低促性腺激素性性腺功能减退的患者中Prader睾丸测量器误差较大
王宇+王伟+季文+何薇+李延兵+廖志红


摘要:目的 睾丸体积的大小与其功能关系密切,关于Prader睾丸测量器的准确性有争议。本文在低促性腺激素性性腺功能减退(HH)的患者中,对比Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量睾丸体积的结果,以评估Prader睾丸测量器测量睾丸体积的准确性及其影响因素。方法 对27名低促性腺激素性性腺功能减退的男性患者(平均年龄25±5岁)进行性激素的治疗并长期随访,患者治疗前及每次3个月复诊都接受Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量睾丸体积,共得到87次测量结果,双侧睾丸一共174组数据。结果 Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量的睾丸平均体积分别为(7.5±3.6)ml、(3.0±2.1)ml。两种测量方法之间具有相关性(r=0.738,P<0.001)。但是Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积平均超过了超声测量结果的(4.5±2.7)ml,相当于超声测量结果的3.2倍。睪丸体积越小,Prader测量器测量结果的误差越大。结论 在HH患者中,使用Prader睾丸测量器测量睾丸体积的误差较大,临床上应仅作为参考。Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积超过实际体积。睾丸体积越大,Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积越接近实际体积。
关键词:低促性腺激素性性腺功能减退;Prader睾丸测量器;睾丸体积;超声测量
In Patients with Hypogonadotropin-induced Hypogonadism,the Prader Testis has a Greater Error
WANG Yu1,WANG Wei2,JI Wen3,HE Wei2,LI Yan-bing4,LIAO Zhi-hong4
(1.Department of Internal Medicine,General Hospital of Chinese people's Armed Police,Shenzhen 518000,Guangdong,China;
2.Department of Ultrasound,the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University,Guangzhou 510080,Guangdong,China;
3.Department of Endocrinology,Huzhou Central Hospital,Huzhou 313000,Zhejiang,China;
4.Department of Endocrinology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University,Guangzhou 510080,Guangdong,China)
Abstract:Objective The relationship between the size of testicular volume and function closely,controversial about the accuracy Prader orchidometer. In hypogonadotropic hypogonadism(HH)in patients with contrast Prader orchidometer and ultrasound two methods of measurement of testicular volume results in accuracy and influencing factors of evaluation of Prader orchidometer the measurement of testicular volume.Methods 27 male patients with lower gonadotropin gonadal hormone of hypogonadism(mean age 25±5 years)for the treatment of sex hormone and long-term follow-up of patients before treatment and every 3 months to accept Prader orchidometer and two ultrasonic method for the measurement of testicular volume,a total of 87 results a total of 174 sets of data,bilateral testes.Results Prader orchidometer and ultrasound measurement of two methods respectively.The average volume of testis(7.5±3.6)ml,(3.0±2.1)ml.Two measurement with the correlation between methods (r=0.738,P<0.001).But Prader is measured by the measurement of testicular volume averaged over the ultrasonic measurement results(4.5±2.7)ml,equivalent to 3.2 times the ultrasonic measurement results.The testicular volume is small,the error of measurement results of Prader measurement instrument is greater.Conclusion In the HH patients,the use of Prader testicular test instrument to measure the testicular volume error is relatively large,should only be used as a reference.The testis volume measured by the Prader gauge exceeds the actual volume.The greater the testis volume,the closer the test volume of the testis to the actual volume.
Key words:Hypogonadotropin hypogonadism;Prader testis;Testicular volume;Ultrasonography
睾丸作为男性的生殖器官,起着产生精子及睾酮的重要作用。睾丸体积的近80%~90%由生精小管和生殖细胞构成[1-2],睾丸的体积大小与其功能有着密切的关系[3]。临床工作中常常需要测量患者的睾丸体积大小,以评估患者的发育情况,特别对于第二性征发育不全患者的疗效评估有重要意义。
为准确、方便地测量睾丸大小,很多测量方法都被尝试过,包括普通尺子、游标卡尺、睾丸测量器、超声等等[4-5]。根据研究发现,超声测量结果最接近睾丸实际体积[6-7],但操作不够便捷,在门诊或临床的应用受到限制。目前,国内外使用较多的测量方法为Prader睾丸测量器,其操作方便快捷,但是它的准确性仍存在争议,多项研究发现其测量的睾丸体积不同程度地超过实际体积[7-8]。因此本研究的目的是在低促性腺激素性性腺功能减退(hypogonadotropic hypogonadism,缩写HH)的患者中,通过对比Prader睾丸测量器与超声两种测量方法测量睾丸体积的差异,评估Prader睾丸测量器测量睾丸体积的准确性及可靠性,探索Prader睾丸测量器在HH临床上的使用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料 本研究对27例HH的男性患者进行性激素的治疗,并于每3个月返院复诊。每位患者治疗前及每次复诊时都需接受Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量睾丸体积。
1.2入排标准 本研究纳入的患者为就诊于我院的第二性征发育不全的男性患者,并同意接受Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量睾丸体积。排除标准为:有睾丸疼痛、阴囊水肿、隐睾及不同意接受检查的患者。
1.3方法 Prader睾丸测量器是由不同体积的串珠组成。测量时,患者平卧于温暖的房间内,由一名经验丰富的主治医师专门负责测量。医生用双手分离出睾丸轮廓,避免挤压睾丸,同时依次跟不同体积的Prader串珠比较,根据串珠的体积记录下测量的睾丸体积。超声测量睾丸体积是由另一位经验丰富的超声医生进行测量,使用超声测量出睾丸的长、宽、高三个径线的长度,睾丸体积由公式“0.71×长×宽×高”计算得出。
1.4统计学处理 统计分析使用SPSS 13.0软件完成。定量资料用(x±s)表示,两样本定量资料间的比较采用t检验,相关性检验采用Pearson相关分析,对一个自变量的回归分析采用简单回归分析并进行多种曲线拟合,对两个自变量的回归分析采用多重线性回归。
2 结果
本研究有27例第二性征發育不全的男性患者进行性激素的治疗并接受长期随访,共得到87次测量结果,双侧睾丸一共有174组数据。
入组患者的年龄是16~34岁,平均(25±5)岁。这些患者至少有治疗前基线数据,最长随访18个月,随访时间平均为(9±5)个月。
入组患者Prader测量器测得睾丸体积为1~17 ml,平均体积为(7.5±3.6)ml,超声测得睾丸体积为0.1~9.7 ml,平均体积为(3.0±2.1)ml。Prader测量器与超声测量值进行两样本的配对t检验得到,Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积平均超过了超声测量结果的(4.5±2.7)ml(P<0.001),相当于超声测量结果的3.2倍。但是对两种测量方法得到的测量值进行Pearson相关性检验,得到相关系数为0.738,P<0.001,说明两者具有相关性。
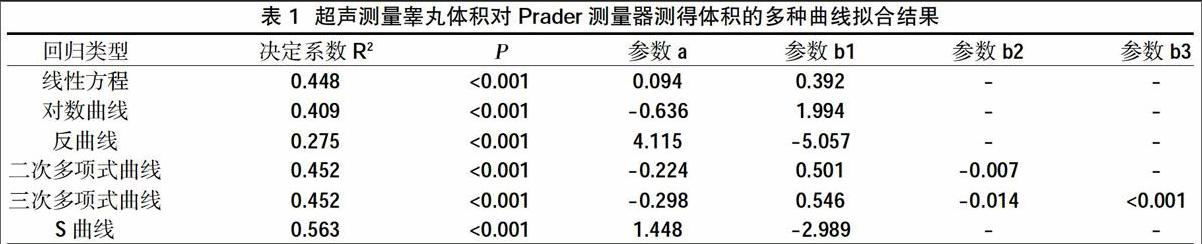
为探讨可否用Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积预测超声测量值,将Prader测量器测得睾丸体积定义为自变量,超声测得睾丸体积为因变量,进行回归分析,结果见表1及图1。结果显示多种曲线拟合的决定系数最高仅为0.563,实际较实用的线性方程是:超声体积(ml)=0.392×Prader测量器测得体积(ml)+0.094,其决定系数仅为0.448。
为探讨睾丸大小本身对Prader测量器测量误差是否有影响,根据超声测量的睾丸长径结果,将测量值分组统计,见表2。结果显示睾丸体积越小,Prader测量器测量体积相当于超声测量体积的倍数越大,Prader测量器测量的误差越大。
3 讨论
目前我们无法获得患者实际的睾丸体积,但有研究发现常用的超声测量睾丸体积计算公式有0.52×长×宽×高、0.52×长×宽2,以及 0.71×长×宽×高,其中最后一个公式的计算结果最接近实际体积[6,9,10]。因此,我们暂且将超声测得睾丸体积看做实际睾丸体积通过对比Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量睾丸体积的结果,探索临床上可否使用Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积预测实际睾丸体积。
国外多项研究结果显示[7,11,12],Prader睾丸测量计与超声两种方法测量的睾丸体积的相关性波动于0.700~0.956不等。Mbaeri等人[8]对62例前列腺癌的患者行切除术前使用Prader测量器测量睾丸体积,切除后的睾丸放入水中得到实际睾丸体积,对比这121组数据,得到结论为Prader测量器测得睾丸体积比实际体积大,超出约2.66±2.37 ml(25.1%)。Sakamoto H等人[7]将使用Prader睾丸测量器、超声测量睾丸体积的结果与实际体积进行比较,发现使用超声测量0.71×长×宽×高这个公式计算得出的睾丸体积最接近实际体积,仅仅超出实际的体积0.80 ml(7.42%),而Prader睾丸测量器测得的睾丸体积与实际体积相差最大,约超出6.68 ml(81.7%)。
本研究174组数据统计结果显示,Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量的睾丸平均体积分别为(7.5±3.6)ml、(3.0±2.1)ml,虽然两种测量方法之间具有相关性(r=0.738,P<0.001),但是Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积平均超过了超声测量结果的(4.5±2.7)ml,相当于超声测量结果的3.2倍,提示使用Prader睾丸测量器测量睾丸体积的误差明显较大。
臨床工作中,我们希望可以通过使用简便快捷的Prader测量器测量的睾丸体积预测实际睾丸体积。因此,本研究对Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积及超声测得的睾丸体积进行回归分析,结果显示多种曲线拟合效果都不理想,线性方程的决定系数仅为0.448,提示Prader测量器测得体积对超声体积的影响只有44.8%。
针对Prader测量器测得睾丸体积误差较大的原因,Diamond等人[13]的研究发现Prader测量器测量误差较大的影响因素有未能分离附睾对测量体积的影响,及操作者技术水平差异。另外,Sakamoto等人[12]的研究发现睾丸体积越小,使用Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积比超声测量结果超出越多。本研究根据超声测量的睾丸长径结果,将测量值分组统计,结果显示睾丸体积越小,Prader测量器测量体积相当于超声测量体积的倍数越大,Prader测量器测量的误差越大。
Sakamoto等人[14]通过使用Prader睾丸测量器及超声两种方法测量397名不育症患者的睾丸体积,并联合他们血中性激素水平、精液量、精子密度、精子总数、精子活率等睾丸功能指标,发现如果要达到正常或接近正常的睾丸功能,Prader测量器测得的睾丸体积需在30~35 ml,超声测得的睾丸体积需20 ml。可见Prader测量器和超声两种方法测量的睾丸体积数值之间具有较大的差异。临床上,使用Prader测量器测量睾丸体积仅能作为参考或随访中的疗效监测指标。对于需要明确睾丸实际体积的情况,不宜使用Prader测量器测量,应进行超声测量。Sakamoto等人提出的两种测量方法的具体参考范围尚待推广和统一,但同时提示我们,今后可进行多中心大样本量的研究,以制定Prader测量器和超声两种测量方法的不同睾丸体积参考范围及相互换算方法,最大程度地方便患者、提升临床诊断水平。
参考文献:
[1]Tanagho E.Smith's General Urology,Seventeenth Edition[J].McGraw-Hill,2007.
[2]Walsh,Patrick C.Campbell's urology[M].Saunders,2002.
[3]Setchell B P,Breed W G.Anatomy,Vasculature,and Innervation of the Male Reproductive Tract[J].Elsevier,2006.
[4]Costabile R A,Skoog S,Radowich M.Testicular volume assessment in the adolescent with a varicocele[J].Journal of Urology,1992,147(147):1348-1350.
[5]KojiShiraishi,HiroshiTakihara,YoriakiKamiryo,et al.Usefulness and limitation of punched-out orchidometer in testicular volume measurement[J].Asian Journal of Andrology,2005,7(1):77-80.
[6]Paltiel H J,Diamond D A,Di C J,et al.Testicular volume:comparison of orchidometer and US measurements in dogs[J].Radiology,2002,222(1):114.
[7]Sakamoto H,Saito K,Oohta M,et al.Testicular volume measurement: comparison of ultrasonography,orchidometry,and water displacement[J]. Urology,2007,69(1):152-157.
[8]Mbaeri T U,Orakwe J C,Nwofor A M,et al.Accuracy of Prader orchidometer in measuring testicular volume[J].Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice,2013,16(16):348-351.
[9]Pilatz A,Rusz A,Wagenlehner F,et al.Reference values for testicular volume,epididymal head size and peak systolic velocity of the testicular artery in adult males measured by ultrasonography[J].2012,34(4):349.
[10]Hsieh M L,Huang S T,Huang H C,et al.The reliability of ultrasonographic measurements for testicular volume assessment:comparison of three common formulas with true testicular volume[J].Asian Journal of Andrology,2009,11(2):261-265.
[11]Goede J,Hack W W,Sijstermans K,et al.Normative Values for Testicular Volume Measured by Ultrasonography in a Normal Population from Infancy to Adolescence[J].Hormone Research in Paediatrics,2011, 76(1):56-64.
[12]Sakamoto H,Saito K,Ogawa Y,et al.Testicular Volume Measurements Using Prader Orchidometer Versus Ultrasonography in Patients with Infertility[J].Urology,2007,69(1):158-62.
[13]Diamond D A,Paltiel H J,Dicanzio J,et al.Comparative assessment of pediatric testicular volume:orchidometer versus ultrasound[J].Journal of Urology,2000,164(3 Pt 2):1111.
[14]Sakamoto H,Ogawa Y,Yoshida H.Relationship between testicular volume and testicular function:comparison of the Prader orchidometric and ultrasonographic measurements in patients with infertility[J].Asian Journal of Andrology,2008,10(2):319-324.

