氮化硼纳米片制备方法研究进展*
赵 迪,柯瑞林,邹 雄,毛 琳,胡行兵,王金合
(1. 上海大学 纳米科学与技术研究中心,上海 200444;2. 深圳市欧姆阳科技有限公司,广东 深圳 518035; 3. 扬州亚光电缆有限公司, 江苏 扬州 225600))
氮化硼纳米片制备方法研究进展*
赵 迪1,柯瑞林2,邹 雄1,毛 琳1,胡行兵3,王金合1
(1. 上海大学 纳米科学与技术研究中心,上海 200444;2. 深圳市欧姆阳科技有限公司,广东 深圳 518035; 3. 扬州亚光电缆有限公司, 江苏 扬州 225600))
近年来,由于氮化硼纳米片独特的结构和性能,在物理、化学、电子及材料学界引起了广泛的研究兴趣。综述了氮化硼纳米片的制备方法,包括:化学气相沉积、化学剥离、超声剥离和球磨等方法,分析比较了各种方法的优缺点,并指出了氮化硼纳米片制备方法的发展趋势。
氮化硼;氮化硼纳米片;制备;研究进展
0 引 言
自2004年石墨烯发现以来,由于其优异的机械、光学和电性能在材料科学的引起了广泛的关注。作为石墨烯等电子、同构型的类似物,氮化硼纳米片(boron nitride nanosheets, BNNSs)同样具有许多独特的性能,从而也备受青睐。其晶格结构如图1所示[1],是由交替的B和N原子sp2杂化组成的六边形二维蜂窝状晶格结构[2]。
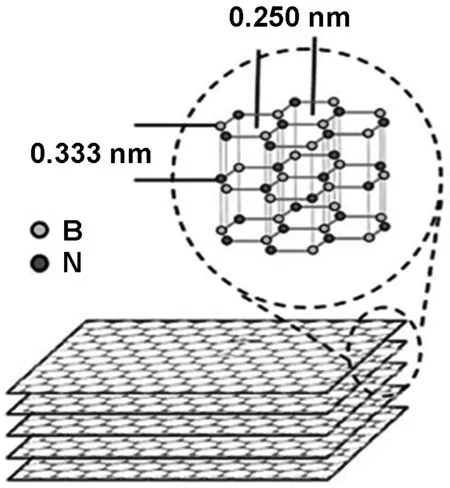
图1 氮化硼纳米片结构基础[1]
BNNSs表现出许多优异的性质,如良好的机械性能(弹性模量700~900 GPa,断裂强度120~160 GPa,断裂应变0.28%~0.33%)[3]、高热稳定性(抗氧化温度约850 ℃,其结构稳定性在真空条件下高达3 000 ℃)[4]和高导热性(常温面内导热系数2 000 W/(m·K))等[5-6],同时BNNSs还具有电绝缘性[7](约5~6 eV的带隙)、抗氧化性[8-9]、润滑性[10-11]、气敏性[12]和电磁性等[13-14]特殊性能。这些优异的性能使得BNNSs材料倍受关注。
由于BNNSs优异的性能,BNNSs在许多领域存在潜在的应用。BNNSs作为无机填料添加到高分子基质中制备高分子复合材料,从而提高复合材料的机械性能[15-17]、导热性能[18-19]、抗氧原子腐蚀作用等等[20]。BNNSs可用于功能性涂料制备,如各种防腐涂料[21-23],自清洁涂料等[24-25]。最近,BNNSs在纳米电子设备[26]和紫外光发射设备[27]上的应用取得了一定的进展。同时,BNNSs作为载体可提高金属颗粒的催化作用[28]和多孔BNNSs的水净化作用[29]的应用上存在着巨大的潜力。虽然BNNSs是近几年才开始研究,但其优异的性能使产业界迅速看到了其在电子、半导体、新能源、功能材料、航天航海、军工等领域可能的应用潜力,成为国内外研究热点和竞争焦点。
然而,BNNSs的制备是其走向应用的关键,如何大规模制备高质量大尺寸低成本的BNNSs是产业化亟待解决的问题。本文详细综述了BNNSs的各种制备方法和机理、各方法的优缺点及目前的研究进展。
1 氮化硼纳米片的制备方法
由于单层或多层BNNSs材料具有独特的性能并且广泛应用于各种领域,单层或多层BNNSs材料的制备方法成为国内外学者的研究焦点。各种制备BNNSs薄层材料的新方法、新技术层出不穷。目前,制备BNNSs薄层材料的方法主要有以下几种。
1.1 微机械剥离法
微机械剥离法是最早用于制备石墨烯的物理方法。而BNNSs首次是由Pacile等[30]在光学显微镜下,附着到300 nm厚的SiO2基板上采用胶带法将h-BN剥离出BN层从而制备BNNSs。虽然微机械剥离是一种简单的制备高质量BNNSs的方法,但是它费时费力,难以精确控制,重复性较差,也难以大规模制备。
1.2 化学气相沉积法
化学气相沉积 (chemical vapor deposition,CVD)是利用气态或蒸汽态的物质在气相或气固界面上反应生成固态沉积物的技术[31]。CVD方法是工业上应用最广泛的一种大规模制备半导体薄膜材料的方法,也是制备BNNSs的一种常用方法,许多研究学者采用CVD方法来制备单层或多层BNNSs。CVD制备工艺技术具有简单易行、高产、面积可控并且可以得到高品质、性能好的固体材料等优点,引发了使用CVD方法制备BNNSs材料的研究热潮。Yu等[32]使用微波等离子体 CVD 技术在硅基板从BF3-N2-H2的混合气体的合成BNNSs,通过BF3和H2的气流速度与其比率的改变控制BNNSs大小、形状和密度,从而制备的BNNSs厚度小至5 nm。Qin等[33]也是运用了微波等离子体 CVD 技术在硅基板从BF3-N2-H2的混合气体的合成BNNSs,不同的是同时调节N2、BF3和H2的气流速度,通过保持BF3和H2的气流速度为常量增加N2气体流速,最终在BF3、H2和N2的流速分别为3,10和1 200 mL/min条件下得到长度范围在0.8~2.5 μm,厚度约为一个或几个原子层的BNNSs。CVD方法制备BNNSs的化学原料通常为BF3/NH3、BCl3/NH3、B2H6/NH3,控制硼源和气体的流速是制备关键。此外,沉积速率受到硼源和NH3的摩尔比影响。Ismach等[34]采用低压化学气相沉积法 (low-pressure chemical vapor deposition, LPCVD),用乙硼烷和氨气作为前驱体制备BNNSs。LPCVD是由生长条件、温度、时间以及气体分压共同控制BNNSs的层数。Chatterjee等[35]则以十硼烷与氨为前驱体在多晶Ni或Cu箔上利用CVD方法有效的合成高质量BNNSs。十硼烷作为前驱体容易处理,且便于输送到CVD炉的反应区中。另外,通过对单一硼源,如环硼氮烷[36](B3N3H6)、三氯代环硼氮烷(B3N3H3Cl3)或六氯环硼氮烷(B3N3Cl6),热解得到BNNSs的方法也有许多研究。Shi等[37]用非气体作为前驱体材料,在多晶Ni片上采用常压化学气相沉积法 (ambient pressure chemical vapor deposition, APCVD) 由环硼氮烷 (B3N3H6) 制备具有光滑表面的少层BNNSs。Tay等[38]用硼烷氨作为前驱体在Cu箔上利用APCVD方法研究h-BN的可控生长。非气体硼源具有许多优点,其中环硼氮烷的毒性较小,然而这种方法同样需要较高的温度。虽然CVD技术有着各种工艺优点,但该方法对设备及外围设施依赖性较强,而且影响因素多,反应过程需要高真空度,使BNNSs制备成本不能得到有效的降低。
1.3 化学剥离法
化学剥离法是反应物在溶液中插入六方晶型BN(h-BN)层层之间,并发生化学反应,利用反应生成物的自由运动克服h-BN层间的范德华力,从而得到BNNSs。该方法操作简单,不需要高温高压,并且可以制备面积大、厚度薄的BNNSs,但也常常伴有BNNSs团聚的现象。Du等[39]利用浓H2SO4、KMnO4和H2O2发生化学反应制备BNNSs。其反应机理如下:(1) 将h-BN粉末和浓H2SO4混合均匀使得H+插入h-BN层间,从而使层间距拉大;(2) 随后,加入的KMnO4与浓H2SO4反应生成MnO2纳米粒子,MnO2纳米粒子也可以插入到增大的氮化硼层间内使BNNSs进一步剥离且阻止其发生团聚;(3) 最后,MnO2纳米粒子由加入的H2O2除去且生成的O2使得层状BN剥落制备了BNNSs。图2表明了剥离机理。
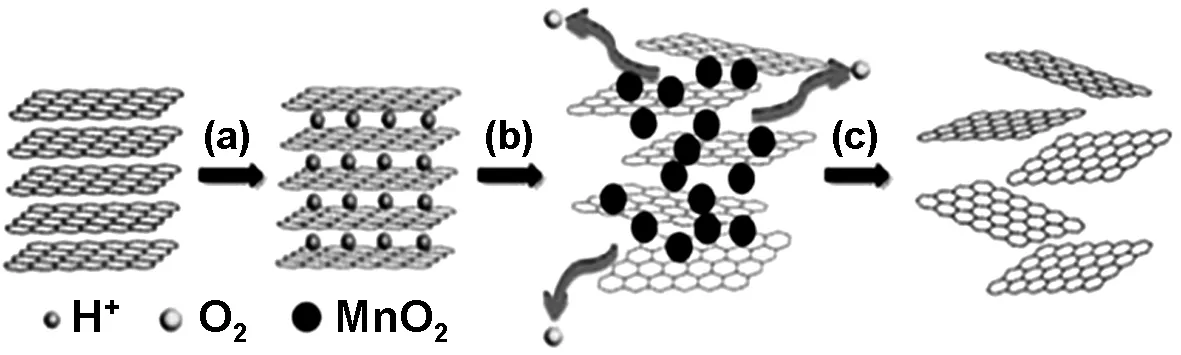
图2 BNNSs从六方氮化硼中剥离的过程[39]
Fig 2 The process of BNNSs exfoliated from h-BN powder[39]
Li等[40]利用熔融的氢氧化物实现h-BN层与层之间的剥离获得卷曲的BNNSs。该方法原材料易得、设备使用简单便宜,但得到的BNNSs产率低且易发生自卷曲。Du等[41]用氟化铵(NH4F)剥离和氟化BNNSs,一步合成具有铁磁性的F-BNNSs。剥离机理为氟化作用使h-BN的表面卷曲,从而铵离子插入剥离。化学剥离法的缺点在于制得的产物在酸性或碱性溶液中,需要处理接近中性,并且这种方法制备得到单层BNNSs产量较少。
1.4 声波降解法
通常直接把h-BN加在某种有机溶剂或水中,借助超声波的作用制备一定浓度的单层或少层BNNSs溶液。采用声波降解法制备BNNSs对所选择的溶剂有一定的要求,若该溶剂是h-BN的良溶剂则有助于BNNSs的剥离得到稳定的BNNSs且不易团聚;若该溶剂是h-BN的不良溶剂常常会使制得的BNNSs发生团聚而无法制得高质量、高产率的BNNSs。图3为良/不良溶剂下BNNSs剥离机理图[42]。
May等[43]研究了溶剂的溶解度参数对二维氮化硼纳米片在溶液中的稳定分散所起的作用,提出溶剂或高分子溶液的表面能和氮化硼表面能相近有助于氮化硼的剥离及稳定分散,该理论为制备氮化硼纳米片高分子复合材料的溶剂选择提供了简便方法。Lin等[44]在超声辅助的作用下以水为分散液超声剥离层状h-BN结构,制备洁净的BNNSs,但由于超声辅助水解作用会使h-BN平面切断从而导致纳米片的横向尺寸减小。
Zhi等[45]则采用强极性溶剂N, N-二甲基甲酰胺 (DMF) 为分散剂超声剥离h-BN材料10 h,通过离心分离制得的BNNSs,BNNSs的平均厚度和离心速率有关,5 000 r/min时得到层数低于20层、厚度小于7 nm的BNNSs,8 000 r/min时层数小于10层、厚度降到3 nm。制得的BNNSs直接应用于聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯 (PMMA) 复合材料,提高了复合材料的机械性能和热性能。Wang等[46]则将0.2 g h-BN分散于在100 mL的甲基磺酸 (MSA) 中超声处理8 h,最后得到0.3 mg/mL BNNSs的MSA溶液,BNNSs的厚度小于3 nm,其产率可高达15%。最近,Cao等[47]利用混合溶剂对h-BN超声处理进行研究,开发了一种新颖温和的混合溶剂,即异丙醇和氨水的混合溶液,并通过声波降解法剥离制备BNNSs。由于h-BN中硼原子缺电子,路易斯酸-碱相互作用被认为是h-BN的剥离的机理。当混合溶液氨水∶异丙醇等于3∶2时,超声剥离35 h得到产率约为20%的BNNSs。Marsh等[48]对简单的溶剂声波降解h-BN的剥离效果进行研究,并讨论溶剂表面张力和分子量在h-BN剥离的作用,提出助溶剂剥离机理,其助溶剂体系为丙酮、甲醇、乙醇、1-丙醇、异丙醇和四丁醇。浓度为2 mg/mL的h-BN粉末超声3 h,在四丁醇水溶液中超声剥离BNNSs效率高且分散稳定。
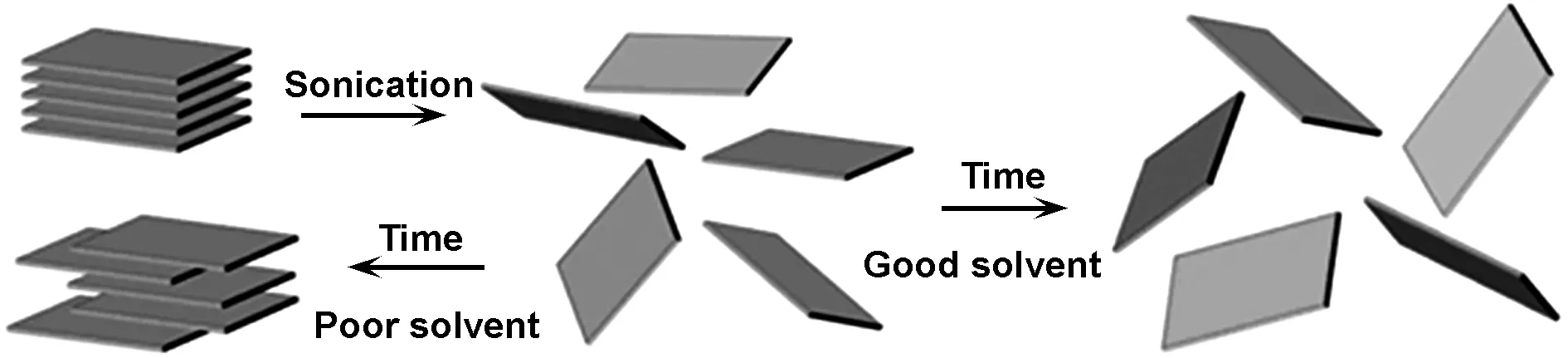
图3 良/不良溶剂对BNNSs剥离机理[42]
声波降解法主要是h-BN在有机溶剂或水中利用超声波的作用将h-BN层与层之间剥离,该方法操作简单,产物易得,但使用的有机溶剂往往有毒,产物的片层面尺寸减小明显。
1.5 球磨法
球磨法是在机械力的作用下将尺寸较大的h-BN经过一段时间的机械力作用得到BNNSs。球磨在h-BN层状材料上产生两种力,剪切力和压缩力。剪切力从它们的外表面切割层状材料,而压缩力从层状材料的边缘剥离纳米片。其制备BNNSs机理如图4所示[49]。

图4 低能球磨机理示意图[49]
Li等[50]采用低能球磨法以苯甲酸苄酯为球磨剂,在气压为200 kPa转速为150 r/min的行星球磨机中球磨15 h,制备了宽度在一百到几百纳米、厚度约为2~4 nm的BNNSs。Lee等[51]将氢氧化物作为辅助物采用简单的球磨法制备BNNSs,该制备过程是化学剥离和机械剪切作用的协同作用,从而提高产率和分散性。最近,Lin等[52]选用N-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮(NMP)作为球磨剂将h-BN粉末球磨48 h制备BNNSs。该方法在不同球磨剂条件下制得了BNNSs,其特点是操作简单、成本低,但产品纯度低、易产生缺陷且尺寸分布不均匀。
1.6 其它制备方法
除上述常用的几种制备BNNSs的路线外,国内外学者仍不断探索BNNSs新的制备途径。Sajjad等[53]在350 ℃利用CO2脉冲激光等离子体沉积(CO2-PLD)技术通过辐射热解h-BN制备了BNNSs,在真空0.2 Pa的压力下得到的多晶BNNSs,或在H2氛围中26 Pa压力下得到的单晶BNNSs,表现出较高的纯度和较好结晶度。Sokoowska等[54]探索了在电场(f=40 Hz,E=7 mV/μm)的作用下通过液相剥离在极性溶剂中制备六方BNNSs的实验,该方法表明电能可以增强h-BN液相剥离效果,电场辅助过程的能量效率较高且与超声剥离相比更加节能。Wang等[55]提出使用化学鼓泡法制备BNNSs,该方法使用硼烷氨为前驱体通过多阶段加热释放出氢气并使生成的BN吹鼓成泡,经过高温热处理和BN泡的塌陷制备出结构有序的BNNSs,BNNSs的产率高达25%(质量分数)。然而,为了制备出高产量高质量的BNNSs,很多学者仍在进行探索。
2 结 语
在相对较短的几年内,BNNSs以其具有的优异的性能及各种潜在的应用前景,推动了BNNSs快速的研究和发展。与此同时,人们需要大量高质量、结构完整的BNNSs,研究者们也致力于在不同领域尝试不同方法制备高质量、 大面积BNNSs材料。微机械法显然不能满足未来工业化的要求,化学气相沉积法虽然可以制备出高质量的BNNSs薄膜材料,但现有的工艺不成熟以及成本较高都限制了其大规模的生产应用;声波降解法和球磨法等机械剥离法能制备出高质量的BNNSs,但产率太低、耗时太长且易团聚,因此还需进一步探索、完善。如何大量、低成本制备出高质量的BNNSs材料并逐步走向产业化仍是未来研究的一个重点。
[1] Lin Y, Connell J W. Advances in 2D boron nitride nanostructures: nanosheets, nanoribbons, nanomeshes, and hybrids with grapheme [J]. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(22): 6908-6939.
[2] Wang Y, Ding Y. Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of the semifluorinated boron nitride bilayer: a first-principles study [J]. J Phys Chem C, 2013, 117(6): 3114-3121.
[3] Han T, Luo Y, Wang C. Effects of temperature and strain rate on the mechanical properties of hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets [J]. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2014, 47(2): 025303-025310.
[4] Meng W, Huang Y, Fu Y, et al. Polymer composites of boron nitride nanotubes and nanosheets [J]. J Mater Chem C, 2014, 47(2): 10049-10061.
[5] Kuang Z, Chen Y, Lu Y, et al. Fabrication of highly oriented hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet/elastomer nanocomposites with high thermal conductivity [J]. Small, 2015, 11(14):1655-1659.
[6] Bari R, Parviz D, Khabaz F, et al. Liquid phase exfoliation and crumpling of inorganic nanosheets [J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17(14): 9383-9393.
[7] Yuan J, Liew K M. Structure stability and high-temperature distortion resistance of trilayer complexes formed from graphenes and boron nitride nanosheets [J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2014, 16(1): 88-94.
[8] Li L H, Cervenka J, Watanabe K, et al. Strong oxidation resistance of atomically thin boron nitride nanosheets [J]. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(2): 1457-1462.
[9] Liu L, Shen Z, Zheng Y, et al. Boron nitride nanosheets with controlled size and thickness for enhancing mechanical properties and atomic oxygen erosion resistance [J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(71): 37726-37732.
[10] Cho D H, Kim J S, Kwon S H, et al. Evaluation of hexagonal boron nitride nano-sheets as a lubricant additive in water [J]. Wear, 2013, 302(1-2): 981-986.
[11] Deepika K, Li L H, Glushenkov A M, et al. High-efficient production of boron nitride nanosheets via an optimized ball milling process for lubrication in oil [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, (4): 7288-7296.
[12] Sajjad M, Feng P. Study the gas sensing properties of boron nitride nanosheets [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2014, 49: 35-38.
[13] Wang Y, Ding Y. Tunable magnetic and electronic properties of BN nanosheets with triangular defects: a first-principles study [J]. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2014, 26(43): 435302.
[14] Si M S, Gao D, Yang D, et al. Intrinsic ferromagnetism in hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets [J]. J Chem Phys, 2014, 140(20):204701.
[15] Wang X, Pakdel A, Zhi C, et al. High-yield boron nitride nanosheets from ‘chemical blowing’: towards practical applications in polymer composites [J]. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2012, 24(31): 314205-314214.
[16] Jan R, May P, Bell A P, et al. Enhancing the mechanical properties of BN nanosheet-polymer composites by uniaxial drawing [J]. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(9): 4889- 4895.
[17] Khan U, May P, O’Neill A, et al. Polymer reinforcement using liquid-exfoliated boron nitride nanosheets [J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(2): 581-587.
[18] Cho H B, Nakayama T, Suzuki T, et al. Formation and structural characteristic of perpendicularly aligned boron nitride nanosheet bridges in polymer/boron nitride composite film and its thermal conductivity [J]. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2011, 50, 01BJ05-6.
[19] Wang X, Pakdel A, Zhang J, et al. Large-surface-area BN nanosheets and their utilization in polymeric composites with improved thermal and dielectric properties [J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2012, (7): 662-668.
[20] Yi M, Shen Z, Zhang W, et al. Hydrodynamics-assisted scalable production of boron nitride nanosheets and their application in improving oxygen-atom erosion resistance of polymeric composites [J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(21): 10660-10667.
[21] Yi M, Shen Z, Zhao X, et al. Boron nitride nanosheets as oxygen-atom corrosion protective coatings [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 104(14): 143101-143105.
[22] Husain E, Narayanan T N, Taha-Tijerina J J, et al. Marine corrosion protective coatings of hexagonal boron nitride thin films on stainless steel [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, (5): 4129-4135.
[23] Gyawali G, Adhikari R, Kim H S, et al. Effect of h-BN nanosheets codeposition on electrochemical corrosion behavior of electrodeposited nickel composite coatings [J]. ECS Electrochemistry Letters, 2013, 2(3): C7-C10.
[24] Pakdel A, Zhi C, Bando Y, et al. Boron nitride nanosheet coatings with controllable water repellency [J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(8): 6507-6515.
[25] Garcia A G, Neumann M, Amet F, et al. Effective cleaning of hexagonal boron nitride for graphene devices [J]. Nano Lett, 2012, 12(9): 4449-4454.
[26] Sajjad M, Morell G, Feng P. Advance in novel boron nitride nanosheets to nanoelectronic device applications [J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013, 5(11): 5051-5056.
[27] Li L H, Chen Y, Cheng B M, et al. Photoluminescence of boron nitride nanosheets exfoliated by ball milling [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100(26):261108.
[28] Huang C, Chen C, Ye X, et al. Stable colloidal boron nitride nanosheet dispersion and its potential application in catalysis [J]. J Mater Chem A, 2013, (1): 12192-12197.
[29] Lei W, Portehault D, Liu D, et al. Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning [J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(2):216-219.
[30] Pacilé D, Meyer J C, Girit C O, et al. The two-dimensional phase of boron nitride: few-atomic-layer sheets and suspended membranes [J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92(13): 133107.
[31] 张迎光, 白雪峰, 张洪林,等. 化学气相沉积技术的进展[J]. 中国科技信息, 2005,12:82.
[32] Yu J, Qin L, Hao Y, et al. Vertically aligned boron nitride nanosheets: chemical vapor synthesis, ultraviolet light emission, and superhydrophobicity [J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(1): 414-422.
[33] Qin L, Yu J, Li M, et al. Catalyst-free growth of mono- and few-atomic-layer boron nitride sheets by chemical vapor deposition [J]. Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(21): 215602.
[34] Ismach A, Chou H, Ferrer D A, et al. Toward the controlled synthesis of hexagonal boron nitride films [J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(7): 6378-6385.
[35] Chatterjee S, Luo Z, Acerce M, et al. Chemical vapor deposition of boron nitride nanosheets on metallic substrates via decaborane/ammonia reactions [J]. Chem Mater, 2011, 23(20): 4414-4416.
[36] Sutter P, Lahiri J, Albrecht P, et al. Chemical vapor deposition and etching of high-quality monolayer hexagonal boron nitride films [J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(9): 7303-7309.
[37] Shi Y, Hamsen C, Jia X, et al. Synthesis of few-layer hexagonal boron nitride thin film by chemical vapor deposition [J]. Nano Lett, 2010, 10(10): 4134-4139.
[38] Tay R Y, Wang X, Tsang S H, et al. A systematic study of the atmospheric pressure growth of large-area hexagonal crystalline boron nitride film [J]. J Mater Chem C, 2014, 2(9): 1650-1657.
[39] Du M, Wu Y, Hao X. A facile chemical exfoliation method to obtain large size boron nitride nanosheets [J]. Cryst Eng Comm, 2013, 15(9): 1782-1786.
[40] Li X, Hao X, Zhao M, et al. Exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride by molten hydroxides [J]. Adv Mater, 2013, 25(15): 2200-2204.
[41] Du M, Li X, Wang A, et al. One-step exfoliation and fluorination of boron nitride nanosheets and a study of their magnetic properties [J]. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2014, 53(14): 3645 -3649.
[42] Nicolosi V, Chhowalla M, Kanatzidis M G, et al. Liquid exfoliation of layered materials [J]. Science, 2013, 340: 1226419-1226436.
[43] May P, Khan U, Hughes J M, et al. Role of solubility parameters in understanding the steric stabilization of exfoliated two-dimensional nanosheets by adsorbed polymers [J]. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116(20):11393-11400.
[44] Lin Y, Williams T V, Xu T B, et al. Aqueous dispersions of few-layered and monolayered hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets from sonication-assisted hydrolysis: critical role of water [J]. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115: 2679-2685.
[45] Zhi C, Bando Y, Tang C, et al. Large-scale fabrication of boron nitride nanosheets and their utilization in polymeric composites with improved thermal and mechanical properties [J]. Adv Mater, 2009, 21(28): 2889-2893.
[46] Wang Y, Shi Z, Yin J. Boron nitride nanosheets: large-scale exfoliation in methanesulfonic acid and their composites with polybenzimidazole [J]. J Mater Chem, 2011, 21(30): 11371-11377.
[47] Cao L, Emami S, Lafdi K. Large-scale exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets in liquid phase [J]. Mater Express, 2014, 4(2): 165-171.
[48] Marsh K L, Souliman M, Kaner R B. Co-solvent exfoliation and suspension of hexagonal boron nitride [J]. Chem Commun, 2015, 51(1): 187-190.
[49] Yao Y, Lin Z, Li Z, et al. Large-scale production of two-dimensional nanosheets [J]. J Mater Chem, 2012, 22(27): 13494-13499.
[50] Li L H, Chen Y, Behan G, et al. Large-scale mechanical peeling of boron nitride nanosheets by low-energy ball milling [J]. J Mater Chem, 2011, 21(32): 11862-11866.
[51] Lee D, Lee B, Park K H, et al. Scalable exfoliation process for highly soluble boron nitride nanoplatelets by hydroxide-assisted ball milling [J]. Nano Lett, 2015, 15: 1238-1244.
[52] Lin Z, Mcnamara A, Liu Y, et al. Exfoliated hexagonal boron nitride-based polymer nanocomposite with enhanced thermal conductivity for electronic encapsulation [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2014, 90: 123-128.
[53] Sajjad M, Ahmadi M, Guinel M J F, et al. Large scale synthesis of single-crystal and polycrystalline boron nitride nanosheets [J]. J Mater Sci, 2013, 48(6): 2543-2549.
[55] Wang X, Zhi C, Li L, et al. “Chemical blowing” of thin-walled bubbles: high-throughput fabrication of large-area, few-layered BN and Cx-BN nanosheets [J]. Adv Mater, 2011, 23(35): 4072-4076.
Research progress on preparation technology of boron nitride nanosheets
ZHAO Di1, KE Ruilin2, ZOU Xiong1, MAO Lin1, HU Xingbing3, WANG Jinhe1
(1. Shanghai University, Nano-Science & Technology Research Center, Shanghai 200444, China;2. Shenzhen Ohm Yang Technology Co. Ltd., Shenzhen 518035, China;3. Yangzhou Yaguang Cable Co. Ltd., Yangzhou 225600, China)
Boron nitride nanosheets has attracted much interest in recent years due to its unique and outstanding properties in physics, chemistry, electronics and materials academia. Preparation methods of boron nitride nanosheets used in recent years are intensively introduced, including chemical vapor deposition, chemical cleavage, ultrasonication exfoliation and low-energy ball milling, ect. Each method’s advantages and shortcomings are further discussed in detail. The preparations of boron nitride nanosheets are also prospected.
boron nitride; boron nitride nanosheets; preparation; research progress
1001-9731(2016)12-12071-05
国家青年科学基金资助项目(51403123);上海市青年科技英才扬帆计划资助项目(14YF1408800)
2016-03-16
2016-06-15 通讯作者:王金合,E-mail: wangjinhe@shu.edu.cn
赵 迪 (1991-),女,安徽宿州人,在读硕士,师承王金合副研究员,从事导热硅橡胶、导热机理研究。
TB321
A
10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2016.12.011

