公司治理、企业社会责任与会计信息相关性
毛志宏,金 龙
(吉林大学 商学院,吉林 长春 130012)
公司治理、企业社会责任与会计信息相关性
毛志宏,金 龙
(吉林大学 商学院,吉林 长春 130012)
本文以我国沪深两市A股上市公司2009-2013年的数据为样本,从会计信息的预测价值出发,实证检验了公司治理和企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响,以及公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性影响的协同效应。研究结果表明,公司治理水平的提高有助于增强会计信息相关性的程度;社会责任表现较好的企业,能够披露会计信息相关性较强的财务报告。进一步研究发现,公司治理会增强企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的促进作用,同时企业社会责任也会增强公司治理对会计信息相关性的积极影响,这表明公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响存在协同效应。本文的研究结论证实了企业社会责任对会计信息质量发挥了治理作用,对今后推广上市公司社会责任履行具有一定的指导意义。
公司治理;企业社会责任;会计信息相关性;协同效应
一、引 言
在改革开放进程的不断深入以及社会主义市场经济体制的逐步形成背景下,中国经济迎来了空前的发展契机。中国企业在经历了30余年的快速发展后,终于实现了农业文明向工业文明的转变。长期的粗放式发展模式,给中国企业带来了丰厚的收获,但也造成了中国企业在软实力的培养和提高方面的缺失,尤为表现在企业道德和社会责任感方面。而随着民族文明的发展以及公民素质的提高,现代社会对企业的要求也渐渐发生了转变,由实现股东利益最大化的单一目标转向创造社会财富与履行社会责任的双重目标。
企业社会责任相关问题的研究开始于20世纪70年代,学者们起初关注的重点集中于企业社会责任与受托经济责任之间的关系。直至最近10年,随着企业社会责任相关概念的不断发展,学者们逐渐将关注的研究视角转向企业社会责任与受托财务责任之间的关系,并将企业社会责任的相关理论纳入到现代公司治理理论中,进而实现二者的融合发展。公司治理作为受托责任系统中的一种控制机制,其最终目的是确保受托责任系统的有效运行[1]。受托财务责任要求企业诚实经营,保护受托财产安全,并遵守相关财经法规,按照公认的会计准则编制财务报告。财务报告信息不仅向市场传递了有关企业绩效和优化资源配置的有用信息,同时还可以揭示管理人员与股东之间代理契约的执行情况。因此,公司治理对会计信息质量的积极影响受到了学者们的广泛支持。企业社会责任的利益相关者理论认为企业作为所有利益相关者的契约集合,应将平等地对待各利益相关者的需求,积极地维护契约的公平性作为企业社会责任的重要表现形式。因此,企业能否满足各利益相关者的多元化信息需求,公平透明的披露财务报告信息成为企业社会责任发挥治理机制的重要表现。所以,企业社会责任对会计信息质量的积极影响成为当前有关企业社会责任颇受关注的问题。
本文以2009-2013年沪深两市A股上市公司为样本,采用会计盈余持续性模型作为会计信息相关性的基础回归模型,实证检验了公司治理对会计信息相关性的影响,企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响,以及公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性影响的协同效应。研究发现,公司治理对会计信息相关性存在正向影响,企业社会责任对会计信息相关性存在正向影响。此外,公司治理和企业社会责任相互调节增强了各自对会计信息相关性的正向影响。
本文的主要贡献在于:第一,本文通过运用主成分分析构建公司治理指数的方法,从公司治理系统整体的角度,考察了公司治理对会计信息相关性的影响。以往的文献大多仅从公司治理的单一因素出发,检验单个因素对会计信息质量的作用,忽视了各因素之间的相互作用。第二,本文以会计信息质量的相关性为研究视角,对企业社会责任与会计信息相关性的关系进行了研究。先前的成果主要以盈余管理作为研究会计信息质量的衡量指标,而未关注到企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响。本文的研究结果表明,企业社会责任对企业披露的会计信息相关性有促进作用。第三,本文通过对会计信息相关性的理论分析,并结合已有相关研究成果,从会计信息自身预测价值的视角,以会计盈余持续性模型作为衡量会计信息相关性的基础模型,对公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响进行了研究。而以往文献大多采用以市场定价有效性为假设的会计信息价值相关性作为研究会计信息相关性的切入点,未能体现非权益投资者对财务报告信息的考虑。第四,本文通过运用构建的两阶段模型,验证了公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响存在协同效应,丰富了公司治理和企业社会责任与会计信息相关性关系的研究成果,证实了企业社会责任治理机制对会计信息披露的约束和会计信息质量的提高能够发挥积极的作用,对我国政府的相关决策部门积极推广上市公司的企业社会责任履行提供了经验证据。
二、文献回顾
关于公司治理与会计信息质量之间关系的研究,国内外学者主要从公司治理的单一因素对会计信息质量的影响进行了研究。Warfield等[2]认为管理人员或机构投资者持股比例增加,可以减少经理人操纵盈余的行为。Porta等[3]发现股权集中度与财务报告质量之间存在负相关关系。Beasley[4]发现外部董事可以减少财务报告舞弊的可能性,抑制公司的盈余管理行为。Marrakchi等[5]发现董事会规模与负向盈余管理负相关。刘立国和杜莹[6]发现法人股比例、执行董事比例、内部人控制度、监事会规模与财务报告舞弊的可能性正相关,流通股比例与财务报告舞弊的可能性负相关。杜兴强和温日光[7]以盈余管理作为会计信息质量的代理变量,研究发现股权集中度、高管薪酬、独立董事比例、监事会会议次数与会计信息质量正相关,董事薪酬与董事会会议次数与会计信息质量负相关。
关于企业社会责任与会计信息质量之间关系的研究,已有文献主要是从企业社会责任与盈余管理之间的关系进行研究。Chih等[8]发现在研究企业社会责任和盈余管理的问题时,采用不同的盈余管理的代理变量,所得到的研究结论也不同。履行社会责任较好的企业更容易进行应计盈余的管理,但是对于盈余平滑和避免亏损的问题上却较少。Prior[9]发现企业社会责任对盈余管理起调节作用。管理层利用履行企业社会责任掩饰无法长时间维持的盈余管理行为。Hong和Andersen[10]采用美国市场的数据对企业社会责任与财务报告质量的关系进行研究,结果发现企业的社会责任越强,其应计利润质量越高,从事真实盈余管理的行为越少。Kim等[11]检验了履行社会责任的企业在经营决策和会计核算方面是否存在差异,研究发现,履行社会责任较好的企业,较少通过应计利润操纵和真实活动操纵进行激进的盈余管理。我国学者对此类问题也进行了一定的研究。高利芳[12]研究发现,独立社会责任报告的发布与会计透明度正相关,但没有发现与信息价值相关性和可靠性的显著关系。朱松[13]研究发现,投资者对盈余信息含量的评价会受企业履行社会责任的情况影响,社会责任表现越好的企业,其盈余的信息含量越高。王霞[14]研究发现,是否披露社会责任报告对操纵性应计利润没有显著影响,自愿披露社会责任报告的公司真实盈余管理程度更低,更少进行财务重述;企业社会责任报告评级得分越高的公司真实盈余管理程度越低,发生财务重述的概率越低。
综合以往研究成果可以发现,对于公司治理和企业社会责任与会计信息质量关系的研究,大多数都是从会计信息质量中的可靠性角度展开的,而相关性作为会计信息质量的另一主要特征,却尚未受到学术界关注。现阶段已有关于会计信息相关性的研究主要以价值相关性作为衡量相关性的指标,但价值相关性的研究是以资本市场有效性为前提,从资本市场定价机制的角度来验证会计信息的决策有用性,而并非是从会计信息自身的相关性进行验证的。因此,本文从会计信息预测价值的视角出发,将会计盈余持续性作为会计信息相关性的衡量指标,对公司治理和企业社会责任与会计信息相关性之间的关系进行研究。
三、理论分析与研究假设
(一)公司治理与会计信息相关性
会计信息的形成与披露受企业管理当局所主导,因此,会计信息质量取决于管理当局对会计准则的执行程度。由于控股股东与中小股东之间存在利益冲突,而控股股东对公司具有绝对控制力,这使得控股股东存在与管理层合谋通过操纵财务信息的形成和披露,以牺牲其他股东的利益为代价追求自身利益最大化[15-16]。此外,委托代理理论认为,由于股东和经理人都以追求自身利益最大化为目标,这种目标函数的不一致导致了股东和经理人之间的代理冲突[17],当经理人有动机在满足某种可靠性要求的前提下,提供更多具有相关性的信息时,企业披露的会计信息质量就会提高。而当披露相关性的会计信息会有损经理人自身利益时,经理人就会对所披露的会计信息采取最优选择,从而导致会计信息质量下降。由此可见,会计信息实际是企业管理当局综合各方面权利和利益的产物。而公司治理是通过一套正式或非正式的、内部或外部的制度或机制来协调公司与所有利益相关者之间的利益关系,以保证公司决策的科学化,从而最终维护公司各方面的利益。因此,良好的公司治理能够对会计信息的披露发挥监督作用。由此,我们提出假设H1。
H1:公司治理水平与会计信息相关性存在正相关关系。
(二)企业社会责任与会计信息相关性
企业履行社会责任的动机不外乎以下两种。一是出于自身经济利益的功利主义行为。企业通过履行社会责任,以满足利益相关者对产品质量和环境质量的隐性需求,实现企业声誉的提高[18],进而获得竞争优势的提升,并最终转化为持续增长的经济收益[19]。企业的社会责任履行情况是投资者分析和判断企业战略制定和执行的重要依据,有助于避免由于逆向选择问题所导致的市场资源错配的现象[20]。而在投资经营决策时,会计信息能够帮助管理层和投资者确定投资项目,减少逆向选择和流动性风险,提高企业经济绩效[21],而会计信息的相关性是会计信息决策有用的前提。基于功利主义视角的分析,社会责任表现较好的企业,应积极地向市场中参与者传递具有预测价值的会计信息,通过提高投资者的投资效率,以赢得更多的社会资本。二是履行企业公民的义务真诚的帮助社会。企业公民理论认为,企业的成功与社会的健康和福利密切相关,因此,企业应全面考虑其对社会环境的影响[22],同时重视利益相关者的需求。利益相关者理论认为企业在对股东承担经济责任的同时,还应当对债权人、政府、供应商、客户、员工、社区等其他利益相关者承担法律责任和道德责任。法律责任要求企业必须在相关的法律法规允许的范围内从事生产经营活动,遵守会计准则和会计信息披露制度。我国会计准则将相关性作为衡量会计信息质量的重要指标,因此,企业基于对道德的真实追求,真诚的履行企业公民的义务,应能够遵守会计准则的规定,向利益相关者提供会计信息相关性较强的财务报告。综合以上两种动机分析,我们认为不论是出于自身经济利益考虑,还是真实的履行企业公民的义务,社会责任表现较好的企业都会为财务报告使用者提供决策有用的会计信息。由此,我们提出假设H2。
H2:企业社会责任表现与会计信息相关性存在正相关关系。
(三)公司治理、企业社会责任与会计信息相关性
有效的内部治理机制和强烈的社会责任感是企业追求真正社会责任的基础,可持续的企业社会责任是公司治理机制保障企业满足各利益相关者需求的驱动因素,这表明公司治理与企业社会责任存在显著地双向互动关系[23]。因此,在研究企业社会责任与会计信息相关性的关系时,如果不同时考虑公司治理的作用,这可能会导致研究科学性的不足。因而,我们对公司治理因素加以控制,进一步对企业社会责任与会计信息相关性的关系进行研究。
公司治理与企业社会责任之间除了呈正相关关系,我们认为二者还会由于相互影响,共同对会计信息相关性产生促进作用。首先,虽然公司治理水平的提高有助于增强会计信息相关性的程度,但一家没有社会责任感的企业,由于其未能公平对待各利益相关者的契约需求,因此,难以有效地发挥公司治理对会计信息决策有用性的监督和约束作用。而企业的社会责任表现为外部投资者提供了一个评价企业的商业伦理和社会责任履行的指标。其次,McWilliam等[24]认为企业履行社会责任是管理层自利动机的行为,目的是利用履行社会责任的机会赢得个人声誉和社会地位提升,以实现个人未来的职业发展。而公司治理机制可以约束管理层无视股东及其他利益相关者权益的行为,尤其是对外部利益相关者的信息需求。综合上述分析,我们认为企业社会责任表现将正向调节公司治理水平对会计信息相关性的积极影响,公司治理水平正向调节企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的促进作用,即公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响存在协同效应。由于这种协同效应的存在,使得企业应当同时重视社会责任的履行和公司治理结构的设置,换言之,企业应制定一套将公司治理机制与社会责任治理机制相融合的内部治理战略。基于上述分析,我们提出假设H3。
H3:公司治理与企业社会责任互相调节增强了各自对会计信息相关性的促进作用。
四、研究设计
(一)样本选择与数据来源
本文选取2009-2013年沪深两市A股中发布企业社会责任报告的上市公司作为初始样本,并按如下标准对样本进行了筛选:(1)剔除金融保险行业上市公司;(2)剔除ST/PT上市公司;(3)剔除缺少模型中所需数据的公司年度。经过上述程序,最后得到5年共计2481个公司年度样本,其中2009年404个,2010年412个,2011年483个,2012年550个,2013年632个。为了消除奇异值的影响,我们对模型中所有连续变量在1%和99%分位上进行了Winsorize缩尾处理。本文所需的财务数据和公司治理数据均来自国泰安(CSMAR),企业社会责任报告的评级得分数据来自于润灵环球责任评级公司(RKS)。数据处理使用EXCEL2007软件进行,实证研究使用STATA12.0完成。
(二)变量定义
1.公司治理的度量
公司治理是通过一系列的制度安排对控股股东或管理人员进行监督,以实现对外部投资者利益的保护。因此,单独选取某一指标都难以对公司治理的整体水平进行全面的反映。故学术界通常采用主成分分析法,构建衡量公司治理整体水平的指标。本文借鉴张学勇和廖理[25]构建公司治理指数的方法,分别选用代表股权结构与股东权益、管理层治理以及董事、监事与其他治理形式的指标,运用主成分分析法构建公司治理指数,并将通过主成分分析法得到的第一大主成分作为衡量公司治理水平的指标(CGI),表1报告了12个变量对第一大主成分的载荷系数,系数的符号基本与理论预期相符。
2.企业社会责任的度量
国内外常用的企业社会责任衡量方法包括:内容分析法、问卷调查法、污染指数法、声誉指数法和专业机构数据库法。而这些方法都有各自的优缺点,例如:内容分析法以披露的字数、句数和人数来衡量企业的社会责任表现,此方法认为信息的数量越多,社会责任表现越好,但在企业社会责任报告中包含一些已量化的信息(税收,慈善捐赠,碳排放等),因此,内容分析法在衡量企业社会责任表现的合理性可能存在缺陷。问卷调查法的缺陷在于,问卷设计过程和调查对象在对企业社会责任表现评价时存在一定的主观性,导致研究数据的信度和效度降低。声誉指数法会受到公司自身特征、媒体关注度、问卷对象经历的影响,并存在样本数量受限的问题。污染指数法衡量企业社会责任表现,主要是从企业对环境保护和治理的角度出发,未能全面的考察社会责任的各方面事项。而专业机构数据库法最突出的优点是拥有专业的评价人员对企业的社会责任表现进行评价,能够提供充足的样本和高质量的评价结果。因此,本文借鉴前人的研究成果,采用润灵环球责任评级公司(RKS)对企业社会责任报告评分作为衡量企业社会责任的指标。

表1 公司治理指数的载荷系数
3.会计信息相关性的度量
美国财务会计准则委员会(FASB)在其发布的第2号财务会计概念公告(SFAS No.2)《会计信息的质量特征》中明确指出,相关性包含预测价值、反馈价值和及时性。其中,预测价值是指会计信息应当有助于使用者对其所关注的事项或未来的结果进行合理预测,并通过减少其在决策中的不确定性,进而有利于使用者的决策差异。反馈价值的实现要求会计信息能够对相关事项或过程的未来结果进行预测和调整,换言之,反馈价值通常看作为预测价值的基础或是前提条件。因此,本文以会计信息的预测价值为切入点对会计信息相关性的问题进行研究。
Jonas和Blanchet[26]在评估财务报告质量时指出,预测价值与会计信息的有用性直接相关,并将盈余持续性作为衡量相关性的重要指标。Dechow等[27]认为盈余持续性反映了企业当期盈余在未来期间盈余的再现程度,即在利用当期业绩预测下一期业绩时,持续性水平越高,预测结果的有用性越强。因此,盈余持续性可以作为衡量盈余相关性的指标。对于盈余持续性的度量,已有研究大多采用一阶自回归模型。该方法通过分公司按时间序列回归,将回归估计的系数作为衡量持续性的指标,即回归系数越接近于1,说明盈余及其组成部分的持续性越强。Fama和French[28]采用横截面模型逐年对盈余滞后值进行回归,并将回归系数的均值和时间序列的标准差作为盈利能力和盈余的预测指标。由于企业报告的财务信息除受自身经营成果和财务状况的影响外,还受到制度环境、经济动机、公司治理等因素的影响,而自回归模型仅适用于受自身历史因素影响较大的经济现象。因此,本文借鉴肖华和张国清[29]的研究方法,并结合研究对象的特征,采用横截面模型对盈余持续性进行度量,以回归系数作为衡量盈余持续性的指标。计算公式如下:
Earnit+1=α0+α1Earnit+vit
其中,Earnit+1,Earnit分别为公司i第t+1年和t年会计盈余(总资产收益率ROA=净利润/期末总资产);vit为模型估计的随机误差。
(三)模型设计
根据前文的分析和提出的假设,并结合会计盈余持续性模型,我们分三步对研究模型进行设计。第一,将代表公司治理水平的变量CGI和交乘项CGI×Earn加入到模型中,得到检验公司治理水平与会计信息相关性关系的回归模型(1)。第二,将代表企业社会责任表现的变量CSR和交乘项CSR×Earn加入到会计盈余模型中,得到检验企业社会责任表现与会计信息相关性关系的回归模型(2)。第三,我们在会计盈余持续性模型的基础上,加入代表公司治理水平的代理变量CGI和交乘项CGI×Earn以及代表企业社会责任表现的代理变量CSR和交乘项CSR×Earn得到考虑同时考虑两因素对会计信息相关性影响的模型(3)。然后为了分析公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性协同影响,我们还将交乘项CGI×CSR和交乘项CGI×CSR×Earn加入到模型(3)中,最终构建得到模型(4)。建立如下模型:
Earnit+1=α0+α1Earnit+α2CGIit+α3CGIit×Earnit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+ΣλjCONSTROLit×Earnit+Year+Industry+εit
(1)
Earnit+1=α0+α1Earnit+α2CSRit+α3CSRit×Earnit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+ΣλjCONSTROLit×Earnit+Year+Industry+εit
(2)
Earnit+1=α0+α1Earnit+α2CSRit+α3CSRit×Earnit+α3CGIit+α4CGIit×Earnit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+ΣλjCONSTROLit×Earnit+Year+Industry+εit
(3)
Earnit+1=α0+α1Earnit+α2CSRit+α3CSRit×Earnit+α3CGIit+α4CGIit×Earnit+α5CGIit×CSRit+α6CGIit×CSRit×Earnit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+ΣλjCONSTROLit×Earnit+Year+Industry+εit
(4)
其中,CSR为企业社会责任,CONSTROL为控制变量。根据已有的研究成果,我们选择了公司规模(SIZE=期末总资产的自然对数)、财务风险(DEBT=期末总负债/期末总资产)、公司成长性(GROWTH,主营业务收入增长率)、无形资产比例(INTAN=无形资产净值/期末总资产)以及是否亏损(LOSS,当期净利润为负时,取值为1,否则为0),Year和Industry分别为控制年度和行业固定效应影响的哑变量。
五、研究结果与分析
(一)描述性统计分析
表1列示了本文主要变量的描述性统计分析。从结果中可以看出,会计盈余的均值都处于0.04-0.05之间,这表明上市公司拥有较好的盈利能力。表2列示了企业社会责任表现的均值为36.245,中值为33.360,这表明上市公司的企业社会责任表现略显左偏态。公司治理指数的最大值和最小值分别为0.819和-0.824,这表明不同上市公司的公司治理水平存在较大差异。资产负债率的均值为0.507,这表明上市公司的整体负债水平较高。公司成长性的均值为0.179,最大值为1.916,最小值为-0.485,这表明上市公司整体具有良好的成长性,但不同公司之间的成长性差异也较大。
(二)相关系数分析
表3为本文主要变量之间的相关系数分析结果。结果显示,会计盈余的当期值与下期值的系数为0.765,表明上市公司的会计盈余具有较高的持续性水平;公司治理和企业社会责任表现与当期会计盈余和下期会计盈余的系数均为正,表明公司治理和企业社会责任对企业的财务绩效均表现出积极影响。此外,各自变量之间的相关性系数小于0.5,表明回归模型中各自变量之间不存在多重共线性问题。

表2 变量的描述性统计分析
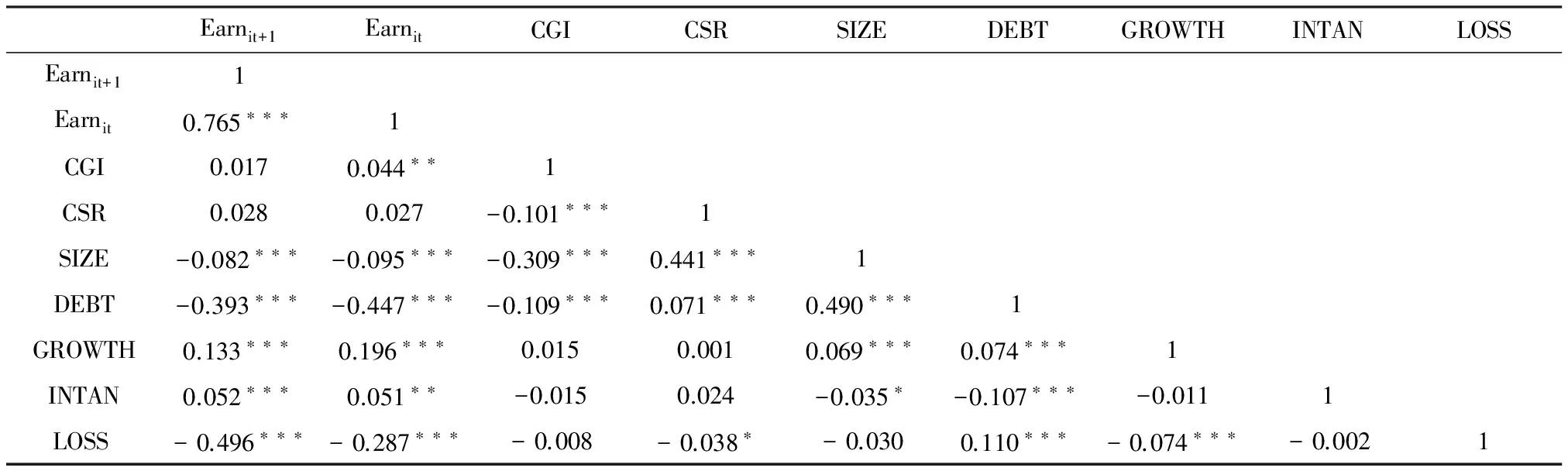
表3 主要变量的Pearson相关分析
注:***、**、*分别表示在1%、5%、10%的水平上显著。
(三)回归分析
表4列示了各解释变量对会计信息相关性影响的回归结果。模型1是检验公司治理对会计信息相关性的直接影响。在回归结果中,公司治理的交乘项CGI×Earn的系数显著为正(ɑ= 0.0969,p<0.1),表明公司治理对会计信息的相关性具有正向影响,假设H1得以验证。模型2是检验企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的直接影响。在回归结果中,企业社会责任的交乘项CSR×Earn的系数显著为正(ɑ= 0.0026,p<0.1),表明企业社会责任对会计信息的相关性具有正向影响,假设H2得以验证。
为验证假设H3,我们在模型1和模型2的基础上构建出一个两阶段模型(模型3和模型4)。模型3将公司治理和企业社会责任两个因素同时加入到模型中,控制其中一个因素来观察另一个因素对会计信息相关性的影响。从模型3的回归结果中可以发现,在控制了公司治理的因素后,企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响程度提高,显著性水平提高且回归系数变大(0.0027>0.0026),说明公司治理增强了企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响。在控制企业社会责任的因素后,公司治理对会计信息相关性的影响程度提高(0.1040>0.0969)。模型4在模型3的基础上加入公司治理与企业社会责任及其对应的交乘项。从模型4的回归结果中可以发现,公司治理与企业社会责任对应的交乘项CGI×CSR×Earn的系数显著为正(ɑ= 0.0067,p<0.05),且公司治理和企业社会责任的交乘项系数依旧显著,并进一步变大(0.1042>0.1040,0.0030>0.0027)。说明公司治理和企业社会责任相互调节增强了各自对会计信息相关性的影响,假设H3得以验证。此外,无形资产比例和是否亏损对应的交乘项系数均表现出显著为负,表明无形资产比重较大的企业或亏损的企业会导致其会计信息相关性降低。
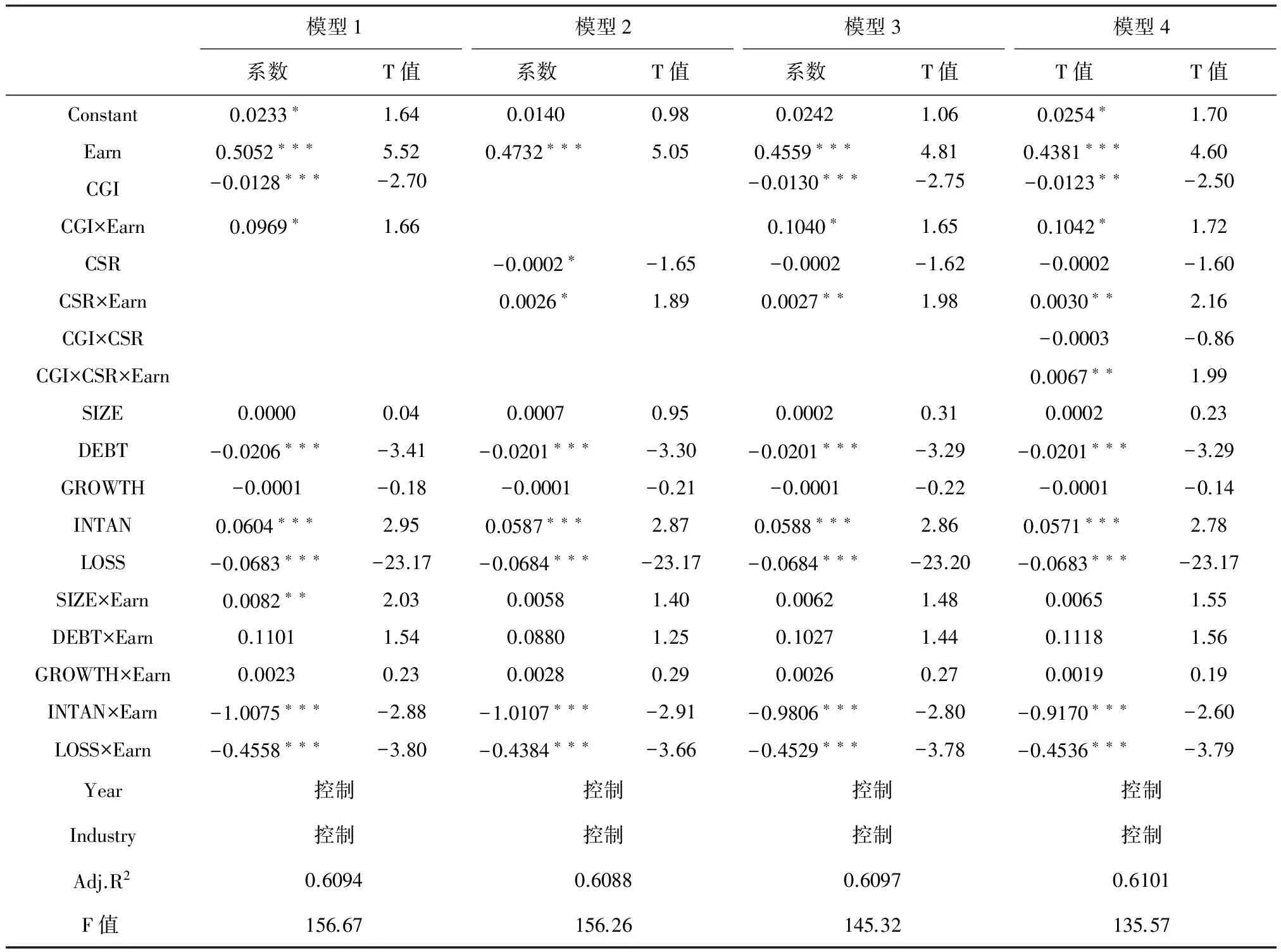
表4 公司治理、企业社会责任与会计信息相关性的回归结果
注:***、**、*分别表示统计量在1%、5%、10%的水平上显著。
(四)稳健性检验
为了验证研究结论的可靠性,本文还进行了如下稳健性检验:
(1)首先,由于会计盈余中包含了非经常性损益部分,而这部分并非由日常经营活动所产生的,无法真实的反映企业的经营状况。其次,在应计利润中包含操纵性应计利润部分,而这部分应计利润具有转回的属性,给予了管理层操纵盈余平滑利润的空间,而非操纵性应计部分则来源于正常的经营活动。因此,我们分别采用扣除非经常性损益后和扣除操纵性应计利润后净利润作为会计盈余的替代变量对研究假设进行重新检验,最终实证结果仍支持研究假设的结论。
(2)国内外学者认为价值相关性是财务报告信息有用性的一种重要表现,即利用资本市场的定价机制,通过股票估值的方式对会计信息决策有用性进行反映。因此,我们参考已有的研究成果,采用价格模型作为衡量会计盈余价值相关性的基础模型,并将代表公司治理的变量CGI和企业社会责任的变量CSR及其对应的交乘项依次加入到价格模型中构建出如下模型。
Pit=α0+α1NIit+α2BVEit+α3CGIit+α4CGIit×NIit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+Year+Industry+εit
(5)
Pit=α0+α1NIit+α2BVEit+α3CSRit+α4CSRit×NIit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+Year+Industry+εit
(6)
Pit=α0+α1NIit+α2BVEit+α3CGIit+α4CGIit×NIit+α5CSRit+α6CSRit×NIit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+Year+Industry+εit
(7)
Pit=α0+α1NIit+α2BVEit+α3CGIit+α4CGIit×NIit+α5CSRit+α6CSRit×NIit+α7CGIit×CSRit+α8CGIit×CSRit×NIit+ΣλjCONSTROLit+Year+Industry+εit
(8)
其中:Pit为公司i从第t+1年4月最后一个交易日的股票收盘价;NIit公司i第t年的每股收益;BVEit公司i第t年的每股净资产;其余变量同前文所述。
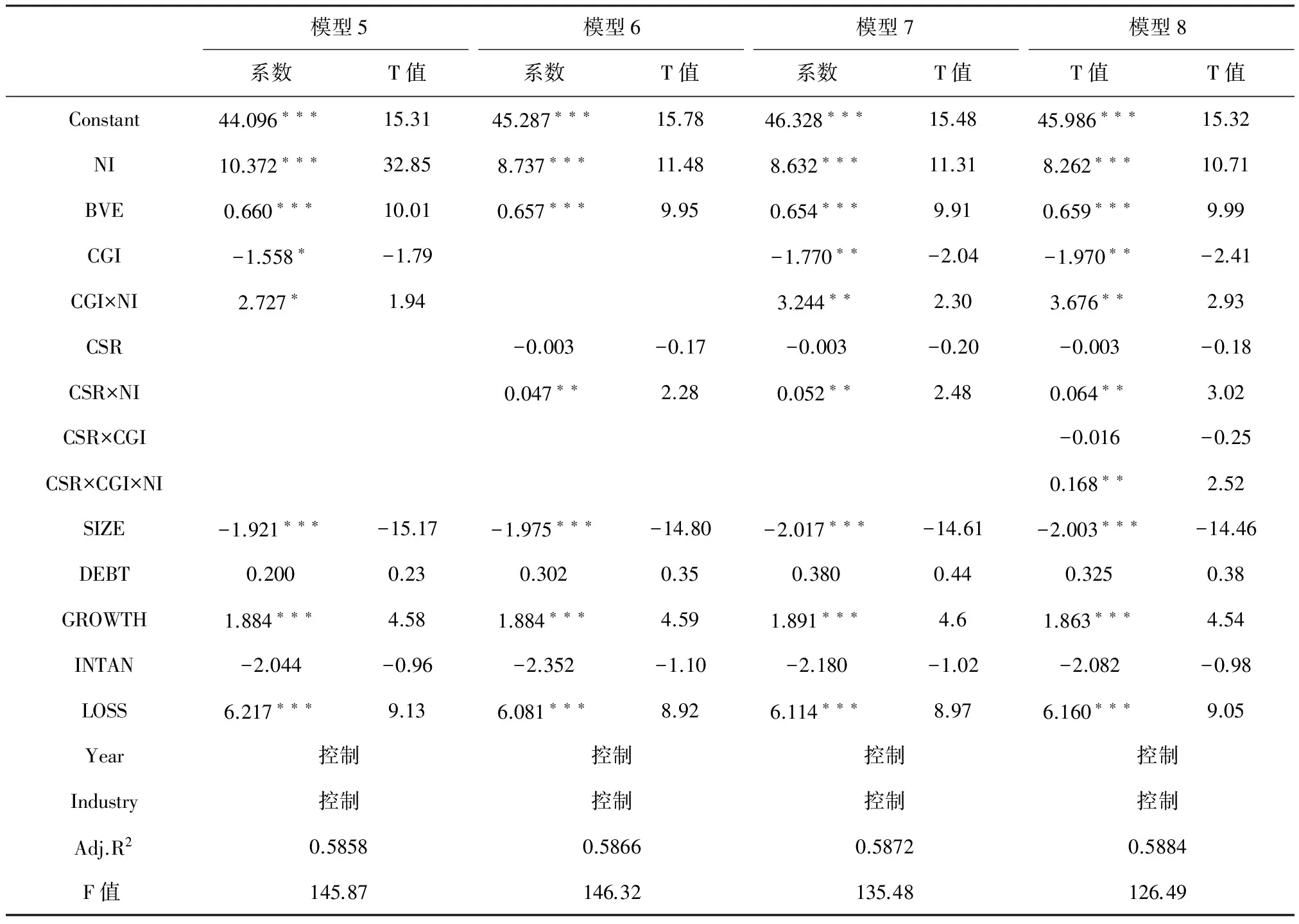
表5 公司治理、企业社会责任与会计盈余价值相关性的回归结果
注:***、**、*分别表示统计量在1%、5%、10%的水平上显著。
表5列示了公司治理和企业社会责任对会计盈余价值相关性影响的回归结果。在模型5中,公司治理的交乘项CGI×NI的系数显著为正(ɑ= 2.727,p<0.1),表明公司治理能够对会计盈余价值相关性产生促进作用,假设H1成立。在模型6中,企业社会责任的交乘项CSR×NI的系数显著为正(ɑ=0.047,p<0.05),表明企业社会责任能够对会计盈余价值相关性产生促进作用,假设H2成立。在以模型5和模型6为基础模型,以模型7和模型8作为扩展模型的比较时发现,在模型7中公司治理的交乘项CGI×NI和企业社会责任的交乘项CSR×NI的系数均显著提高(3.244>2.727,0.052>0.047),在模型8中公司治理与企业社会责任对应的交乘项CSR×CGI×NI的系数显著为正(ɑ=0.168,p<0.05),且公司治理和企业社会责任的交乘项系数进一步变大(3.676>3.244,0.064>0.052),表明公司治理和企业社会责任相互调节增强了各自对会计盈余价值相关性的影响,假设H3成立。
六、结 论
本文以我国2009-2013年沪深两市A股中发布社会责任报告的上市公司为研究样本,以会计信息的预测价值为研究视角,实证检验了公司治理对会计信息相关性的影响,企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响以及公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的协同影响。研究结果表明:(1)良好的公司治理机制能够有效地缓解由于委托代理问题而导致的信息不对称现象,从而实现企业对外披露会计信息相关性水平的提高,这说明公司治理能够对会计信息相关性发挥监督和促进作用。(2)履行社会责任较好的企业,能够切实的遵守公认会计准则的规定,披露会计信息相关性较强的财务报告。因此,企业的受托社会责任表现与受托财务责任存在正相关关系。(3)公司治理与企业社会责任互相调节增强了各自对会计信息相关性的积极影响。公司治理水平的提高增强了企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的促进作用,同时企业社会责任意识的提高也会增强公司治理对会计信息相关性的监督作用,即公司治理与企业社会责任对会计信息相关性的影响存在协同效应。
本文的研究结论也给了我们以下三方面的启示。首先,不论是基于自身经济利益考虑,还是真诚的履行企业公民的义务,履行社会责任较好的企业都能够对外披露相关性较强的会计信息。这表明在我国当前市场环境下,企业的受托社会责任表现与受托财务责任存在正相关关系,企业社会责任能够对会计信息质量发挥治理作用。所以,企业社会责任并非外生于企业的公司治理结构,而是嵌入于现代公司治理体系之中的。其次,企业应当在加强公司治理结构建设的同时进一步加强对管理层履行社会责任意识的培养,提高企业内部公司治理效率,进而完善内部公司治理体系,在社会责任战略的制定和执行时,应同时加强对公司治理机制的完善,切实提高企业的公民意识。如前文所述,如果企业没有社会责任感,那么便不会重视与各利益相关者契约的公平性,公司治理就难以发挥对信息披露质量的监督和约束作用。因此,企业应实现公司治理与企业社会责任相融合的整体性治理战略的制定。最后,我国政府有关决策部门应积极推广上市公司的社会责任履行,不仅是注重企业在社会资源使用后回馈社会的要求,还应着眼于社会责任意识在企业管理层受托责任履行中发挥的监督和约束作用,进而实现公司治理效率的提高以及现代企业公司治理结构的完善。
[1] 王光远, 瞿曲. 公司治理中的内部审计——受托责任视角的内部治理机制观[J]. 审计研究, 2006(2):29-37.
[2] Warfield T D, Wild J J, Wild K L. Managerial ownership, accounting choices, and informativeness of earnings[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 1995, 20(1): 61-91.
[3] Porta R L, Lopezdesilanes F, Shleifer A, et al. Law and Finance[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 1996, 106(6):1113-1155.
[4] Beasley M S. An empirical analysis of the relation between the board of director composition and financial statem[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 1996, 218(5):668-668.
[5] Marrakchi Chtourou S, Bédard J, Courteau L. Corporate governance and earnings management[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2001, 23(23):3295-3314.
[6] 刘立国, 杜莹. 公司治理与会计信息质量关系的实证研究[J]. 会计研究, 2003(2):28-36.
[7] 杜兴强, 温日光. 公司治理与会计信息质量:一项经验研究[J]. 财经研究, 2007, 33(1):122-133.
[8] Chih H L, Shen C H, Kang F C. Corporate social responsibility, investor protection, and earnings management: some international evidence[J]. Journal of Business Ethics, 2008, 79(1-2): 179-198.
[9] Prior D, Surroca J, Tribó J A. Are socially responsible managers really ethical? exploring the relationship between earnings management and corporate social responsibility[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2008, 16(3):160-177.
[10] Hong Y, Andersen M L. The relationship between corporate social responsibility and earnings management: an exploratory study[J]. Journal of Business Ethics, 2011, 104(4):461-471
[11] Kim Y, Park M S, Wier B. Is earnings quality associated with corporate social responsibility?[J]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2011, 87(3):177-177.
[12] 高利芳,曲晓辉,张多蕾. 企业社会责任报告与会计信息质量——基于深市上市公司的实证研究[J]. 财经论丛,2011(03): 99-105.
[13] 朱松. 企业社会责任, 市场评价与盈余信息含量[J]. 会计研究,2011(11): 27-34.
[14] 王霞, 徐怡, 陈露. 企业社会责任信息披露有助于甄别财务报告质量吗?[J]. 财经研究, 2014 (05): 133-144.
[15] Schadewitz H J, Blevins D R. Major determinants of interim disclosures in an emerging market[J]. American Business Review, 1998, 16(1): 41.
[16] Porta R, Lopez-de-Silanes F, Shleifer A. Corporate ownership around the world[J]. The journal of finance, 1999, 54(2): 471-517.
[17] Jensen M C, Meckling W H. The theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure[J]. Journal of Financial Economic Policy,1976, 15(3):305-360.
[18] Johnson H H. Does it pay to be good? social responsibility and financial performance[J]. Business Horizons, 2003, 46(6):34-40.
[19] Porter M E, Kramer M R. Strategy and society: the link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility[J]. Harvard Business Review, 2006, 84(12):78-92, 163.
[20] 肖红军, 张俊生, 李伟阳. 企业伪社会责任行为研究[J]. 中国工业经济, 2013(6):109-121.
[21] Bushman R M, Smith A J. Financial accounting information and corporate governance[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 2001, 32(1): 237-333.
[22] Logsdon J M, Wood D J. Business citizenship: from domestic to global level of analysis[J]. Business Ethics Quarterly, 2002, 12(02): 155-187.
[23] Jamali D, Safieddine A M, Rabbath M. Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility synergies and Interrelationships[J]. Corporate Governance An International Review, 2008, 16(5):443-459.
[24] McWilliams A, Siegel D S, Wright P M. Corporate social responsibility: strategic implications[J]. Journal of management Studies, 2006, 43(1): 1-18.
[25] 张学勇, 廖理. 股权分置改革、自愿性信息披露与公司治理[J]. 经济研究, 2010(04):28-39.
[26] Jonas G J, Blanchet J, Jonas G J, et al. Assessing quality of financial reporting[J]. Accounting Horizons, 2000, 14(3):353-363.
[27] Dechow P, Ge W, Schrand C. Understanding earnings quality: a review of the proxies, their determinants and their consequences[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 2010, 50(2): 344-401.
[28] Fama E F, French K R. Forecasting profitability and earnings[J]. Journal of Business, 2000, 73(2):161-75.
[29] 肖华, 张国清. 内部控制质量、盈余持续性与公司价值[J]. 会计研究, 2013(05):73-80.
责任编辑、校对:李斌泉
Abstract: Using the sample of Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share listed companies from 2009-2013, this paper empirically examines the impact of corporate governance and corporate social responsibility on accounting information relevance, the synergy effect of corporate governance and corporate social responsibility on the accounting information relevance. The result shows that the improvement of the corporate governance is helpful to enhance the degree of relevance of accounting information; the better social responsibility performance of enterprises, the higher financial report accounting information relevance. Further study found that corporate governance can enhance the promoting effect of corporate social responsibility on the accounting information relevance, corporate social responsibility can enhance the positive impact of corporate governance on the accounting information relevance. It indicates that corporate governance and corporate social responsibility have a synergistic effect on the relevance of accounting information. The conclusions confirm that the corporate social responsibility plays a role of the governance of accounting information quality and has a certain guiding significance in promoting social responsibility performance of listed companies in the future.
Keywords: Corporate governance; Corporate social responsibility; Accounting information relevance; Synergistic effect
“The Comprehensively Deepening Reform Theory” and China’s Crossing “Middle-income Trap”
FENG Genfu1,2
(1.School of Economics and Finance, Xi’an JiaoTong University, Xi’an 710061, China;2.XJTU-SIDVC Financial and Investment Research Center, Suzhou 205000,China)
The third plenary session of the 18th central committee of the communist party of China puts forward the theory of comprehensively deepening reform, which was firstly proposed from the historical experience and realistic height by Comrade Xi Jinping as general secretary. It is a significant development of the theory of socialism with Chinese characteristics. Using the theory of comprehensively deepening reform to analyze the historical problems left over from the economic and social development in China since the reform and opening-up and the new problems emerging at present, it can be found that the uncoordinated economic system reform, political system reform, social system reform, cultural system reform and ecological civilization reform are the key issues that restrict China to overcome the “middle income trap” in the future. Therefore, we must, under the guidance of the comprehensively deepening reform theory put forward by the third plenary session of the 18th central committee of the communist party of China, comprehensively and orderly promote economic, political, social, cultural, ecological civilization and other fields to achieve a coordinated development of economy, politics, society, culture and ecology civilization. Only in this way, China will be able to overcome and resolve various social contradictions and risks, and successfully cross the “middle income trap” to achieve the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
The comprehensively deepening reform theory; Coordinated development of the economic society; Crossing middle-income trap
Re-measuring Chinese Factor Income Distribution
TAN Xiaopeng, CHAO Xiaojing
(School of Economic and Management, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, China)
Abstract: This paper uses the related data about Chinese flow of funds and provincial income approach of GDP, and calculates the factor income distribution structure of China and its every region from 1992 to 2014 on the basis of adjusting individual business owners’ mixed income and state farm operating surplus. The results demonstrate that, from the overall situation of the whole country, the share of labor income has stayed in a low level steady state since 1992, the share of capital income appears a long-term and moderate upward trend and the share of government appears a cyclical fluctuation. On the regional level, the provinces’ fluctuations and trends are significantly different. The common is that, the percentile of government income is smallest and the fluctuation extent is obscure. The provinces with obvious change trend include Liaoning, Jiangsu, Beijing city, Shaanxi, Jiangxi and Anhui.
Keywords: Factor income distribution; Flow of funds; Provincial income approach GDP; Individual business owners’ mixed income; State farm operating surplus
Promoting Capital Market Reform Surrounding Third Great Forces of Asset Pricing
WANG Ren, WEI Jie
(1.School of Finance and Finance, Chongqing Technology and Business University, Chongqing 400067, China;2.School of Economics and Management, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: The reform of Chinese capital market could not be confined to enhancing the quality of listed companies or restricting the behavior of listed companies and investors, but paying more attention to those third great forces such as investor protection, listing and trading system, micro market structure which is enough to affect asset pricing. Perfecting the system of securities legislation and law enforcement oriented to investor protection, and constricting the destructive growth behaviors is the institutional cornerstone of regulating the development of capital market. Breaking the threshold of access to capital market, and replacing the verification-based stock-issuing system with registration-based stock-issuing system is the guarantee of preventing unfair competition and rent seeking. Filling the technical loopholes in the transaction process to ensure the harmony of futures and spot, leverage and forward delivery, price limit and trade halts system is the firewall to ensure the smooth performance of capital market and prevent those potential financial risks. Developing different institutional investors, optimizing the micro market structure is the lasting and stable development road of China’s capital market.
Keywords:Investor protection; Market structure; Trading system
Basic Research or Applied Research: Who can Promote TFP Growth More?—Adjustment Effect of Ownership and Factor Market Distortion
WANG Wen, SUN Zao
(School of Economics and Finance, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, China)
Abstract: During the period of economic transition, the influencing mechanism of different types of research and development activities on the total factor productivity (TFP) in China is more complicated than that in the mature market economies. This paper first analyzes the different effects of basic research and applied research on innovation between state-owned enterprises and private enterprises due to their difference of resource endowment and institutional logic, and then analyzes the adjusting effect of factor market distortion and joint adjusting effect of ownership and factor market distortion on the relationship between two kinds of research and development activities and regional TFP. Further Empirical analysis results based on the provincial panel data of China from 1998 to 2014 and the finite distributed lag model show that, basic research contributed more to TFP growth than applied research in the regions with high proportion of state-owned economy, and applied research contribute more to TFP growth than basic research in the regions with low proportion of state-owned economy. It is also shown that factor market distortion will weaken the influence of basic research and applied research on TFP, among which the influence of basic research was weaken more, and the adjusting effect of ownership also relied on the factor market distortion. The discovery of this paper could provide further empirical evidence for scientifically determining the adjustment direction and implementation focus of national innovation support policy.
Keywords:Basic research; Applied research; Regional TFP; Ownership; Factor market distortion
A Study of the Forced Mechanism of the Low Carbon Constraint on Energy Intensity
PAN Xiongfeng, PAN Xianyou, LI Changyu
(Faculty of Management and Economics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China)
Abstract: From the perspective of basic relationship between low carbon constraint and energy intensity, this paper theoretically argues direct and indirect impacts of carbon productivity on energy intensity. On this basis, this paper empirically analyzes China’s provincial panel data from the period 2000-2014. The results demonstrate that the trajectory of the direct effects of carbon productivity on energy intensity is U-shape. For China’s current situation, carbon productivity can effectively keep energy intensity down, but the marginal effects of “energy saving” that carbon productivity brings about are weakening because of the rise of the cost of energy saving. Moreover, carbon productivity regulation inversely force the industry structure to upgrade itself, changing the effects that industry restructure have on energy intensity; Secondly, the technology innovation induced by carbon constraint may somewhat have rebound effects on energy intensity; At last, foreign direct investment, as one of the effective measures to reduce energy intensity, whose technology spillover and capital accumulation will be influenced by the acceleration effects of carbon productivity
Keywords: Carbon productivity; Energy intensity; Forced mechanism; Dual effect
The Win-win Relationship between Environmental Regulation and Economic Growth:Evidence from TCZ Policies in China
WU Mingqin1,2, ZHOU Shimin2, CHEN Jiachang2
(1.South China Market Economy Research Center, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China;2.School of Economics and Management, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract:We take the “Acid Rain Control Zone and SO2Pollution Control Zone” (TCZ) policy that was implemented in 1998 as a natural experiment. Based on a large society and economy development dataset of 280 key cities in China from 1992-2009, this paper investigates the relationship between the policy of the TCZ and economic growth by employing the empirical method of difference-in-difference (DID). The results demonstrate that the policy of TCZ caused the GDP per capita to increase by 8.30% and the industrial GDP per capita to increase by 16.30%. This implies that implement of the appropriate and draconian environmental regulation can significantly promote economic development, and achieve a win-win situation for both the environmental protection and economic growth. Finally, the results are robust to a series of specification tests which include the test of difference of the geography, spatial distribution and the political factors in the TCZ cities.
Keywords:Environmental regulation; Economy growth; TCZ policy; DID
Uncertainty Shocks, Bank Risk-taking and Economic Fluctuations
MA Xutao, SHEN Yue
(School of Economics and Finance, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, China)
Abstract:Considering the uncertainty shocks, this paper constructs a continuous time DSGE model including banking sector to analyze the mechanism of bank risk-taking, explores the impacts of uncertainty shocks on bank risk-taking and economic fluctuations and reveals the bank risk-taking channel of uncertainty shock affecting economic fluctuations. The result finds that bank risk-taking behavior is related to bank capital quantity and economic uncertainty degree. The bank will increase risk-taking with the rise in bank capital or economic stability. The impulse response analysis demonstrates that economic shocks have direct effects on bank capital and economic uncertainty degree and are transmitted and amplified through this two mechanisms, and that the uncertainty shocks still is a non-ignorable factor contributing to economic fluctuations.
Keywords: Uncertainty shock; Bank risk-taking; Economic fluctuations; Continuous time DSGE Model
Life Expectation and National Saving—Based on the Analysis of Aggregate Equation with Variable Coefficient of GDP Growth Rate
JIN Gang1, ZHANG Qiuqiu2
(1.Institution of Population Research, Liaoning University, Shenyang 110036, China;2.School of Business Administration, Shenyang Univesity, Shenyang 110044, China)
Abstract:By relaxing on the assumption of traditional life-cycle theory about fixed time span of both life and working, this paper introduces survival function into analytical framework of traditional life-cycle theory. The results find that GDP growth rate in aggregate saving equation with survival function has variable coefficient, which should be constant in aggregate saving equation without survival function. The improvement of life expectation from 15 years old would increase the coefficient of GDP growth rate while the improvement of life expectation from 15 years old to 60 years old would decrease that. The result of empirical analysis of panel data based on 218 countries around the world during 1981-2010 supports the above conclusions. Along with the improvement of life expectation, the coefficient of GDP growth rate in aggregate saving equation is increasing. But the amplification of the coefficient of GDP growth rate of some countries or districts is apparently bigger than others, which might cause the improvement of national saving rate is faster than that of GDP growth rate in these countries or districts.
Keywords: Life expectation; Working period; Economic growth rate; National saving rate; Variable coefficient of GDP Growth Rate; Aggregate saving equation
Effectiveness of Monetary Policy on the Financial Asset Structure and Macro-economic Fluctuations
XU Mei
(School of Economics, Northwest University of Politics and Law, Xi’an 710063, China)
Abstract:The adjustment of monetary policy can affect the consumption and investment of the individuals. The accumulation of individual behavior will result in the creation of the macro financial asset structure. Through credit and financing, the financial capital will be converted to physical capital and thus have an impact on macroeconomic. In this paper, by constructing Sidrauski model, the effects of monetary policy path hypothesis are put forward. Then ARDL-ECM is build to argue that the monetary policy effect on the structure of financial assets is more effective than macroeconomic, short-term adjustment is more effective than long-term.
Keywords:Monetary policy; Financial assets structure; Macro-economic fluctuation; Sidrausiki model; ARDL-ECM
Decentralization, Local Debt and Modern Financial Reform—Based on the Effect Analysis from Different Angles of Fiscal Decentralization
WANG Jieru
(Institute of Finance and Taxation, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Jinan 250014,China)
Abstract:It is generally recognized by domestic academia that local debt was born within fiscal decentralization. The mainstream view is that payment imbalance will lead to the expansion of local government spending scale. Another view supports the “leviathan” hypothesis, and points out that fiscal decentralization can limit the excessive expansion of local government spending. But how fiscal decentralization functions specifically in local debt remains to be further research. This article sets up a theoretical framework of fiscal decentralization associated with local government debt, and conducts empirical tests from three angles of expenditure decentralization, revenue decentralization and vertical fiscal imbalance. The results show that the decentralization effects should not be treated as the same. Improving revenue decentralization, reducing expenditure decentralization and vertical fiscal imbalance will be helpful to a lower level of the local debt. To build the modern government relationship, it needs to increase central general transfer payment after the “split 50-50”, with strict management of government spending. At the same time, moderately relaxing revenue management, giving the local government limited tax revenue legislative right, and building a local tax system is very important.
Keywords:Debt level of local government; Expenditure decentralization; Revenue decentralization; Vertical fiscal imbalance
Formal Credit Constraints and Influencing Factors of Specialized Farmers:Evidence from 725 Apple Growers in China
MA Yanni, HUO Xuexi
(Western Rural Development Research Center School of Economics and Management,Northwest Agriculture and Forest University, Yangling 712100,China)
Abstract: The specialized household has a difficulty of financing. This paper comparatively analyzes formal credit constraints condition and causes of specialized households with different scales by using the micro-data of 725 apple growers in China and the status of leading specialized households. The results show that the specialized households generally are subject to credit constraints of formal financial institutions, and are given priority to that of demand type. Leading specialized households are vulnerable to credit constraints of supply type, and the cumbersome financial procedure, a long time of examination and approval are the main reasons that led to the credit constraints. The Logistic analysis shows that the farmers in the western region are vulnerable to credit constraints. In addition, the farmers with more family labor and apple planting area, less family net incomes, greater the distance to bank outlets, and larger amount of each loan, will be subject to credit constraints.
Keywords: Leading specialized household; Formal credit constraints; Logistic model; Influencing factors
The Effect of Housing Demolition on the Household Entrepreneurship in the Process of Urbanization
FAN Cijun, ZHANG Donghao
(Research Institute of Economics and Management, Southwestern University of Finance and Economics,Chengdu 611130, China)
Abstract: Since the reform and opening up, China’s urbanization level has substantially been improved, and the housing demolition also gradually accelerates. Using Chinese Household Finance Survey 2011 data, this paper studies the effect of housing demolition on household entrepreneurship. We find that the housing demolition significantly decreases the probability of entrepreneurship and the amount of company assets. In further studies, we show the negative relationship between the demolition and entrepreneurship varies in housing state. Those who have houses suffer less from this negative relationship. At last, we also find that the effects of demolition on entrepreneurship are heterogeneous, the negative effect of demolition is biggest for the renters, is smaller for households having one house and is smallest for households having multiple houses.
Keywords: Housing demolition; Entrepreneurship; Housing ownership; Heterogeneity
Corporate Governance, Corporate Social Responsibility and Accounting Information Relevance
MAO Zhihong, JIN Long
(Business School, Jilin University, Changchun 130012; China)
2016-06-28
教育部人文社会科学研究规划基金项目“公允价值分层披露的经济后果研究”(批准号:14YJA630043)。
毛志宏(1961-),吉林省吉林市人,吉林大学商学院教授,会计系主任,博士生导师,研究方向:财务会计;金龙(1988-),吉林省长春市人,吉林大学商学院博士研究生,研究方向:财务会计,公司金融。
A
1002-2848-2016(06)-0112-10

