城市防震减灾
城市防震减灾
·编者按·
我国是世界上遭受地震灾害最为严重的国家之一。我国地震灾害损失严重。死亡人口占世界50%左右,损失比例一直居高不下,抗震设防水平与抗震先进国家仍有相当差距,重救轻防不当意识仍很严重,城市遭受特大和重大地震灾害损失风险很高。城市人口、经济、工程密度越来越高,生命线系统规模和复杂程度日益提高,基础设施抗震应急保障能力偏低,不满足抗震设防标准和抗震未设防房屋建筑存量巨大。我国防震减灾除了包括地震部门防震减灾内容外,还包括建设、交通、水利等部门的抗震防灾内容。
习近平总书记在唐山地震40周年的讲话中强调,更加重视预防亦即工程抗震设防和抗震风险防控,指出:“坚持以防为主、防抗救相结合,坚持常态减灾和非常态救灾相统一,努力实现从注重灾后救助向注重灾前预防转变,从应对单一灾种向综合减灾转变,从减少灾害损失向减轻灾害风险转变,全面提升全社会抵御自然灾害的综合防范能力。”
城市的防震减灾是国家公共安全的重要组成部分,它承担着保护城镇人民群众生命财产安全和经济社会可持续发展的重任,是构建和谐社会和全面建设小康社会的重要保障。如何建立完善的防震减灾工作,大幅提升城市的灾害监测预警、防灾备灾、应急处置、灾害救助、恢复重建能力等以减少伤亡破坏和财产损失,是我国城市发展长期面临的一项重大任务。
本专题得到专家马东辉教授(北京工业大学抗震减灾研究所)、刘经纬研究员(中国地震局地壳应力研究所)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2017年2月5日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“城市(urban)”“地震(earthquake)”“防震减灾(seismic resistance and disaster reduction)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为1004条与1618条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)(续表)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)(续表)
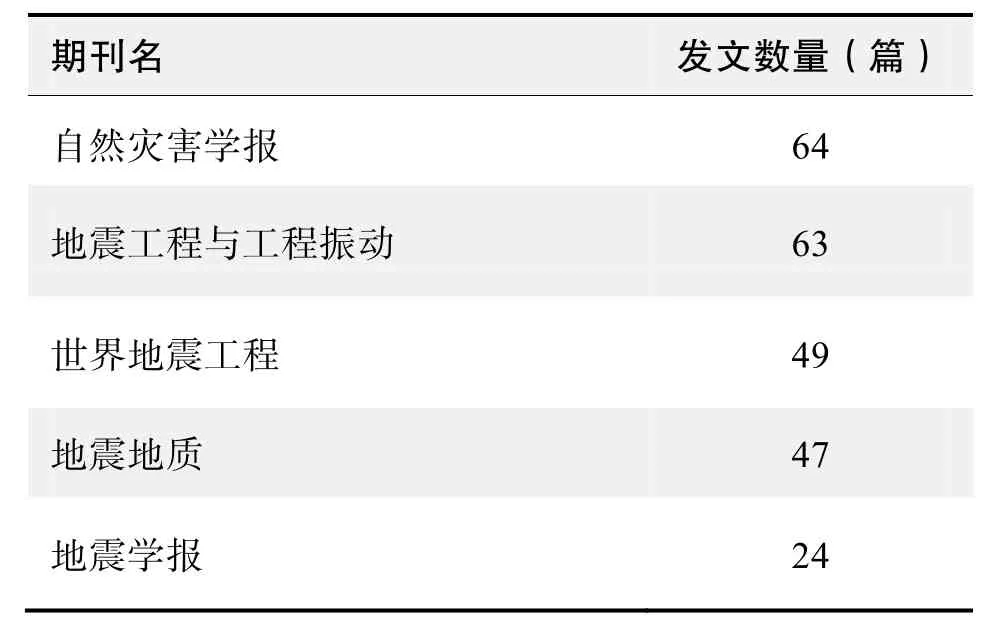
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
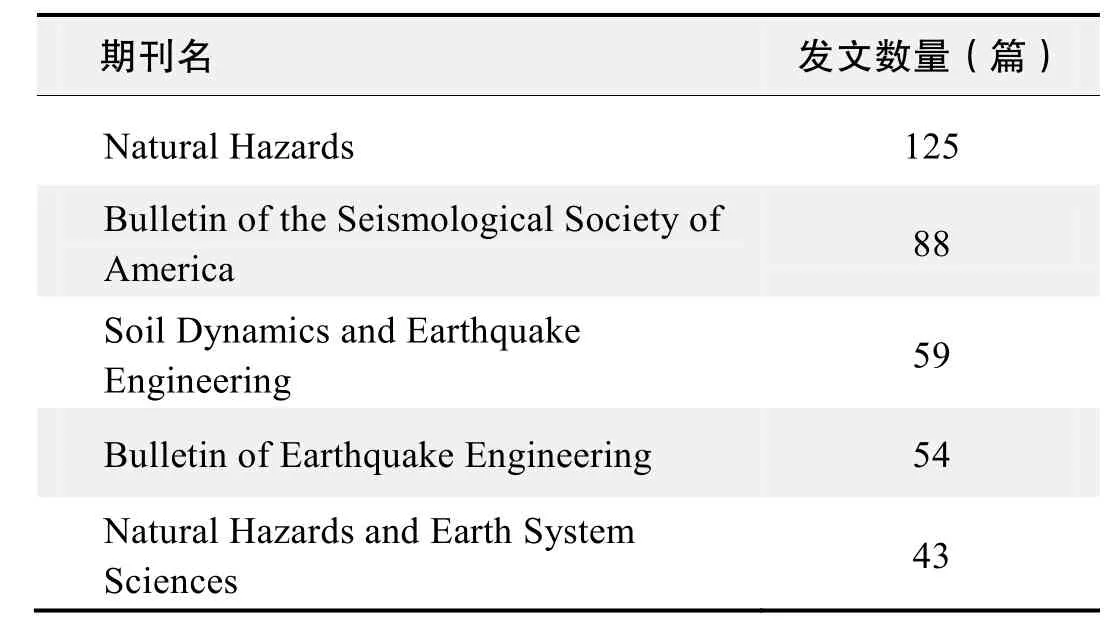
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“城市(urban)”“地震(earthquake)”“防震减灾(seismic resistance and disaster reduction)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为1004条与1618条为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“城市(urban)”“地震(earthquake)”“防震减灾(seismic resistance and disaster reduction)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为1004条与1618条为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
We calculate the probability of strong shaking in Istanbul, an urban center of 10 million people, from the description of earthquakes on the North Anatolian fault system in the Marmara Sea during the past 500 years and test the resulting catalog against the frequency of damage in Istanbul during the preceding millennium. Departing from current practice, we include the time-dependent effect of stress transferred by the 1999 moment magnitudeM=7.4 Izmit earthquake to faults nearer to Istanbul. We find a 62+/-15% probability (one standard deviation) of strong shaking during the next 30 years and 32+/-12% during the next decade.
来源出版物:Science, 2000, 288(5466): 661-665
Decorrelation of SAR data by urban damages caused by the 1995 Hyogoken-nanbu earthquake
Yonezawa, C; Takeuchi S
Abstract:Large part of urban area of around Kobe city were damaged by the 1995 Hyogoken-nanbu earthquake. For detecting the damaged area, the authors computed correlation coefficients from single-look complex ERS-1/ SAR data. Two types of correlations, intensity correlation and coherence were computed. Decorrelation was found in the damaged urban built-up area in the data pair of which interval included the earthquake occurrence. The similarity of the decorrelation between the intensity correlation and the coherence indicated that major factor of the decorrelation is closely related to interferometric processes, which results in the change of speckle patterns in the single-look intensity images. A normalized difference was calculated from the correlation coeffcients between the data pair including the earthquake occurrence and the pair before the earthquake. The distribution patterns of the pixels for which normalized difference was higher than a threshold showed good correspondence with the result of the ground survey. The result of this study indicates the possibility of detecting urban disasters using the decorrelation of SAR data.
来源出版物:International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2001, 22(8): 1585-1600
Earthquake damage assessment of buildings using VHR optical and SAR imagery
Brunner, Dominik; Lemoine, Guido; Bruzzone, Lorenzo
Abstract:Rapid damage assessment after natural disasters (e. g., earthquakes) and violent conflicts (e. g., war-related destruction) is crucial for initiating effective emergency response actions. Remote-sensing satellites equipped with very high spatial resolution (VHR) multispectral and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging sensors can provide vital information due to their ability to map the affected areas with high geometric precision and in anuncensored manner. In this paper, we present a novel method that detects buildings destroyed in an earthquake using pre-event VHR optical and post-event detected VHR SAR imagery. The method operates at the level of individual buildings and assumes that they have a rectangular footprint and are isolated. First, the 3-D parameters of a building are estimated from the pre-event optical imagery. Second, the building information and the acquisition parameters of the VHR SAR scene are used to predict the expected signature of the building in the post-event SAR scene assuming that it is not affected by the event. Third, the similarity between the predicted image and the actual SAR image is analyzed. If the similarity is high, the building is likely to be still intact, whereas a low similarity indicates that the building is destroyed. A similarity threshold is used to classify the buildings. We demonstrate the feasibility and the effectiveness of the method for a subset of the town of Yingxiu, China, which was heavily damaged in the Sichuan earthquake of May 12, 2008. For the experiment, we use QuickBird and WorldView-1 optical imagery, and TerraSAR-X and COSMO-SkyMed SAR data.
来源出版物:Communications of the ACM, 2004, 47 (6): 53-57
Ambient noise horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio in site effects estimation and correlation with seismic damage distribution in urban environment: The case of the city of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece)
Panou, AA; Theodulidis, N; Hatzidimitriou, P; et al.
Abstract:The validity of the estimation of seismic site response characteristics from ambient noise measurements was investigated in the downtown district of the city of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece), which was strongly affected by the 20/6/1978 (M = 6.5) damaging earthquake. For this purpose 250 ‘single site’ ambient noise measurements were performed in a dense grid of points covering the center of the city. The ambient noise H/V spectral ratio for each site was calculated and the fundamental frequency (fo) and corresponding H/V amplitude level (Ao) were estimated. Contour maps of both, to and Ao, were compared with results from geological and geotechnical studies as well as with macroseismic data of the 1978 earthquake and were found to be well correlated. These comparisons provide strong evidence that ambient noise measurements properly processed with the (H/V) spectral ratio technique can be used as an inexpensive and fast tool for microzonation studies in urban environments.
来源出版物:Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2005, 25(4): 261-274
Tsunami damage investigation of built-up areas using multitemporal spaceborne full polarimetric SAR images
Chen, Si-Wei; Sato, Motoyuki
Abstract:This paper explores the use of full polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) images for tsunami damage investigation from the polarimetric viewpoint. The great tsunami induced by the earthquake of March 11th, 2011, which occurred beneath the Pacific off the northeastern coast of Japan, is adopted as the study case using the Advanced Land Observing Satellite/Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar multitemporal PolSAR images. The polarimetric scattering mechanism changes were quantitatively examined with model-based decomposition. It is clear that the observed reduction in the double-bounce scattering was due to a change into odd-bounce scattering, since a number of buildings were completely washed away, leaving relatively a rough surface. Polarization orientation (PO) angles in built-up areas are also investigated. After the tsunami, PO angle distributions from damaged areas spread to a wider range and fluctuated more strongly than those from the before-tsunami period. Two polarimetric indicators are proposed for damage level discrimination at the city block scale. One is the ratio of the dominant double-bounce scattering mechanism observed after-tsunami to that observed before-tsunami, which can directly reflect the amount of destroyed ground-wall structures in built-up areas. The second indicator is the standard deviation of the PO angle differences, which is used to interpret the homogeneity reduction of PO angles. Experimental results from after-and before-tsunami comparisons validate the efficiency of these indexes, since the built-up areas with different damage levels can be well discriminated. In addition, comparisons between before-tsunami pairs further confirm the stability of the two polarimetric indexes over a long temporal duration. These interesting results also demonstrate the importance of full polarimetric information for natural disaster assessment.
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Geosciences and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51 (4): 1985-1997
典
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 Heightened odds of large earthquakes near Istanbul: An interaction-based probability calculation Parsons, T Science, 2000, 288(5466): 661-665 2 Decorrelation of SAR data by urban damages caused by Yonezawa, C International Journal of Remote Sensing, the 1995 Hyogoken-nanbu earthquake 2001, 22(8): 1585-1600 3 Earthquake damage assessment of buildings using VHR Brunner, Communications of the ACM, 2004, 47 optical and SAR imagery Dominik (6): 53-57 Ambient noise horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio in site 4 effects estimation and correlation with seismic damage Panou, AA Soil Dynamics and Earthquake distribution in urban environment: The case of the city Engineering, 2005, 25(4): 261-274 of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece) 5 Tsunami damage investigation of built-up areas using Chen, Si-Wei IEEE Transactions on Geosciences and multitemporal spaceborne full polarimetric SAR images Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4): 1985-1997
Heightened odds of large earthquakes near Istanbul: An interaction-based probability calculation
Parsons, T; Toda, S; Stein, RS; et al.

