以芳香烃受体为药物靶点的肿瘤治疗研究
刘 颖,张洪英,唐 涛,刘飞飞,吴 谓,罗 瑛,张继虹(.昆明理工大学医学院衰老与肿瘤分子遗传学实验室,云南昆明 650500;.寿光市人民医院羊口分院,山东寿光 674)
以芳香烃受体为药物靶点的肿瘤治疗研究
刘颖1,张洪英2,唐涛1,刘飞飞1,吴谓1,罗瑛1,张继虹1
(1.昆明理工大学医学院衰老与肿瘤分子遗传学实验室,云南昆明650500;2.寿光市人民医院羊口分院,山东寿光262714)
网络出版时间:2016-4-26 11:06网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20160426.1106.008.html
芳香烃受体(aryl hydrocarbon receptor,AhR)是一种配体依赖性转录因子,可调控如2,3,7,8-四氯代苯并二恶英(2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins,TCDDs)等外源性配体化合物的毒性作用。通过参与细胞增殖与凋亡、免疫代谢等过程,AhR影响肿瘤的生长、存活、迁移和侵袭。AhR对肿瘤的调控具有双重作用,在多环芳烃、卤代芳烃等配体作用下,AhR可促进肿瘤生成;但苯并噻唑、氨基黄酮等化合物激活AhR后,可发挥抑癌功能,有望成为治疗肿瘤的药物靶点。该文主要讨论AhR在肿瘤中的作用、以AhR为靶点的药物作用机制以及目前AhR靶向药物的研究现状。
芳香烃受体;肿瘤;配体;靶向药物;作用机制;研究现状
芳香烃受体(aryl hydrocarbon receptor,AhR)是碱性螺旋-环-螺旋(basic helix-loop-helix,bHLH)
超家族的亚家族
很多化合物与AhR紧密结合后,以配体依赖的方式改变其活性,AhR被高度激活时,容易产生毒性物质,影响肿瘤细胞的生长和分化。根据AhR对二恶英反应元件(dioxin response element,DRE)依赖和非依赖的转录活性,将AhR配体分为完全激动剂、选择性调节因子(selective AhR modulators,SahRMs)和纯粹拮抗剂三类[6]。卤代芳烃(halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons,HAHs)(如TCDDs、二苯并呋喃和多氯联苯)、多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,PAHs)(如苯并[a]芘、苯并蒽)通常作为AhR完全激动剂发挥作用,调控AhR的转录水平和蛋白水平,产生的毒性物质能够诱发肿瘤。而属于SahRMs的配体具有组织特异性的AhR激动或拮抗作用[7-8],如山柰酚作为激动剂,可以在MCF-7细胞中诱导AhR调控的CYP1A1,造成DNA损伤,导致细胞死亡;但当有TCDDs存在时,其又是AhR拮抗剂,降低被TCDDs激活的AhR活性,减少TCDD代谢毒物的产生,保护机体[8-9]。而GNF351[N-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-9-isopropyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-3-yl)-9H-purin-6-amine]只能通过DRE调控反应,抑制AhR转录活性,并可以抑制由内源性配体或外源性激动剂诱导的DRE调控反应,体现出AhR完全拮抗剂的特点[6]。
在没有配体存在的情况下,AhR在肿瘤中的作用主要从以下几方面来体现[10]:①抑制p53和BRCA1等抑癌基因的功能性表达[11-12];②促进干细胞的转化和血管生成;③通过影响细胞周期、凋亡、细胞接触性抑制作用、细胞外基质代谢和改造、细胞-基质相互作用等生理过程,改变细胞的存活、增殖和分化过程;④ 与雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)和炎症信号通路的交互作用[13]。一般情况下,AhR是通过与配体结合来削弱自身致癌作用或加强其抑癌功能的,因为在配体的作用下,AhR与核转位蛋白(AhR nuclear translocator,ARNT)形成异源二聚体,诱导多种细胞色素P450(CYP)酶的转录,影响肿瘤的代谢和生物活性[1]。因此,AhR可能是肿瘤治疗的小分子靶点。目前,以AhR为靶点的多种化合物如苯丙噻唑类化合物{2-[(4-aminophenyl)benzothiazoles,2-(4-氨基苯基)苯并噻唑],Phortress}和氨基黄酮(aminoflavone,AF)都体现出抗肿瘤的效果,但存在肿瘤及细胞的选择特异性。本文将基于AhR及其配体对肿瘤的作用,重点阐述以AhR为靶点的肿瘤治疗研究现状。
1 AhR与肿瘤的关系
AhR作为转录因子,可以编码异型物质代谢酶(如CYP酶)的转录调控,其功能的异常与肿瘤的发生存在密切关系[14],如Fig 1所示。
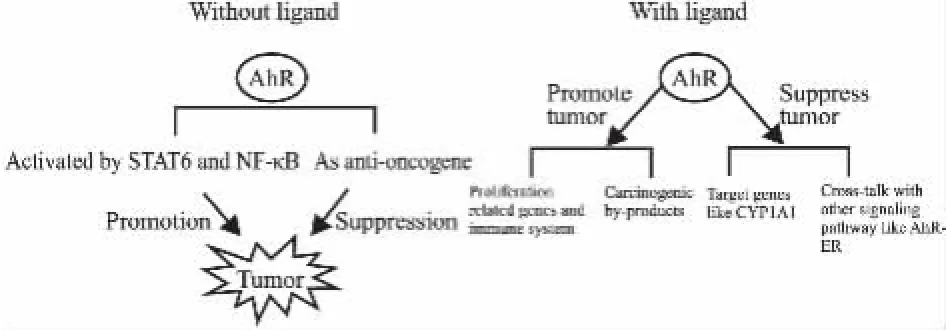
Fig 1 Relationship between AhR and tumor
1.1肿瘤发生过程中AhR的表达和功能在肿瘤的起始阶段,AhR促进Ⅰ相代谢酶(CYP1A1、CYP1A2和CYP1B1等)的表达,使TCDDs、BaP等致癌物被代谢活化成具遗传毒性的中间产物或终产物,导致DNA损伤的产生,促进肿瘤形成;但肿瘤中AhR表达增强的调控机制尚不清楚。在没有配体存在的情况下,AhR在乳腺癌、肺癌、胃癌、成人T细胞白血病、胰腺癌、前列腺癌、泌尿上皮癌、人神经胶质瘤细胞以及髓母细胞瘤中表达水平高于癌旁组织[10,15-24],这与信号转导子和转录激活子(STAT6)以及核因子κB(NF-κB)相关,IL-4以STAT6依赖的方式在鼠或人B细胞中诱导AhR激活;而在分化的免疫细胞中,NF-κB的活性涉及到RelA-依赖性AhR的表达,并增强AhR调控的基因活性,所以STAT6 与NF-κB有促进AhR在肿瘤中表达的可能[25-26]。此时敲低AhR会使肿瘤细胞增殖减少、侵袭和迁移能力降低[27-28],减缓肿瘤发生进程,说明AhR具有致癌作用;而Ahr-/-♂小鼠中,非AhR配体-二乙基亚硝胺(diethylnitrosamine,DEN)诱导肝癌的发生率高于野生型小鼠,因为高水平的氧化应激(reactive oxygen species,ROS)和稳定表达的TGF-β会促进Ahr-/-小鼠发生肿瘤[29],体现出AhR在肿瘤形成之前的抗肿瘤活性。
正常情况下,AhR作为芳烃类化合物毒性和代谢机制中的重要蛋白,主要在人的肺、胸腺、肾、肝脏中表达[30],它的促癌途径主要有两种,第一种是在TCDDs、PAHs、HAHs等天然配体化合物作用下,AhR影响增殖相关基因和免疫系统,促进肿瘤发生。如AhR协同性地诱导炎症信号通路中的IL-6[31]或介导类白介素-1(IL-1-like)细胞因子受体通路[32];AhR激动剂犬尿氨酸可抑制能识别肿瘤抗原的免疫细胞的聚集,促进神经胶质瘤的发展;另一种促癌途径是AhR诱导的异型生物质代谢中某些酶可以产生致癌副产物,如影响Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路对BaP代谢和基因毒性的抑制作用,所有由激活的AhR诱导的CYP1A1能在BaP-二醇上产生BaP-二醇环氧化物等致 DNA损伤的高致癌性中间产物[2,33]。
1.2AhR在配体作用下对肿瘤的影响AhR是配体依赖性受体,与AhR结合的配体分为内源性配体和外源性配体。AhR内源性配体包括吲哚类、四吡咯类化合物、花生四烯酸代谢产物等,与AhR的亲和力均较弱,不足以激活AhR[34]。而AhR外源性配体PAHs、HAHs等与AhR有着高亲和力作用,激活后AhR在很大程度上导致细胞周期的紊乱,包括G0/G1期和G2/M期的阻滞、DNA复制能力减弱和细胞增殖的抑制,进一步影响肿瘤的发生[35]。AhR在配体作用下可以经由两条通路被配体激活,分别是DRE调节的DNA结合通路即经典信号通路和无DRE调节的蛋白与蛋白相互作用的通路,两者都可以导致下游CYP1A1等基因表达水平的变化,影响肿瘤的发生[35]。TCDDs是与AhR有着高亲和力的完全激动剂,在胞质中,TCDDs与AhR结合并使之激活,调节代谢酶靶基因的表达,诱导自身代谢,尤其可以促进机体对外源性有毒物质的氧化代谢,保护机体;但TCDDs自身产生毒性代谢产物与DNA结合,产生遗传毒性,诱导肿瘤的发生。此外,TCDDs激活AhR,降解蛋白酶体依赖性的ER,抗激素依赖性肿瘤(如乳腺癌、子宫内膜癌和前列腺癌等),但同时促进非激素依赖性肿瘤(如腺癌、鳞癌等)的形成[36-37]。由于完全激动剂会表现出DRE依赖的基因毒性,而SahRMs既是AhR激动剂又是拮抗剂,作为SahRMs的MCDF通过抑制ER来抑制阴性乳腺癌细胞的增殖,表现出激动剂活性,但在有效剂量内不会激活DRE依赖的基因毒性。GNF351是AhR纯粹拮抗剂,能够抑制DRE依赖和非依赖调控的AhR活性和炎症相关细胞因子诱导的急性期基因(如IL-6等)表达,以抑制肿瘤的生长[6]。
AhR配体防止肿瘤发生的途径有两种,一是AhR下游靶基因(如CYP1A1、CYP1A2和CYP1B1)的表达产物Ⅰ相或Ⅱ相外源物质代谢酶,可促进机体对外源性毒物的代谢,从而保护机体不受外源物质影响[2];二是间接干预AhR与其他肿瘤相关信号通路[如AhR-ER、AhR-丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinases,MAPKs)等[38]]的交互作用,防止肿瘤的发生。而Phrotress作为AhR配体,在治疗肿瘤过程中表现出依赖于DRE调控的AhR激动剂活性,但与传统TCDDs等激动剂不同的是,它可以在代谢酶的作用下,在核内形成DNA加合物,从而导致细胞死亡。

Fig 2 Structures of AhR ligand compounds
因此,在以AhR为靶点进行肿瘤治疗的研究中,主要是通过AhR配体与AhR结合,根据不同的肿瘤和肿瘤细胞,利用AhR配体针对性的调节AhR活性和表达水平,使AhR[39]通过参与外源性化合物代谢或影响细胞周期、凋亡等过程,抑制肿瘤的生长[8,40]。
2 以AhR为靶点的药物研究
越来越多的研究证明,AhR是乳腺癌、肾癌、肝癌、胰腺癌等多种肿瘤治疗的药物靶点[1,8,41-42],作用机制主要是AhR激动剂、SahRMs或AhR拮抗剂以配体依赖的方式改变AhR活性,AhR与核转位蛋白(AhR nuclear translocator,ARNT)形成异源二聚体,诱导多种CYP酶的转录,影响肿瘤的代谢和生物活性[1]。
目前,以AhR为药物靶点进行的配体化合物研究主要包括 Phortress、AF、奥美拉唑(omeprazole,OM)、MCDF及NK150460等(Fig 2),其中Phortress、AF已分别进入Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期临床[42-43];针对OM、MCDF等AhR激动剂的研究也在体外的乳腺癌细胞、胰腺癌细胞等肿瘤细胞以及移植瘤动物模型中进行[27,44-45];而NK150460作为新合成的化合物,能抑制E2依赖性转录活性,激活AhR/ARNT依赖性通路并诱导CYP1A1表达,而被它激活的AhR参与ER-α依赖性通路,选择性地抑制乳腺癌细胞生长[46]。
Phortress是一种代谢性激活的药物前体,可导致DNA加合物的形成,并带来随后的药物毒性[39,47]。在早期筛选过程中发现,乳腺癌细胞MCF-7、卵巢癌细胞IGROV-1是对Phortress敏感的细胞株,随后研究发现,Phortress及其衍生物5F203、GW610等可穿过细胞膜进入细胞质,与从 AhRHSP90复合物上脱落的AhR结合,并转位至细胞核,与核内ARNT作用后,结合到 CYP1A1基因的启动子上,促进CYP1A1 mRNA的表达。在药物代谢酶类的作用下,胞质中的CYP1A1含量增加,与5F203结合,使其转变成具有生物活性的物质,并进入核内与DNA作用,形成DNA加合物,引发DNA单链和双链的断裂,导致DNA损伤,直至细胞死亡[48-49];而在不敏感的细胞株乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-435、前列腺癌PC-3等细胞中,该类化合物不能引起AhR在核内、胞质中的蛋白表达量和CYP1A1 mRNA水平的明显变化,也不能形成DNA加合物、造成DNA损伤,继而引发细胞的死亡[50]。这体现出Phortress等的苯并噻唑类化合物在肿瘤细胞中具有选择性抑癌作用,且它们的抗肿瘤活性可能与CYP1A1活性及DNA加合物有关[51](Fig 3)。
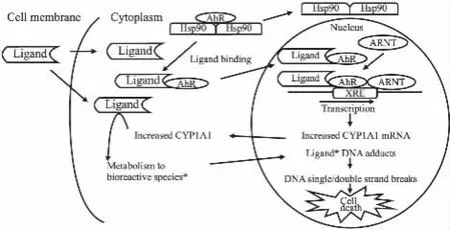
Fig 3 Classical targeting pathway of AhR
AF与Phortress在MCF-7等的雌激素受体阳性(ER+)乳腺癌细胞中有着类似的作用机制,都是通过诱导CYP1A1 或CYP1A2的表达,激发自身代谢活性,引发细胞毒DNA损伤及细胞周期 S期阻滞,从而导致细胞凋亡[34,50,52]。与Phrotress作用机制不同的是,AF作用于ER(-)α三阴性乳腺癌(triple negative breast cancers,TNBC)细胞和前列腺癌细胞时,不存在药物诱导的乙氧基异吩恶唑脱乙基酶(ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase,EROD)活 性 和CYP1A1、CYP1B1基因表达增加,且AhR一直存在于核内,并不影响经瞬时转染的细胞中DRE启动的荧光素酶活性和CYP1A1启动子序列上蛋白-DNA复合物的合成[53],且AF能够引起TNBC细胞的DNA损伤、S期阻滞以及衰老,但其调控的生长抑制不需要内源性AhR或者下游AhR靶基因CYP1A1和CYP1B1的表达,即AhR的表达与否及AhR信号通路是否正常,AF抑制细胞生长的功能不会受到影响[54]。
此外,许多AhR活性药物在体外实验中抑制癌细胞的侵袭和增殖[55]。如NK150460和MCDF在乳腺癌细胞中具有依赖于AhR/ARNT和靶蛋白CYP1A1的抗肿瘤活性,但NK150460是通过诱导CYP1A1和CYP1B1在mRNA水平的表达,抑制肿瘤细胞生长与增殖[46];MCDF能够激活CYP1A1依赖性的EROD活性,抑制ER(-)乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-468的增殖,通过诱导TGF-α和AhR调控的microRNA-335(miR-335)的表达来分别抑制细胞的生长和侵袭[27];OM将AhR募集到含有DREs的趋化因子受体4(C-XC chemokine receptor type 4,CXCR4)启动子区域,伴随着启动子上RNA聚合酶-Ⅱ(PolⅡ)的缺失,通过抑制CXCR4转录来抑制肿瘤侵袭,调节体内代谢[7,44]。这为以AhR为靶点的其他肿瘤治疗提供了参考依据。
除了研究乳腺癌的AhR靶向治疗外,研究者还对其他的肿瘤进行了尝试。通过对人肾癌细胞株及来源于患者的肾癌细胞研究发现,AF能够导致AhR诱导的细胞凋亡[42];OM可以通过AhR在转录水平上诱导人腺癌细胞H441中CYP1A1的表达[56],并通过非基因型AhR通路抑制前列腺癌细胞的侵袭[45];大麻二醇在肝癌细胞HepG2中诱导通过AhR通路调控CYP1A1的表达[57];3,3'-二吲哚基甲烷激活AhR信号通路,从而抑制胃癌的发展[58]。
目前的研究结果显示,AhR的靶向药物主要集中于对乳腺癌的研究,同时也涉及其他肿瘤,但由于AhR配体具有肿瘤和肿瘤细胞的特异性,这给以AhR为靶点的药物筛选增加了难度。因此,希望能在全面认识AhR与肿瘤关系的基础上,找出导致配体在肿瘤中表现出特异性的原因,使AhR靶向药物在治疗肿瘤的过程中体现广谱性。
3 总结与展望
肿瘤的发生、发展与遗传基因、外在环境、饮食习惯等多种因素相关,实现肿瘤的个性化治疗需要充分了解肿瘤在细胞生物学和分子生物学等方面的作用机制,使用合适的化合物进行靶向治疗。多种研究表明,AhR是治疗肿瘤的潜在新型药物靶点,但AhR在肿瘤病理中的分子机制比较复杂,目前还没有完全研究清楚[10]。AhR既可以促癌亦可以抑癌,在治疗不同肿瘤中作为 AhR配体的激动剂、拮抗剂和SAHRMs并不能都发挥有效抑癌作用[1]。因此,在不同肿瘤的不同病理阶段,深入研究AhR相关分子机制将是新的挑战。许多抗肿瘤药物作为与AhR有着高亲和力的外源性配体,参与AhR经典途径进行肿瘤治疗,同时也可通过AhRER等信号通路的交互作用发挥功能,并经由AhR调控的CYP1家族代谢酶降低药物毒副作用[59]。目前已有很多化合物(如Phrotress、AF等)靶向AhR治疗乳腺癌,但对于不同的乳腺癌细胞,同种化合物的作用效果不同,为实现以AhR为药物靶点的多种肿瘤治疗,需要进一步的研究AhR在肿瘤中的作用机制,并在前人的基础上优化药物结构、开发新型靶向药物,用不同类别的AhR配体进行特异性治疗。
[1]Murray I A,Patterson A D,Perdew G H.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer:friend and foe[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2014,14(12):801-14.
[2]Bersten D C,Sullivan A E,Peet D J,Whitelaw M L.bHLH-PAS proteins in cancer[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2013,13(12):827-41.
[3]Esser C,Rannug A.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology,immunology,and toxicology[J].Pharmacol Rev,2015,67(2):259-79.
[4]Abel J,Haarmann-Stemmann T.An introduction to the molecular basics of aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology[J].Biol Chem,2010,391(11):1235-48.
[5]Fujii-Kuriyama Y,Kawajiri K.Molecular mechanisms of the physiological functions of the aryl hydrocarbon(dioxin)receptor,a multifunctional regulator that senses and responds to environmental stimuli[J].Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci,2010,86(1):40 -53.
[6]Smith K J,Murray I A,Tanos R,et al.Identification of a high-affinity ligand that exhibits complete aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2011,338(1):318-27.
[7]Jin U H,Lee S O,Safe S.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AHR)-active pharmaceuticals are selective AHR modulators in MDA-MB-468 and BT474 breast cancer cells[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2012,343(2):333-41.
[8]Safe S,Lee S O,Jin U H.Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as a drug target[J].Toxicol Sci,2013,135(1):1-16.
[9] 王宇光,陈强,李晗,等.人参皂苷Rg1对TCDD致HepG2细胞CYP1A1诱导的抑制作用[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29 (10):1382-6.
[9]Wang Y G,Chen Q,Li H,et al.The inhibitory effect of Rg1 on TCDD induced CYP1A1 in HepG2 cell[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2013,29(10):1382-6.
[10] Feng S,Cao Z,Wang X.Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in cancer[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,2013,1836(2):197-210.
[11]Wohak L E,Krais A M,Kucab J E,et al.Carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce CYP1A1 in human cells via a p53-dependent mechanism[J].Arch Toxicol,2016,90(2):291-304.
[12]Papoutsis A J,Borg J L,Selmin O I,Romagnolo D F.BRCA-1 promoter hypermethylation and silencing induced by the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor-ligand TCDD are prevented by resveratrol in MCF-7 cells[J].J Nutr Biochem,2012,23(10):1324-32.
[13]Bradshaw T D,Trapani V,Vasselin D A,Westwell A D.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in anticancer drug discovery:friend or foe [J].Curr Pharm Des,2002,8(27):2475-90.
[14]Yin X F,Chen J,Mao W,et al.Downregulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression decreases gastric cancer cell growth and invasion[J].Oncol Rep,2013,30(1):364-70.
[15]Korzeniewski N,Wheeler S,Chatterjee P,et al.A novel role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AhR)in centrosome amplificationimplications for chemoprevention[J].Mol Cancer,2010,9:153.
[16]Cheng Y H,Huang S C,Lin C J,et al.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor protects lung adenocarcinoma cells against cigarette sidestream smoke particulates-induced oxidative stress[J].Toxicol Appl Pharmacol,2012,259(3):293-301.
[17]Peng T L,Chen J,Mao W,et al.Potential therapeutic significance of increased expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in human gastric cancer[J].World J Gastroenterol,2009,15(14):1719-29.
[18]Hayashibara T,Yamada Y,Mori N,et al.Possible involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AhR)in adult T-cell leukemia(ATL)leukemogenesis:constitutive activation of AhR in ATL[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2003,300(1):128-34.
[19]Koliopanos A,Kleeff J,Xiao Y,et al.Increased arylhydrocarbon receptor expression offers a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer[J].Oncogene,2002,21(39):6059-70.
[20]Gluschnaider U H G,Cojocaru G,Yutkin V,et al.b-TrCP inhibition reduces prostate cancer cell growth via upregulation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].PLoS One,2010,5(2):e9060.
[21]Ishida M,Mikami S,Kikuchi E,et al.Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway enhances cancer cell invasion by upregulating the MMP expression and is associated with poor prognosis in upper urinary tract urothelial cancer[J].Carcinogenesis,2010,31 (2):287-95.
[22]Gramatzki D,Pantazis G,Schittenhelm J,et al.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor inhibition downregulates the TGF-beta/Smad pathway in human glioblastoma cells[J].Oncogene,2009,28(28):2593-605.
[23]Dever D P,Opanashuk L A.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor contributes to the proliferation of human medulloblastoma cells[J]. Mol Pharmacol,2012,81(5):669-78.
[24]Yang X,Liu D,Murray T J,et al.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor constitutively represses c-myc transcription in human mammary tumor cells[J].Oncogene,2005,24(53):7869-81.
[25]Tanaka G,Kanaji S,Hirano A,et al.Induction and activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by IL-4 in B cells[J].Int Immunol,2005,17(6):797-805.
[26]Vogel C F,Khan E M,Leung P S,et al.Cross-talk between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and the inflammatory response:a role for nuclear factor-kappaB[J].J Biol Chem,2014,289(3):1866-75.
[27]Zhang S,Lei P,Liu X,et al.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a target for estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer chemotherapy [J].Endocr Relat Cancer,2009,16(3):835-44.
[28]Abdelrahim M,Smith R 3rd,Safe S.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene silencing with small inhibitory RNA differentially modulates Ah-responsiveness in MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cells[J].Mol Pharmacol,2003,63(6):1373-81.
[29]Fan Y,Boivin G P,Knudsen E S,et al.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor functions as a tumor suppressor of liver carcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Res,2010,70(1):212-20.
[30]Enan E,Matsumura F.Identification of C-SK as the integral component of the cytosolic ah receptor complex,transducing the signal of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin(TCDD)through the protein phosphorylation pathway[J].Biochem Pharmacol,1996,52:1599-612.
[31]DiNatale B C,Schroeder J C,Francey L J,et al.Mechanistic insights into the events that lead to synergistic induction of interleukin 6 transcription upon activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and inflammatory signaling[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(32):24388 -97.
[32]Kennedy G D,Nukaya M,Moran S M,et al.Liver tumor promotion by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin is dependent on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and TNF/IL-1 receptors[J].Toxicol Sci,2014,140(1):135-43.
[33]Kabatkova M,Zapletal O,Tylichova Z,et al.Inhibition of betacatenin signalling promotes DNA damage elicited by benzo[a]pyrene in a model of human colon cancer cells via CYP1 deregulation [J].Mutagenesis,2015,30(4):565-76.
[34]Denison M S,Nagy S R.Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals [J].Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,2003,43:309-34.
[35]Marlowe J L,Puga A.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor,cell cycle regulation,toxicity,and tumorigenesis[J].J Cell Biochem,2005,96 (6):1174-84.
[36]Korkalainen M,Huumonen K,Naarala J,et al.Dioxin induces genomic instability in mouse embryonic fibroblasts[J].PLoS One,2012,7(5):e37895.
[37]Callero M A,Loaiza-Perez A I.The role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and crosstalk with estrogen receptor in response of breast cancer cells to the novel antitumor agents benzothiazoles and aminoflavone [J].Int J Breast Cancer,2011,2011:923250.
[38]McLean L S,Watkins C N,Campbell P,et al.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand 5F 203 induces oxidative stress that triggers DNA damage in human breast cancer cells[J].Chem Res Toxicol,2015,28(5):855-71.
[39]Gasiewicz T A,Henry E C,Collins L L.Expression and activity of aryl hydrocarbon receptors in development and cancer[J].Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr,2008,18(4):279-321.
[40]Tsuji N,Fukuda K,Nagata Y,et al.The activation mechanism of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AhR)by molecular chaperone HSP90[J].FEBS Open Bio,2014,4:796-803.
[41]Safe S,Qin C,McDougal A.Development of selective aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators for treatment of breast cancer[J].Expert Opin Investig Drugs,1999,8(9):1385-96.
[42]Callero M A,Suarez G V,Luzzani G,et al.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by aminoflavone:new molecular target for renal cancer treatment[J].Int J Oncol,2012,41(1):125-34.
[43]Bradshaw T D,Wren J E,Bruce M,et al.Preclinical toxicokinetic evaluation of phortress[2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole lysylamide dihydrochloride]in two rodent species [J].Pharmacology,2009,83(2):99-109.
[44]Jin U H,Lee S O,Pfent C,Safe S.The aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand omeprazole inhibits breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis[J].BMC Cancer,2014,14:498.
[45]Jin U H,Kim S B,Safe S.Omeprazole inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion through a nongenomic aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway[J].Chem Res Toxicol,2015,28(5):907-18.
[46]Fukasawa K,Kagaya S,Maruyama S,et al.A novel compound,NK150460,exhibits selective antitumor activity against breast cancer cell lines through activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor [J].Mol Cancer Ther,2015,14(2):343-54.
[47]Prudhomme G J,Glinka Y,Toulina A,et al.Breast cancer stemlike cells are inhibited by a non-toxic aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist[J].PLoS One,2010,5(11):e13831.
[48]Callero M A,Luzzani G A,De Dios D O,et al.Biomarkers of sensitivity to potent and selective antitumor 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole(5F203)in ovarian cancer[J].J Cell Biochem,2013,114(10):2392-404.
[49]Tan B S,Tiong K H,Muruhadas A,et al.CYP2S1 and CYP2W1 mediate 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole(GW-610,NSC 721648)sensitivity in breast and colorectal cancer cells [J].Mol Cancer Ther,2011,10(10):1982-92.
[50]Bradshaw T D,Westwell A D.The development of the antitumour benzothiazole prodrug,Phortress,as a clinical candidate[J].Curr Med Chem,2004,11(8):1009-21.
[51]Bradshaw T D,Bibby M C,Double J A,et al.Preclinical evaluation of amino acid prodrugs of novel antitumor 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)benzothiazoles[J].Mol Cancer Therap,2002,1(4):239-46.
[52]Kuffel M J,Schroeder J C,Pobst L J,et al.Activation of the antitumor agent aminoflavone(NSC 686288)is mediated by induction of tumor cell cytochrome P450 1A1/1A2[J].2002,62(1):143 -53.
[53]Loaiza-Perez A I,Kenney S,Boswell J,et al.Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation of an antitumor aminoflavone:basis of selective toxicity for MCF-7 breast tumor cells[J].Mol Cancer Ther,2004,3(6):715-25.
[54]Brinkman A M,Wu J,Ersland K,Xu W.Estrogen receptor alpha and aryl hydrocarbon receptor independent growth inhibitory effects of aminoflavone in breast cancer cells[J].BMC Cancer,2014,14:344.
[55]Hu W,Sorrentino C,Denison M S,et al.Induction of CYP1A1 is a nonspecific biomarker of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation:results of large scale screening of pharmaceuticals and toxicants in vivo and in vitro[J].Mol Pharmacol,2007,71(6):1475-86.
[56]Zhang S,Patel A,Moorthy B,Shivanna B.Omeprazole induces NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 via aryl hydrocarbon receptor-independent mechanisms:role of the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2015,467(2):282-7.
[57]Yamaori S,Kinugasa Y,Jiang R,et al.Cannabidiol induces expression of human cytochrome P450 1A1 that is possibly mediated through aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in HepG2 cells[J]. Life Sci,2015,136:87-93.
[58]Xiao F,Yin J C,Wei M,et al.A selective aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulator 3,3'-diindolylmethane inhibits gastric cancer cell growth[J].J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2012,31(46):1-9.
[59]Okino S T,Pookot D,Basak S,Dahiya R.Toxic and chemopreventive ligands preferentially activate distinct aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathways:implications for cancer prevention[J].Cancer Prev Res(Phila),2009,2(3):251-6.
Anti-tumor therapy for targeting aryl hydrocarbon receptor
LIU Ying1,ZHANG Hong-ying2,TANG Tao1,LIU Fei-fei1,WU Wei1,LUO Ying1,ZHANG Ji-hong1
(1.Lab of Molecular Genetics of Aging&Tumor,Faculty of Medicine,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming650500,China;2.Yangkou Branch Hospital of the People’s Hospital of Shouguang,Shouguang Shandong262714,China)
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor(AhR)is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that mediates the toxicity of xenobiotic ligands like 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins(TCDDs). AhR influences tumor growth,survival,migration and invasion by regulating proliferation,apoptosis and immune metabolism of tumor cells.AhR has two ways to regulate tumor development,and ligands like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs),halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons(HAHs)can induce tumorigenesis.However,some compounds such as benzothiazole and aminoflavone can activate AhR,which suppresses the tumor progression and suggests that AhR may be a novel drug target for antitumor therapy.The paper discussed the role of AhR in tumorigenesis,the mechanism of the drugs targetting AhR and the status of studying AhR as a potential target in anticancer therapy.
aryl hydrocarbon receptor;tumor;ligand;targeted drugs;mechanism;present state
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.05.004
A
1001-1978(2016)05-0607-06
R-05;R392.11;R730.22;R730.5
2015-12-08,
2016-01-08
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No 81260501);云南省应用基础研究计划项目(No 2014FD011)
刘颖(1991-)女,硕士生,研究方向:遗传学,E-mail:lianqlying@hotmail.com;张继虹(1972-)女,博士,教授,研究方向:分子药理学,通讯作者,E-mail:zhjihong2000@126.com bHLH-PAS(bHLH-PER-ARNT-SIM)成员之一,是bHLH-PAS家族中唯一可以被配体激活的受体[1,2]。AhR参与细胞周期、上皮屏障功能、细胞迁移和免疫作用等多种细胞过程,对维持细胞内稳态有着重要作用[1,3],其通过介导天然或人工合成化合物的生物化学和毒性作用,发挥致癌或抑癌功能[4-5]。

