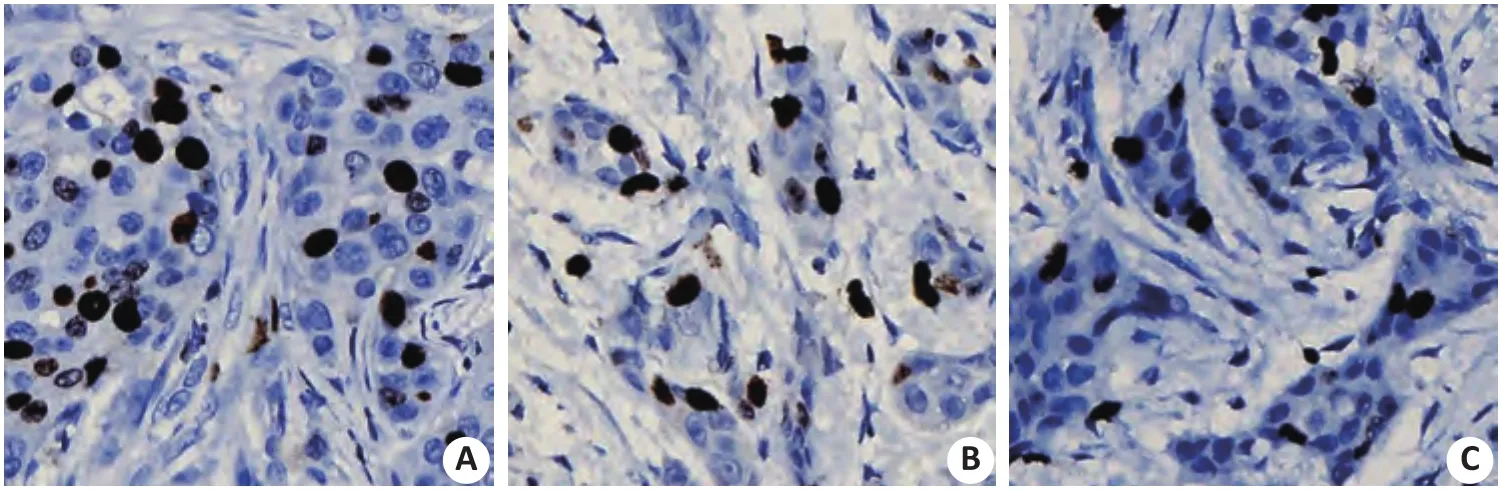
图1 大鼠乳腺癌细胞核ER阳性表达(免疫组化检测,×400)
表1 不同分组大鼠乳腺癌组织雌激素受体表达情况(,n=30)
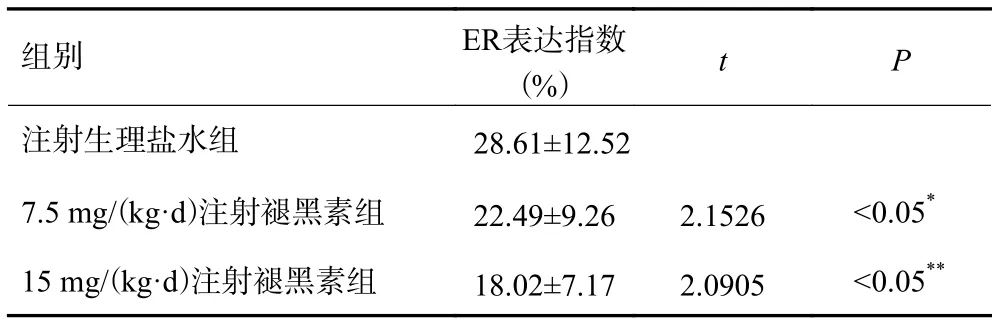
表1 不同分组大鼠乳腺癌组织雌激素受体表达情况(,n=30)
*P<0.05 vs 注射生理盐水组;**P<0.05 vs 7.5 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组.
组别ER表达指数(%)tP注射生理盐水组 28.61±12.52 7.5 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组22.49±9.262.1526<0.05*15 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组18.02±7.172.0905<0.05**
2.2 注射不同剂量褪黑素对大鼠乳腺癌组织雌激素受体表达的影响
7.5 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组大鼠乳腺癌组织ER表达指数高于15 mg/(kg·d)注射褪黑素组(22.49±9.26)% vs (18.02±7.17)%,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,表1)。
3 讨论
褪黑素是由松果体分泌的一种神经内分泌激素,属于吲哚类激素,是L-色氨酸前体物质,化学名为N-乙酰-5-甲氧基色胺[5]。该激素于1958年由Aron等[6]首次从牛松果体中发现,当青蛙摄入此激素后会使深色蛙皮褪色,故被称为褪黑素。褪黑素具有多种生理作用,涉及神经-内分泌-免疫调节、生物节律、激素分泌调节、抗氧自由基损伤等方面,其异常分泌与肿瘤的发生关系密切[7-8]。在多种肿瘤中的研究表明[9-10],褪黑素具有抑制恶性肿瘤进展的作用,其机制尚未完全明确。根据流行病学调查,长期从事夜班工作的妇女乳腺癌发生率比盲人妇女明显增高,由于对夜间光线的回避能使褪黑素分泌量上升,从而提示褪黑素分泌量高可能是盲人妇女乳腺癌发病率低的因素[11]。González等[12]研究表明,机体内褪黑素分泌量与雌激素分泌量呈负相关,但异常的褪黑素及雌激素分泌在肿瘤发生发展中的影响机制尚未明确。
雌激素通过与位于乳腺上皮细胞的雌激素受体结合,改变雌激素受体构象,调控细胞内环磷酸腺苷/蛋白激酶A等信号转导途径[13],刺激多种促进细胞生长的基因高表达,提高乳腺上皮细胞增殖活性,抑制细胞凋亡,导致乳腺癌的发生[14]。Chuffa等[15]研究表明褪黑素对机体内雌激素分泌的调节主要通过神经内分泌-生殖轴影响卵巢功能,下调卵巢的雌激素分泌量;而褪黑素对肿瘤组织中ER表达的调控则有待进一步研究。本研究结果显示,腹腔注射褪黑素的大鼠乳腺癌组织中ER表达指数低于腹腔注射生理盐水的大鼠乳腺癌组织(P<0.05),提示褪黑素会抑制乳腺癌组织中雌激素受体的表达。褪黑素高剂量组大鼠乳腺癌组织中ER表达指数低于褪黑素低剂量组(P<0.05),表明褪黑素在抑制雌激素受体表达上具有一定的剂量依赖性,进一步提示褪黑素能通过下调雌激素受体表达拮抗乳腺癌的发生发展。研究表明,褪黑素抵抗雌激素受体表达的主要机制是褪黑素通过细胞膜结合蛋白Gi与褪黑素受体偶联[16],抑制腺苷酸环化酶活性,使环磷酸腺苷水平下降,进而抑制由雌二醇诱导的ER转录活性[17],下调ER的表达。
目前国内外关于褪黑素与乳腺癌发生发展关系的研究主要集中于褪黑素对机体雌激素分泌的影响,褪黑素能通过调节下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴[18]和卵巢粒层细胞功能[19]下调卵巢的雌激素产生水平,从而拮抗乳腺癌的发生发展。有关褪黑素对乳腺癌雌激素受体的影响主要是通过乳腺癌MCF-7细胞体外实验研究,表明褪黑素能通过调节细胞内信号转导而抑制MCF-7细胞ER转录活性[20-21]。本研究则通过建立荷乳腺癌大鼠动物模型,从癌细胞接种日起以褪黑素干预实验组乳腺癌的生长,通过体内实验研究在大鼠乳腺癌细胞增殖过程中褪黑素对雌激素受体表达的影响,研究结果更直接体现乳腺癌生长过程中褪黑素对雌激素受体的影响。本研究结果显示机体内褪黑素水平与乳腺癌组织中ER的表达指数呈负相关,提示褪黑素除了直接降低雌激素分泌效应之外,还能通过下调乳腺癌组织中雌激素受体的表达,阻碍雌激素作用的通路,从而抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖及侵袭转移能力,因此褪黑素有望在乳腺癌的治疗中发挥重要作用。
[1]Savukaitytė A, Ugenskienė R, Jankauskaitė R, et al. Investigation of prognostic value of polymorphisms within estrogen metabolizing genes in Lithuanian breast cancer patients[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2015, 16(8): 2.
[2]Zekas E, Prossnitz ER. Estrogen-mediated inactivation of FOXO3a by the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER[J]. BMC Cancer, 2015, 15(4): 702-7.
[3]Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Urinary melatonin levels and breast cancer risk[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2005, 97(14): 1084-7.
[4]Haus EL, Smolensky MH. Shift work and cancer risk: potential mechanistic roles of circadian disruption, light at night, and sleep deprivation[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2013, 17(4): 273-84.
[5]Letra-Vilela R, Sá nchez-Sá nchez AM, Rocha AM, et al. Distinct roles of N-acetyl and 5-methoxy groups in the antiproliferative and neuroprotective effects of melatonin[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2016,434(11): 238-49.
[6]Chowdhury I, Sengupta A, Maitra SK. Melatonin: fifty years of scientific journey from the discovery in bovine pineal gland to delineation of functions in human[J]. Indian J Biochem Biophys,2008, 45(5): 289-304.
[7]Codenotti S, Battistelli M, Burattini S, et al. Melatonin decreases cell proliferation, impairs myogenic differentiation and triggers apoptotic cell death in rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines[J]. Oncol Rep,2015, 34(1): 279-87.
[8]Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Manchester LC, et al. Melatonin in the biliary tract and liver: health implications[J]. Curr Pharm Des,2014, 20(30): 4788-801.
[9]Wei JY, Li WM, Zhou LL, et al. Melatonin induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through HDAC4 nuclear import mediated by CaMKII inactivation[J]. J Pineal Res, 2015, 58(4): 429-38.
[10]Sigurdardottir LG, Markt SC, Rider JR, et al. Urinary melatonin levels, sleep disruption, and risk of prostate cancer in elderly men[J]. Eur Urol, 2015, 67(2): 191-4.
[11]Stevens RG. Light-at-night, circadian disruption and breast cancer:assessment of existing evidence[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2009, 38(4):963-70.
[12]González A, Alvarez-Garcí a V, Martí nez-Campa C, et al. In vivo inhibition of the estrogen sulfatase enzyme and growth of DMBA-induced mammary tumors by melatonin[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2010, 10(3): 279-86.
[13]Carascossa S, Dudek P, Cenni B, et al. CARM1 mediates the ligand-independent and tamoxifen-resistant activation of the estrogen receptor alpha by cAMP[J]. Genes Dev, 2010, 24(7): 708-19.
[14]Renoir JM. Estradiol receptors in breast cancer cells: associated cofactors as targets for new therapeutic approaches[J]. Steroids, 2012,77(12): 1249-61.
[15]Chuffa LG, Seiva FR, Fá varo WJ, et al. Melatonin reduces LH, 17 beta-estradiol and induces differential regulation of sex steroid receptors in reproductive tissues during rat ovulation[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2011, 9(12): 108-14.
[16]Maurice P, Daulat AM, Turecek R, et al. Molecular organization and dynamics of the melatonin MT receptor/RGS20/G(i) protein complex reveal asymmetry of receptor dimers for RGS and G(i)coupling[J]. EMBO J, 2010, 29(21): 3646-59.
[17]Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Mediavilla MD, Alonso-Gonzalez C, et al.Breast cancer therapy based on melatonin[J]. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, 2012, 6(2): 108-16.
[18]Cos S, González A, Martínez-Campa C, et al. Estrogen-signaling pathway: a Link between breast cancer and melatonin oncostatic actions[J]. Cancer Detect Prev, 2006, 30(2): 118-28.
[19]Hill SM, Cheng C, Yuan L, et al. Age-related decline in melatonin and its MT1 receptor are associated with decreased sensitivity to melatonin and enhanced mammary tumor growth[J]. Curr Aging Sci, 2013, 6(1): 125-33.
[20]Srinivasan V, Spence DW, Pandi-Perumal SR, et al. Melatonin,environmental light, and breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,2008, 108(3): 339-50.
[21]Treeck O, Haldar C, Ortmann O. Antiestrogens modulate MT1 melatonin receptor expression in breast and ovarian cancer cell lines[J]. Oncol Rep, 2006, 15(1): 231-5.
Correlation of melatonin and estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer
HUANG Yudian1, CHEN Yizhong2, ZHOU Ruixiang3, ZHENG Xi1, XUE Yuqin1, WU Jin11Department of Pathology, Fuzhou First Hospital Affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350009, China;2Department of Immunology;3Department of Anatomy and Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350000, China
ObjectiveTo study the effect of melatonin on the expression of estrogen receptor in rats breast cancer, and to analyze the role of melatonin in the development of breast cancer.MethodsNinety female rats of clean grade SD in age 2 months were selected, and the breast cancer cells were inoculated in the rats. The rats were randomly divided to control group injected with saline, group injected with melatonin at a dose of 7.5 mg/(kg·d), group injected with melatonin at a dose of 15 mg/(kg·d). The breast cancer tumor bearing models of rats were established on the 10th day after inoculating, and the tissues of breast cancer were taken out. The expression of estrogen receptor in breast cancer was detected by immunohistochemistry method.ResultsThe estrogen receptor expression index of rats breast cancer tissues in the group injected with melatonin was lower than that in the control group injected with saline, the estrogen receptor expression index further decreased with the increase of the dose of melatonin. Above differences were statistically significant.ConclusionMelatonin can inhibit the expression of estrogen receptor in breast cancer tissues, which may be one of the ways to prevent the development of breast cancer.
melatonin; breast cancer; estrogen receptor
2016-11-30
福建省自然科学基金(2015J01503)
黄玉钿,副主任医师,硕士,E-mail: hydfz0591@163.com;

