邻域粗糙集中不确定性的熵度量方法*
陈玉明,曾志强,田翠华
1.厦门理工学院 计算机与信息工程学院,福建 厦门 361024
2.江西师范大学 国家网络化支撑软件国际科技合作基地,南昌 330027
邻域粗糙集中不确定性的熵度量方法*
陈玉明1,2+,曾志强1,田翠华1
1.厦门理工学院 计算机与信息工程学院,福建 厦门 361024
2.江西师范大学 国家网络化支撑软件国际科技合作基地,南昌 330027
CHEN Yuming,ZENG Zhiqiang,TIAN Cuihua.Uncertainty measures using entropy and neighborhood rough sets.Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology,2016,10(12):1793-1800.
针对传统粗糙集理论中不确定度量方法难以适用于邻域粗糙集模型的问题,引入信息熵的度量方法,提出了基于信息熵的邻域粗糙集不确定性度量方法。该方法采用邻域关系对连续型数据进行信息粒化,基于粒化后的数据定义邻域系统中的近似精度、邻域信息熵、加权邻域信息熵等不确定性度量。进一步提出邻域系统不确定性度量的公理化表示,证明邻域系统的近似精度、邻域信息熵、加权邻域信息熵都是公理化度量;给出其最大最小值,证明其满足单调性原理。理论分析与实验表明邻域系统中的信息熵度量优于近似精度度量。
邻域粗糙集;邻域信息熵;不确定性度量;信息系统;近似精度
1 引言
粗糙集理论由波兰科学家Pawlak于1982年提出[1],是一种处理不精确、不确定与海量数据的理论与方法,近二十年来被广泛应用于机器学习[2]、数据挖掘[3]、图像处理[4]、离群点检测[5]、特征选择[6]、大数据分析与处理等领域[7]。粗糙集理论中度量方法的研究是机器学习领域关键的研究内容之一。良好的度量工具能有效评价信息系统与决策系统的不确定性,提高机器学习中聚类与分类的精度与效率。
粗糙集理论中的不确定性度量是评价系统分类能力及提高分类精度的重要工具,国内外众多学者对此进行了研究。Pawlak[8]采用上下近似的比值构造的精度来度量等价类集合的不确定性,进一步用近似精度来度量决策系统的不确定性。精度与近似精度是随属性的增加而递增的函数,Pawlak同时提出了粗糙度与近似粗糙度两个单调性递减的度量工具。然而,Pawlak的不确定性度量并不精细,存在精度或者粗糙度一样而等价类集合却不一样的情况。因此,很多学者从不同角度进行了改进,提出了信息质量[9]、近似质量[10]、知识粒度[11]、信息粒度[12]等度量。苗夺谦、梁吉业等人将熵的概念引入粗糙集领域,提供了更加有效而精细的度量工具,主要包括信息熵[13]、条件熵[14]、互信息[13]与粗糙熵[15]等度量。
粗糙集理论中的这些度量工具与方法已经广泛应用于机器学习与数据挖掘的研究。经典粗糙集主要适用于具有离散型数据的决策系统,而对于广泛存在的连续型数据,需进行离散化预处理,但为此造成了分类信息丢失,分类精度降低等问题。胡清华等人提出了邻域粗糙集模型[16],能够处理具有连续型数据的知识分类系统,已经广泛用于属性约简[17]、特征选择与提取[18]、分类与聚类[19]、基因选择[20]、图像处理[21]等领域。然而,邻域关系并不是严格的等价关系,经典的不确定性度量工具与方法并不适用于邻域知识分类系统。
本文在深入研究经典粗糙集度量工具与方法的基础上,针对连续型数据的特点,引入邻域粗糙集模型与信息熵度量,提出基于邻域信息熵的不确定性度量方法。首先,对信息系统进行邻域粒化,构造邻域类集合;其次,定义邻域精度与邻域粗糙度概念度量邻域类集合的不确定性,采用邻域近似精度与邻域近似粗糙度概念度量邻域决策系统的不确定性;进一步,提出邻域信息熵、加权邻域信息熵等概念,用于度量连续型知识分类系统的不确定性及分类能力,证明了邻域精度、邻域信息熵及加权邻域信息熵度量的单调性原理;最后,通过理论分析与实验表明邻域系统中的邻域信息熵度量及加权邻域信息熵度量优于近似精度度量。
2 邻域粗糙集模型及其度量
Pawlak粗糙集理论对离散型数据进行等价类划分,形成等价类集合。而对于现实世界广泛存在的连续型数据,需要进行离散化处理后构造合适的等价类,但是离散化过程容易造成分类信息的丢失。为此,针对Pawlak粗糙集理论的局限性,引入邻域粗糙集模型,给出邻域粗糙集的相关概念[16],并讨论邻域粗糙集的精度度量与粗糙度度量。



3 基于信息熵的邻域系统不确定性度量
信息熵是一种有效而精细的不确定性度量工具。经典粗糙集中基于信息熵的度量并不适用于邻域粗糙集模型,需要进行扩展与改进。因此,根据邻域粗糙集模型的特点,引入信息熵理论,定义邻域系统中邻域信息熵的概念,证明该概念是一种公理化度量,给出其最大最小值,并证明其满足单调性原理。进一步定义了基于邻域信息熵与邻域近似精度的加权度量,证明了相关性质。




Table 1 The first medicine decision system表1 医疗决策系统之一


从以上例子可知,邻域近似精度、邻域信息熵与加权邻域信息熵度量都是随特征子集的增加而递增,不确定性增加,能够度量邻域系统的不确定性。然而,邻域近似精度度量不够精细。特征子集从{a}增加到{a,b},不确定性发生变化,邻域近似精度的值却没有变化,邻域信息熵和加权邻域信息熵度量的值都增大,说明这两个度量优于邻域近似精度度量。
4 实验分析
为验证邻域信息熵度量的有效性,分别采用表1和表2中的数据进行不确定性度量实验。度量方法分别采用精度度量、邻域信息熵度量、加权邻域信息熵度量。实验中邻域粒化采用欧氏距离,表1中的邻域参数为0.3,表2中的邻域参数为0.45。实验结果如图1和图2所示。

Table 2 The second medicine decision system表2 医疗决策系统之二

Fig.1 Measure result of Table 1图1 表1数据的度量结果
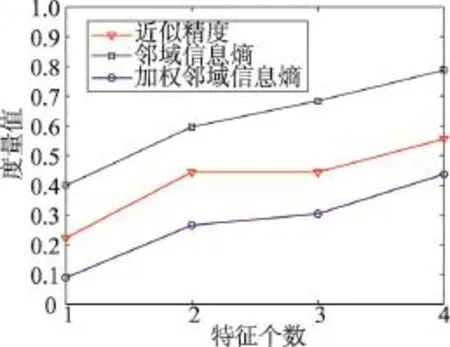
Fig.2 Measure result of Table 2图2 表2数据的度量结果
由图1与图2中的度量结果可知,近似精度、邻域信息熵、加权邻域信息熵的值随特征个数的增加而单调递增,不确定性增加,能够度量数据的不确定性。进一步分析可知,图1中,特征个数从1增加到2,近似精度没有变化,而邻域信息熵和加权邻域信息熵递增;图2中,特征个数从2增加到3,近似精度没有变化,而邻域信息熵和加权邻域信息熵递增。这些结果表明近似精度度量不够精细,有时并不能反映不确定性的变化,而邻域信息熵与加权邻域信息熵则具有更好的不确定性度量性能。
5 结论与展望
传统Pawlak粗糙集模型主要处理离散型数据集,对于连续型数据集则需要离散化预处理过程。然而,离散化算法不可避免会造成重要信息的损失,甚至降低机器学习算法的分类精度。为此,针对连续型的数据集的特点,在决策系统中引入邻域关系、信息熵理论,定义邻域近似精度、邻域信息熵与加权邻域信息熵等概念度量连续型数据的不确定性,并证明了邻域近似精度、邻域信息熵与加权邻域信息熵的单调性,为机器学习相关分类算法的研究提供了理论基础。
邻域系统中的近似精度、邻域信息熵等能够度量数据的不确定性,不仅适用于连续型数据集,而且也适用于离散型数据集。因此,这些度量能够应用于现实世界大量存在的同时具备以上两种类型的复杂数据集,进一步可以基于不确定性度量构造特征重要度,应用于属性约简、特征选择等领域。
[1]Pawlak Z.Rough sets[J].International Journal of Information and Computer Sciences,1982,11(1):341-356.
[2]Duan Jie,Hu Qinghua,Zhang Lingjun,et al.Feature selection for multi-label classification based on neighborhood rough sets[J].Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015,52(1):56-65.
[3]Tseng T L,Huang C C,Fraser K,et al.Rough set based rule induction in decision making using credible classification and preference from medical application perspective[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine,2016, 127(4):273-289.
[4]Yue Xiaodong,Miao Duoqian,Zhong Caiming.Roughness measure approach to color image segmentation[J].Acta Automatica Sinica,2010,36(6):807-816.
[5]Jiang Feng,Du Junwei,Ge Yan,et al.Sequence outlier detection based on rough set theory[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011,39(2):345-350.
[6]Chen Yumin,Miao Duoqian,Wang Ruizhi.A rough set approach to feature selection based on ant colony optimization [J].Pattern Recognition Letters,2010,31(3):226-233.
[7]Qian Jin,Lv Ping,Yue Xiaodong,et al.Hierarchical attribute reduction algorithms for big data using MapReduce[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2015,73:18-31.
[8]Pawlak Z.Rough sets[M].Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic Publishers,1991:45-64.
[9]Liang Jiye,Li Ru,Qian Yuhua.Distance:a more comprehensible perspective for measures in rough set theory[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2012,27(11):126-136.
[10]Dai Jianhua,Xu Qing.Approximations and uncertainty measures in incomplete information systems[J].Information Sciences,2012,198:62-80.
[11]Miao Duoqian,Fan Shidong.The calculation of knowledge granulation and its application[J].Systems Engineering-Theory&Practice,2002,22(1):48-56.
[12]Zhang Wenxiu,Wu Weizhi,Liang Jieye,et al.Rough set theory and methods[M].Beijing:Science Press,2001.
[13]Miao Duoqian,Wang Jue.An information representation of the concepts and operations in rough set theory[J].Journal of Software,1999,10(2):113-116.
[14]Wang Guoyin,Zhang Qinghua.Uncertainty of rough sets in different knowledge granularities[J].Chinese Journal of Computers,2008,31(9):1588-1598.
[15]Liang Jiye,Shi Zhongzhi,Li Deyu.Information entropy, rough entropy and knowledge granulation in incomplete information systems[J].International Journal of General System,2006,35(6):641-654.
[16]Hu Qinghua,Yu Daren,Xie Zongxia.Neighborhood classifiers[J].Expert Systems with Applications,2008,34(2): 866-876.
[17]Liu Yong,Huang Wenliang,Jiang Yunliang,et al.Quick attribute reduct algorithm for neighborhood rough set model [J].Information Sciences,2014,271:65-81.
[18]Xie Juanying,Li Nan,Qiao Zirui.Feature subset selection algorithms for incomplete decision systems based on neighborhood rough sets[J].Journal of Nanjing University:Natural Sciences,2011,47(4):383-390.
[19]Yao Ping Y,Lu Yongheng.Neighborhood rough set and SVM based hybrid credit scoring classifier[J].Expert Systems withApplications,2011,38(9):11300-11304.
[20]Meng Jun,Zhang Jing,Luan Yushi.Gene selection integrated with biological knowledge for plant stress response using neighborhood system and rough set theory[J].IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2015,12(2):433-444.
[21]Yu Ying,Pedrycz W,Miao Duoqian.Neighborhood rough sets based multi-label classification for automatic image annotation[J].International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2013,54(9):1373-1387.
[22]Chen Yumin,Wu Keshou,Chen Xuhui,et al.An entropybased uncertainty measurement approach in neighborhood systems[J].Information Sciences,2014,279:239-250.
附中文参考文献:
[2]段洁,胡清华,张灵均,等.基于邻域粗糙集的多标记分类特征选择算法[J].计算机研究与发展,2015,52(1):56-65.
[4]岳晓冬,苗夺谦,钟才明.基于粗糙性度量的彩色图像分割方法[J].自动化学报,2010,36(6):807-816.
[5]江峰,杜军威,葛艳,等.基于粗糙集理论的序列离群点检测[J].电子学报,2011,39(2):345-350.
[11]苗夺谦,范世栋.知识的粒度计算及其应用[J].系统工程理论与实践,2002,22(1):48-56.
[12]张文修,吴伟志,梁吉业,等.粗糙集理论与方法[M].北京:科学出版社,2001.
[13]苗夺谦,王珏.粗糙集理论中概念与运算的信息表示[J].软件学报,1999,10(2):113-116.
[14]王国胤,张清华.不同知识粒度下粗糙集的不确定性研究[J].计算机学报,2008,31(9):1588-1598.
[18]谢娟英,李楠,乔子芮.基于邻域粗糙集的不完整决策系统特征选择算法[J].南京大学学报,2011,47(4):383-390.

CHEN Yuming was born in 1977.He received the Ph.D.degree from Tongji University in 2010.Now he is an associate professor at Xiamen University of Technology,and the member of CCF.His research interests include rough sets and feature selection,etc.
陈玉明(1977—),男,江西吉安人,2010年于同济大学获得博士学位,现为厦门理工学院副教授,CCF会员,主要研究领域为粗糙集,特征选择等。

ZENG Zhiqiang was born in 1971.He received the Ph.D.degree from Zhejiang University in 2007.Now he is the vice dean at College of Computer and Information Engineering,Xiamen University of Technology.His research interests include artificial intelligence and pattern recognition,etc.
曾志强(1971—),男,福建厦门人,2007年于浙江大学获得博士学位,现为厦门理工学院计算机与信息工程学院副院长,主要研究领域为人工智能,模式识别等。

TIAN Cuihua was born in 1970.She received the Ph.D.degree from Northeastern University in 2008.Now she is an associate professor at Xiamen University of Technology.Her research interests include data mining and big data,etc.
田翠华(1970—),女,辽宁沈阳人,2008年于东北大学获得博士学位,现为厦门理工学院副教授,主要研究领域为数据挖掘,大数据等。
Uncertainty Measures Using Entropy and Neighborhood Rough Sets*
CHEN Yuming1,2+,ZENG Zhiqiang1,TIAN Cuihua1
1.College of Computer and Information Engineering,Xiamen University of Technology,Xiamen,Fujian 361024,China
2.State International S&T Cooperation Base of Networked Supporting Software,Jiangxi Normal University,Nanchang 330027,China
+Corresponding author:E-mail:cym0620@163.com
In view of the fact that the uncertainty measures of classical rough set theory are difficult to be suitable for neighborhood rough set model,this paper proposes an uncertainty measurement method based on information entropy and neighborhood rough sets.By the definitions of neighborhood relation,each object in the universe is assigned with a neighborhood subset,called neighborhood granule.Some uncertainty measures of neighborhood granule are defined,including approximate accuracy,information entropy and weighted information entropy in the neighborhood system.Furthermore,this paper presents the axiomatic concept of measure,and proves that the three measures are axiomatic uncertainty measures.This paper also gives the maximum and minimum of these measures and proves their monotonicities.Theoretical analysis and experiments show that the information entropy measure in the neighborhood system is better than the approximate accuracy measure.
10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1605037
A
TP18
*The National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61573297(国家自然科学基金);the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province under Grant Nos.2015J01277,2016J01324(福建省自然科学基金);the Project of Department of Education of Fujian Province under Gant Nos.JA09217,JB13152(福建省教育厅项目);the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province(福建省高校新世纪优秀人才支持计划).
Received 2016-04,Accepted 2016-06.
CNKI网络优先出版:2016-06-27,http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5602.TP.20160627.0929.002.html
Key words:neighborhood rough sets;neighborhood information entropy;uncertainty measure;information system; approximation accuracy

