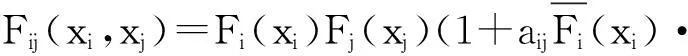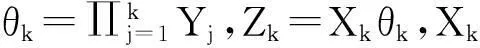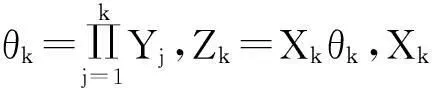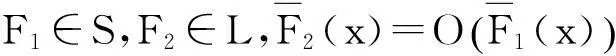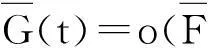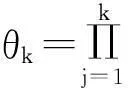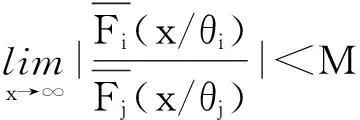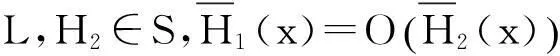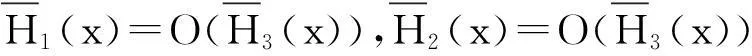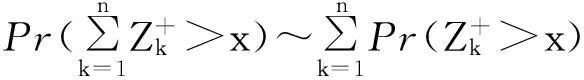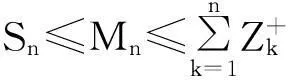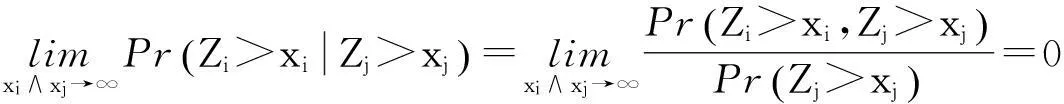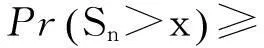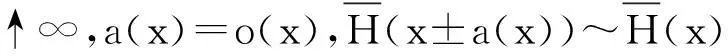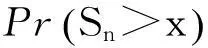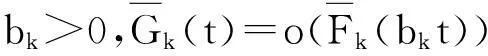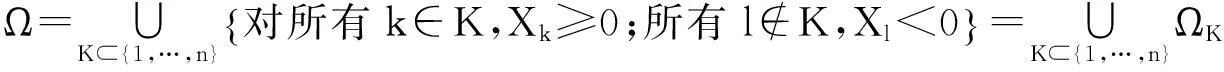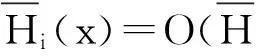保险和金融风险相依的破产概率研究
郭晓莉,文丽壹
(重庆理工大学 数学与统计学院,重庆 400054)
保险和金融风险相依的破产概率研究
郭晓莉,文丽壹
(重庆理工大学 数学与统计学院,重庆400054)
摘要:考虑一家保险公司暴露于保险风险和金融风险两种风险环境,分别用两组随机变量量化这两种风险,用离散时间风险模型表述保险公司盈余过程,研究了在保险风险和金融风险渐近独立相依假设下的保险公司有限时间破产概率问题。当保险风险的分布属于次指数分布族或长尾分布族时,分别推导了有限时间破产概率的渐近等价关系式,这将简化保险公司在风险评估中的计算问题。
关键词:保险风险;金融风险;破产概率;次指数;长尾
考虑一个离散时间保险风险模型。设保险公司的初始资本金为x≥0,保险公司第k年内的净收入由实值随机变量Ak(k=1,2,…,n)表示,保险公司在第k年将资金投入到有风险和无风险市场所产生的综合收益率由非负随机变量Bk(k=1,2,…,n)表示。假设保险公司的净收入Ak在第k年的年末计算,则保险公司在第k年末的盈余值Uk满足以下递归等式:
(1)
由式(1)递归可以得到:
(2)
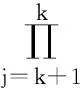
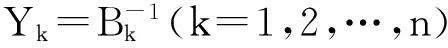
(3)
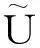
(4)
保险公司有限时间内的破产概率ψ(x;n)可重新表示为:
(5)
在实际应用中,直接计算保险公司在有限时间内的破产概率ψ(x;n)是相当繁琐甚至不现实的,因此本文主要研究当x→∞时ψ(x;n)的渐近等价表达式。在现有文献研究中,{Xk;k=1,2,…,n}和{Yk;k=1,2,…,n}分别被称为保险风险和金融风险。离散时间保险风险模型的破产概率问题已经被广泛研究。根据保险风险和金融风险相依关系分类,研究方向主要分以下3类:① {Xk;k=1,2,…,n}和{Yk;k=1,2,…,n}都是独立随机变量序列,且两序列之间独立,如文献[1-4];② {Xk;k=1,2,…,n}和{Yk;k=1,2,…,n}中至少有一组是相依的,但两序列之间独立,见文献[5-7];③ {Xk;k=1,2,…,n}和{Yk;k=1,2,…,n}两序列之间存在相依关系,见文献[8-11]。
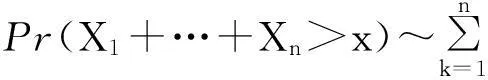
1预备知识和主要结论
本文除非另有说明,所有的极限关系都是在x→∞时成立。对于两个正函数f(·)和g(·),若limf(x)/g(x)=1,则记为 f(·)~g(·);若liminff(x)/g(x)≥1,则记为 f(x)g(x);若limsupf(x)/g(x)≤1,则记为f(x)g(x)。除此之外,定义x+=max{x,0}为实数x的正部。
1.1重尾分布族
这一部分给出重尾及两类重尾分布族的定义,其余重尾分布族的介绍可参看文献[12]。
定义1称随机变量X或者它的分布函数V是重尾的,如果对任意的s>0满足
这里把重尾分布族记为K。
相反,称随机变量X或者它的分布函数V是轻尾的,如果存在一个s0>0,使得对所有0 定义2称定义在R上的分布函数V属于长尾分布族,若对任意的y≠0,满足 记作V∈L。 定义3称定义在R+上的分布函数V属于次指数分布族,若对某任意的n≥2,满足 记作V∈S。 在一般情况下,若定义在R上的分布函数V满足V+(x)=V(x)I(x≥0)∈S,则也称V∈S。 假设随机变量X1,…,Xn独立同分布,且分布函数V∈S,则有 显然S⊂L,因为对任意定义在R+上的分布函数V∈S,x≥y>0,有 则当x→∞,V(x)-V(y)≠0时, 故V∈L。 1.2相依结构 考虑本文的离散时间保险风险模型,对k=1,2,…,n,实值随机变量Xk满足下面的相依结构: 显然,假设A包含以下两种情形: 常见的FGM相依也满足渐近独立条件。因为若随机变量X1,…,Xn服从n维FGM分布: 1.3主要结论 (6) (7) 2引理及证明 首先给出3个基本的引理,这3个引理在结果的证明中将会被用到。其中:引理1来自Cline[14]的推论2.5;引理2是文献[2]中引理3.2的一个特例,即r=0的情形;引理3源自文献[2]中引理3.10。针对所有引理,这里不再给出证明。 引理1如果随机变量X的分布函数F∈S,随机变量Y有界,则XY对应的分布函数H∈S。 因为Fk∈S,θk有界,则由引理1得Hk∈S。 H1*H2∈S且Pr(Z1+Z2>x)~Pr(Z1>x)+Pr(Z2>x) H1*H2*H3∈S且Pr(Z1+Z2+Z3>x)~Pr(Z1>x)+Pr(Z2>x)+Pr(Z3>x) 以此类推,得H1*…*Hn∈S且Pr(Z1+…+Zn>x)~Pr(Z1>x)+…+Pr(Zn>x),即 Pr(Zi>xi,Zj>xj)=o(1)Pr(Zj>xj) 因此: 又因为 故定理1得证。 根据文献[6]引理4.1,由数学归纳法可得Sn的分布函数属于L,即对某个A≠0,有 其中,M′是θl的上界。故定理2得证。 参考文献: [1]NYRHINEN H.On the ruin probabilities in a general economic environment[J].Stochastic Processes and their Applications,1999,83(2):319-330. [2]TANG Q,TSITSIASHVILI G.Precise estimates for the ruin probability in finite horizon in a discrete-time model with heavy-tailed insurance and financial risks[J].Stochastic Processes and their Applications,2003,108(2):299-325. [3]CHEN Y,XIE X.The finite time ruin probability with the same heavy-tailed insurance and financial risks[J].Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica(English Series),2005,21(1):153-156. [4]CHEN Y,SU C.Finite time ruin probability with heavy-tailed insurance and financial risks[J].Statistics & Probability Letters,2006,76(16):1812-1820. [5]SHEN X,LIN Z,ZHANG Y.Uniform estimate for maximumof randomly weighted sums with applications to ruin theory[J].Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability,2009,11(4):669-685. [6]CHEN Y,NG K W,YUEN K C.The maximum of randomly weighted sums with long tails in insurance and finance[J].Stochastic Analysis and Applications,2011,29(6):1033-1044. [7]ZHOU M,WANG K,WANG Y.Estimates for the finite-time ruin probability with insurance and financial risks[J].Acta Mathematicae Applicatae Sinica(English Series),2012,28(4):795-806. [8]GELUK J,TANG Q.Asymptotic Tail Probabilities of Sums of Dependent Subexponential Random Variables[J].Journal of Theoretical Probability,2009,22(4):871-882. [9]CHEN,Y.The finite-time ruin probability with dependent insurance and financial risks[J].Journal of Applied Probability,2011,48(4):1035-1048. [10]YANG Y,WANG K,LEIPUS R,et al.A note on the max-mum equivalence of randomly weighted sums of heavy-tailed random variables[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Modelling and Control,2013,18(4):519-525. [11]CHEN Y,LIU J,LIU F.Ruin with insurance and financial risks following the least risky FGM dependence structure[J].Insurance: Mathematics and Economics,2015,62:98-106. [12]EMBRECHTS P,KLUPPELBERG C,MIKOSCH T.Modelling Extremal Events for Insurance and Finance[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag,1997. [13]MAULIK K,RESNICK S.Characterizations and examples of hidden regular variation[J].Extremes,2004,7(1):31-67. [14]CLINE D B H,SAMORODNITSKY G.Subexponentiality of the product of independent random variables[J].Stochastic Processes and their Applications,1994,49(1):75-98. (责任编辑刘舸) The Ruin Probability with Dependent Insurance and Financial Risks GUO Xiao-li, WEN Li-yi (Department of mathematics and statistics, Chongqing University of Technology,Chongqing 400054, China) Abstract:Considering an insurance company exposed to an environment that contains insurance and financial risks, these two kinds of risks were quantified by two sets of random variables and the surplus process of the insurance company was described by a discrete-time risk model. This paper investigated the finite-time ruin probability with asymptotic independence insurance and financial risks. When the distributions of the insurance risk belong to the subexponential distribution class or the long-tailed distribution class, we derived some asymptotic equivalent relationships for the finite-time ruin probability, respectively. These will simplify the calculation of the insurance companies in the risk assessment. Key words:insurance risk; financial risk; ruin probability; subexponentiality; long tail 收稿日期:2015-12-16 基金项目:国家社会科学基金资助项目(14BJY200) 作者简介:郭晓莉(1991—),女,河南周口人,硕士研究生,主要从事应用数学研究。 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2016.05.024 中图分类号:O211.9 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1674-8425(2016)05-0135-06 引用格式:郭晓莉,文丽壹.保险和金融风险相依的破产概率研究[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2016(5):135-140. Citation format:GUO Xiao-li1, WEN Li-yi.The Ruin Probability with Dependent Insurance and Financial Risks[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science),2016(5):135-140.