探讨BV2细胞活化中是否存在p38MAPK及JAK2-STAT通路的磷酸化激活①
房艳宇 罗晓光 苏 阳 谢 欣 田旭聪 范丽婷 任 艳
(齐齐哈尔医学院附属第三医院神经内科,齐齐哈尔161000)
探讨BV2细胞活化中是否存在p38MAPK及JAK2-STAT通路的磷酸化激活①
房艳宇罗晓光苏阳谢欣田旭聪范丽婷任艳
(齐齐哈尔医学院附属第三医院神经内科,齐齐哈尔161000)
[摘要]目的:探索CD200R在LPS诱导的小胶质细胞炎症模型中的作用以及是否有pho-p38MAPK及phoJAK2-STAT通路的激活。方法:采用小胶质细胞进行研究,将细胞用CD200R抗体及LPS处理,ELISA检测TNF-α及IL-1β的分泌。Western blot检验p38MAPK、JAK2、pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT表达。为证实这两条通路是炎症的下游通路,分别应用两者的阻断剂处理细胞后再次检测炎症因子的分泌。结果:在小胶质细胞表面有CD200R的表达;应用CD200R的阻断性抗体后,TNF-α及IL-1β分泌均增多,较对照组及LPS组比较差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),并且有pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT的激活;阻断剂SB203580及AG490均能抑制TNF-α及IL-1β的分泌。结论:pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT两条通路是LPS及CD200R抗体诱导的小胶质细胞炎症反应的下游通路。
[关键词]CD200R;BV2 细胞;TNF-α;IL-1β;pho-p38MAPK;pho-JAK2-STAT
帕金森病(PD)是中枢神经系统常见的变性病,其发病机制尚不完全清楚,目前认为:遗传因素、环境因素、免疫/炎症反应等参与了其病理过程[1,2]。众所周知,小胶质细胞是中枢神经系统内的常驻免疫细胞,在中枢神经系统固有免疫中发挥重要作用[3],然而,小胶质细胞的慢性活化可以导致TNF-α、IL-1β及IL-6等炎性因子的异常分泌,进而引发神经炎症及神经变性疾病[4]。近年来的研究表明,CD200-CD200R通路是中枢神经系统内下调小胶质细胞活化的重要机制[5,6]。CD200主要表达在包括神经元在内的多种细胞中,而其受体CD200R则特异表达在包括小胶质细胞在内的髓系细胞(Myeloid)中,两者结构相似,均属于跨膜糖蛋白[7-10]。动物炎症模型中,阻断两者中任何一方的表达均可以使小胶质细胞激活,并且在细胞活化过程中伴有炎症相关通路的激活,而MAPK(Mitogen-activated protein kinase,丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)及JAK-STAT(Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription,酪氨酸激酶-信号转导子与转录激活子)[11]是与炎症密切相关的两条通路。本实验应用BV2细胞代替小胶质细胞,应用CD200R抗体及LPS处理细胞诱导其活化,发现了其下游有pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT通路的激活。
1材料与方法
1.1细胞培养用含10% FBS的DMEM高糖培养基(购自Hyclone,美国)培养BV2细胞(购自北京协和细胞库)每2~3 d传代一次,待细胞生长良好贴壁达到90%左右时用于实验。
1.2方法
1.2.1具体分组A:CD200R抗体(Abcam公司,美国)及LPS(Sigma公司,美国)处理组;B:LPS处理组;C:对照组;收集各组中的细胞及上清液。
1.2.2免疫荧光检测CD200R的表达96孔板培养BV2细胞,4%多聚甲醛固定15 min后,0.3%Triton打孔15 min,5%BSA封闭0.5 h,加入1∶1000稀释的CD200R过夜,荧光二抗孵育1.5 h,每步骤之间均用PBS洗3次,每次5 min,荧光显微镜下观察。
1.2.3ELISA检测TNF-α及IL-1β的分泌以非处理组上清做对照,每孔均设立2个复孔,实验共重复3次,分别按照TNF-α(R&D)及IL-1β(R&D)的使用说明书,在抗体包被的96孔板中分别加入标准样品及待测样本、生物标记二抗及酶标试剂,37℃,反应1 h,洗板5次,加入显色剂A、B,37℃显色10 min,加终止液,以酶标仪检测波长为450nm的光密度值。
1.2.4Western blot检测p38MAPK、pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT的浓度分别收集A、B、C三组细胞,提取蛋白,BCA蛋白定量法用PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液配制等体积等浓度的待测蛋白,配胶、上样电泳,冰上转膜,5%BSA封闭1 h,敷一抗p38MAPK(1∶1 000稀释,cellsignal)、pho-p38MAPK(1∶1 000稀释,cellsignal),pho-JAK2-STAT(1∶1 000稀释,Abcam),α-tubulin(1∶1 000稀释,CST),4℃过夜,TBST洗膜后,二抗孵育2 h,ECL发光仪发光。

2结果
2.1免疫荧光结果荧光显微镜(20倍下)观察BV2细胞为单层贴壁细胞,胞体细长呈梭形,发出较多分支,见图1。结果表明:CD200R可表达于BV2细胞表面,这为我们接下来使用CD200R阻断性抗体阻断BV2细胞表面CD200R的表达使细胞更大程度上活化,进而研究细胞活化过程中相关激活的炎症通路奠定了基础。
2.2ELISA检测炎症因子表达结果在不加任何处理因素的情况下TNF-α及IL-1β均有基础分泌,单加LPS后细胞活化,两者分泌增多,而用CD200R抗体及LPS处理后较单独的LPS处理而言,BV2细胞活化更加明显,见图2、3,两种炎症因子分泌继续增多,各组比较差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。

图1 BV2细胞表面CD200R的表达情况Fig.1 Expression of CD200R on surface of BV2 cellsNote: A.CD200R;B.Hoechst;C.Merge.

图2 TNF-α分泌(ng/L)Fig.2 Expression of TNF-α(ng/L)Note: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.
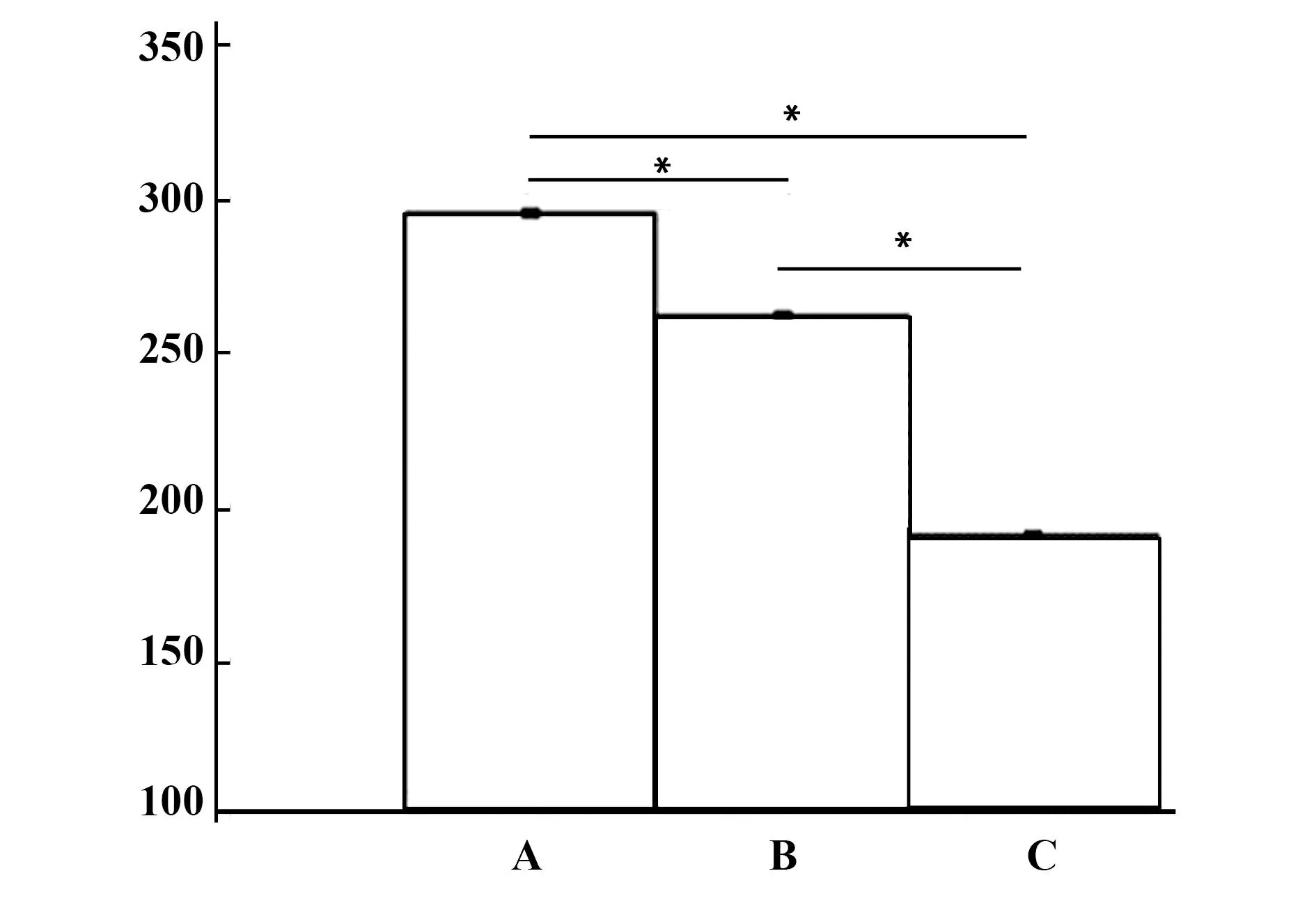
图3 IL-1β分泌(ng/L)Fig.3 Expression of IL-1β(ng/L)Note: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.

图4 pho-p38MAPK及p38MAPK的表达Fig.4 Expression of pho-p38MAPK and p38MAPKNote: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.

图5 pho-p38MAPK与p38MAPK比值Fig.5 Ratio of pho-p38MAPK and p38MAPKNote: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.

图6 pho-JAK2-STAT 表达Fig.6 Expression of pho-JAK2-STATNote: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.

图7 pho-JAK2-STAT与α-tubulin比值Fig.7 Ratio of pho-JAK2-STAT and α-tubulinNote: A.The group of CD200R and LPS handle the microglia;B.The group of LPS handle the microglia;C.Control group.*.P<0.05.
2.3Western blot 结果Western blot检测三组中P38MAPK、pho-P38MAPK、pho-JAK2-STAT及α-Tubulin的表达,并进行灰度值分析,结果如图4~7。两种磷酸化蛋白及半定量分析待测蛋白与内参比而言,A组显著高于B组、显著高于C组,说明在CD200R抗体及LPS共刺激BV2细胞后p38MAPK级JAK2-STAT的磷酸化表达显著增加,各组间比较差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.4加入两条通路阻断剂后再次检测两种炎症因子的表达加入足量的两条通路阻断剂后,两种炎性因子分泌均有所降低,各组间比较差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)说明,pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT通路参与了CD200R抗体及LPS诱导的小胶质细胞的激活。
3讨论
帕金森病是常见的神经系统变性疾病,近年来其发病呈现逐年上升的趋势,临床上主要表现为:静止性震颤、肌张力增高、运动迟缓及姿势步态异常。病理上改变为:黑质多巴胺神经元大量变性丢失及胶质细胞活化。研究表明:神经系统炎症参与了PD的发病过程[12],小胶质细胞是神经系统的免疫监视细胞,在炎症、创伤、缺血等损伤下可以被激活,释放炎症因子、活性氧自由基等毒性分子[12,13],小胶质细胞表面存在许多受体,本实验中的CD200R就是特异性表达于小胶质细胞、巨噬细胞等髓系细胞表面的保护性受体,而其配体CD200则广泛表达在神经元、B细胞等细胞表面,正常情况下,两者平衡可维持小胶质细胞处于静息状态[14-16]。在本实验我们首先证实小胶质细胞存在CD200R的表达(见图1),这与之前的研究结果是一致的,接下来我们应用了CD200R的阻断性抗体阻断小胶质细胞表面CD200R的表达进而引发细胞炎性反应。为了验证CD200R在细胞活化作用,我们应用CD200R的阻断性抗体及LPS处理小胶质细胞,并分别检测了三组中TNF-α及IL-1β的分泌情况,结果表明:在抗体组中炎症因子分泌均显著增高,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)(见图2、3)。美中不足在于:市场上未能找到CD200R激动剂诱导其表达以抑制小胶质细胞活化。为了验证细胞活化中是否有pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT的激活以及总的p38MAPK表达有无改变,我们用Western blot法分别检测了上述三种蛋白的表达情况,结果:pho-p38MAPK及pho-JAK2-STAT较其余两组发生了明显的激活,而p38MAPK表达无差异(如图4、6),分别进行灰度值分析后发现,抗体组中两种磷酸化蛋白比值明显高于药物组及对照组,组间比较具有显著意义(P<0.05)(见图5、7)。
神经炎症在神经变性疾病中发挥着重要作用,那么随着研究的深入,寻找PD等与神经炎症密切相关的神经变性疾病共同的且具有特异性的病因,并从根本上阻断这些病因或诱发因素,可以减少帕金森等疾病的发生,但该研究任重而道远,同时探索一种在基因或蛋白水平维持CD200/CD200R通路的平衡进而维持小胶质细胞处于静息状态的治疗手段,必然会给帕金森患者的治疗带来福音。我们的研究也为是否可以通过预防性的、并在安全范围内应用疾病相关的炎症通路的阻断剂,尽可能削弱神经炎症,似乎可能成为帕金森病的新的治疗靶点。
参考文献:
[1] Hatherley D,Barclay AN.The CD200 and CD200 receptor cell surface proteins interact through their N-ter minal immunoglobulin-like domains[J].Eur J Immunol,2004,34(6):1688-1694.
[2] Le W,Rowe D,Xie W.Microglial activation and dopaminergic cell injury:an in vitro model relevant to Parkinson′s disease[J].J Neurosicience,2001,21(21):8447-8455.
[3]Masocha W.Systemic lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced microglial activatoion results in different temporal reduction of CD200 and CD200 receptor gene expression in the brain[J].J Neuroimmunol,2009,214(1-2):78-82.
[4] Aedín M minogue,JamesPBarrett,Marina A Lynch.LPS-induced release of IL-6 from glia modulates production of IL-1β in a JAK2-dependent manner[J].J Neuroinflammation,2012,126(9):1186-1742.
[5] Dutta G,Zhang P.The lipopolysaccharide Parkinson′s disease animal model:mechanistic studies and drug discovery[J].Fundamental Clin Pharmacol,2008,22(5):453-464.
[6] Rosenblum MD.Expression of CD200 on epithelial cells of the murine hair follicle:a role in tissue-specific immune tolerance?[J].Invest Dermatol,2004,123(5):880-887.
[7] Barclay AN,Wright GJ,Brooke G.CD200 and membrane protein interactions in the control of myeloid cells[J].Trends Immunol,2002,23(6):285-290.
[8]Cox FF,Camey D,Miller AM,etal.CD200 fusion protein decreases microglial activation in the hippocampus of aged rats[J].Brain Behav Immun,2012,26(5):789-796.
[9] Koning N,Swaab DF,Hoek RM,etal.Distribution of the immune inhibitory molecules CD200 and CD200R in the normal central nervous system and multiple sclerosis lesions suggest neuronglia and glia-glia interaction[J].Neuropathol Exp Neurol,2009,68(2):159-167.
[10]Hoek RM,Ruuls SR,Murphy CA.Down-regulation of the macrophage lineage through interaction with OX2(CD200)[J].Science,2000,290(5497):1768-1771.
[11]Linlin Yin,Yongyan Chen,Zhao Qu.Involvement of JAK/STAT signal-Ing in the effect of cornel iridoid glycoside on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis amelioration in rats[J].J Neuroimmunol,2014,274(6):28-37.
[12]Meuth SG,Simon OJ,Grimm A.CNS inflammation and neuronal degeneration is agravattedby impaired CD200-CD200R mediated macrophage silencing[J].Neuroimmunology,2008,194(1-2):62-69.
[13]Walker DG,DalsingHernandez JE,Campbell NA.Decreased expression of CD200 and CD200R in Alzheimer′s disease:A potential mechanism for chronic inflammation[J].Exp Neurol,2009,215(1):5-19.
[14]Wright GJ,Cherwinski H,Foster-Cuevas M.Characterization of the CD200R family in mice and humans and their interactions with CD200[J].J Immunol,2003,171(6):3034-3036.
[15] Barclay AN,Wright GJ,Brooke G.CD200 and membrane protein interactions in the control of myeloid cells[J].Trends Immunol,2002,23(6):285-290.
[16]Luo XG,Zhang JJ,Zhang CD,etal.Altered regulation of CD200 receptor in monocyte-derived macrophages from individuals with parkinson′s disease[J].Neurochem Res,2010,35(4):540-547.
[收稿2015-08-15修回2015-08-28]
(编辑倪鹏)
Investigate whether p38MAPK and JAK2-STAT pathways can be phosphorylated activation when BV2 cells are activated
FANGYan-Yu,LUOXiao-Guang,SUYang,XIEXin,TIANXu-Cong,FANLi-Ting,RENYan.
DepartmentofNeurology,theThirdAffiliatedHospitalofQiqihaerMedicalUniversity,Qiqihaer161000,China
[Abstract]Objective:To explore the important role of CD200R in the microglia inflammation model induced by LPS as well as whether there is the activation of the pho-p38MAPK and pho-JAK2-STAT pathway or not.Methods: Microglia was used for this study.Immunofluorescence confirms there was the expression of CD200R in microglia.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detected the secretory content of TNF-α and IL-1β after using CD200R-blocking antibody and LPS handle the microglia.Western blot disclose whether p38MAPK and JAK2-STAT pathway can be phosphorylated or not.Finally,we detect the secretion of TNF-α,IL-1β after applicating different doses of channel blockers.Results: We observed that CD200R expresses on the surface of microglia.To determine the relationship of CD200R and inflammatory cytokines,we tested whether blocking CD200R promotes the release of inflammatory cytokines or not.After using administrating antibodies of CD200R,TNF-α and IL-1β secreted by microglia was significantly increased and pho-p38MAPK and pho-JAK2-STAT were activated,which let us predict that pho-p38MAPK and phoJAK2-STAT participate in the microglia activation of LPS induction.To further confirm the pho-p38MAPK and pho-JAK2-STAT pathway were involved in microglia activation,we apply SB203580 and AG490 to inhibit both pathways respectively,and then we found that the number of TNF-α and IL-1β was significantly decreased,and the number of TNF-α and IL-1β was negatively correlation with the concentration of AG490 and SB203580.Conclusion: Not only pho-p38MAPK but also pho-JAK2-STAT are involved in microglia activation induced by LPS and CD200R antibody response.
[Key words]CD200R;BV2 cells;TNF-α;IL-1β;pho-p38MAPK;pho-JAK2-STAT
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2016.05.005
作者简介:房艳宇(1986年-),女, 硕士,医师,主要从事神经病学方面研究。通讯作者及指导教师:罗晓光(1972年-),女,博士后,主任医师,博士生导师,主要从事帕金森病的基础与临床研究,E-mail: grace_shenyang@163.com。
中图分类号R724.5
文献标志码A
文章编号1000-484X(2016)05-0629-04
①本文为国家自然科学基金(81371421)、辽宁省教育厅科研项目计划(L2010560)资助支持项目。