脑积水合并颅骨缺损同期手术与分期手术的效果比较
徐才邦
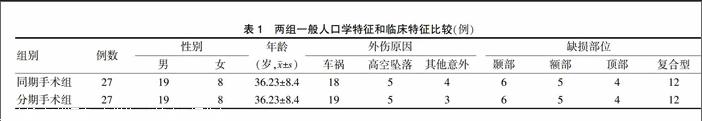
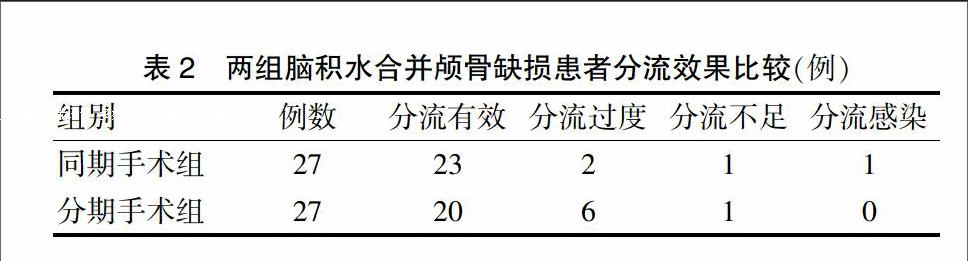
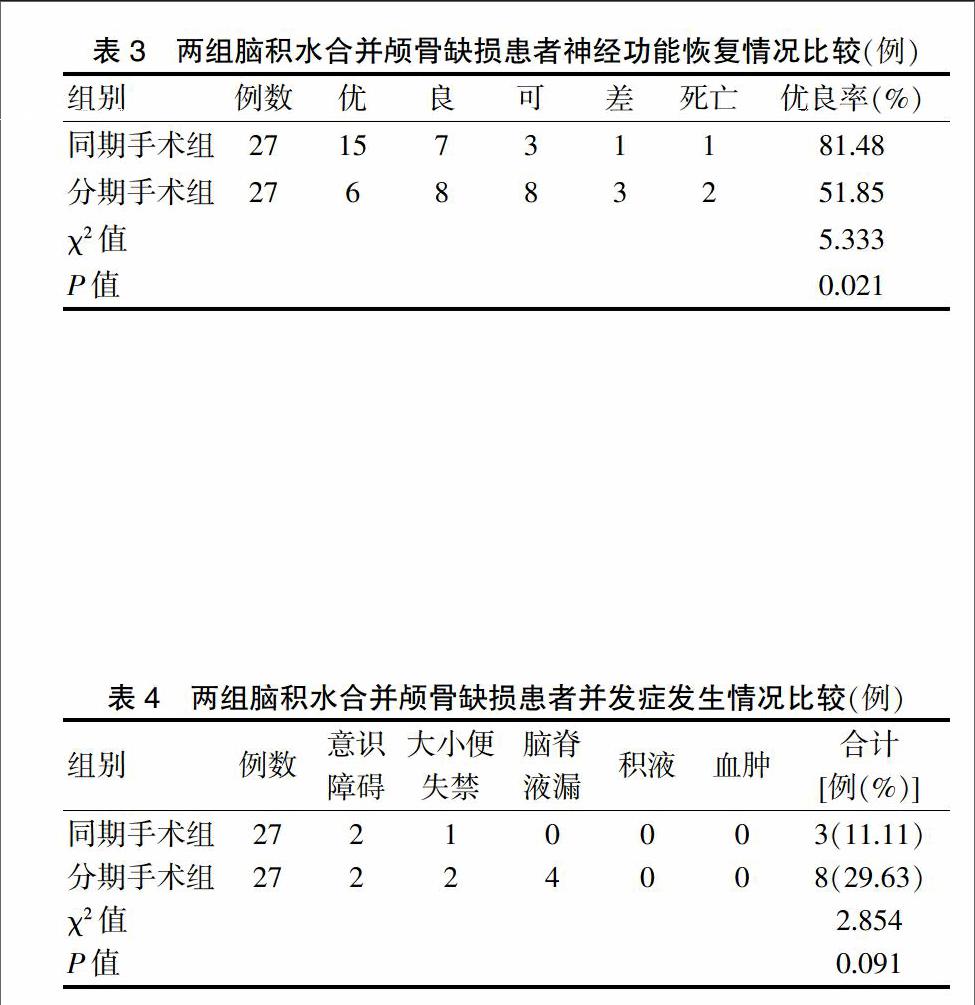
[摘要] 目的 比較分析脑积水合并颅骨缺损同期手术与分期手术的效果。 方法 选择2012年2月~2014年1月广西壮族自治区江滨医院收治的54例脑积水合并颅骨缺损患者,根据随机数字表法将其随机分为同期手术组(27例)和分期手术组(27例),同期手术组同期行脑室-腹腔分流术和颅骨修补术,分期手术组在脑室-腹腔分流术后4周~7个月后行颅骨修补术,比较两组患者分流效果、神经功能恢复情况、并发症发生率、生活质量、医疗费用、再次手术情况。 结果 两组分流效果比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);同期手术组神经功能恢复的优良率显著高于分期手术组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);同期手术组并发症发生率为11.11%,分期手术组为29.63%,两组比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);同期手术组健康调查简表(SF-36)中的心理健康和总体健康评分均显著高于分期手术组(P < 0.05);同期手术组的医疗费用显著低于分期手术组(P < 0.05);两组均有1例患者行再次手术。 结论 虽然同期行脑室-腹腔分流术和颅骨修补术在脑积水合并颅骨缺损中的分流效果与分期手术无异,但它在神经功能恢复、并发症、患者心理健康和医疗费用上更具优势,值得临床优先考虑使用。
[关键词] 脑积水;颅骨缺损;脑室-腹腔分流术;颅骨修补术;同期手术;分期手术
[中图分类号] R742.7 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2016)12(b)-0076-04
Effect comparison of synchronous operation and asynchronous operation for hydrocephalus combined with skull defect
XU Caibang
Department of Neurosurgery, Jiangbin Hospital, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530021, China
[Abstract] Objective To compare and analyze the effects of synchronous operation and asynchronous operation for hydrocephalus combined with skull defect. Methods Fifty-four patients with hydrocephalus combined with skull defect admitted to Jiangbin Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region from February 2012 to January 2014 were selected and randomly divided into synchronous operation group (27 cases) and asynchronous operation group (27 cases) by random number table method. The synchronous operation group was taken ventriculo peritoneal shunt and skull prosthesis at the same time, while the asynchronous operation group was taken skull prosthesis at 4 weeks to 7 months after ventriculo peritoneal shunt. The shunt effect, conditions of nerve function recovery, incidence of complications, quality of life , medical costs, conditions of reoperation in the two groups were compared. Results The difference of shunt effect between the two groups was not statistically significant (P > 0.05); the excellent rate of nerve function recovery in the synchronous operation group was higher than that of asynchronous operation group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); the incidence of complications in the synchronous operation group was 11.11%, which of asynchronous operation group was 29.63%, the difference between the two groups was not statistically significant (P > 0.05); the scores of psychological health and general health of the MOS item short from health survey (SF-36) in the synchronous operation group were all higher than those of asynchronous operation group (P < 0.05); the medical cost of synchronous operation group was significantly lower than that of asynchronous operation group (P < 0.05); both groups had one case of reoperation. Conclusion The shunt effect of ventriculo peritoneal shunt and skull prosthesis at the same time for hydrocephalus combined with skull defect is similar to that of asynchronous operation, but it has more advantages in nerve function recovery, complications, psychological health and medical costs, which is worthy of clinical priority use.

