垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削系统稳定性研究
赵 波, 赵斌斌, 范凯洋, 张跃敏
(河南理工大学机械与动力工程学院 焦作, 454000)
垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削系统稳定性研究
赵 波, 赵斌斌, 范凯洋, 张跃敏
(河南理工大学机械与动力工程学院 焦作, 454000)
为研究垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削系统的稳定性,建立了垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削稳定性模型,采用全离散法对二维超声振动铣削稳定性进行了研究,利用Matlab软件进行了数值仿真,获得了系统的稳定性叶瓣图。铣削钛合金材料颤振实验结果表明,主轴转速在1 000~3 500 r/min范围内,数值仿真结果与实验结果吻合较好,验证了垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削稳定性模型的正确性。在垂直平面内施加二维超声振动能提高系统的稳定性,轴向切深极限最大提高了约13.6%。
二维超声振动铣削;全离散法;稳定性;叶瓣图
引 言
钛合金是一种具有强度高、密度小、耐腐蚀性好及耐热性高等特点的金属,被广泛应用于航空航天等领域。虽然钛合金具有上述优点,但其存在工艺性能差、切削加工困难等缺点。为了解决钛合金等难加工材料的加工问题,业内普遍采用的做法是合理选择合适的加工设备和加工参数,来提高难加工材料的加工质量和加工效率。
高速铣削具有高精度、高效率等优点,但在加工过程中,如果加工参数选择不当,则存在切削颤振。切削颤振不仅严重影响着零件的加工质量,还可能会破坏机床设备及刀具。因此,许多学者都对切削颤振进行了研究。Budak等[1-2]运用频率法预测铣削稳定性。Altintas等[3]考虑了用时域周期系数矩阵的时滞微分方程组描述再生效应的动态铣削过程,利用频率法得出铣削系统稳定性。Insperger[4]提出在时域内运用半离散法,并对一自由度和两自由度铣削模型进行了铣削稳定性分析。Ding等[5]提出了能有效提升计算效率的全离散法,并分析了铣削系统稳定性。姜燕等[6]提出了一种时间有限元预测法预测铣削系统的稳定性。上述都是基于Floquet理论,将无穷维时滞系统离散为有限维系统,利用系统传递矩阵特征值的模小于1时系统稳定性的原理,但都需要大量实验验证其理论的正确性,因此存在经济性差的问题。
超声振动加工是一种能够提高加工系统稳定性的方法[7],被广泛应用在精密加工领域中。速度系数k是超声振动加工的重要参数之一,其将超声振动加工分为分离型(k<1)和不分离型(k≥1)。文献[8-9]研究了不分离型超声椭圆振动切削力,研究表明,超声椭圆振动切削在不分离区仍然能够有效降低切削力。唐军等[10]研究了分离型超声纵扭复合铣削系统稳定性的影响,并通过铣削加工碳纤维复合材料(C/C)进行实验验证。超声振动加工具有经济效益好、装置简单等优点,但目前对不分离型超声振动铣削系统稳定性的研究还不是很多。
考虑到目前还没有利用全离散法对二维超声振动铣削系统稳定性进行研究,因此,笔者综合利用全离散法和超声振动加工法,提出垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削模型,建立垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削系统的稳定性模型。利用全离散法分析二维超声振动铣削稳定性,应用Matlab软件进行数值分析并得出二维超声铣削稳定性叶瓣图。最后,通过二维超声振动铣削钛合金实验验证二维超声复合铣削稳定性模型的正确性。
1 二维超声振动铣削稳定性模型
考虑到超声振动分别施加在工件和刀具上,如图1(a)所,在xOy平面上由于超声振动的存在,因此当速度系数k≥1时,属于不分离型超声振动加工;k<1时,则属于分离型超声振动加工。速度系数表示为
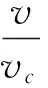
(1)
其中:v为刀尖相对于工件的瞬时线速度;vc为临界切削速度;A为超声振幅;f为超声振动频率。
但分离型振动加工还要满足必要条件[11]:λ为奇数,A>fz,其中λ为wc/wz,wc和wz分别表示周转转角速度和超声波发生器角频率,fz为超声铣削系统进给量。根据图1,若不考虑刀具齿位角的变化和沿轴向超声振动切削厚度的影响,则考虑再生效应的二维超声振动切削的切厚表达式为
hj(t)=g(t)[sc]T(hjs(t)+hjd(t))
(2)
其中:g(t)为超声振动切削分离判定系数,当铣刀在切削工件时且满足分离型振动加工的必要条件时,g(t)=1,否则为零;s=sin(Φj(t));c=cos(Φj(t));Φj为刀尖转角;hjs(t)为静态切厚,hjs(t)=[fz+Asin(2πf1t+φ1) 0]T;f1为进给方向上超声振动频率;φ1为初始相位;hjd(t)为动态切厚,hjd(t)=[x(t)-x(t-τ)y(t)-y(t-τ)]T;τ=2π/(zwc)。
根据式(2),采用指数型的二维超声振动铣削力学模型[12-13]可简化表示为
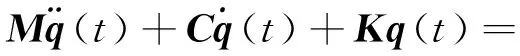
(3)
其中:M,C和K分别为模态质量、模态阻尼和模态刚度;q(t)=[x(t)y(t)]T为刀齿的动态位移;B,f1和φ2分别为轴向超声振动的振幅、超声振动频率和初始相位。
当Φst(t)<Φj(t)<Φet(t)时,w(Φj(t))=1;否则w(Φj(t))=0。Φet(t)和Φet(t)分别为刀具切入角和切出角。

dv/dt=A0v(t)+A(t)v(t)+B(t)v(t-T)
(4)
其中:A0为常数矩阵;A(t)和B(t)分别代表周期函数矩阵,且A(t)=-B(t);T=60/(ZΩ),Ω为主轴转速。
在主轴旋转的一个刀齿周期T内,把T离散为m等分,把矩阵A(t),v(t)和v(t-T)分别在每个离散的小区间上进行拉格朗日插值法代替,根据Floquet理论,使传递函数特征值的模小于1,则可得到二维超声铣削系统的稳定性叶瓣图。由于笔者研究的是超声不分离型振动铣削,即此时g(t)=1。
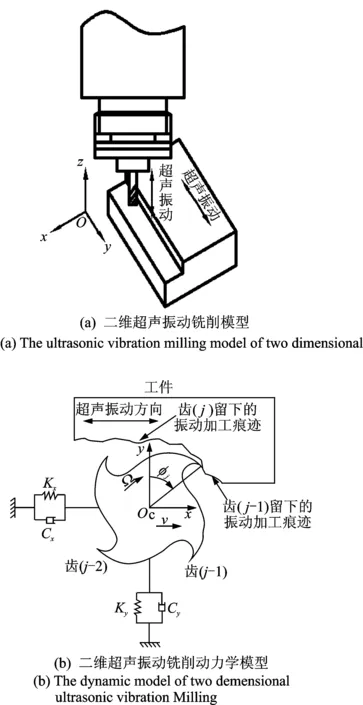
图1 二维超声振动铣削Fig.1 The ultrasonic vibration milling of two dimensional
2 稳定性模型实验验证
2.1 二维超声振动铣削系统稳定性预测图
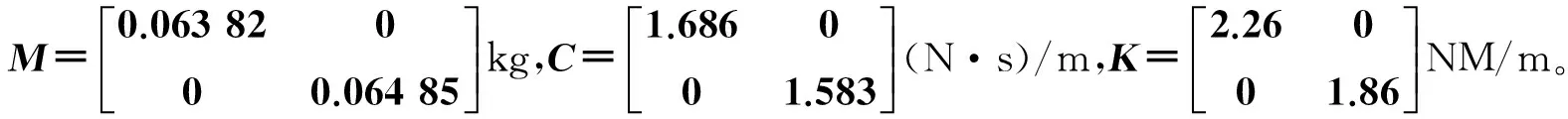
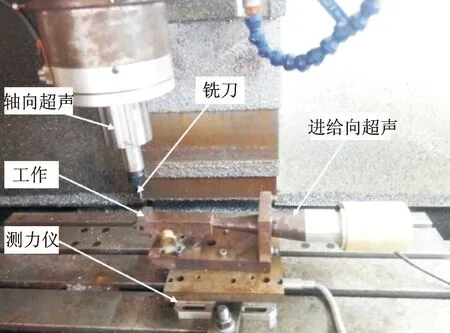
图2 实验装置Fig.2 The devices of experiment
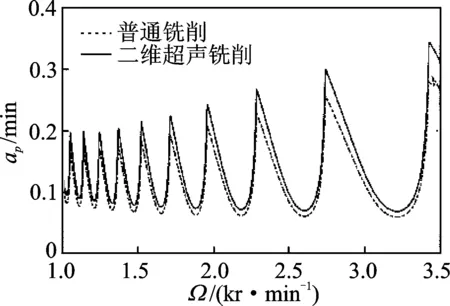
图3 稳定性叶瓣图Fig.3 The diagram of the stability lobes
图3表明,与普通铣削相比,垂直平面内的二维超声振动铣削系统,其最大提高铣削系统切削深度的极限值约为13.6%,同时也增大了稳定性的区域,即采用全离散法分析的二维超声振动铣削系统不仅可以预测铣削系统的稳定性,同时还可以提高铣削系统的稳定性。这是因为在铣削过程中,由于刀具沿主轴方向和工件沿刀具进给方向的高频振动(两个方向的超声振动频率远大于主轴转速),破环了前后刀齿留下的加工振纹,从而降低了颤振的几率。此外,在两个方向超声振动的作用下,刀具与工件为不分离切削,同时刀尖在工件上呈现多维运动,这就使得加工区域更能充分地接触到切削液,从而改善了工况,更有利于切削加工。由于刀具在主轴方向上具有超声振动,造成加工表面形成点状的超声振动凹坑,这些凹坑的存在影响着零件加工表面的应力分布。
2.2 稳定性实验验证
在不同主轴转速下验证垂直平面内的二维超声振动铣削稳定性叶瓣图,如图4所示,其中“0”,“▯”和“×▯”等分别表示系统稳定点、颤振点和无法判断铣削稳定性的点。图4中A,B和D点在普通铣削中为不稳定铣削点;而在二维超声振动型铣削下A点转为临界点,B和D点则变成稳定铣削点;C点在两种加工条件下均为稳定性点。
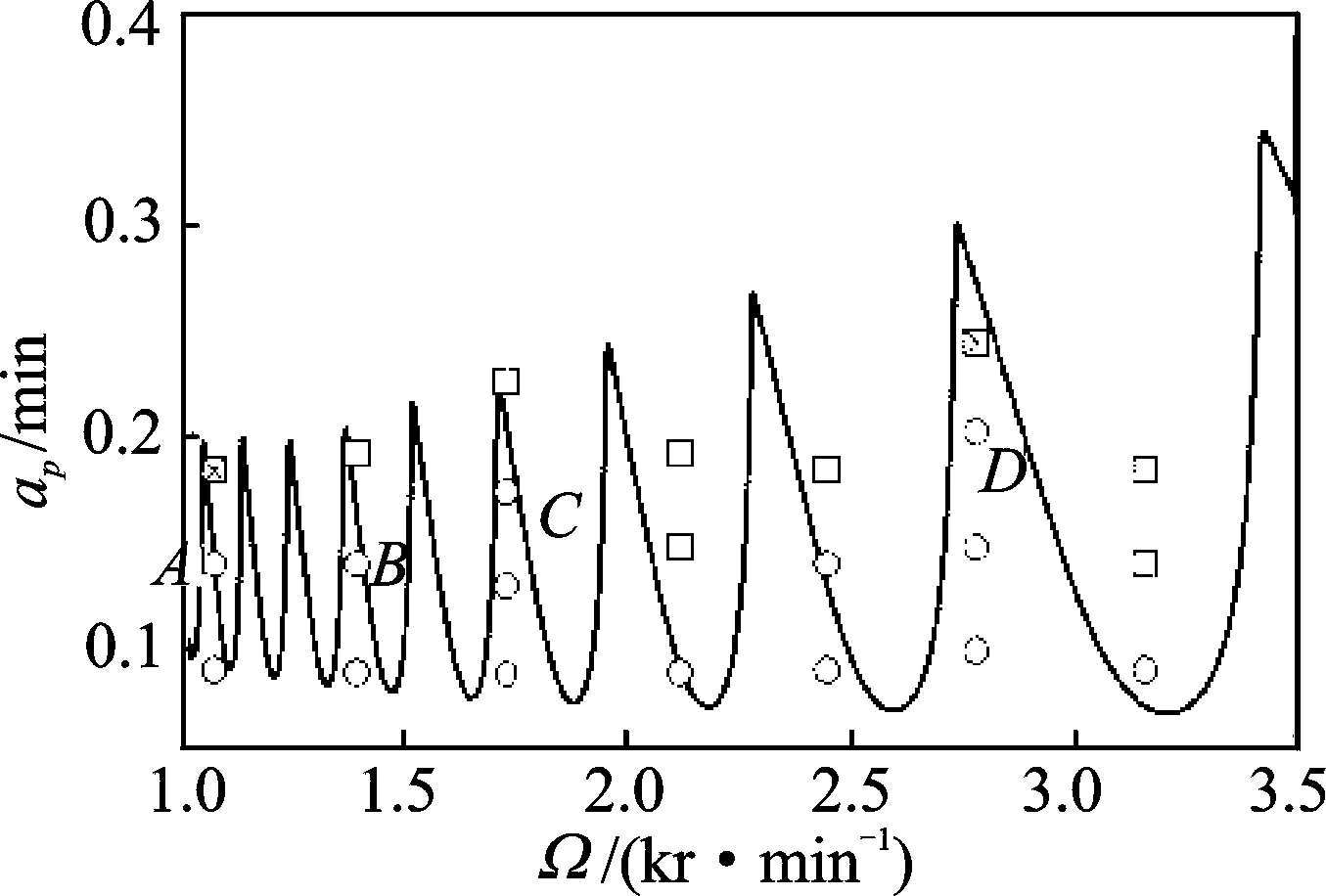
图4 铣削稳定性预测图及实验验证参数点Fig.4 The milling stability prediction diagram and experimental verification parameters
为了比较二维超声振动铣削与普通铣削的区别,从图4中选择C(1 750r/min,0.15 mm)点进行研究,由于y方向没有施加超声振动,因此只有普通铣削和二维超声振动铣削条件下的x,z向切削力时域信号、频谱图以及加工后的零件形貌图,如图5和图6所示。
由图5和图6可以看到,普通铣削下的切削力和二维超声振动铣削下的切削力大小基本相等。但从频谱图中可以明显看出,二维超声振动铣削下的谐波分量明显被抑制,因此提高了铣削系统的稳定性,验证了笔者所提出的不分离型超声复合铣削稳定性模型的正确性。
3 结束语
笔者利用全离散法和超声振动加工法,提出垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削模型,建立了垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削稳定性模型。运用全离散法分析的垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削系统能够准确地预测铣削系统稳定性叶瓣图,通过在数控加工中心VMC850E铣削钛合金实验,验证了垂直平面内二维超声振动铣削稳定性模型和稳定性叶瓣图的正确性,同时还能够提高普通铣削系统的稳定性。该实验装置是在自行研制的声学设备的基础上改造而来,因此,大大提高了设备的利用率和加工的经济效益。
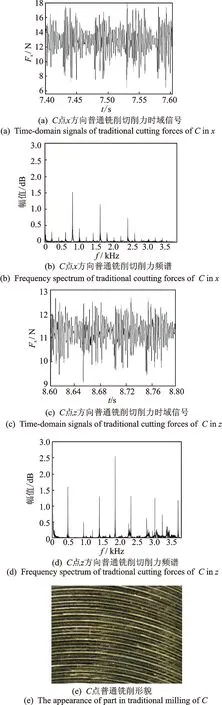
图5 C点普通铣削力信号及工件表面形貌Fig.5 The signals of traditional milling forces and the workpiece appearance of C
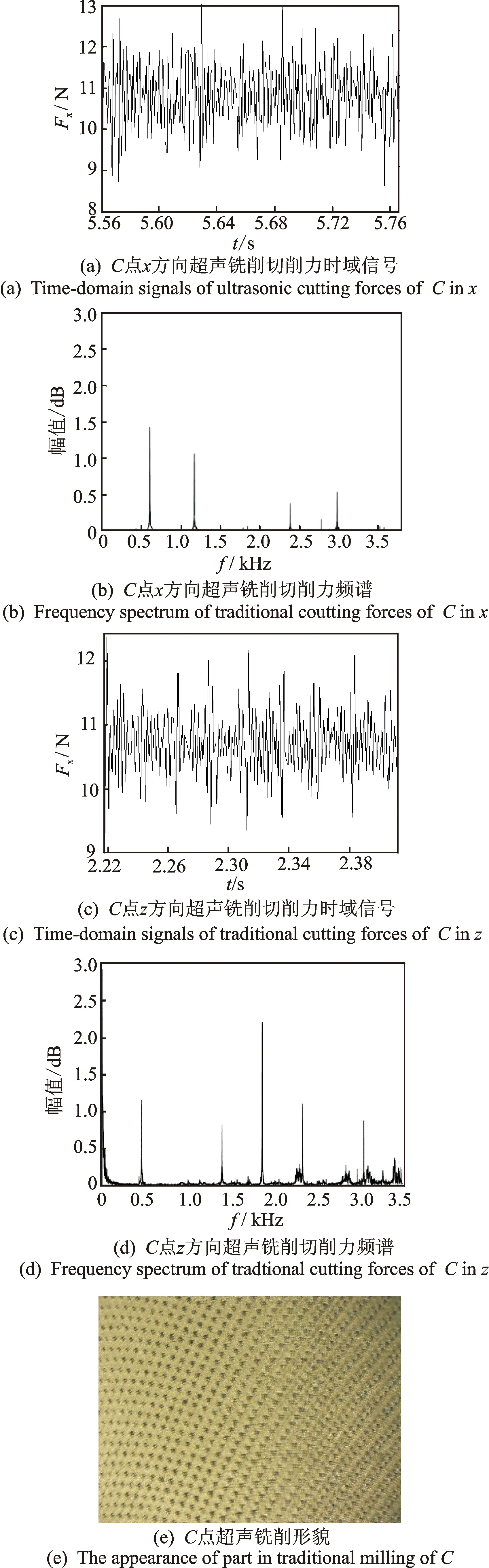
图6 C点二维超声铣削力信号及工件表面形貌Fig.6 The signals of two-demension ultrasonic milling forces and the workpiece appearance of C
[1] Budak E, Altintas Y. Analytical prediction of chatter stability in milling—part I:general formulation[J]. Journal of Dynamic System, Measurement, and Control, 1988,120:22-30.
[2] Budak E. An analytical design method for milling cutters with nonconstant pitch to increase stability, part 2: application[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2003, 125:35-38.
[3] Altintas Y, Stepan G , Merdol D, et al.Chatter stability of milling in frequency and discrete time domain [J].CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology,2008, 1(1): 35-44.
[4] Insperger T. Updated semi-discretization method for periodic delay-differential equation with discrete delay[J]. International Journal for Numerical Mehods in Engineering,2004,61: 117-141.
[5] Ding Ye, Zhu Limin, Zhang Xiaojian, et al. A full-discretization method for prediction of milling stability[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2010,50:502-509.
[6] 姜燕,郭强,赵波.铣削稳定性预测的时间有限元法[J].河南理工大学学报:自然科学版,2016,35(5):672-676.
Jiang Yan,Guo Qiang,Zhao Bo. The method on the stability limit prediction for milling process based on time-finite-element theory [J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University: Natural Science, 2016,35(5):672-676.(in Chinese)
[7] 于劲,周小勤. 基于高频变速特征的不分离型超声波振动车削抑制颤振机理[J].兵工学报,1993,14 (1) : 52-57.
Yu Jin,Zhou Xiaoqin. On the mechanism of chatter suppression with high frequency and vari-speed unseparated type ultrasonic vibration turning[J].Acta Armamentarii,1993,14(1) : 52-57. (in Chinese)
[8] 李勋,张德远. 不分离型超声椭圆振动切削实验研究[J]. 机械工程学报,2010,46(19):177-182.
Li Xun, Zhang Deyuan. Experimental study on the unseparated ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010,46(19):177-182.(in Chinese)
[9] 李文,尹礁,吕垒平,等. 不分离型超声椭圆振动切削力特性研究[J]. 航空学报,2013,34(9): 2241-2248.
Li Wen, Yin Jiao, Lü Leiping, et al. Study on the unseparated ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting force[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronnutica Sinica, 2013,34(9):2241-2248.(in Chinese)
[10] 唐军,赵波. 分离型纵-扭复合超声铣削的稳定性分析[J]. 兵工学报,2015,36(7):1318-1325.
Tang Jun, Zhao Bo. Stability analysis of the separated longitudinal-torsional composite ultrasonic milling [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(7): 1318-1325.(in Chinese)
[11] 张建华. 超声振动辅助微细铣削运动学分析[EB/OL]. (2012-12-28) [2016-09-10].http:∥www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201212-1173.
[12] Faassen R P H, van de Wouw N, Oosterling J A J, et al. Prediction of regenerative chatter by modelingand analysis of high-speed milling[J].International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture,2003,43:1437-1446.
[13] 宋清华,艾兴,万熠,等. 小径向切深下的进给量对铣削稳定性的影响[J].中国机械工程,2008,19(10):1148-1152.
Song Qinghua, Ai Xing, Wan Yi, et al. Stability prediction for high-speed milling including feed rate in low radial immersion [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2008, 19(10):1148-1152.(in Chinese)

Gear Crack Damage Localization of the Planetary Gearbox Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition
LIUHaohua1,LIFangyi1,LIGuoyan1,WANGYifan2,ZHANGShanshan1,DONGDehao1
(1.Key Laboratory of High Efficiency Clean Mechanical Manufacture,Ministry of Education, Shandong University Jinan, 250061, China)(2.Shanghai Aerospace Equipments Manufacturer Shanghai, 200245, China)
Abstract In order to solve the problem that it is difficult to extract the characteristic frequency and identify the location of the gear crack damage in planetary gearboxes, a gear local damage diagnosis method based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and frequency demodulation analysis is put forward. Based on the vibration signal model of typical gear local damages, the method can process vibration signals of the sun, ring and planet gear with crack damage by EEMD and frequency demodulation analysis. The local damage characteristic frequency of the gear is extracted from the frequency spectrum, and the location of the gear with crack damage in the gearbox is identified. Simulation analysis and experimental results show that the method based on EEMD and frequency demodulation analysis can effectively extract the characteristic frequency from the sun, ring and planet gear with crack damage. Besides, the damage localization of the gear with crack damage in the planetary gearbox is completed.
Keywords gearbox; frequency demodulation; damage localization; ensemble empirical mode decomposition
Vibration Control Analysis of Trailing Edge Flap Smart Rotor with Limited Deflection Angle
LIUShiming,YANGWeidong,YUZhihao,DONGLinghua,LUKaihua
(National Key Laboratory of Rotorcraft Aeromechanics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract An optimization method for vibration reduction of small-scaled smart rotor with trailing edge flaps is presented. Both the inertial forces and aerodynamic forces due to the deflection of trailing edge flaps are concerned in this model. A surrogate model is developed to calculate the aerodynamic forces of flapped airfoils. The aeroelastic dynamic equations are solved with the implicit trapezoid method to get the elastic response of blade, and the vibratory blade loads and hub loads are predicted with a force integration method. The flap deflection harmonics are the design variables and the amplitutes of vibratory hub load are chosen as the objective function. The best flap deflection law for hub vibration control is found with the steepest descent method. Results show that both structural and aerodynamic loads of rotor can be precisely calculated with the current model. Hub vertical vibratory load can be effectively reduced with properly controlled flaps at different advance ratios. The lack of deflection ability can be simulated with the direct constraint method or the objective weight method. The deflection ability of trailing edge flaps significantly influences the vibration reduction effect. Despite the limited deflection angle due to the ability of actuator, vibratory loads can still be reduced with actively controlled flaps.
Keywords helicopter; rotor; vibration; trailing edge flap; optimization method
Research on Ultrasonic Guided Wave-Based Damage Localization for Pipeline Structure
WANGGuofeng,LIFucai,LIUZhiqiang,MENGGuang
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanical System and Vibration, Shanghai Jiaotong University Shanghai, 200240, China)
Abstract Structure damage will affect the propagation of ultrasonic guided waves. Hence, non-destructive testing technology based on ultrasonic guided waves can realize structural health monitoring (SHM). A pipe with 174mm inner-diameter and 194mm outer-diameter, made of 20#carbon steel is used to investigate the damage localization in this study. Based on dispersion equations, numerical method is applied to obtain longitudinal and circumferential guided waves in the pipe structure. Central frequency of the incident signal is selected 80 kHz by simultaneously considering the dispersion curves and wave structure. Finite element method (FEM) is used to verify characteristics of guided wave propagation. According to the FEM analyses, characteristics and wave structures of longitudinal modes are close to those of circumferential waves, moreover, both of them are similar to those of Lamb waves in plate structure. Elliptical damage localization method is therefore proposed with one excitation and multiple captures for damage localization in the structure. Notch and hole are introduced to the pipe to verify effectiveness of the proposed method, and then analyzed influencing factors of damage localization deviation.
Keywords guided wave; pipe; dispersion; damage localization; structural health monitoring (SHM)
A Forecasting Method of Positioning Accuracy for CNC Machine Tools Feed System Based on BP Neural Network
DENGChao1,QIANYousheng1,WUJun2,XIONGYao3,DUANChaoqun1
(1.State Key Lab of Digital Manufacturing Equipment & Technology,
Huazhong University of Science & Technology Wuhan, 430074, China)
(2.Institute of Ship and Ocean Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan, 430074, China)
(3.Wuhan Second Ship Design and Research Institute Wuhan, 430070, China)
Abstract Aimed at the difficulty in forecasting the positioning accuracy of machine tool feed system,a new model has been established, analyzing the positioning accuracy degradation of the mechanical transmission system of feed system. Firstly, a computer numerical control(CNC) machine tool feed system model is made using a dynamic simulation software Adams to obtain positioning accuracy values for different initial state. Then, a mapping model is set up between the positioning accuracy and the gap, the ball tilt and the workpiece loading by BP neural network. According to the mapping model, the prediction method of the positioning accuracy is discussed in detail. Finaly, the method is proved to be correct and effective by conducting the test experiment of positioning accuracy on the test platform of precision motion reliability.
Keywords feed system; BP neural network; mapping model; Adams; positioning accuracy prediction
Research on Impact Location by Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor Network
CAOLiang1,WANGJinglin1,HEZhaohua1,LIANGDakai2,SHANTianmin1,LINZeli1
(1.Aviation Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Fault Diagnosis and Health Management, Shanghai Aero Measurement & Control Technology Research Institute Shanghai, 201601, China)
(2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract In view of the demand of monitoring the impact and vibration of laminated composite plates, a new method of low speed impact identification based on wavelet packet decomposition and distributed fiber Bragg grating sensing network is proposed. The sensor network layout is designed according to the load form of clamped plate structure and the sensing characteristics of fiber Bragg grating sensor. Then, the impact response signals monitored by fiber Bragg grating sensor network are analyzed by the fast Fourier transformation and wavelet packet decomposition to obtain the time domain characteristics of impact characteristics. On this basis, the mutual correlation coefficient between each characteristic decomposition signal and its corresponding time domain original signal is calculated to be the weight of the similarity. The characteristics of the impact response signals of all samples are decomposed, and the sample database is constructed. Finally, the location coordinates of impact points are determined according to the similarity calculated based on the Haudorff distance between the test signal and the sample information. The research shows that this method can realize the identification of the low speed impact position on the structure of the laminated plates.
Keywords fiber Bragg grating sensor network; laminated plate; wavelet packet decomposition; impact location
The Coupling Dynamic Model and Vibration Response of Straddle Type Monorail Vehicle
WENXiaoxia1,DUZixue2,XUZhouzhou1,YINYanli1,WEIHanbing1
(1.School of Electrical and Vehicle Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University Chongqing, 400074, China)
(2.Institute of Urban Rail, Chongqing Jiaotong University Chongqing, 400074, China)
Abstract In order to investigate the vibration response characteristics and evaluate the stability and comfort of the straddle type monorail vehicle within the designed speed, the topology relationships among the traveling wheels, guide wheels, stabilizing wheels and bogie central traction devices are analyzed. A monorail vehicle spatial coupling dynamic model, which consists of three wheel-rail contact modes, is established based on Hamilton equation. The contacts to be studied are the one between the traveling wheel and the top surface of beam, and the contact of the side surface of the rail beam with the guide wheel and stabilizing wheel respectively. Several prominent characteristics such as the vibration dynamic responses of monorail lateral and vertical acceleration are obtained based on the coupling dynamic model when the roughness is designated to be the excitation source given the vechicle moving with a constant speed. Finally, the coupling dynamic model is validated with the comparison of the related experimental results. In this way, vibration response characteristics of monorail vehicle for different design speed are obtained under three rail surface roughness excitation. According to the simulated vibration results, the monorail vehicle stability and comfort performance through straight line is evaluated. The results infer that the monorail vehicle had outstanding comfort performance and excellent running stability.
Keywords monorail vehicle; coupling dynamic model; contact model; rail uneven excitation; vibration; stability performance
Laplacian Eigenmaps-Support Vector Domain Description Method for Complex Electromechanical System
YASENJIANG·Jiarula1,2,GAOJianmin1,GAOZhiyong1,JIANGHongquan1.CHENZisheng1
(1.State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing Systems Engineering, Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China)
(2.School of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University Urumqi, 830046, China)
Abstract The monitoring data of the complex electromechanical system has obvious high-dimensional nonlinear and complex distribution characteristics. In order to meet the requirements of complex system anomaly identification which are difficult to be satisfied by the traditional method, a kind of Laplacian eigenmaps-support vector domain description method (LE-SVDD) is proposed. On account of the fact that the points which are close in the high-dimensional feature space should also be close after being projected to the low-dimensional feature space, the improved LE method uses a weighted undirected graph to describe a popularity and find the low-dimensional embedment with an embedded method, thereby status popular structures can be found in the high-dimensional data. In the simulation experiments based on the standard Tennessee - Eastman process (TE process) test and training data, the accurate results of nonlinear feature extraction and anomaly identification at different time are given. Respectively, the average false negative rate and false alarm rate are 6.063, 6 and 5.625, 3.125, which are relatively low. It shows that LE-SVDD method has excellent non-linearity and high-dimensional data processing capability in condition monitoring, which is suitable for the monitoring and diagnosis of engineering system.
Keywords complex electromechanical systems; anomaly detection method; feature extraction; Laplacian eigenmaps-support vector domain description method (LE-SVDD); Tennessee - Eastman proces
Rolling Bearing Reliability Assessment and Life Prediction Based on KPCA and WPHM
WANGFengtao,CHENXutao,LIUChenxi,LIHongkun,HANQingkai,ZHUHong
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology Dalian, 116024, China)
Abstract The remaining useful life (RUL) prediction of rolling bearing is significant for proactive maintenance of equipment, and selecting the features which can accurately reflect the performance degradation process as the inputs of the life prediction model is the premise of accurate RUL prediction. A novel method based on kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) and Weibull proportional hazard model (WPHM), is proposed to assess the reliability and predict the RUL of the rolling bearing. High relative feature set is constructed by selecting the effective features through extracting the time domain, frequency domain and time-frequency domain features of lifetime bearing. The kernel principal components (KPCs) which can accurately reflect the performance degradation process are obtained by KPCA. Then the KPCs are used as the covariates of WPHM to assess the reliability and predict the RUL. An example of bearing test is provided to demonstrate that this method can accurately assess the reliability and predict the RUL to provide timely maintenance resolution. Meanwhile, as the relative features are extracted, the differences in manufacturing, installation and working condition of the same type bearings are reduced, which enhances the practicability and stability of the method.
Keywords rolling bearing; life prediction; kernel principal component analysis; Weibull proportional hazard model; relative feature
Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Gearbox Based on KFCM Optimized by Particle Swarm Optimization
LIZhuang1,LIUYibing1,TENGWei1,LINYang1,2
(1.School of Energy, Power and Mechanical Engineering, North China Electric Power University Beijing,102206, China)
(2.Beijing Huaneng Xinrui Control Technique Co.,Ltd Beijing, 102209, China)
Abstract A method based on kernel fuzzy c-means clustering (KFCM) optimized by particle swarm optimization is proposed for fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox. Firstly, the clustering model is built based on wrong classification rate of training samples. The training samples are classified by kernel fuzzy c-means clustering. Then particle swarm optimization is introduced for solving the clustering model while the initial clustering center and parameter of kernel function are chosen as optimization variables. The class centers of optimal clustering result are acquired. Finally, the similarity parameters in kernel space between new data samples and the class centers are calculated for diagnosing whether the new data sample belongs to knows faults. The results show that the proposed method can diagnose both the known faults and unknown faults effectively compared to traditional neural network based on supervised learning.
Keywords kernel fuzzy c-means clustering; particle swarm optimization; wind turbine; gearbox; fault diagnosis
A Single-Mode-Drive and Tower-Shaped Ultrasonic Motor with an Asymmetric Stator
CHENQianwei,JUQuanyong,GAOSumeiYANGChuansen
(School of Mechatronic Engineering, Jinling Institute of Technology Nanjing, 211169, China)
Abstract In order to solve the problem that the existing single-mode-drive USMs either move unidirectionally or wear and tear seriously, a single-mode-drive and tower-shaped USM that can move bi-directionally is presented. The USM is composed of an asymmetric stator and a mover, and the stator is designed as an asymmetric Langevin vibrator. A low-order and a higher-order asymmetric working mode is utilized to the stator, and the scheme of PZTs′ polarization and arrangement location are designed accordingly. Switching between the low-order and the higher-order mode can drive the motor bi-directionally by the single mode. Firstly, the working principle of the motor is analyzed. Then the prototype of the motor is fabricated. Finally, the tests of vibration mode and mechanical characteristics on the prototype are accomplished. Experimental results show that under the condition of single phase excitation through phase A, the motor is working under the low-order mode, and the mover is driven forward with the maximal velocity of 112 mm/s and the maximal driving force of 2N; under the condition of single phase excitation through phase B, the motor is working under the higher-order mode, and the mover is driven backward with the maximal velocity of 94 mm/s and the maximal driving force of 3 N.
Keywords single mode; asymmetric; ultrasonic motor; piezoelectric
Damage Identification of Transmission Tower Based on Cross Correlation Functions Amplitude and Support Vector Machine
HUOLinsheng1,LIXu1,LIHongnan1,ZHANGZhuoqun2
(1.Faculty of Infrastructure Engineering, Dalian University of Technology Dalian, 116023, China)
(2.State Nuclear Electric Power Planning Design & Research Institute Beijing, 100095, China)
Abstract A damage detection method for transmission tower is presented based on integrating the cross correlation function amplitude and the support vector machine (SVM). The proposed method consists of two stages. Firstly, the data features, which are defined as the difference of the cross correlative function amplitude between initial and current states, is calculated from the approximate signal of single mode responses. The data features are then used to train the SVM classifier to turn the damage identification problem into classification problem. The feasibility of the method is verified by the vibration test of the transmission tower model. The results show that the proposed method only uses the dynamic responses from small number of sensors, and can identify the damage status with strong noise robustness during arbitrary excitations.
Keywords the cross correlative function; support vector machine; damage identification; transmission tower
The Yaw Error Compensation Method of Large Stroke Precision Positioning Platform
LIUJizhu1,2,LIJian1,2,ZHANGWenwen1,2,WANGYangjun1,2,PANMinqiang1,2,CHENLiguo1,2
(1.School of Mechanical and Electric Engineering, Soochow University Suzhou, 215021, China)
(2.Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science and Technology, Soochow University Suzhou, 215021, China)
Abstract In order to reduce the impact of high precision positioning platform yaw error and improve the positioning accuracy. This paper studies the yaw error compensation method of the platform based on linear motor drive, air support and guide rails. According to the dynamic characteristics of the positioning platform's yaw errors, a highly frequent responding and non-contact yaw error detection system combined flat feet and micro displacement sensor is designed, a detection algorithm model is established, and anx,ytwo-dimensional micro-displacement compensation mechanism based on piezoelectric ceramic driver is designed. Using spring mass damper system simplified by flotation rail slider deputy, positioning platform deflection of two degrees of freedom vibration model iss established. The deflection error compensation experiments based on the error compensation system shows that positioning accuracy of precision positioning platform has been greatly improved, the final positioning accuracy of the positioning platform is better than 2 μm.
Keywords yaw error; vibration model; pb-based lanthanumdoped zirconate titanates (PZT); error compensation
Research on Lamb Wave and Linear PZT Array Scanning Based on Directional Damage Imaging and Evaluation
WANGQiang
(College of Automation,Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications Nanjing, 210023, China)
Abstract Damage evaluation method is one of the key techniques in structural health monitoring. Research efforts are concentrated on Lamb wave based directional damage quantitative monitoring and evaluation method. Based on linear pb-based lanthanumdoped zirconate titanates (PZT) sensor array and phase information in different sensing signals of PZT elements, phase delay of directional damage reflection could be scanned and detected to decide the orientation and central position of damage. Time reversal damage imaging method is also improved based on linear sensor array tuning after the orientation of the damage is decided to realize the directional damage imaging and evaluation. Experiments on aluminum plate indicate the effect of the new method on damage orientation and dimension quantitative evaluation and the better anti-interference and accuracy than existing damage imaging methods.
Keywords structural health monitoring; damage evaluation; imaging; directional damage; Lamb waves
Modeling and Simulating of a Two-Stage Pressure Hydro-pneumatic Spring for Off-Road Vehicle
LIZhongxing1,GUOZiquan1,WANGChuanjian2,LIMei3,MAZili1
(1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering, Jiangsu University Zhenjiang, 212013, China)
(2.Jingjiang College, Jiangsu University Zhenjiang, 212013, China)
(3.Mechanical and Electrical Engineering College, Hainan University Haikou, 570228, China)
Abstract In order to relieve the contradiction of dynamic performance between different loading conditions, a two-stage pressure hydro-pneumatic spring which is designed for off-load vehicle is proposed. Taking the compressibility of oil into consideration, a nonlinear mathematical model is established. A test bench for hydro-pneumatic spring is built and the accuracy of the model is verified. The one-quarter model of vehicle is built up to compare the simulations of vehicles equipped with single-accumulator hydro-pneumatic suspension to that with two-stage pressure hydro-pneumatic suspension under random road excitation. The results show that, compared with the former situation, the body acceleration root mean square (RMS) value under the latter condition decreases by 20.1% (paved road/full-load) and 10.7% (off-road/empty-load) respectively, and the tire dynamic load decreases by 36.8% and 10.4% respectively. Although the RMS value of dynamic travel of suspension increases by 11.8% and 1.9%, the probability of collision to set blocks is less than 0.1%, remaining in a reasonable range.
Keywords off-road vehicle; two-stage pressure hydro-pneumatic; ride comfort; modeling and simulation
Hybrid Modeling Input and Output for a Rhombic Micro-displacement Amplifier
ZHANGChunlin,HEGuojing,YIJing
(College of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Central South University of Forestry and Technology Changsha, 410004, China)
Abstract This paper proposes a rhombic micro-displacement amplifier (RMDA) for piezoelectric actuator. The amplifier consists of three parts: piezoelectric actuator (PA), flexible hinge and rhombic amplification part. However, the key drive part of RMDA is PA. PA has hysteresis effects, it is mean that the RMDA also has. To ensure the accuracy for amplifiers, the hybrid model which is based on discrete classical Preisach model (CPM) and support vector machine (SVM), is introduced to accounts for hysteresis effects. Finally, the hybrid model and its inversion model of the amplifier are modeled and successfully validated via experimental results. The results demonstrate that hybrid modeling have high accuracy for express the input/output relations of RMDA which have hysteresis effects.
Keywords displacement amplifier; piezoelectric actuator (PA); hysteresis effects; hybrid modeling
Acoustic Emission Mechanism and Testing of Leakage in Natural Gas Pipeline Ball Valve
LIZhenlin1,2,ZHANGHaifeng3,HAOYibo4,ZHANGNing1,2,LEIHongxiang1,2,CHENXin1,2,LIUZhichao1,2
(1.School of Mechanical and Transportation Engineering, China University of Petroleum-Beijing Beijing, 102249, China)
(2.Beijing Key Laboratory of Process Fluid Filtration and Separation Beijing,102249, China)
(3.PetroChina Pipeline R & D Center Langfang, 065000, China)
(4.PetroChina Eastern Pipeline Co., Ltd Shanghai, 200120, China)
Abstract The jet gas from the internal leakage in a ball valve, which is an indispensable equipment in a high-pressure natural gas transmission pipeline, can produce acoustic emission (AE) signals. Thus, the research on the characteristic rule of the AE signals will be helpful for the quantitative detection of the valve leakage flow. In dealing with this problem, the AE mechanism and testing of internal leakage in a ball valve are investigated. An AE testing system is used to measure the leakage in ball valves of three different sizes. In the analysis process of the testing data, the spectrum distribution characteristics of the AE signals on leakage levels are described, and the characteristic parameters of signals (information entropy, root mean square (RMS) and frequency peak) are extracted using the wavelet packet analysis method. On this basis, fitted curves about the characteristic parameters and the leakage flow are established, and the correlation is evaluated using the R-square (determination coefficient). The evaluation results show that the RMS value with the highest correlation (R-square =0.979) can be used for the quantitative detection of leakage in a ball valve in the natural gas pipeline.
Keywords natural gas pipeline; ball valve; acoustic emission mechanism; testing experiment
Sensitivity Analysis of Wheel Quality and Location on Rotor Critical Speed
PANHonggang1,2,YUANHuiqun1,ZHAOTianyu1,YANGWenjun1
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering & Automation, Northeastern University Shenyang, 110819, China)
(2.School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shenyang Institute of Engineering Shenyang, 110136, China)
Abstract To improve the efficiency of thermal power unit and reduce the pollutant emissions, the steam turbine unit in series of transformation on flow is changed, the quality and center position of mass of the rotor is changed, which leads to the change of rotor critical speed and a certain effects on the run. In this paper, using the experiment to measure the different wheel quality and position of the rotor critical speed, the results are compared with the theoretical calculation result analysis, and the sensitivity analysis methods is introduced to analyze the influence of the quality of wheel and position on changing of steam turbine rotor critical speed. Experimental study agrees well with the theoretical analysis: the rotor critical speed is decreased with the increasing of the wheel quality and is increased with the increasing of the wheel offset. The sensitivity coefficient of wheel offset on the critical speed is between 0.25 and 2.4, the greater the offset, the higher the sensitivity coefficient; the sensitivity coefficient of the quality on the critical speed is between -0.35 and -0.001, the greater the increasing ratio of the quality, the smaller the sensitivity coefficient; the influence of the offset on the critical speed is far greater than the influence of the quality, which is about 7~10 times. When the quality offset of the same wheel is greater than 40%, and the rotor critical speed changes obviously. In the same offset location, the increasing of the mass is less than 50%,, and the rotor critical speed changes obviously. The method proposed can be used to solve the problem of the adjustment of the steam turbine rotor critical speed.
Keywords critical speed; sensitivity; offset; Bode diagram
The Calculating Method and Application of Evidence Weight Based on Fault Sensitivity
HUJinhai1,2,GAOXingwei1,ZHANGYu1,RENLitong1,PENGJingbo1
(1.Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering Institute, Air Force Engineering University Xi′an, 710038, China)
(2.Co-Innovation Center for Advanced Aero-Engine Beijing, 100191, China)
Abstract With a focus on the problem of the typical evidence weight calculating method that it cannot define the weight and complete the decision fusion in the high conflict evidence D-S fusion problem where only a few sensors make the judgments correctly while the most incorrectly, the paper proposes an evidence weight calculating method based on fault sensitivity. Firstly, kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) is used to obtain the nonlinear sensitive feature; then, calculating the sensitivity based on such feature and obtaining sensor decision weight based the fault detection sensitivity; applying the weight obtained above and that obtained from equal weight method and decision-making distance based method to the fusion diagnosis of the simulated fault in the rotor where three sensor are installed. The results show that: the weight obtained through the method proposed in the paper can reflect the sensitivity of different sensors when detecting the faults. High weight is given to the sensors which contain much fault information and sensitive to fault and low weight will be given to the sensors of the opposite kind. In the method proposed, evidence weights play the role as a “regulator”, which makes it possible to obtain better decision fusion result whether in the cases where only a few sensors manage to find the fault and give the correct diagnosis or in the cases where few or no conflict exists.
Keywords multi-sensor information fusion; D-S evidence theory; fault diagnosis; fault sensitivity; evidence weight
Optimization of Support Vector Machine and Its Application in Intelligent Fault Diagnosis
WANGBaojian1,ZHANGXiaoli2,FUYANGAoxiao1,CHENXuefeng1
(1.State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing and Systems Engineering, Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China)
(2.Key Laboratory of Road Construction Technology and Equipment, Ministry of Education, Chang′an University Xi′an, 710064, China)
Abstract Single support vector machine has low precision in fault diagnosis of bearing and gear system, the sample feature extraction method of support vector machine and the method of parameter optimization of support vector machine are studied to improve the accuracy of the support vector machine in the fault diagnosis of bearing gear system. The input samples of support vector machines are constructed by the kernel principal component analysis to reduce data redundancy, extract high dimension information of the data, then particle swarm optimization algorithm is used to optimize the kernel function parameter and penalty factor of SVM, finally, the optimized support vector machine model is used for fault diagnosis. A comparative experiment on the fault diagnosis of bearing gear is carried out in order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, the results show that the proposed method improves the diagnostic accuracy significantly in comparison with the general support vector machines,the effectiveness and advantages of the intelligent diagnosis method are verified.
Keywords support vector machine; kernel principal component; particle swarm optimization algorithm; fault diagnosis
Dynamic Testing and Modeling of a Magnetorheological Damper
MEIZhen1,2,GAOYichao1,2,GUOZixiong1,2
(1.College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University Xiamen, 361021, China)
(2.Key Laboratory of Structural Engineering and Disaster Prevention of Fujian Province Xiamen, 361021, China)
Abstract Establishing precise mechanical models of magnetorheological dampers is an important prerequisite not only for the response analysis and design of structures with the dampers, but also for obtaining good vibration control effect. In this paper, the dynamic performance test of a magnetorheological damper with the nominated maximum damping force of 10 kN is first carried out. Based on the test results, parametric and non-parametric dynamic models of the damper are developed and the effectiveness of the proposed models is verified. Finally, the results of the two different modeling approaches are compared. Results show that the formulated hyperbolic tangent hysteresis model (parametric model) could well describe the dynamic behavior of the magnetorheological damper. Besides, both the forward and reverse back propagation (BP) neural network models (non-parametric models) have good performance in fitting training data, generalization ability and noise immunity. Furthermore, the BP neural network models fit with a higher accuracy than the hyperbolic tangent hysteresis models, while the later enjoy a simpler expression of the damping force which is relatively easier to implement in software.
Keywords magnetorheological damper; dynamic performance test; hyperbolic tangent hysteresis model; BP neural network model
Multidimensional Performance Limit States for Fragility Analyze of Plane Irregular Structure
HUANGXiaoning1,DUYongfeng1,2,LIHui1,2
(1.Institute of Earthquake Protection and Disaster Mitigation, Lanzhou University of Technology Lanzhou, 730050, China)
(2.Western Center of Disaster Mitigation in Civil Engineering of Ministry of Education, Lanzhou University of Technology Lanzhou, 730050, China)
Abstract Based on the introduction of the critical angle, a new method for multidimensional performance limit states is developed to analyze the structural fragility of plane irregular frame-shear-wall structures. First, the critical angle of seismic wave is determined using the wavelet transform in Matlab. Then, concerning the dependency of the limit states, the probability of exceedance can be calculated by adopting the inter-story drift and inter-story torsion angle as the quantitative indexes. The fragility curves are achieved under two dimensional performance limit states. Using this method to analyze the aforementioned structure, the fragility curves under four performance levels are obtained, which are normal operation, immediate occupancy, life safety, and collapse prevention. The results indicated that the critical angle of seismic wave has a significant impact on the performance of the plane irregular structures. In order to avoid overestimating seismic performance of plane irregular structures, inter-story drift and inter-story torsion angle should be simultaneously considered. Therefore, for plane irregular estimate, the analysis method of fragility under multidimensional performance limit states is more safe and reliable.
Keywords plane irregular structures; fragility analyze; multidimensional performance limit states; inter-story drift; inter-story torsion angle
Investigation on Gas Effect of Displacer for Free-Piston Stirling Engine
LIWei1,2,MOUJian1,2,HONGGuotong1
(1.Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing, 100190, China)
(2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing, 100049, China)
Abstract In order to have a deep understanding of the kinematical characteristics of the displacer of free-piston stirling engine, the effects of gas force, which is driven by the displacer only, is analyzed. And the running experiment of displacer individually is designed. During the course of the experiment a new calculation formula for natural frequency of displacer is proposed. In this paper, the gas force acting on the displacer is analyzed in the case of leading or lagging displacement of piston. And the acting mechanism of gas force is stated by means of rotation vector decomposition. The results show that a part of gas force is regarded as gas spring. The gas spring and the mechanical spring are parallelly arranged and the natural frequency of the system increases in the case of the pressure wave in advance or delaying the displacement of piston less than 90°. But the gas force is regarded as gas inertia force and the natural frequency of the system decreases in the case of the pressure wave in advance or delaying the displacement of piston greater than 90° but less than 180°. And the higher the temperature of the heat source, the smaller the natural frequency of the system. The accuracy of the effects of gas force and calculation formula for natural frequency are verified by an experimental text on a free-piston stirling engine which is designed by our laboratory.
Keywords stirling engine; free-piston; displacer; the effects of gas; natural frequency
Comprehensive Position Error of Delta Robot and Analysis of Its Coupling Characteristics
ZHENGKunming1,2,ZHANGQiuju1,2
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangnan University Wuxi, 214122, China)
(2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment & Technology Wuxi, 214122, China)
Abstract Taking Delta robot as the object of analysis, studying the position error model of the moving platform, and the coupling characteristic of the error source is analyzed. Using the position characteristic of driven arms, based on the method of geometry space vector, the mechanism error model of Delta robot is established; Using the principle of mathematical statistics and space vector as the basic, the joint clearance error model of Delta robot is derived; Based on finite element theory, on the basic of elastic dynamic model of Delta robot, the flexible error model is eatablished; Then, considering the three kinds of error source, the comprehensive position error model of Delta robot is established. Finally, by use of simulation software of Adams and Workbench, numerical calculation of Matlab and field experiment of FARO laser tracker, the correctness of comprehensive position error model is verified, and coupling characteristics of the error sources are analyzed, the relationship between position error and the axis's azimuth of system coordinate is elaborated. The results show that the error sources that affect the position error of the Delta robot's moving platform are not simply superimposed, but with obvious coupling properties, and the directional position error of the moving platform changes with the azimuth of the coordinate axis.
Keywords Delta robot; mechanism error model; clearance error model; flexible error model; comprehensive position error; coupling characteristics
Investigation on the Blade Tip Clearance Monitoring of Turbomachinery Based on the Pulse-Trigger Method
WANGWeimin,SHAOHuajin,CHENLifang,QUWei
(School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology Beijing, 100029, China)
Abstract Blade tip clearance (BTC) and blade vibration measuring are the principal tools for blade health monitoring (BHM), which can improve the efficiency and reliability of turbomachinery. In this paper, a BTC monitoring method based on pulse-trigger of eddy current sensor (ECS) is presented, in the light of the sub-Nyquist sampling caused by the limit of narrow-band, especially for the high linear velocity. The proposed method optimizes the static radial and circumferential calibration technology to obtain the sensitivity of ECS in the different relative location against the tip of blade and to obtain the function of impedance of the ECS that relates to the distance and the contact ratio of the ECS from the tip of blade. Combining blade tip timing (BTT) technology into BTC monitoring, this method calculated the contact ratio of the ECS from the blade, in order to obtain the accurate clearance depends on the function obtained before for all sampling points. Also, a BTC monitoring rig is established to validate the feasibility of this method under varying rotating speed. The results show that this method can solve the problem of sub-Nyquist sampling caused by the limit of narrow-band for ECS in the condition of high linear velocity. Compared with the location obtained by peak picking, the method presented in this paper can significantly improve the accuracy of BTC monitoring. This research can provide the basis for BTC active control and BHM based on ECS.
Keywords turbine blades; blade tip clearance(BTC) monitoring; pulse-trigger; optimize static calibration technology; eddy current sensor (ECS)
Fault Diagnosis and Simulation of Aircraft Air Conditioning System Based on FMEA
LIBingyue1,SUNJianhong1,LIUHaigang2,SUNZhi1,CHENQiang1
(1.College of Aerospace Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
(2.Shenyang Aircraft Design and Research Institute Shenyang, 110035, China)
Abstract In this paper, in order to ensure the safety and reliability of the aircraft conditioning system, the failure mode and effects analysis(FMEA) of the main parts of aircraft air conditioning system is carried out. The whole air conditioning is simulated by Matlab/Simulink, and the failure diagnosis criteria of the key parts of an air conditioning system are regulated. Then, the abnormal cabin temperature of the aircraft is taken as an example to demonstrate the fault tree analysis method (FTA). The results show that the failure of the turbine has the largest influence on the abnormal cabin temperature, which should be took into serious consideration when it comes to the work of design and maintenance.
Keywords fault simulation; fault tree analysis; failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA); aircraft air conditioning system; severity
Numerical Simulation and Study on Flow-Induced Noise During Automotive Throttle Quick-Opening Process
YANGShuai1,2,WEIYanan1,2,XUELiangjun3,CHANGGuofeng1,2
(1.New Energy Automotive Engineering Center, Tongji University Shanghai, 201804, China)
(2.School of Automotive Studies, Tongji University Shanghai, 201804, China)
(3.Qishuyan Locomotive Co., Ltd Qishuyan, 213011, China)
Abstract The influence of the throttle motion on the air flow-induced noise process is studied. By applying the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and computational aeroacoustics (CAA) coupling approach and the moving mesh technique, a 3-dimensional air transient flow and flow-induced noise process is simulated to realize the throttle quick-opening from the closed position to the fully open position. The principle of the air flow and flow-induced noise is analyzed when the throttle is opening at different rotation angle. At the beginning period of the throttle rotation, the vortex appears in the flow field behind the throttle, the pressure drops distinctly between the front and the back of the throttle, two flow-induced noise fields appear near the top and bottom position of the throttle and move towards the downstream and then merge gradually, the maximum value of the acoustic power level appears when the throttle rotation angle is opening near 40 degree, the flow-induced noise acoustic power level firstly increases and then decreases. With the opening angle increasing, the vortex is weaken and the value of pressure drop decreases between the two sides of the throttle. The time-frequency domain numerical simulation results fo the flow-induced noise show that during the throttle quick-opening process the flow-induced noise is mainly a kind of middle and low frequency broadband noise, the main part of the noise is frequency noise below about 100 Hz, the acoustic pressure is higher and does not reduce significantly with the increase of the distance between the measurement point and the throttle center. Reducing the low frequency noise plays a key role in the flow-induced noise control of the throttle.
Keywords throttle; flow-induced noise; transient flow; numerical simulation
Limit Cycle Oscillation of Subspan Oscillation for Two Bundled Conductors by Using Incremental Harmonic Balance Method
YUYangyang1,2,3,GUOHulun1,3,CAOShuqian1,3,LIUBin4,CHENYushu1,3,5
(1.Department of Mechanics, Tianjin University Tianjin, 300072, China)
(2.Tianjin University Renai College Tianjin, 301636, China)
(3.Tianjin Key Laboratory of Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Control Tianjin, 300072, China)
(4.China Electric Power Research Institute Beijing, 100192, China)
(5.School of Astronautics, Harbin Institute of Technology Harbin, 150001, China)
Abstract Subspan oscillation on bundled conductors is one of the most important failures of overhead transmission lines, which is due to the leeward conductor lying in the wake of the windward conductor. In this paper, considering the aerodynamic nonlinearities, a 2-DOF subspan oscillation dynamic model of the leeward conductor lying in the wake of the windward conductor is given firstly. And then, the incremental harmonic balance method (IHB) is used to derive high-order limit cycle oscillation of subspan oscillation system, and the first to the third harmonic responses of the limit cycle oscillation are obtained. Results show that subspan oscillation only exists in a certain range of wind velocity. Moreover, the higher order of the harmonic the weaker impact it is, and the first harmonic response agree with numerical results of Runge-Kutta well. Lastly, the influence of span and original position of the leeward conductor on subspan oscillations has been analyzed, which can provide the technical support for suppression or prevention subspan oscillation.
Keywords bundled conductors; subspan oscillation; limit cycle oscillation; incremental harmonic balance method
Fault Diagnosis Under Variable Conditions Based on Parameter Optimized Variational Mode Decomposition and Envelope Order Spectrum
JIANGZhanwei,ZHENGJinde,PANHaiyang,PANZiwei
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Anhui University of Technology Maanshan, 243032, China)
Abstract Based on the parameter optimized variational mode decomposition (POVMD) and envelope order spectrum, a new fault diagnosis method is proposed to extract the fault features of rolling bearing under variable speed condition. First, the vibration signal of rolling bearing is decomposed into several intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) by POVMD. Second, each IMF is resampled in the angular domain and transformed into stationary signals. Then, the Hilbert transform is used to estimate the envelope function of the resampled signals. The obtained envelope functionsare are analyzed using the order tracking technology and the fault feature information is read from the order spectrum. The comparisons show the superiority of POVMD over empirical mode decomposition by analyzing the simulation signals. Finally, the proposed fault diagnosis method for rolling bearing with variable speed is applied on the experimental data analysis and the results show that the propose method can effectively achieve the fault diagnosis of rolling bearing in variable speed.
Keywords variational mode decomposition; variable conditions; envelope order spectrum; rolling bearing; fault diagnosis
Study on the Stability of Two Dimensional Ultrasonic Vibration Milling System in Vertical Plane
ZHAOBo,ZHAOBinbin,FANKaiyang,ZHANGYuemin
(School of Mechanical and Power Engineering, Henan Polytechnic University Jiaozuo, 454000, China)
Abstract In order to study the stability of the two dimension ultrasonic vibration milling system in vertical plane, the stability model of a two-dimensional ultrasonic vibration milling in vertical plane is established. The stability of the two dimensional ultrasonic vibration milling is studied using the full discrete method. The stability of the system is obtained by numerical simulation using Matlab software. The results of chatter test for milling titanium alloy material show that the numerical simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results when the speed was 1 000~3 500 r/min. The correctness of the stability model of two dimensional ultrasonic vibration milling in vertical plane is verified. The stability of the system can be improved by applying two dimensional ultrasonic vibration in the vertical plane. The axial depth limit maximum of cut is increased by about 13.6%. The research fills up the blank of the two-dimensional ultrasonic vibration assisted milling stability study.
Keywords two dimensional ultrasonic vibration milling; full-discretization method; stability; lobe diagram
The vibration monitoring method is the main approach of condition monitoring for wind turbine transmission system. The vibration monitoring strategy and the process of each component′s vibration feature extraction of wind turbine transmission system are analyzed firstly, and the trend indicators of vibration feature such as sideband power factor (SBPF) and sideband energy ratio (SER) are introduced especially. Then, it is pointed out that the key to retrieve the huge economic losses caused by the fault of wind turbine transmission system is incipient fault prediction for wind turbine transmission system, and the generalization manifold learning-based incipient fault prediction method for wind turbine transmission system is introduced especially. Finally, the function and characters of the existing vibration monitoring system for wind turbine transmission system are analyzed including system architecture, data acquisition configuration and monitoring analysis methods. Furthermore, it is pointed out that big data-based predictive analytics and intelligent maintenance based on multi-source information fusion technique would be the important development trend of health management for wind turbine transmission system.
wind turbine transmission system; vibration monitoring; feature extraction; incipient fault prognosis; big data
10.16450/j.cnki.issn.1004-6801.2017.03.030
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51475148)
2016-06-29;
2016-11-05
TB115; TB552; TH113
赵波,男,1956年8月生,博士、教授、博士生导师。主要研究方向为先进制造技术、硬脆材料精密加工理论与装备等。曾发表《分离型纵-扭复合超声铣削的稳定性分析》(《兵工学报》2015年第36卷第7期)等论文。 E-mail:zhaob@hpu.edu.cn
Research Progress of Vibration Monitoring for Wind Turbine Transmission System
TANGBaoping,LUOLei,DENGLei,HANYan(The State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University Chongqing, 400030, China)

