慢性病防治
慢性病防治
·编者按·
随着我国社会经济的迅速发展,居民生活质量的不断提高,城市化、工业化、老龄化等进程不断推进,我国人群的疾病谱和死因谱发生了重大变化。《中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2015 年)》指出,以糖尿病、心脑血管疾病、癌症及慢性呼吸系统疾病等为代表的慢性非传染性疾病(以下简称慢性病)的患病率逐年上升,已成为威胁我国居民健康的“头号公敌”。慢性病由于其发病率高、死亡率高、知晓率低、控制率低,并且病因复杂、病程长,常需长期甚至终身治疗,对人群健康影响显著,社会负担增加明显,严重吞噬着我国经济发展的成果。因此,加强对慢性病的防控显得尤为重要,这不仅是我国重要的公共卫生问题,也是当前世界面临的重大健康威胁。
本专题得到专家潘安教授(华中科技大学公共卫生学院)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至 2017 年 2 月 20 日,中国知网(CNKI)和 Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“慢性病(chronic diseases)”“防治(prevention and treatment)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为 1038 条与 13084 条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“慢性病(chronic diseases)”“防治(prevention and treatment)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“慢性病(chronic diseases)”“防治(prevention and treatment)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下
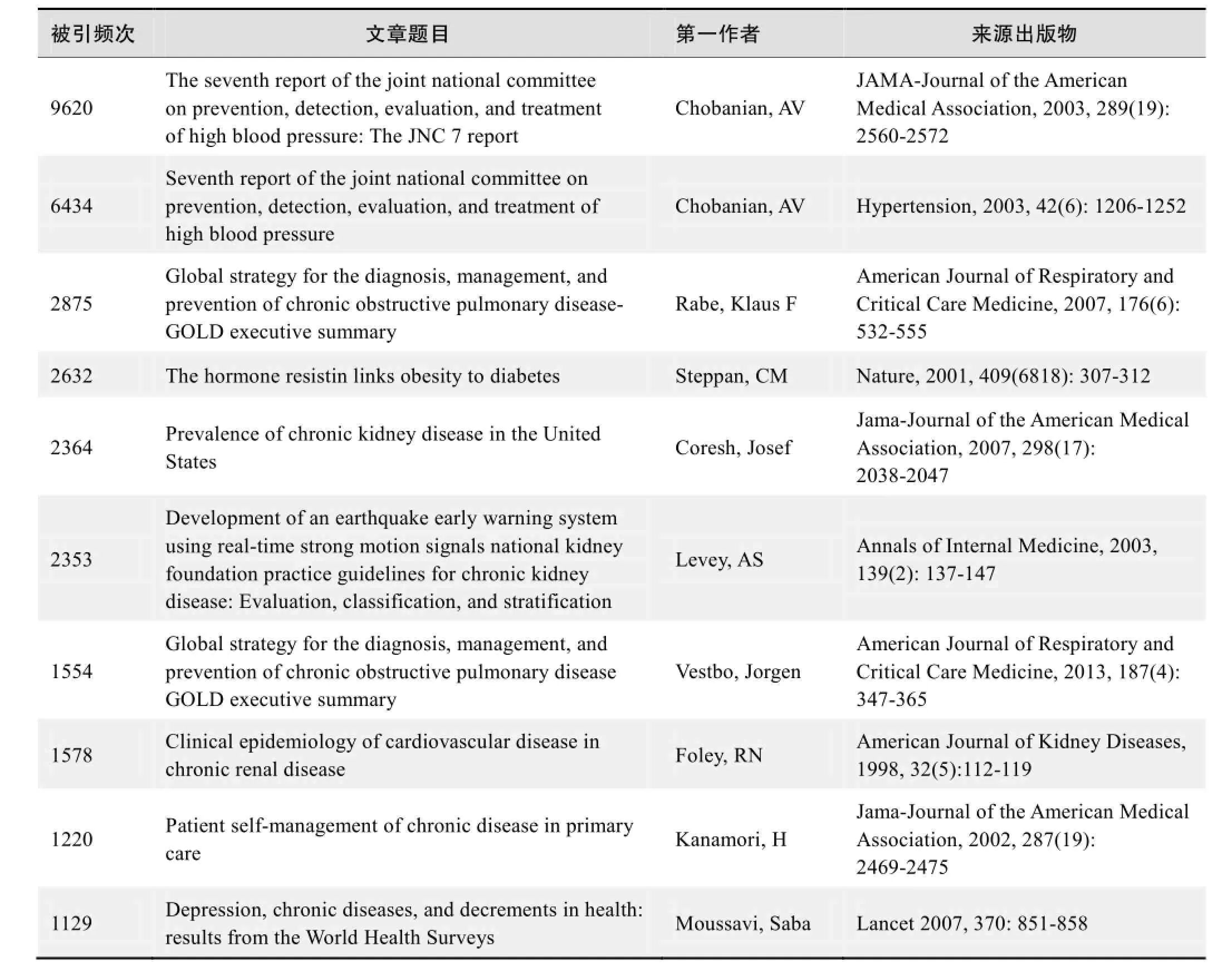
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于 Web of Science 检索结果,利用 Histcite 软件选取 LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物:American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2013, 187(4): 347-365 and classification system, and (3) identify a collaborative research agenda and plan that would improve the evidence base and facilitate implementation of the definition and classification of CKD. The K/DOQI definition and classification were accepted, with clarifications. CKD is defined as kidney damage or glomerular filtration rate (GFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2for 3 months or more, irrespective of cause. Kidney damage in many kidney diseases can be ascertained by the presence of albuminuria, defined as albumin-to-creatinine ratio >30 mg/g in two of three spot urine specimens. GFR can be estimated from calibrated serum creatinine and estimating equations, such as the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study equation or the Cockcroft-Gault formula. Kidney disease severity is classified into five stages according to the level of GFR. Kidney disease treatment by dialysis and transplantation should be noted. Simple, uniform classifications of CKD by cause and by risks for kidney disease progression and CVD should be developed.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; glomerular filtration rate; proteinuria; albuminuria; KDIGO
来源出版物:Kidney International, 2005, 67(6): 2089-2100
Abstract: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a worldwide public health problem, with adverse outcomes of kidney failure, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and premature death. A simple definition and classification of kidney disease is necessary for international development and implementation of clinical practice guidelines. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) conducted a survey and sponsored a controversies conference to (1) provide a clear understanding to both the nephrology and nonnephrology communities of the evidence base for the definition and classification recommended by Kidney Disease Quality Outcome Initiative (K/DOQI), (2) develop global consensus for the adoption of a simple definition
Abstract: Chronic diseases are the largest cause of death in the world. In 2002, the leading chronic diseasescardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disease, and diabetes-caused 29 million deaths worldwide. Despite growing evidence of epidemiological and economic impact, the global response to the problem remains inadequate. Stakeholders include governments, the World Health Organization and other United Nations bodies, academic and research groups, nongovernmental organizations, and the private sector. Lack of financial support retards capacity development for prevention, treatment, and research in most developing countries. Reasons for this include that up-to-date evidence related to the nature of the burden of chronic diseases is not in the hands of decision makers and strong beliefs persist that chronic diseases afflict only the affluent and the elderly, that they arise solely from freely acquired risks, and that their control is ineffective and too expensive and should wait until infectious diseases are addressed. The influence of global economic factors on chronic disease risksimpedes progress, as does the orientation of health systems toward acute care. We identify 3 policy levers to address these impediments: elevating chronic diseases on the health agenda of key policymakers, providing them with better evidence about risk factor control, and persuading them of the need for health systems change. A more concerted, strategic, and multisectoral policy approach, underpinned by solid research, is essential to help reverse the negative trends in the global incidence of chronic disease.
来源出版物:JAMA-Journal of the American Medical Association, 2004, 291(21): 2616-2622
Abstract: We review the rationale for the use of synthetic oleanane triterpenoids (SOs) for prevention and treatment of disease, as well as extensive biological data on this topic resulting from both cell culture and in vivo studies. Emphasis is placed on understanding mechanisms of action. SOs are noncytotoxic drugs with an excellent safety profile. Several hundred SOs have now been synthesized and in vitro have been shown to: 1) suppress inflammation and oxidative stress and therefore be cytoprotective, especially at low nanomolar doses, 2) induce differentiation, and 3) block cell proliferation and induce apoptosis at higher micromolar doses. Animal data on the use of SOs in neurodegenerative diseases and in diseases of the eye, lung, cardiovascular system, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney, as well as in cancer and in metabolic and inflammatory/autoimmune disorders, are reviewed. The importance of the cytoprotective Kelch-like erythroid cellderived protein with CNC homology-associated protein 1/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2/antioxidant response element (Keap1/Nrf2/ARE) pathway as a mechanism of action is explained, but interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PARP gamma), inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B kinase complex (IKK), janus tyrosine kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)/ErbB2/neu, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the thiol proteome are als SOs to reactive cysteine residues in specific molecular targets triggers biological activity. Ultimately, SOs are multifunctional drugs that regulate the activity of entire networks. Recent progress in the earliest clinical trials with 2-cyano-3, 12-dioxooleana-1, 9(11)-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO) methyI ester (bardoxolone methyI) is also summarized.
来 源 出 版 物 : Pharmacological Reviews, 2012, 64(4): 972-1003
The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: The JNC 7 report
Chobanian, AV; Bakris, GL; Black, HR; et al.
“The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure” provides a new guideline for hypertension prevention and management. The following are the key messages: (1) In persons older than 50 years, systolic blood pressure (BP) of more than 140 mm Hg is a much more important cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor than diastolic BP; (2) The risk of CVD, beginning at 115/75 mm Hg, doubles with each increment of 20/10 mm Hg; individuals who are normotensive at 55 years of age have a 90% lifetime risk for developing hypertension; (3) Individuals with a systolic BP of 120 to 139 mm Hg or a diastolic BP of 80 to 89 mm Hg should be considered as prehypertensive and require health-promoting lifestyle modifications to prevent CVD; (4) Thiazide-type diuretics should be used in drug treatment for most patients with uncomplicated hypertension, either alone or combined with drugs from other classes. Certain high-risk conditions are compelling indications for the initial use of other antihypertensive drug classes (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers); (5) Most patients with hypertension will require 2 or more antihypertensive medications to achieve goal BP (<140/90 mm Hg or <130/80 mm Hg for patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease); (6) If BP is more than 20/10 mm Hg above goal BP, consideration should be given to initiating therapy with 2 agents, 1 of which usually should be a thiazide-type diuretic; and (7) The most effective therapy prescribed by the most careful clinician will control hypertension only if patients are motivated. Motivation improves when patients have positive experiences with and trust in the clinician. Empathy builds trust and is a patent motivator. Finally, in presenting these guidelines, the committee recognizes that the responsible physician’s judgment remains paramount.来源出版物:JAMA-Journal of the American Medical Association, 2003, 289(19): 2560-2572Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease GOLD executive summaryVestbo, Jorgen; Hurd, Suzanne S; Agusti, Alvar G; et al.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a global health problem, and since 2001, the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD)has published its strategy document for the diagnosis and management of COPD. This executive summary presents the main contents of the second 5-year revision of the GOLD document that has implemented some of the vast knowledge about COPD accumulated over the last years. Today, GOLD recommends that spirometry is required for the clinical diagnosis of COPD to avoid misdiagnosis and to ensure proper evaluation of severity of airflow limitation. The document highlights that the assessment of the patient with COPD should always include assessment of (1) symptoms, (2) severity of airflow limitation, (3) history of exacerbations, and (4) comorbidities. The first three points can be used to evaluate level of symptoms and risk of future exacerbations, and this is done in a way that splits patients with COPD into four categories-A, B, C, and D. Nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic management of COPD match this assessment in an evidence-based attempt to relieve symptoms and reduce risk of exacerbations. Identification and treatment of comorbidities must have high priority, and a separate section in the document addresses management of comorbidities as well as COPD in the presence of comorbidities. The revised document also contains a new section on exacerbations of COPD. The GOLD initiative will continue to bring COPD to the attention of all relevant shareholders and will hopefully.
COPD; clinical assessment; COPD management; exacerbations; comorbidities
Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)
Levey, AS; Eckardt, KU; Tsukamoto, Y
The global burden of chronic diseases: Overcoming impediments to prevention and control
Yach, D; Hawkes, C; Gould, CL; et al.
Synthetic oleanane triterpenoids: Multifunctional drugs with a broad range of applications for prevention and treatment of chronic disease
Liby, Karen T.; Sporn, Michael B
典
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 T h e s e v e n t h r e p o r t o f t h e j o i n t n a t i o n a l c o m m i t t e e o n p r e v e n t i o n , d e t e c t i o n , e v a l u a t i o n , a n d t r e a t m e n t o f h i g h b l o o d p r e s s u r e : T h e J N C 7 r e p o r t C h o b a n i a n , A V J A M A -J o u r n a l o f t h e A m e r i c a n M e d i c a l A s s o c i a t i o n , 2 0 0 3 , 2 8 9 ( 1 9 ) : 2 5 6 0 -2 5 7 2 G l o b a l s t r a t e g y f o r t h e d i a g n o s i s , m a n a g e m e n t , a n d p r e v e n t i o n A m e r i c a n J o u r n a l o f R e s p i r a t o r y a n d 2 o f c h r o n i c o b s t r u c t i v e p u l m o n a r y d i s e a s e G O L D e x e c u t i v e V e s t b o , C r i t i c a l C a r e M e d i c i n e , 2 0 1 3 , 1 8 7 ( 4 ) : s u m m a r y J o r g e n 3 4 7 -3 6 5 D e f i n i t i o n a n d c l a s s i f i c a t i o n o f c h r o n i c k i d n e y d i s e a s e -A 3 p o s i t i o n s t a t e m e n t f r o m K i d n e y D i s e a s e : I m p r o v i n g G l o b a l L e v e y , A S K i d n e y I n t e r n a t i o n a l , 2 0 0 5 , 6 7 ( 6 ) : O u t c o m e s ( K D I G O ) 2 0 8 9 -2 1 0 0 4 T h e g l o b a l b u r d e n o f c h r o n i c d i s e a s e s : O v e r c o m i n g Y a c h , D J A M A -J o u r n a l o f t h e A m e r i c a n M e d i c a l i m p e d i m e n t s t o p r e v e n t i o n a n d c o n t r o l A s s o c i a t i o n , 2 0 0 4 , 2 9 1 ( 2 1 ) : 2 6 1 6 -2 6 2 2 S y n t h e t i c o l e a n a n e t r i t e r p e n o i d s : M u l t i f u n c t i o n a l d r u g s w i t h 5 a b r o a d r a n g e o f a p p l i c a t i o n s f o r p r e v e n t i o n a n d t r e a t m e n t o f L i b y , K a r e n T P h a r m a c o l o g i c a l R e v i e w s , 2 0 1 2 , 6 4 ( 4 ) : c h r o n i c d i s e a s e 9 7 2 -1 0 0 3

