乙型肝炎病毒小表面抗原各拓扑区段对其表达和分泌的影响
沈忠良,饶玉良,王葳,马张妹,刘晶1,,潘少坤,4,谢幼华1,
1.复旦大学生物医学研究院,上海 200032; 2.复旦大学基础医学院教育部/卫生部医学分子病毒学重点实验室,上海 200032; 3.上海健康医学院基础医学院,上海 201318; 4.上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院口腔预防科,上海 200011
·论著·
乙型肝炎病毒小表面抗原各拓扑区段对其表达和分泌的影响
沈忠良1,2,*,饶玉良3,*,王葳2,马张妹2,刘晶1,2,潘少坤2,4,谢幼华1,2
1.复旦大学生物医学研究院,上海 200032; 2.复旦大学基础医学院教育部/卫生部医学分子病毒学重点实验室,上海 200032; 3.上海健康医学院基础医学院,上海 201318; 4.上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院口腔预防科,上海 200011
乙型肝炎病毒小表面抗原(small hepatitis B virus surface antigen,SHB)在细胞内质网上表达,沿着细胞分泌途径分泌到胞外。为系统分析SHB拓扑结构对SHB表达和分泌的影响,首先通过生物信息学预测临床病毒株HBV C8和8种基因型(A~H)代表株的SHB拓扑结构,发现这些SHB均为四次跨膜蛋白,拥有基本相同的拓扑结构。相对内质网膜而言,SHB的拓扑结构拥有3个内质网腔内区段(Inside1~Inside3)、4个跨膜螺旋区(Tmhelix1~Tmhelix4)和2个内质网膜外区段(Outside1和Outside2)。6种基因型(基因型A、B、C、D、E和G)代表株与病毒株C8的SHB拓扑结构预测结果完全相同,而基因型F和H的SHB有4个区段与C8等不完全一致。通过对C8的SHB拓扑结构各区段进行缺失突变研究,发现Inside1区段不是SHB表达和分泌所必需的;Outside1、Tmhelix2和Inside2区段是SHB表达和分泌所必需的;Tmhelix1和Outside2不是SHB表达所必需的,但为SHB分泌所必需;Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4对SHB表达有重要影响,也是SHB分泌所必需的。进一步对Outside1和Outside2进行小片段(6个氨基酸)的缺失突变研究,发现小片段缺失基本不显著影响SHB的表达,但Outside1的氨基酸55~78及Outside2是SHB分泌所必需的。本研究首次系统性分析了SHB的拓扑结构各区段对SHB表达和分泌的影响,为深入探索SHB结构与功能的关系提供了线索。
乙型肝炎病毒小表面抗原;缺失突变;表达;分泌
乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis B virus,HBV)感染会引起慢性肝炎、肝硬化和肝癌,是全球性的公共卫生问题,给患者尤其是发展中国家的患者带来沉重负担[1]。HBV为有包膜的DNA病毒,病毒颗粒直径约42 nm。基因组含4个开放读码框架(open reading frame,ORF),其中包膜蛋白S基因(preS1/preS2/S-ORF)编码HBV大表面抗原(large HBV surface antigen,LHB)、HBV中表面抗原(middle HBV surface antigen,MHB)和HBV小表面抗原(small HBV surface antigen,SHB)[2]。MHB比SHB在N端多了preS2区段,LHB又比MHB在N端多了preS1区段,这3个蛋白合称为HBV表面抗原(HBV surface antigen,HBsAg),是HBV感染的重要标记之一[3]。临床上乙型肝炎患者发生HBsAg血清学转换一般预示着痊愈,但HBV隐匿性感染即HBsAg阴性而HBV DNA阳性也有报道[4-5]。在HBV感染者血清中,存在完整病毒颗粒和仅由表面抗原组成的亚病毒颗粒,SHB是这些颗粒包膜的主要蛋白组成成分[1]。由SHB组装形成的球形亚病毒颗粒也是目前使用的HBV疫苗的免疫原[6]。
SHB的合成、折叠、组装成颗粒等过程均在细胞内质网完成。SHB中影响这些步骤的重要氨基酸位点虽已鉴定[7-10],但由于缺乏SHB的三维结构模型,总体上对影响SHB表达和分泌的氨基酸区段或位点尚缺乏系统的研究。
本研究首先对HBV基因型A~H的SHB进行拓扑结构预测,然后运用缺失突变方法系统研究拓扑结构中各区段对SHB表达和分泌的影响,为深入研究SHB结构与功能的关系提供新线索。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
大肠埃希菌(Escherichiacoli,E.coli)DH5α、人肝癌细胞株Huh7由本实验室保存。真核表达质粒pcDNA3.1-N-Flag为Invitrogen公司产品,1.3拷贝HBV基因组质粒p1.3HBV/C8(毒株C8基因型为C型,GenBank序列号为AF461363)和增强绿色荧光蛋白(enhanced green fluorescent protein,EGFP)过表达质粒pEGFP由本实验室保存。8种HBV基因型(A~H)参考序列依次为:X02763.1、D00329、X04615、X65259、X75657、X69798、AF160501和AY090454。
1.2方法
1.2.1拓扑结构预测将HBV C8和8种基因型代表株的SHB氨基酸序列提交至http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/,依据隐马尔可夫模型(hidden Markov model,HMM)理论,采用TMMOD(改良TMHMM)法对SHB拓扑结构进行预测。
1.2.2质粒构建以p1.3HBV/C8为模板,聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)扩增其SHB(核苷酸157~837)片段,克隆至pcDNA3.1-N-Flag的BamHⅠ和NotⅠ双酶切位点,构建SHB表达质粒pcDNA3.1-N-Flag-SHB(简称pS)。pS缺失突变质粒构建采用KOD-Plus-Mutagenesis Kit(Toyobo公司)。质粒测序及鉴定由上海博尚生物技术有限公司完成。
1.2.3细胞培养将Huh7细胞置于含10%(V/V)胎牛血清、100 U/mL青/链霉素、2 mmol/LL-谷氨酰胺的DMEM完全培养基(以上试剂均购自Gibco BRL)中,37 ℃,5% CO2细胞培养箱中培养。
1.2.4细胞转染转染前1 d每孔接种1×105个Huh7细胞于24孔培养板中,第2天至细胞生长至80%~90%后,每孔转染1 μg目的质粒和0.1 μg pEGFP。转染试剂采用TurboFectTM(ThermoFisher公司)。转染后6 h,将无血清培养基换成含血清培养基,48 h后进行酶联免疫吸附试验(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)和蛋白免疫印迹检测。
1.2.5ELISA检测采用上海科华生物工程股份有限公司的ELISA试剂盒检测细胞上清液和胞内SHB。检测方法如下:将适量待检样本加入酶标板反应孔中,设置复孔及阳性、阴性和空白对照孔,每孔加入50 μL酶结合物均匀混合,37 ℃孵育30 min。洗5次后加入显色剂A和B各50 μL,均匀混合,37 ℃孵育30 min。每孔加入50 μL终止液,终止反应。用Bench Mark ELISA酶标仪(BioRad公司)获得波长为450 nm的读数。
1.2.6蛋白免疫印迹检测采用蛋白免疫印迹法检测细胞内SHB和EGFP的表达情况。将转染培养48 h后的细胞裂解物电泳、转膜,用5%脱脂牛奶封闭,一抗使用Flag标签单克隆抗体(Sigma公司)或EGFP单克隆抗体(Abcam公司),稀释度均为1∶3 000,二抗为羊抗鼠抗体(Santa Cruz公司),稀释度1∶3 000,再用化学发光试剂(Millipore公司)发光,用Bio-Rad ChemiDoc XRS+凝胶成像系统扫描检测。
2 结果
2.1SHB拓扑结构预测
首先将HBV C8毒株的SHB氨基酸序列提交至http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/,对SHB拓扑结构进行预测。由于SHB在内质网合成与加工,因此以内质网膜作为参考。预测结果显示,SHB为四次跨膜蛋白(图1),可分为9个区段,分别为3个内质网腔内区段(inside):Inside1(氨基酸1~6)、Inside2(氨基酸99~169)和Inside3(氨基酸225~226);4个跨膜螺旋区段(transmembrane helix,Tmhelix):Tmhelix1(氨基酸7~29)、Tmhelix2(氨基酸80~98)、Tmhelix3(氨基酸170~192)和Tmhelix4(氨基酸202~224); 2个内质网膜外区段(outside):Outside1(氨基酸30~79)和Outside2(氨基酸193~201)。

SHB topological structure was predicted online using the SHB protein sequence of strain C8 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/).The transmembrane domains are shown as blue rectangles.The regions inside the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen (Inside) and at the cytoplasmic side (Outside) of ER are depicted as lines.The amino acid positions in SHBs are shown.Tmhelix: transmembrane helix.
图1SHB的拓扑结构示意图
Fig.1Schematic presentation of SHB topological structure
同时对HBV基因型A~H 8个代表性毒株的SHB进行拓扑结构预测。8种基因型的SHB均含有226个氨基酸,在内质网膜上均为四次跨膜,含有3个Inside区和2个Outside区。基因型A、B、C、D、E和G代表株的SHB拓扑结构中各区段氨基酸位置与C8的SHB完全一致。基因型F和H代表株的SHB拓扑结构中各区段氨基酸位置完全一致,但与C8的SHB不完全一致(表1,加粗)。其中4个区段(Inside2、Tmhelix3、Outside2和Tmhelix4)与C8的SHB存在差异:前者的Inside2(氨基酸99~178)比后者(氨基酸99~169)多9个氨基酸;前者的Tmhelix3(氨基酸179~201)与后者(氨基酸170~192)长度相同,但起始和结尾氨基酸位置不同;前者的Outside2(氨基酸202~204)比后者(氨基酸193~201)少6个氨基酸;前者的Tmhelix4(氨基酸205~224)比后者(氨基酸202~224)少3个氨基酸,但两者结尾氨基酸位置相同(表1)。
2.2SHB拓扑结构中各区段缺失突变对SHB表达和分泌的影响
将C8的SHB表达质粒pS及其拓扑结构各区段缺失的质粒分别转染Huh7细胞,48 h后ELISA检测胞内和上清液中的SHB(表2)。Inside1和Inside3区段缺失质粒转染组的胞内和上清液中均可检测到SHB。Outside1、Tmhelix2和Intside2区段缺失质粒转染组的胞内和上清液中均检测不到SHB。Tmhelix1、Tmhelix3、Outside2和Tmhelix4区段缺失质粒转染组的胞内可检测到SHB,而上清液中检测不到。同时利用Flag抗体检测胞内上述各质粒的表达情况,结果如图2所示,Inside1、Tmhelix1、Tmhelix3、Outside2、Tmhelix4和Inside3缺失质粒转染组的胞内均可检测到SHB,Inside1缺失质粒转染组只检测到糖基化条带,Tmhelix1、Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4缺失质粒转染组只检测到非糖基化条带,Outside2和Inside3缺失质粒转染组可检测到SHB的糖基化和非糖基化条带。Outside1、Tmhelix2和Inside2缺失质粒转染组的胞内均检测不到SHB。
Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4缺失突变体转染组的胞内可检测到SHB表达,但含量均低于野生型(pS)组,上清液中检测不到SHB可能是由于SHB胞内表达不足。增大这两个突变质粒的转染量使SHB胞内表达量达到野生组水平,但在细胞上清液中仍检测不到SHB(表2,加粗),表明SHB的Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4区段缺失后上清液中检测不到SHB并不是细胞内表达不足引起的。
2.3SHB拓扑结构中Outside1区小片段缺失对SHB表达和分泌的影响
由于用Outside1区段缺失质粒pS_del 30/79转染 Huh7细胞后ELISA和蛋白免疫印迹法均检测不到胞内SHB,提示该区段影响SHB表达。为寻找该区段中影响SHB表达的关键氨基酸序列,对SHB中氨基酸25~84这60个氨基酸每隔6个氨基酸依次构建缺失突变体(共10个):pS_del 25/30、pS_del 31/36、pS_del 37/42、pS_del 43/48、pS_del 49/54、pS_del 55/60、pS_del 61/66、pS_del 67/72、pS_del 73/78和pS_del 79/84。这些突变体分别转染Huh7细胞,48 h后ELISA检测胞内和上清液中SHB(表3)。其中pS_del 25/30、pS_del 31/36、pS_del 37/42、pS_del 43/48、pS_del 49/54共5个缺失突变转染组的胞内可检测到与野生组接近的SHB表达;pS_del 25/30、pS_del 37/42和pS_del 49/54缺失突变组的上清液中还能检测到较低量的SHB分泌;pS_del 31/36和pS_del 43/48缺失突变组的上清液中完全检测不到SHB分泌。其余5个缺失突变体(pS_del 55/60、pS_del 61/66、pS_del 67/72、pS_del 73/78和pS_del 79/84)转染后胞内SHB含量均不到野生型的60%,且上清液中检测不到SHB。为排除这5个缺失突变组上清液中无法检测到SHB分泌是胞内SHB表达不足所致,增加这些缺失突变体转染量(表3,加粗),使其胞内表达量与野生型一致,但上清液中仍检测不到SHB。
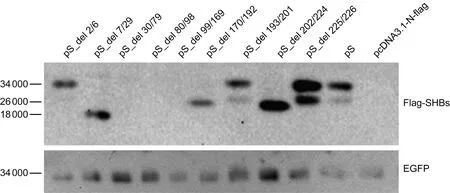
Flag-tagged wild-type or deletion mutant SHB expression plasmid was co-transfected with the reference plasmid pEGFP into Huh7 cells.At 48 h post-transfection,intracellular SHBs and EGFP were examined with Western blotting using anti-Flag.pS_del 2/6: Inside1 (aa 2-6) deleted; pS_del 7/29: Tmhelix1 (aa 7-29) deleted; pS_del 30/79: Outside1 (aa 30-79) deleted; pS_del 80/98: Tmhelix2 (aa 80-98) deleted; pS_del 99/169: Inside2 (aa 99-169) deleted; pS_del 170/192: Tmhelix3 (aa 170-192) deleted; pS_del 193/201: Outside2 (aa 193-201) deleted; pS_del 202/224: Tmhelix4 (aa 202-224) deleted; pS_del 225/226: Inside3 (aa 225-226) deleted; aa: amino acid; Inside/Outside: topological region inside/outside of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen; Tmhelix: transmembrane helix.
图2SHB拓扑结构中各区段缺失对SHB表达的影响
Fig.2Impact of the deletion of SHB topological regions on SHB expression
表1不同基因型的HBV毒株SHB的拓扑结构预测和分类
Tab.1Prediction and classification of SHB topological structures of different HBV genotypes

C8/A/B/C/D/E/GStartEndLength(aa)F/HStartEndLength(aa)Inside1166166Tmhelix17292372923Outside1307950307950Tmhelix2809819809819Inside299169719917880Tmhelix31701922317920123Outside219320192022043Tmhelix42022242320522420Inside322522622252262
SHB topological structures were predicted online using HBV strain C8 and 8 genotypes (A-H) (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/).Inside/Outside: the topological region inside/outside of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen; Tmhelix: transmembrane helix.Numbers represent the start and end amino acid positions of each topological region in the respective SHBs.The start positions,end positions and the lengths of some SHB topological regions of genotypes F and H that differ from other genotypes are in boldface.
表2SHB拓扑结构各区段缺失对SHB表达和分泌的影响
Tab.2Impact of the deletion of SHB topological regions on SHB expression and secretion

PlasmidDeletedaa(start-end)DeletedtopologicalregionSHBexpressionSHBsecretionpS++++++pS_del2/62-6Inside1++++++pS_del7/297-29Tmhelix1+++-pS_del30/7930-79Outside1--pS_del80/9880-98Tmhelix2--pS_del99/16999-169Inside2--pS_del170/192170-192Tmhelix3++-pS_del193/201193-201Outside2+++-pS_del202/224202-224Tmhelix4++-pS_del225/226225-226Inside3++++pS_del170/192170-192Tmhelix3+++-pS_del202/224202-224Tmhelix4+++-
Flag-tagged wild-type or deletion mutant SHB expression plasmid was co-transfected with the reference plasmid pEGFP into Huh7 cells cultured in 24-well plates.Transfection efficiency was normalized by measuring EGFP expression using Western blotting.At 48 h post-transfection,intracellular and supernatant SHBs were tested with ELISA.Transfections were performed in duplicates and repeated three times independently.“-”: SHB not detected; “+”: the level of SHB lower than 33% of that of the pS transfectant; “++”: the level of SHB higher than 33% but lower than 66% of that of the pS transfectant; “+++”: the level of SHB higher than 66% of that of the pS transfectant.The mutant plasmids in boldface indicate that they were transfected with a high dose so that the intracellular SHB was adjusted to be comparable to that of the pS transfectant.aa: amino acid; Tmhelix: transmembrane helix; Inside/Outside: topological region inside/outside of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen.
表3SHB的 Outside1区小片段缺失对SHB表达和分泌的影响
Tab.3Impact of the serial deletions of Outside1 region on SHB expression and secretion
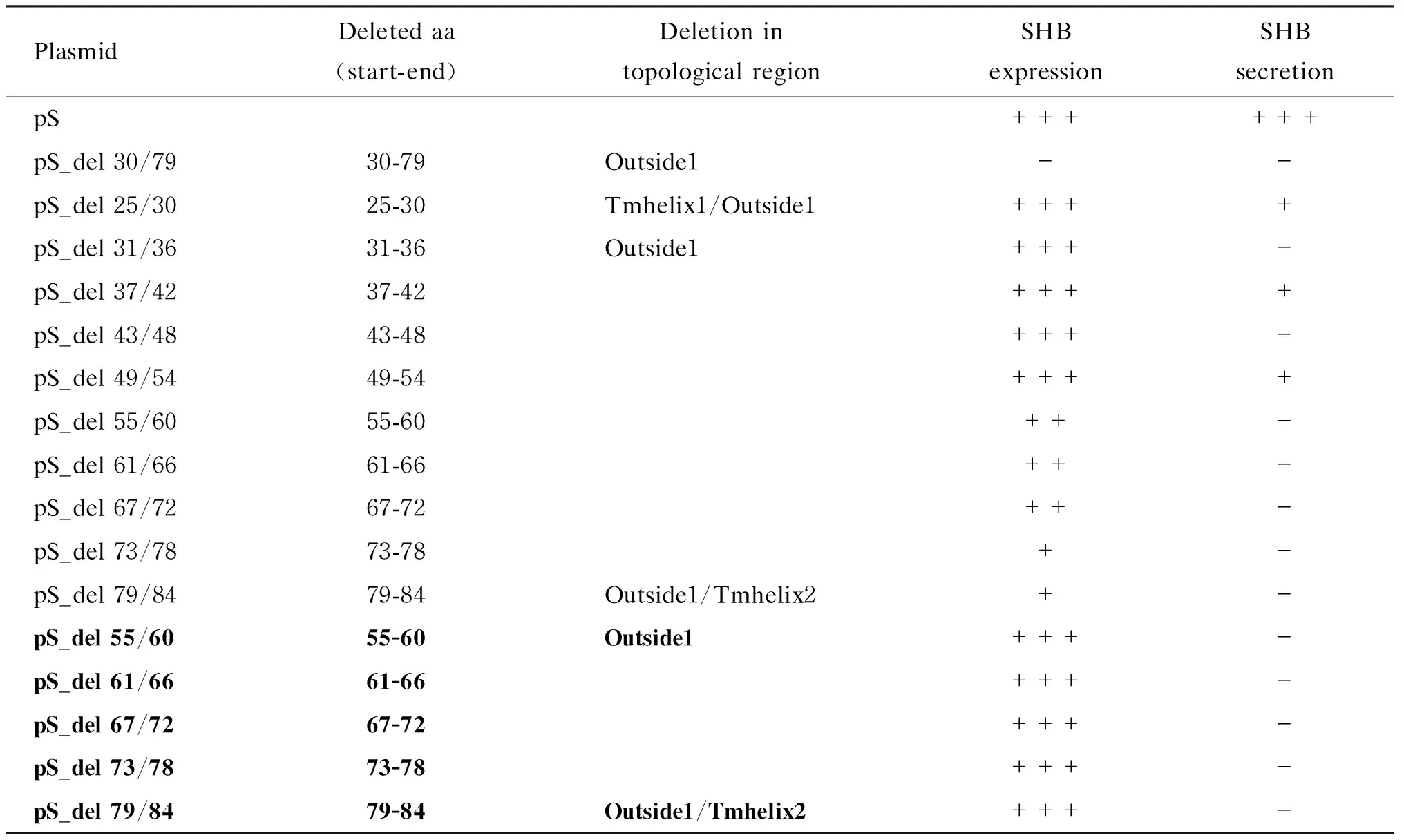
PlasmidDeletedaa(start-end)DeletionintopologicalregionSHBexpressionSHBsecretionpS++++++pS_del30/7930-79Outside1--pS_del25/3025-30Tmhelix1/Outside1++++pS_del31/3631-36Outside1+++-pS_del37/4237-42++++pS_del43/4843-48+++-pS_del49/5449-54++++pS_del55/6055-60++-pS_del61/6661-66++-pS_del67/7267-72++-pS_del73/7873-78+-pS_del79/8479-84Outside1/Tmhelix2+-pS_del55/6055-60Outside1+++-pS_del61/6661-66+++-pS_del67/7267-72+++-pS_del73/7873-78+++-pS_del79/8479-84Outside1/Tmhelix2+++-
Flag-tagged wild-type or deletion mutant SHB expression plasmid was co-transfected with the reference plasmid pEGFP into Huh7 cells cultured in 24-well plates.Transfection efficiency was normalized by measuring EGFP expression using Western blotting.At 48 h post-transfection,intracellular and supernatant SHBs were tested with ELISA.Transfections were performed in duplicates and repeated three times independently.“-”: SHBs not detected; “+”: the level of SHB lower than 33% of that of the pS transfectant; “++”: the level of SHB higher than 33% but lower than 66% of that of the pS transfectant; “+++”: the level of SHB higher than 66% of that of the pS transfectant.The mutant plasmids in boldface indicate that they were transfected with a high dose so that the intracellular SHB was adjusted to be comparable to that of the pS transfectant.aa: amino acid; Tmhelix: transmembrane helix; Inside/Outside: topological region inside/outside of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen.
2.4SHB拓扑结构中Outside2区小片段缺失对SHB表达和分泌的影响
Outside2区段中只有9个氨基酸(氨基酸193~201),其缺失突变后不影响SHB胞内表达,但为分泌所必需(表2)。同样每隔6个氨基酸依次构建缺失突变体(2个):pS_del 193/198和pS_del 199/204。两个突变体转染Huh7细胞48 h后,用ELISA检测胞内和上清液中的SHB(表4)。两个缺失突变体转染组的胞内均可检测到SHB,上清液中检测不到。增大pS_del 199/204转染量,上清液中仍检测不到SHB(表4,加粗)。
表4SHB的 Outside2区小片段缺失对SHB表达和分泌的影响
Tab.4 Impact of the serial deletions of Outside2 region on SHB expression and secretion

PlasmidDeletedaa(start-end)Deletedtopologicalregion(locatedinendoplasmicreticulum)SHBexpressionSHBsecretionpS++++++pS_del193/201193-201Outside2+++-pS_del193/198193-198Inside2+++-pS_del199/204199-204Inside2/Tmhelix4++-pS_del199/204199-204Inside2/Tmhelix4+++-
Flag-tagged wild-type or deletion mutant SHB expression plasmid was co-transfected with the reference plasmid pEGFP into Huh7 cells cultured in 24-well plates.Transfection efficiency was normalized by measuring EGFP expression using Western blotting.At 48 h post-transfection,intracellular and supernatant SHBs were tested with ELISA.Transfections were performed in duplicates and repeated three times independently.“-”: SHBs not detected; “+”: the level of SHB lower than 33% of that of the pS transfectant; “++”: the level of SHB higher than 33% but lower than 66% of that of the pS transfectant; “+++”: the level of SHB higher than 66% of that of the pS transfectant.The mutant plasmids in boldface indicate that they were transfected with a high dose so that the intracellular SHB was adjusted to be comparable to that of the pS transfectant.aa: amino acid; Tmhelix: transmembrane helix; Inside/Outside: topological region inside/outside of the endoplasmic reticulum lumen.
3 讨论
HBsAg持续表达是HBV慢性感染最典型的特征之一,其与机体细胞免疫和体液免疫密切相关。HBsAg为膜蛋白,其三维结构目前尚不清楚。有限的研究认为SHB是四次跨膜蛋白,其N端和C端均位于病毒包膜外侧(胞内位于内质网腔);此外SHB还有一个包膜外环(胞内位于内质网腔)和两个包膜内环(胞内位于内质网外细胞质面)[2,11]。
为了解SHB的拓扑结构及各区域对SHB表达和分泌的作用,首先通过生物信息学对HBV 8种基因型(A~H)代表株及临床病毒株C8的SHB进行拓扑结构预测(图1、表1)。结果显示,预测的SHB皆包含4个跨膜区(Tmhelix1~ Tmhelix4),以内质网膜为参考,其N端和C端位于内质网腔内(分别为Inside1和Inside3),内质网腔内还含有1个环状结构(Inside2),内质网膜外侧(胞质侧)含有2个环状结构(Outside1和Outside2)。生物信息学预测结果与前人研究相符合。基因型A、B、C、D、E和G代表株的SHB拓扑结构各区段氨基酸位置与HBV C8完全一致,但基因型F和H代表株的SHB拓扑结构中仅5个区段与其他基因型完全相同,余下4个区段中Inside2(氨基酸99~178)、Tmhelix3(氨基酸179~201)、Outside2(氨基酸202~204)和Tmhelix4(氨基酸205~224)与C8和其他基因型的SHB在氨基酸数目或位置上不一致(表1)。这4个区段对应的氨基酸区段共126个残基(氨基酸99~224)。在这126个残基中,基因型F和H的SHB第178位为亲水性氨基酸天冬酰胺,而基因型A、B、C、D、E和G此位置为疏水的脯氨酸,这种变化可能导致F和H型SHB中Inside2区段增加了9个氨基酸。
SHB的免疫原性主要集中于Inside2区域,即主要亲水区域(major hydrophilic region,MHR),中和抗体也是针对该区域[3]。该区域中的“a”决定簇决定了HBV的血清型。“a”决定簇通过两个二硫键(124/137和139/147)维持MHR构象稳定(图1)[12]。MHR内相关位点突变影响HBsAg合成、折叠、组装和分泌,特别是免疫逃逸[13-16]。目前对SHB的研究主要集中在该区域,而对SHB拓扑结构中其他区域尚缺乏系统的研究。
为确定SHB拓扑结构中这9个区段对SHB表达和分泌的影响,在毒株C8的SHB表达质粒基础上分别构建这些区段的缺失突变体。这些突变体转染Huh7细胞后,ELISA检测结果表明Inside1缺失突变不影响SHB的胞内表达和胞外分泌;Inside3缺失不影响SHB的表达,但降低SHB的分泌;Outside1、Tmhelix2和Inside2缺失完全抑制SHB的表达;Tmhelix1和Outside2缺失不影响SHB的表达,但完全抑制SHB的分泌;Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4缺失下调SHB的表达,且完全抑制SHB的分泌(表2)。同时,采用蛋白免疫印迹法检测胞内SHB,表明Outside1、Tmhelix2和Inside2缺失完全抑制SHB的表达,Inside1缺失后只能检测到糖基化条带,Tmhelix1、Tmhelix3和Tmhelix4缺失后只能检测到非糖基化条带,Outside2和Inside3缺失后可检测到SHB的糖基化和非糖基化条带(图2),表明不同区段对SHB的表达和修饰也有影响。后续可通过缩小缺失突变范围,确定具体位点上氨基酸残基对SHB表达和修饰的影响。
目前,关于Outside1(氨基酸30~79)和Outside2(氨基酸193~201)区内氨基酸突变对SHB表达和分泌的影响研究很少。有研究表明,Outside1区内氨基酸56~80和L49突变影响HBsAg与病毒核心蛋白结合,进而影响病毒包装[17-20]。本研究重点探讨了Outside1区段对SHB表达和分泌的影响,发现氨基酸31~54中每隔6个氨基酸的缺失不影响其表达,但均不同程度地抑制SHB分泌,而氨基酸31~36和氨基酸43~48是分泌必需的。氨基酸55~78中每隔6个氨基酸的缺失均降低SHB的表达,同时完全抑制SHB的分泌(表3)。对Outside2区段的研究发现,其也为SHB分泌所必需,推测Outside1和Outside2可能是SHB相互作用的关键区段(表4)。
本研究仅用免疫学方法对SHB及各种突变体的表达和分泌进行了定性和定量分析。SHB突变体的表达水平可能与突变体自身蛋白或mRNA稳定性相关。目前尚无SHB突变表达水平与突变体自身蛋白或mRNA稳定性相关的报道,后续工作将结合这两个因素对SHB的突变体展开深入研究。
综上所述,本研究首次系统分析了HBV 8种基因型SHB的拓扑结构,发现不同基因型的SHB拥有相似的拓扑结构,但基因型F和H的SHB结构有自身特点。在此基础上,利用缺失突变方法较为系统地研究了SHB拓扑结构各区段对SHB表达和分泌的影响,为深入研究SHB结构与功能的关系提供了新线索。
[1]Liang TJ.Hepatitis B: the virus and disease [J].Hepatology,2009,49(5): S13-S21.
[2]Seeger C,Mason WS.Hepatitis B virus biology [J].Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,2000,64(1): 51-68.
[3]Tsai HT,Tsai TH,Lu TM,Yang CC.Immunopathology of hepatitis B virus infection [J].Int Rev Immunol,2008,27(6): 427-446.
[4]Huang CH,Yuan Q,Chen PJ,Zhang YL,Chen CR,Zheng QB,Yeh SH,Yu H,Xue Y,Chen YX,Liu PG,Ge SX,Zhang J,Xia NS.Influence of mutations in hepatitis B virus surface protein on viral antigenicity and phenotype in occult HBV strains from blood donors [J].J Hepatol,2012,57(4): 720-729.
[5]Pollicino T,Raimondo G.Occult hepatitis B infection [J].J Hepatol,2014,61(3): 688-689.
[6]Chen DS.Hepatitis B vaccination: the key towards elimination and eradication of hepatitis B [J].J Hepatol,2009,50(4): 805-816.
[7]Chua PK,Wang RY,Lin MH,Masuda T,Suk FM,Shih C.Reduced secretion of virions and hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen of a naturally occurring HBV variant correlates with the accumulation of the small S envelope protein in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus [J].J Virol,2005,79(21): 13483-13496.
[8]Coppola N,Onorato L,Minichini C,Di Caprio G,Starace M,Sagnelli C,Sagnelli E.Clinical significance of hepatitis B surface antigen mutants [J].World J Hepatol,2015,7(27): 2729-2739.
[9]Ito K,Qin Y,Guarnieri M,Garcia T,Kwei K,Mizokami M,Zhang J,Li J,Wands JR,Tong S.Impairment of hepatitis B virus virion secretion by single-amino-acid substitutions in the small envelope protein and rescue by a novel glycosylation site [J].J Virol,2010,84(24): 12850-12861.
[10]Prange R,Nagel R,Streeck RE.Deletions in the hepatitis B virus small envelope protein: effect on assembly and secretion of surface antigen particles [J].J Virol,1992,66(10): 5832-5841.
[11]Eble BE,Lingappa VR,Ganem D.Hepatitis B surface antigen: an unusual secreted protein initially synthesized as a transmembrane polypeptide [J].Mol Cell Biol,1986,6(5): 1454-1463.
[12]Mangold CM,Unckell F,Werr M,Streeck RE.Secretion and antigenicity of hepatitis B virus small envelope proteins lacking cysteines in the major antigenic region [J].Virology,1995,211(2): 535-543.
[13]Sayiner AA,Agca H,Sengonul A,Celik A,Akarsu M.A new hepatitis B virus vaccine escape mutation in a renal transplant recipient [J].J Clin Virol,2007,38(2): 157-160.
[14]Yang Y,Nan Y,Cai J,Xu J,Huang Z,Cai X.The Thr to Met substitution of amino acid 118 in hepatitis B virus surface antigen escapes from immune-assay-based screening of blood donors [J].J Gen Virol,2016,97(5): 1210-1217.
[15]Besharat S,Katoonizadeh A,Moradi A.Potential mutations associated with occult hepatitis B virus status [J].Hepat Mon,2014,14(5): e15275.
[16]O’Malley B,Lazinski D.A hepatitis B surface antigen mutant that lacks the antigenic loop region can self-assemble and interact with the large hepatitis delta antigen [J].J Virol,2002,76(19): 10060-10063.
[17]Poisson F,Severac A,Hourioux C,Goudeau A,Roingeard P.Both pre-S1 and S domains of hepatitis B virus envelope proteins interact with the core particle [J].Virology,1997,228(1): 115-120.
[18]Bruss V,Lu X,Thomssen R,Gerlich WH.Post-translational alterations in transmembrane topology of the hepatitis B virus large envelope protein [J].EMBO J,1994,13(10): 2273-2279.
[19]Jenna S,Sureau C.Effect of mutations in the small envelope protein of hepatitis B virus on assembly and secretion of hepatitis delta virus [J].Virology,1998,251(1): 176-186.
[20]Blanchet M,Sureau C.Analysis of the cytosolic domains of the hepatitis B virus envelope proteins for their function in viral particle assembly and infectivity [J].J Virol,2006,80(24): 11935-11945.
s.PAN Shaokun,E-mail: span10@fudan.edu.cn;XIE Youhua,E-mail: yhxie@fudan.edu.cn
Impact of topological regions of small hepatitis B virus surface antigen on its expression and secretion
SHEN Zhongliang1,2,*,RAO Yuliang3,*,WANG Wei2,MA Zhangmei2,LIU Jing1,2,PAN Shaokun2,4,XIE Youhua1,2
1.Institute of Biomedical Sciences,Fudan University,Shanghai 200032,China; 2.Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Virology of Ministries of Education and Health,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Fudan University,Shanghai 200032,China; 3.School of Basic Medicine,Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Science,Shanghai 201318,China; 4.Department of Preventive Dentistry,Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200011,China
The small hepatitis B virus surface antigen (SHB) is expressed on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is secreted along the cellular secretory pathway.To analyze the impact of SHB domains on its expression and secretion,SHB proteins of eight HBV genotypes (A-H) plus a clinical strain C8 were subjected to a domain analysis.All the SHBs have four transmembrane motifs (Tmhelix1-4),three regions in the ER lumen (Inside1-3),and two regions outside of the ER (Outside1-2).The topological regions of SHBs in C8 and genotypes A,B,C,D,E and G were identical,while four topological regions of SHBs in genotypes F and H were slightly different from that in C8.Deletion analysis of SHB topological regions in C8 indicated that Inside1 region was not required for SHB expression and secretion; Outside1,Tmhelix2 and Inside2 regions were required for both SHB expression and secretion; Tmhelix1 and Outside2 regions were dispensable for SHB expression but needed for SHB secretion; Tmhelix3 and Tmhelix4 regions were important for SHB expression and necessary for SHB secretion.Finer deletion (6 amino acids) mapping in Outside1 and Outside2 regions showed that amino acids 55-78 of Outside1 and Outside2 were required for SHB secretion.This is the first systematic analysis of the impact of SHB topological regions on SHB expression and secretion,which has provided valuable clues for future study of the structure-function relationship of SHB.
Small hepatitis B virus surface antigen; Deletion mutant; Expression; Secretion
国家重点基础研究发展计划(2012CB519002)
潘少坤,谢幼华
*同为第一作者
2016-06-03)

