生物沸石薄层覆盖削减亚热带水源水库氮负荷*
周真明,刘啟迪,刘 彤,黄华山,马红芳,曾庆玲,苑宝玲
(华侨大学土木工程学院,厦门 361021)
生物沸石薄层覆盖削减亚热带水源水库氮负荷*
周真明,刘啟迪,刘 彤,黄华山,马红芳,曾庆玲,苑宝玲
(华侨大学土木工程学院,厦门 361021)
以福建泉州水源地山美水库和惠女水库的表层底泥和上覆水为研究对象,室内静态模拟试验研究了生物沸石薄层覆盖削减水源水库氮负荷的效果及可行性,探讨了上覆水体溶解氧(DO)浓度对削减氮负荷的影响,分析了削减氮负荷的作用机理. 结果表明,覆盖强度为1 kg/m2的生物沸石覆盖(厚度约1 mm)对上覆水中总氮的削减率为58.89%~65.75%,对底泥中总氮的削减率为10.39%~13.08%,对底泥中铵态氮的削减率为32.35%~44.56%,对底泥中有机氮的削减率为8.41%~11.04%;对于以硝态氮为主要形态氮的上覆水体,DO浓度越低,越有利于高效菌脱氮;可见,生物沸石薄层覆盖能有效削减水源水库氮负荷,利用生物沸石薄层覆盖技术削减水源水库氮负荷是可行的,但需要进一步研究水源水库底泥生物沸石薄层覆盖修复过程中氮的迁移转化机制.
底泥;薄层覆盖;氮;生物沸石;水源水库
水体富营养化是全球重要水质难题之一[1]. 氮和磷是水体富营养化的主要限制因子,控制水体氮和磷浓度能有效抑制水体富营养化[2]. 水源水库内源(底泥)氮、磷释放,是水库氮、磷主要来源途径之一,在外源氮和磷得到有效控制的条件下,削减底泥氮、磷释放将成为控制水源水库富营养化的有效方法之一[3]. 当前,削减底泥氮、磷释放的主要方法有清淤法和原位覆盖法[4],由于清淤法存在费用高、底泥再悬浮、运输和处置过程存在二次污染、破坏水底生态环境等不足[5],使得原位覆盖法成为国内外学者研究热点,并在欧美、日本等地得到广泛工程应用[4]. 原位覆盖法由传统物理厚层覆盖[6-7]发展到当今活性薄层覆盖[8-12],覆盖层作用机理也从物理掩蔽[6-7]发展到物理化学吸附及生物化学转化[8-15]. 目前研究和应用中,针对水源水库的污染底泥覆盖材料主要有改性沸石的磷钝化剂(Z2G1)[10, 16]和镧改性膨润土(锁磷剂phoslock©)[12, 17-18];实验室研究表明[16],Z2G1覆盖不仅能完全抑制底泥氮和磷释放,而且还削减了上覆水中氮和磷,但在新西兰Okaro水库实际应用中表明,投加0.35 kg/m2的Z2G1后,水库中氮、磷负荷削减不明显[10],有待进一步开发研究. 锁磷剂phoslock©是澳洲工业科学研究协会于1990年研发的,于2002年商品化的,到目前为止,锁磷剂广泛应用于澳洲、欧洲、美国、加拿大、新西兰等水库和湖泊[18],大规模应用案例超过120处,但锁磷剂主要针对削减水源水库磷负荷,针对削减水源水库氮负荷的底泥原位覆盖法研究不多,对底泥不同形态氮削减效果鲜见报道.
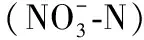

1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料


表1 上覆水和底泥间隙水的水质指标*
*ND表示低于检测限值.


表2 底泥物理化学性质及矿物成份
试验所用的生物沸石是将天然斜发沸石浸置在由2株高效异养硝化细菌(WGX10和WGX18,均为芽孢杆菌属,Bacillussp.)和2株高效好氧反硝化菌(HF3和HF7,均为不动杆菌属,Acinetobactersp.)组成的混合菌液中,通过连续曝气挂膜方法制备而成;4株菌的生理生化特性及生物沸石制备过程详见参考文献[13, 22].
1.2 试验装置与方法
试验在容积为10 L、直径为200 mm的广口玻璃瓶中进行;上覆水水深为20 cm,底泥厚度为5 cm,生物沸石的覆盖强度为1 kg/m2(覆盖厚度约1 mm).
试验共有16个广口玻璃瓶,分为8组,每组2个平行,编号为1#~8#,其中,1#为山美水库底泥,无覆盖,广口瓶敞开,命名为“SM-NC”;2#为山美水库底泥,生物沸石覆盖,广口瓶敞开,命名为“SM-C”;3#为山美水库底泥,无覆盖,广口瓶密封,密封前,先将加入瓶中的上覆水充N2,使其DO浓度<0.1 mg/L,然后加入玻璃瓶中,再充N2,使玻璃瓶中上覆水DO浓度<0.1 mg/L(下同),命名为“SM-NC-A”;4#为山美水库底泥,生物沸石覆盖,广口瓶密封,命名为“SM-C-A”;5#为惠女水库底泥,无覆盖,广口瓶敞开,命名为“HN-NC”;6#为惠女水库底泥,生物沸石覆盖,广口瓶敞开,命名为“HN-C”;7#为惠女水库底泥,无覆盖,广口瓶密封,命名为“HN-NC-A”;8#为惠女水库底泥,生物沸石覆盖,广口瓶密封,命名为“HN-C-A”.


1.3 测定方法


1.4 数据处理
上覆水体和底泥中不同形态氮削减率(P)的计算公式为:
(1)
式中,CCi为取样时生物沸石覆盖系统上覆水或底泥中不同形态氮浓度(mg/L或mg/kg);CNCi为取样时未覆盖系统上覆水或底泥中不同形态氮浓度(mg/L或mg/kg);i为取样次数.
采用Excel软件对生物沸石覆盖系统与未覆盖系统之间削减氮污染物效果的差异进行方差分析.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 削减上覆水体中氮负荷的能力



图1 山美水库(a)和惠女水库(b)各系统上覆水中浓度ü Reservoir(b)
SM-C系统对TN的削减率为37.38%~80.28%,平均值为58.89%;SM-C-A系统对TN的削减率为39.03%~75.06%,平均值为62.22%;HN-C系统对TN的削减率为52.96%~88.04%,平均值为65.75%;HN-C-A系统对TN的削减率为28.33%~78.92%,平均值为62.64%(图2). 方差分析表明,SM-NC和SM-C、SM-NC-A和SM-C-A、HN-NC和HN-C、HN-NC-A和HN-C-A系统中TN浓度均存在明显差异(P<0.01),可见,在不同实验条件下,生物沸石覆盖均能有效削减上覆水中氮负荷,说明通过生物沸石覆盖削减水源水库氮负荷是可行的.

图2 山美水库(a)和惠女水库(b)各系统上覆水中TN浓度Fig.2 TN concentration of overlying water in each system from Shanmei Reservoir(a) and Huinü Reservoir(b)
2.2 削减底泥中氮负荷的能力


表3 试验前后各系统底泥中不同形态氮含量
2.3 上覆水体DO浓度对削减氮负荷效果的影响

2.4 削减氮负荷的作用机理分析



2.5 野外原位应用时生物沸石覆盖厚度讨论
污染底泥原位生物沸石薄层覆盖技术在野外原位应用时,存在的实际问题有:1)薄层覆盖厚度太小,实际投加时,很难均匀覆盖,会有部分底泥表面未被生物沸石覆盖,影响生物沸石覆盖削减氮负荷效果,例如Özkundakci等[11]开发了一种以沸石改性的磷钝化剂(Z2G1或Aqual-PTM),以Z2G1为活性层覆盖材料原位控制沉积物氮和磷释放,富营养化Okaro湖实际应用结果表明:投加Z2G1后,湖泊中氮、磷负荷降低不明显,归因于Z2G1覆盖不均匀(Z2G1堆积密度为2 g/cm3,覆盖强度为0.35 kg/m2,水下摄像机显示实际覆盖强度为0.115~1.52 kg/m2),且部分沉积物表层未被覆盖;2)若水下底泥有机腐殖质较多,底泥表层较为松散,生物沸石也会容易沉入表层浮泥中,减弱生物沸石覆盖削减氮负荷的效果;3)加上野外风浪扰动,生物沸石薄层覆盖层很难完全阻止底泥再悬浮. 因此,建议通过如下措施来消除或缓解上述问题:1)若底泥表层浮泥较多,可先通过清淤方式将表层浮泥清除掉,或先覆盖5~10 cm厚度的干净沙子,再覆盖生物沸石;2)在经济条件允许情况下,适当增加生物沸石覆盖厚度,如2~5 mm;3)采用多层覆盖方式,即下层覆盖沙子,中层覆盖生物沸石,上层覆盖沙子.
3 结论

3)水源水库底泥生物沸石薄层覆盖修复过程中氮迁移转化机制需要进一步试验研究,可借助于微生物分子生态学技术及氮平衡原理讨论分析,同时需要考察其他因素的影响,如碳源、上覆水氮负荷等.
[1] Lürling M, Mackay E, Reitzel Ketal. Editorial—A critical perspective on geo-engineering for eutrophication management in lakes.WaterResearch, 2016, 97: 1-10.
[2] Lewis WM,Wurtsbaugh WA, Paerl HW. Rationale of control of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus to reduce eutrophication of inland waters.EnvironmentalScience&Technology, 2011, 45: 10300-10305.
[3] Zhong Jicheng, Liu Guofeng, Fan Chengxinetal. Environmental effect of sediment dredging in lake (I): The role of sediment dredging in reducing internal phosphorus release.JLakeSci, 2009, 21(1): 84-93. DOI:10.18307/2009.0111. [钟继承, 刘国锋, 范成新等. 湖泊底泥疏浚环境效应:I. 内源磷释放控制作用. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(1): 84-93.]
[4] Förstner U, Apit SE. Sediment remediation: U.S. focus on capping and monitored natural recovery. Fourth international conference on remediation of contaminated sediment.JournalofSoilsandSediments, 2007, 7: 351-358.
[5] Perelo LW. Review:Insituand bioremediation of organic ollutants in aquatic sediments.JournalofHazardousMaterials, 2010, 177: 81-89.
[6] Kim G, Jung W. Role of sand capping in phosphorus release from sediment.JournalofCivilEngineering, 2010, 14(6): 815-821.
[7] Lampert D, Sarchet WV, Reible DDetal. Assessing the effectiveness of thin-layer sand caps for contaminated sediment management through passive sampling.EnvironmentalScience&Technology, 2011, 45(19): 8437-8443.
[8] Jacobs PH, Förstner U. Concept of subaqueous capping of contaminated sediments with active barrier system (ABS) using natural and modified zeolite.WaterResearch, 1999, 33(9): 2083-2087.
[9] Berg U, Neumann T, Donnert Detal. Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes-efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilize phosphorus.AppliedGeochemistry, 2004, 19(11): 1759-1771.
[10] Lin JW, Zhan YH, Zhu ZL. Evaluation of sediment capping with active barrier system (ABS) using calcite/zeolite mixtures to simultaneously manage phosphorus and ammonium release.ScienceoftheTotalEnvironment, 2011, 409: 638-646.
[11] Özkundakci D, Hamilton DP, Gibbs MM. Hypolimnetic phosphorus and nitrogen dynamics in a small, eutrophic lake with a seasonally anoxic hypolimnion.Hydrobiologia, 2011, 661: 5-20.
[12] Meis S, Spears BM, Maberly SCetal. Sediment amendment with phoslock®in Clatto reservoir (Dundee, UK): Investigating changes in sediment elemental composition and phosphorus fractionation.JournalofEnvironmentalManagement, 2012, 93(1): 185-193.
[13] Huang TL, Zhou ZM, Xu JLetal. Biozeolite capping for reducing nitrogen load of the ancient canal in Yangzhou City.WaterScienceandTechnology, 2012, 66 (2): 336-344.
[14] Yin HB, Kong M. Reduction of sediment internal P-loading from eutrophic lakes using thermally modified calcium-richattapulgite-based thin-layer cap.JournalofEnvironmentalManagement, 2015, 15: 178-185.
[15] Yang MJ, Lin JW, Zhan YHetal. Immobilization of phosphorus from water and sediment using zirconium-modified zeolites.EnvironmentalScienceandPollutionResearch, 2015, 22(5): 3606-3619.
[16] Gibbs M,Özkundakci D. Effects of a modified zeolite on P and N processes and fluxes across the lake sediment-water interface using core incubations.Hydrobiologia, 2011, 661: 21-35.
[17] Meis S, Spears BM, Maberly SCetal. Assessing the mode of action of Phoslock®in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (Loch Flemington, UK).WaterResearch, 2013, 47(13): 4460-4473.
[18] Dithmer L, Nielsen UG, Lürling Metal. Responses in sediment phosphorus and lanthanum concentrations and composition across 10 lakes following applications of lanthanum modified bentonite.WaterResearch, 2016, 97: 101-110.
[19] Huang TL, Zhou ZM, Su JFetal. Nitrogen reduction in eutrophic landscape river using bioactive multilayer capping (BMC) with biozeolite and sand.JournalofSoilsandSediments, 2013, 13(7): 1309-1317.
[20] Zhou ZM, Huang TL, Yuan BLetal. Remediation of nitrogen-contaminated sediment using bioreactive, thin-layer capping with biozeolite.Soil&SedimentContamination, 2016, 25(1): 89-100.
[21] Zhou ZM, Huang TL, Yuan BL. Nitrogen reduction using bioreactive thin-layer capping (BTC) with biozeolite: A field experiment in a eutrophic river.JournalofEnvironmentalSciences, 2016, 42: 119-125.
[22] Zhou Zhenming.Insituremediation of contaminated sediment using combined biological and physicochemical technology in the urban rivers and lakes[Dissertation]. Xi′an: Xi′an University of Architecture & Technology, 2013.[周真明. 城市河湖污染底泥原位生物/物化组合修复技术研究[学位论文]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2013.]
[23] “Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method” editorial board of State Environmental Protection Administration of China ed. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater: fourth edition. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. [国家环境保护总局《水和废水监测分析方法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法: 第4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002.]
[24] Agricultural chemical professional committee of soil science society of China ed. Soil and agricultural chemistry general analysis. Beijing: Science Press, 1983.[中国土壤学会农业化学专业委员会. 土壤农业化学常规分析方法. 北京: 科学出版社, 1983.]
[25] Jin Xingcan, Tu Qingying eds. Eutrophication investigation specification of lakes: 2th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990.[金相灿, 屠清瑛. 湖泊富营养化调查规范: 第2版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.]
[26] Bao Shidan ed. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis: 3th ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2005.[鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析: 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005.]
[27] Sha Qian, He Jun, Zhang Weihaoetal. Nitrogen release from sediments in different types of urban lakes.EnvironmentalScience&Technology, 2013, 36(4): 89-91.[沙茜, 何君, 张维昊等. 不同类型湖泊沉积物中氮释放规律研究. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(4): 89-91.]
[28] Jung JY, Chung YC, Shin HSetal. Enhanced ammonia nitrogen removal using consistent biological regeneration and ammonium exchange of zeolite in modified SBR process.WaterResearch, 2004, 38: 347-354.
[29] Wei YX, Ye ZF, Wang YLetal. Enhanced ammonia nitrogen removal using consistent ammonium exchange of modified zeolite and biological regeneration in a sequencing batch reactor process.EnvironmentalTechnology, 2011, 32(12): 1337-1343.
Thin-layer capping with biozeolite for nitrogen load reduction in the water-supply source reservoirs, subtropical China
ZHOU Zhenming, LIU Qidi, LIU Tong, HUANG Huashan, MA Hongfang, ZENG Qingling & YUAN Baoling
(CollegeofCivilEngineering,HuaqiaoUniversity,Xiamen361021,P.R.China)
In this study, samples were collected from overlying water and surface sediment in Shanmei Reservoir and Huinü Reservoir in Quanzhou City, Fujian Province. The efficiency of nitrogen load reduction by thin-layer capping with biozeolite in the source water reservoirs was investigated through a series of laboratory-scale static simulating experiments. The effect of dissolve oxygen concentration in overlying water on reducing nitrogen load was discussed and the mechanism to reduce nitrogen load by thin-layer capping with biozeolite was also explored. The results showed that the reduction efficiency of total nitrogen in overlying water ranged from 58.89% to 65.75% by thin-layer capping with biozeolite at a dose rate of 1 kg/m2(the thickness of 1 mm), and the reduction efficiencies of total nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen and organic nitrogen in sediments were in the range of 10.39%-13.08%, 32.35%-44.56% and 8.41%-11.04%, respectively. To overlying water of the main form of nitrate, the lower the dissolve oxygen concentration of overlying water, the better the efficiency of biological denitrogenation by high efficient bacteria. Therefore, thin-layer capping with biozeolite is efficient and feasible to reduce nitrogen load in the source water reservoirs. However, it is urgent to understand the mechanisms of nitrogen transportation and transformation in remediation process of sediment using thin-layer capping with biozeolite.
Sediment; thin-layer capping; nitrogen; biozeolite; water-supply source reservoir
*国家自然科学基金项目(51408243)、福建省自然科学基金项目(2015J01213)、福建省科技计划对外合作重点项目(2014I0013)、中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金项目(11QZR07)和华侨大学中青年教师科研提升资助计划项目(ZQN-PY313)联合资助. 2016-03-09收稿;2016-08-08收修改稿. 周真明(1981~),男,博士,副教授;E-mail: zhenming@hqu.edu.cn.

