持续泵入瑞芬太尼对甲状腺患者生命体征及脑电双频指数值的影响
王君艳 穆新华 白栓成.内蒙古自治区包头市中心医院重症医学科,内蒙古包头04040;.内蒙古自治区包头医学院第一附属医院麻醉科,内蒙古包头0400;.内蒙古自治区包头市中心医院麻醉科,内蒙古包头04040
持续泵入瑞芬太尼对甲状腺患者生命体征及脑电双频指数值的影响
王君艳1穆新华2白栓成3
1.内蒙古自治区包头市中心医院重症医学科,内蒙古包头014040;2.内蒙古自治区包头医学院第一附属医院麻醉科,内蒙古包头014010;3.内蒙古自治区包头市中心医院麻醉科,内蒙古包头014040
目的探讨颈丛神经阻滞复合不同剂量的瑞芬太尼在甲状腺手术中的应用效果及最适宜的用药浓度。方法选择2013年7月~2014年10月在包头市中心医院行甲状腺手术的患者120例为研究对象,采用随机数字表法将其随机分为四组:A组[瑞芬太尼0.05 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞]、B组[瑞芬太尼0.08 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞]、C组[瑞芬太尼0.10 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞]和D组(空白对照,单纯颈丛神经阻滞),每组30例。记录四组患者入手术室后安静平卧10 min(T1)、颈丛神经阻滞后1 min(T2)、切皮时(T3)、分离甲状腺上下极时(T4)、缝皮时(T5)和术毕(T6)的平均动脉压(MAP)、心率(HR)、脉搏血氧饱和度(SpO2)。测定T1、T4、T6时间点的脑电双频指数(BIS)及进行Ramsay镇静评分。记录患者不良反应发生情况,评价术后满意度。结果与D组比较,A、B、C组发生疼痛、恶心、呕吐等不良反应较低,差异均有高度统计学意义(P<0.01);与D组比较,A、B、C组的术后满意度均较高,差异有高度统计学意义(P<0.01)。与D组比较,A、B、C组T2、T3、T4、T5时间点MAP降低,T2、T3、T4、T5时间点心率降低,C组T2、T3、T4、T5时间点SpO2降低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);与T1时点比较,A、B、C组T3、T4、T5的MAP升高,A、B组T3、T4、T5的HR增快,D组T2、T3、T4、T5的MAP升高,HR增快,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。A、B、C组T1、T4、T6BIS值与D组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。C组镇静指数Ramsay评分明显高于A、B组和D组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论颈丛神经阻滞复合不同剂量瑞芬太尼均能满足甲状腺手术术中镇痛,与丙泊酚联合,发挥协同作用,对血流动力学影响较单纯颈丛神经阻滞小,对维持麻醉期间生命体征的平稳有帮助,但其对呼吸的抑制作用随剂量的增加而明显。
颈丛神经阻滞;瑞芬太尼;脑电双频指数;Ramsay评分;甲状腺手术
[Abstract]Objective To discuss the effect of different doses of Remifentanil combined with cervical plexus block in thyroid surgery and to explore the appropriate dose of Remifentanil.Methods One hundred and twenty patients from July 2013 to October 2014 in Baotou Central Hospital scheduled for thyroid surgery were divided into 4 groups by random number table:group A[0.05 μg/(kg·min)Remifentanil],group B[0.08 μg/(kg·min)Remifentanil],group C[0.1 μg/(kg·min)Remifentanil]and group D(blank control),each group with 30 cases.All the patient were given the cervical plexus block.The mean arterial pressure(MAP),heart rate(HR)and pulse oxygen saturation(SpO2)were recorded at 10 min after the patient came into the operating room(T1),1 min after cervical plexus nerve block(T2),cut the skin(T3),separation of the thyroid gland on or off the pole(T4),sewing leather(T5)and end of the surgery(T6).The value of bispectral index(BIS)and Ramsay sedation scores were detected at T1,T4and T6.The adverse reactions and the satisfaction postoperative were collected.Results The occurrence of adverse reaction such as pain,nausea and vomiting in group A,B,C was lower compared with the group D,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.01),the degree of satisfaction in group A,B,C was higher compared with the group D,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.01);Compared with the group D,MAP of the group A,B,C was reduced at T2,T3,T4,T5,andthe HR was reduced at T2,T3,T4,SpO2of the group C was lower at T5,T2,T3,T4,T5,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05);compared with T1,MAP of the group A,B,C was increased at T3,T4,T5,HR of the group A and B was increased at T3,T4,T5,MAP and HR of the group D were increased at T2,T3,T4and T5,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The value of BIS in group A,B,C had statistically significant difference compared with group D at T1,T4and T6(P<0.05).The Ramsay score in group C was markedly higher than those in the group A,B and group D,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion Different doses of remifentanil Combined with cervical plexus block can meet analgesia and sedation in thytoid surgery.Moreover,the impact on hemodynamic is small compared with the simple cervical plexus block.It can help maintain stable vital signs during anesthesia.The effect of inhibition of respiration is significantly increasing along with the dose rises.
[Key words]Cervical plexus block;Remifentanil;Bispectral index;Ramsay score;Thyroid surgery
甲状腺在解剖结构上外邻迷走神经及交感神经干,后邻喉返神经,易受迷走神经的喉上神经支配。甲状腺疾病的外科治疗主要包括甲状腺良性肿瘤切除术、甲状腺癌根治术等[1-5],即便颈丛阻滞完善,切皮时无疼痛感,当手术剥离甲状腺或甲状腺瘤时,特别是处理甲状腺上、下极或牵拉气管时,患者都会感到疼痛不适,严重时影响术者操作及患者安全。对于临床实践中最常见的甲状腺腺瘤和甲状腺结节,颈丛神经阻滞仍然具有显著的临床价值[6]。研究证实,颈丛神经阻滞是甲状腺手术麻醉中常用的一种安全的麻醉方法,麻醉效果确切可靠,且麻醉费用低[7-9]。单独使用颈神经丛阻滞不能提供完善的阻滞效果,如何辅助静脉药物,减少应激对患者的伤害,提高手术安全性是麻醉医师面临的问题。
1 对象与方法
1.1对象
本研究选择2013年7月~2014年10月在包头市中心医院接受甲状腺切除术治疗的患者120例,男49例,女71例;年龄18~65岁,体重45~75 kg。剔除标准:年龄<18岁或>65岁;合并糖尿病、严重高血压、心脏病、急慢性呼吸系统疾病、甲状腺功能亢进;体重指数>30 kg/m2;严重神经精神疾患者。所有患者均知情同意并签署知情同意书,本研究经相关医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2方法
采用随机数字表法将其随机分为四组:A组,瑞芬太尼(湖北宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,批号:080807)0.05 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞;B组,瑞芬太尼0.08 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞;C组,瑞芬太尼0.10 μg/(kg·min)+颈丛神经阻滞;D组,空白对照,单纯颈丛神经阻滞;每组各30例。入手术室后即开放下肢静脉通路,随后靶控输注(TCI)瑞芬太尼,A组:瑞芬太尼0.05 μg/(kg·min)持续静脉输注,B组:瑞芬太尼0.08 μg/(kg·min)持续静脉输注,C组:瑞芬太尼0.10 μg/(kg·min)持续静脉输注,D组:等量生理盐水。患者安静平卧10 min为第1个时间观察点,记为T1,随后进行颈丛神经阻滞,用C4横突法阻滞患侧深丛及双侧颈浅丛神经,方法是以胸锁乳突肌后缘中点为进针点,针尖触及C4横突后,回抽无血液及脑脊液后深丛注入利布合剂(2%利多卡因+0.75%布比卡因)4 mL,浅丛双侧各10 mL。神经阻滞操作后1 min记为第2个时间观察点T2,5 min后常规静注丙泊酚(四川国瑞药业有限责任公司,批号:0908202)25~50 mg,切皮时记为T3、分离甲状腺上下极时记为T4、缝皮时记为T5、术毕记为T6。待患者出院后电话随访,调查患者对术中麻醉是否满意,记录满意或不满意人数,计算满意度(满意度=每组满意人数/每组总人数)。
1.3观察指标
观察患者6个时间点的平均动脉压(MAP)、心率(HR)、脉搏血氧饱和度(SpO2),记录T1、T4、T6的脑电双频指数(BIS)及Ramsay评分指标,观察患者术前、术中及用药后疼痛、恶心、呕吐的发生情况,出现任何一项记为不良反应发生。
1.4统计学方法
采用SPSS 17.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料数据用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD-t检验;以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1四组患者一般情况、满意度与不良反应比较
四组患者一般情况,年龄、性别、体重比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与D组比较,A、B、C组疼痛、恶心、呕吐等不良反应发生率较低,差异有高度统计学意义(P<0.01);与D组比较,A、B、C组术后满意度均较高,差异有高度统计学意义(P<0.01)。见表1。
2.2四组患者各时间点MAP、HR、SPO2比较
与D组比较,A、B、C组T2、T3、T4、T5时间点MAP降低,T2、T3、T4、T5时间点心率降低,C组T2、T3、T4、T5时间点SpO2降低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);与T1时点比较,A、B、C组T3、T4、T5的MAP升高,A、B组T3、T4、T5的HR增快,D组T2、T3、T4、T5的MAP升高、HR增快,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。

表1 四组患者一般资料、满意度及不良反应比较

表2 四组患者各时间点MAP、HR、SPO2比较(x±s)
2.3四组患者各时间点BIS值的比较
T1、T4、T6时间点A、B、C组BIS值与D组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),C组下降最为明显。见表3。
2.4四组患者镇静指数Ramsay评分指标比较
C组镇静指数Ramsay评分明显高于A、B组和D组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
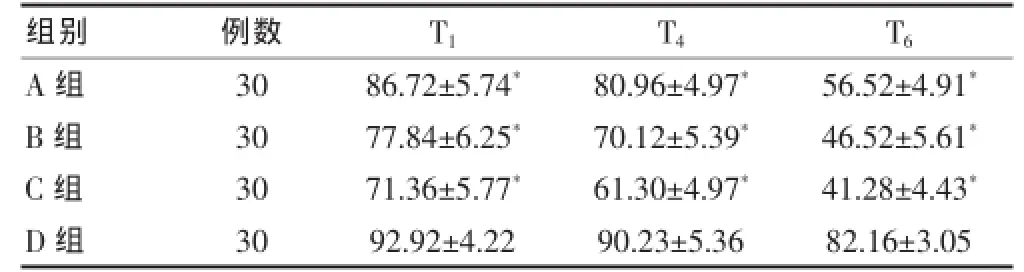
表3 四组患者各时间点BIS值的比较(x±s)

表4 四组患者各时间点Ramsay评分比较(x±s)
3 讨论
对于手术范围较小的浅表腺瘤等可选用颈丛神经阻滞,通过配合小剂量镇痛、镇静药既能达到满意的麻醉效果,术后恢复快,又可使患者在术中保持清醒,随时了解发音情况,深受术者欢迎[10-11]。从解剖结构上看,甲状腺上极受来自于迷走神经的喉上神经支配,外邻迷走神经及交感神经干,后邻喉返神经,因此,即使颈丛阻滞完善,切皮时无疼痛感,当手术剥离甲状腺或甲状腺瘤时,特别是处理甲状腺上、下极或牵拉气管时,患者都会感到疼痛不适。因此,需要静脉辅助应用镇痛、镇静药,传统的方法是使用氟哌利多加哌替啶或芬太尼,虽有一定的效果,但并不理想。
传统的麻醉辅助方式是由麻醉医师单次或反复注射一定剂量的镇静、镇痛药物,但因地西泮、咪达唑仑等药物的给药方式无法随时调整或维持恒定的血药浓度,且由于患者个体差异,易造成用药过量或不足。瑞芬太尼为超短效的阿片类镇痛药,镇痛作用强,起效快,副作用小,代谢时不受肝肾功能影响,能够及时减轻伤口疼痛[12-13],与芬太尼比较,用于麻醉诱导及维持时能更好地抑制心血管系统应激反应,维持术中血流动力学稳定,值得临床推广应用[14-16]。瑞芬太尼是完全的μ受体激动剂,临床上其效价与芬太尼相似,为阿芬太尼的15~30倍[17],在人体内1 min左右迅速达到血-脑平衡,在组织和血液中被迅速水解,长期或反复输注,其代谢速度无变化、体内无蓄积,是“快通道”麻醉必不可少的麻醉性镇痛药物[18]。瑞芬太尼不可避免地存在一些缺点,诸如使用者会出现恶心呕吐、心动过缓、呼吸抑制和低血压等不良反应症状,并且瑞芬太尼心血管抑制效应有剂量的依赖性,一次性的使用量过大或者持续输注的速度过快,患者血压和心率可能会出现异常的反应,而本研究因有颈丛神经阻滞的基础镇痛作用,用量相对小,故不会产生此种不良反应。由于瑞芬太尼起效快,作用时间短,消除快,代谢不受肝、肾功能的影响,且能够使患者处于意识清醒而无痛觉的状态,明显增强了患者的合作程度,降低了手术中副损伤的风险,增加了安全性。已有研究发现,持续静脉输注瑞芬太尼0.05~0.10 μg/(kg·min)30 min用于术后镇痛时,58%~78%的患者达到了满意的镇痛效果[19-20]。术后镇痛要求减轻术后疼痛,对呼吸循环几乎无影响,不良反应发生率低,故瑞芬太尼剂量0.05~0.10 μg/(kg·min)可以认为是相对安全剂量。另外,本研究采用BIS来判断术中麻醉深度情况,与麻醉中的镇静、催眠效果关系密切,该值会随麻醉加深或变浅呈顺序变化,一般在麻醉恢复期,BIS是逐步升高,反映镇静过程与恢复期镇静深度的渐变,是一个监测镇静深度的较好的指标。本研究中的阿片类药物瑞芬太尼虽然不能直接引起BIS的变化,但其可抑制伤害性刺激所导致的不良反应,减弱或消除唤醒功能,且随着剂量的增加,减弱功能增强。结果显示,三组BIS值在第一个观察时间点、分离甲状腺上下极、术毕与D组比较,差异显著。四组镇静指数Ramsay评分指标比较,差异显著,提示颈丛神经阻滞复合不同剂量瑞芬太尼均能满足甲状腺手术术中镇痛,与丙泊酚联合,发挥协同作用,对血流动力学影响较单纯颈丛神经阻滞小,对维持麻醉期间生命体征的平稳有帮助,在严密监测下是平稳及安全的,但其对呼吸的抑制作用随剂量的增加而明显。
由于颈丛麻醉没有气管插管的保障,麻醉过深容易引起呼吸抑制,麻醉深度的监测尤为重要。BIS作为神经电生理指标,研究证实与镇静程度之间有良好的相关性,能反映大脑皮层的功能状况,是目前国内外学者认为较为客观的镇静监测指标,可用于评判镇静深度和意识状态,指导镇静用药,控制镇静深度,避免镇静不足或过量等[12]。本研究中患者皆常规面罩吸氧,同时有BIS监测,故有效地避免了低氧血症的发生。总之,持续输注小剂量的瑞芬太尼,能有效抑制颈丛阻滞下甲状腺手术的牵拉反应,对维持麻醉期间生命体征的平稳有帮助,安全性更高,效果更佳。
[1]De Sanctis V,Soliman AT,Di Maio S,et al.Thyroid hemiagenesis from childhood to adulthood:review of literature and personal experience[J].Pediatr Endocrinol Rev,2016,13(3):612-619.
[2]Villacorte M,Delmarcelle AS,Lernoux M,et al.Thyroid follicle development requires Smad 1/5 and endothelial cell dependent basement membrane assembly[J].Development, 2016,143(11):1958-1970.
[3]PolatSB,OguzO,SacikaraM,etal.Thyroiddisordersinyoung females with polycystic ovary syndrome and correlation of thyroid volume with certain hormonal parameters[J].J Reprod Med,2016,61(1-2):27-32.
[4]Kovacic M,Kovadcic I.Incidence and surgical importance of pyramidal lobe and tubercle of the thyroid gland:a prospective study[J].Lijec Vjesn,2015,137(11-12):357-360.
[5]Onorati M,Uboldi P,Bianchi CL,et al.Solitary thyroid metastasis from colon cancer:fine-needle aspiration cytology and molecular biology approach[J].Pathologica,2015,107(3-4):192-196.
[6]Davies M,Jagannathan S.Superficial cervical plexus block,muscle twitch and analgesia[J].Anaesthesia,2015,70(11):1326.
[7]MatsunamiS,KomasawaN,FujiwaraS,etal.Anestheticmanagement using frontal nerve,greater occipital nerve,and superficial cervical plexus block for posterior cervical spinal fusion in a patient with athetoid cerebral palsy[J]. Masui,2015,64(5):549-551.
[8]Al-Shather H,El-Boghdadly K,Pawa A.Awake laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy under paravertebral and superficial cervical plexus blockade[J].Anaesthesia,2015,70(10):1201-1210.
[9]Tasar M,Kalender M,Karaca OG,et al.Regional cervical plexus blockage for carotid endarterectomy in patients with cardiovascular risk factors[J].Heart Surg Forum,2015,18(4):E140-E142.
[10]Barone M,Brigand C,Sonnek T,et al.Intermediate cervical plexus block for cervical esophagus diverticulectomy[J].Acta Anaesthesiol Belg,2015,66(2):59-61.
[11]Kale S,Aggarwal S,Shastri V,et al.Evaluation of the analgesic effect of bilateral superficial cervical plexus block for thyroid surgery:a comparison of presurgical with postsurgical block[J].Indian J Surg,2015,77(Suppl 3):1196-2000.
[12]SantoshBS,MehandaleSG.Doesdexmedetomidineimprove analgesia of superficial cervical plexus block for thyroid surgery?[J].Indian J Anaesth,2016,60(1):34-38.
[13]Su Y,Zhang Z,Zhang Q,et al.Analgesic efficacy of bilateral superficial and deep cervical plexus block in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal failure[J].Ann Surg Treat Res,2015,89(6):325-329.
[14]Sait KA,Kavrut ON,Umut AR,et al.Comparison of combined(deep and superficial)and intermediate cervical plexus block by use of ultrasound guidance for carotid endarterectomy[J].J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth,2016,30(2):317-322.
[12]Ma J,Wang JH.131I-Labeled-Metuximab Plus Transarterial Chemoembolization in Combination Therapy for UnresectableHepatocellularCarcinoma:Resultsfroma Multicenter Phase IV Clinical Study[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2015,16(17):7441-7447.
[13]Song MJ,Bae SH,Lee JS,et al.Combination transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation therapy for early hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Korean J Intern Med,2016,31(2):242-252.
[14]Chen CS,Li FK,Guo CY,et al.Tumor vascularity and lipiodol deposition as early radiological markers for predicting risk of disease progression in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(6):7241-7252.
[15]Li Z,Zhou JX,Ren JZ,et al.Clinical value of iodine131I metuximab infusion combined with TACE for treatment of patients with post-intervention relapse of mid or ad vanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi,2013,21(10):728-733.
[16]Zhu S,Li Y,Zhang Y,et al.Expression and clinical implications of HAb18G/CD147 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Hepatol Res,2015,45(1):97-106.
[17]Ru NY,Wu J,Chen ZN,et al.HAb18G/CD147 is involved in TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatocellular carcinoma invasion[J].Cell Biol Int,2015,39(1):44-51.
[18]Wu L,Shen F,Xia Y,et al.Evolving role of radiopharmaceuticals in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment[J].Anticancer Agents Med Chem,2016.
[19]许国辉,张智慧,李政文,等.131I肝癌单抗片段HAb18F(ab)2灌注治疗原发性肝癌的临床研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2005,14(6):596-598.
[20]Dai D,Xu W,Liu J,et al.Safety and efficacy of a peripheral intravenous bolus of Licartin for the treatment of advancedhepatocellularcarcinoma[J].ExpTherMed,2013,6(6):1417-1422.
Effect of continuous pump infusion of remifentanil on vital signs and BIS values in patients with thyroid
WANG Junyan1MU Xinhua2BAI Shuancheng3
1.Department of ICU,Baotou Central Hospital,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region,Baotou014040,China;2.Department of Anesthesiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region,Baotou014010,China;3.Department of Anesthesiology,Baotou Central Hospital,Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region,Baotou014040,China
R614
A
1673-7210(2016)09(a)-0088-05
2016-05-20本文编辑:赵鲁枫)
王君艳(1971-),女,硕士,主任医师;研究方向:麻醉与危重症。
白栓成(1970-),男,硕士,主任医师,主要从事麻醉与危重症工作。

