航空发动机失谐叶盘动态特性研究进展*
姚建尧,高 阳,王建军
(1.重庆大学航空航天学院,重庆 400044;2.中国航空工业集团公司贵州航空发动机研究所,贵阳 550081;3.北京航空航天大学能源与动力工程学院,北京 100191)

姚建尧
重庆大学航空航天学院研究员,主要从事航空发动机结构强度、振动和可靠性,流固耦合理论及应用等方面的研究。
叶盘结构是航空发动机中的关键构件,其工作状态直接影响到整机的结构完整性和工作可靠性[1]。随着结构设计、材料和加工工艺等方面的不断进步,现代航空发动机的压气机/风扇中广泛采用整体叶盘(环),与高效气动设计相结合,使压气机/风扇的效率提高、流动损失降低,发动机整机的性能参数显著改善。先进的气动和结构设计使得叶盘所承受的气动负荷增加,而结构本身却变得更为轻巧,因此其振动问题也更加突出,严重地威胁着航空发动机的结构强度和寿命[2]。
叶盘结构以往的设计和分析中,通常假设各扇区是一致的。由于材料分散性、加工误差、使用中的不均匀磨损、抑制颤振而引入错频等因素,叶盘各扇区间总是不可避免地存在微小的差别,称为失谐[3]。失谐的存在破坏了结构的周期对称性,某些情况下会造成明显的振动局部化和振动幅值放大现象,使得叶盘结构的结构完整性和可靠性问题更为严峻。
叶盘结构的失谐问题一直受到工程界和学术界的关注,国内外学者从理论、试验和工程应用等方面都进行了深入的研究[3-8]。近几十年来,随着理论和计算水平的不断进步,失谐叶盘的研究也经历了从简化模型到高保真模型、从单级叶盘到多级叶盘、从假设失谐到真实失谐的过程,建模和计算分析精度不断提高,为叶盘结构设计及其安全性和可靠性的保障提供了有力的支持。本文将从建模、减缩和分析评价3个方面对失谐叶盘结构动态特性的国内外相关研究进展进行总结。
失谐叶盘建模技术
合理、准确地建模是叶盘动态特性分析的基础,基于叶盘结构的特点,失谐叶盘结构分析模型主要有集中参数模型、连续参数模型和高保真有限元模型3类[9]。在最近的研究中也报道了精确几何失谐和多级叶盘结构的建模技术。下面分别对其进行介绍。
1 集中参数模型
集中参数模型采用集中质量模拟叶片和轮盘的质量,采用弹簧来模拟叶片刚度、轮盘刚度和耦合刚度,如图1所示[10-12]。该类模型规模小,能很好地反映叶盘的一族或少数几族谐调和失谐的动态特性,广泛应用于失谐叶盘的机理研究,并取得良好的效果。
叶盘集中参数模型的建模过程是一个典型的反问题(参数识别),需要通过已知的模态或响应特性来获取集中参数,并使得集中参数模型的响应特性与高保真有限元模型接近。Mignolet和Lin[13]利用最小二乘估计(Least square estimation)、最大似然估计(Maximum likelihood estimation)以及两者的组合等3种方法建立起已知的失谐响应和未知的集中参数的关系,并进行求解来获取系统中的参数。同样地,也可以利用随机模态刚度法(Radom modal stiffness approach)或最大似然估计方法,通过模态数据来获取集中参数模型中的参数[14-15]。集中参数模型也应用至叶盘结构的鲁棒性分析[16-17]以及多级叶盘失谐动态特性分析中[18-19]。
2 连续参数模型
叶盘结构的集中参数模型精度有限,难以模拟叶片和叶盘结构的复杂的振动及耦合振动特性。为了提高动态特性的分析精度,也有学者采用连续参数模型模拟叶盘。在这类模型中,通常采用梁模拟叶片,采用板模拟轮盘,而叶片间的耦合仍用集中参数的弹簧进行模拟,典型结构如图2[20-21]所示。
连续参数模型可以方便地考虑剪切变形、旋转惯性、离心效应、科氏力等[22-24]。采用该模型也可以方便地引入叶盘裂纹,考察其在旋转状态下的耦合振动特性[25-27]。叶先磊等[28]采用该类模型研究了大小叶片整体叶盘的耦合振动特性,其结果与有限元模型的计算结果具有良好的一致性。
与集中参数模型相比,基于梁和板构件的连续参数模型能够提高模拟精度,但由于该模型仍难以模拟实际的叶片和轮盘的复杂振动形式,计算分析精度仍然较低,因此也多用于失谐机理的研究。
3 高保真有限元模型
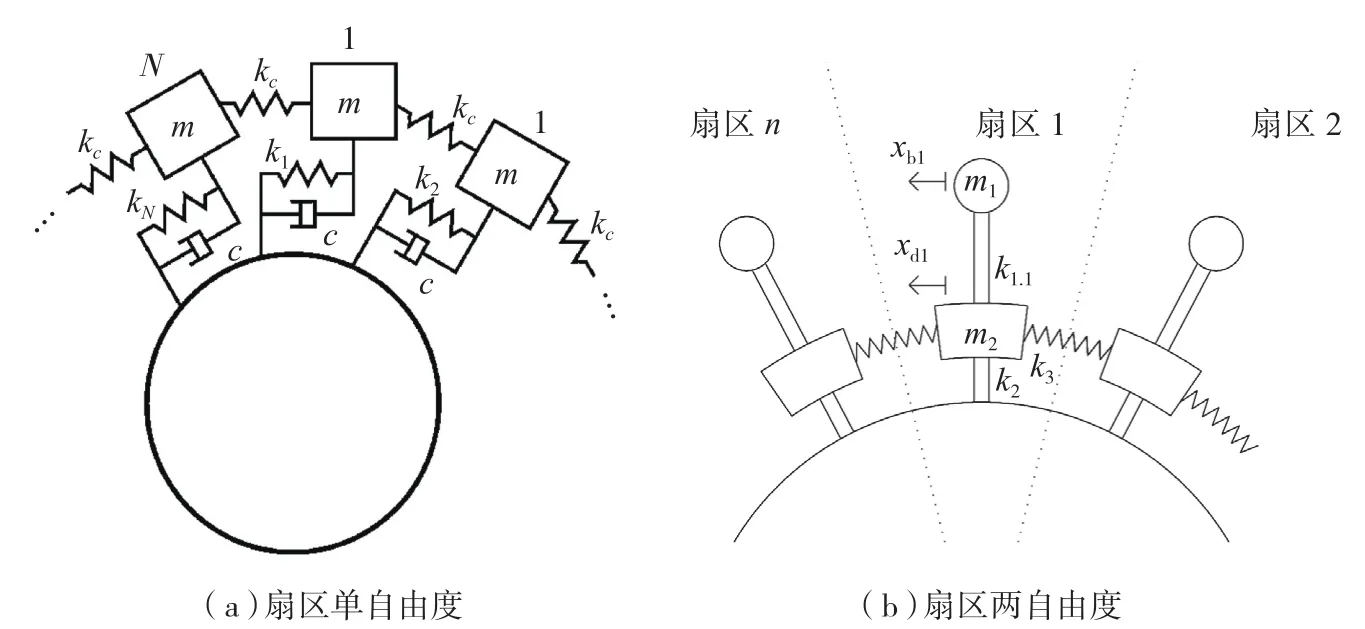
图1 叶盘结构集中参数模型Fig.1 Lumped-parameter model for bladed disk
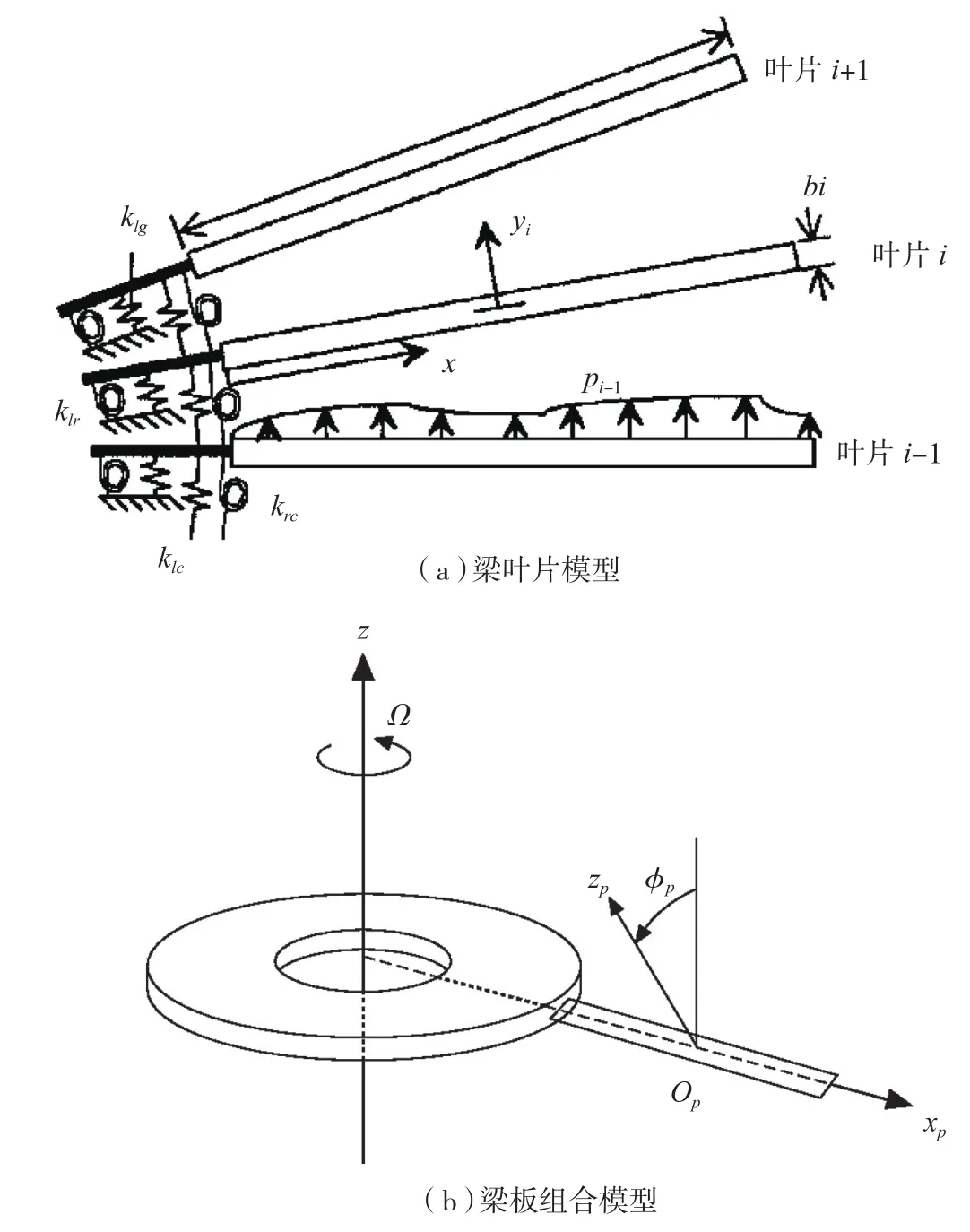
图2 叶盘结构连续参数模型Fig.2 Beam blade model for bladed disk
前面介绍的两种建模方法都是针对叶盘结构动态特性而提出的简化模型,虽然能反映出叶盘结构的基本振动特征,但并不能精确描述某一特定叶盘的振动特性,如模态特性和响应水平等。随着硬件和软件水平的不断提高,叶盘结构的高保真有限元模型得到越来越广泛的应用,目前已成为通用做法。失谐叶盘有限元建模的关键在于如何将失谐引入至有限元模型中,目前主要通过改变叶片材料属性和改变叶片几何形状来模拟和实现失谐。
通过改变叶片材料属性(通常为弹性模量)来模拟失谐是最简便的方法,这种失谐类型通常被称为“比例失谐(proportional mistuning)[29]”,所谓比例失谐是指失谐量与谐调情况的质量或刚度矩阵成比例,失谐前后固有频率变化很小,模态振型也与谐调时基本一致。这种方式能很好地反映失谐造成的各叶片间的频率差,模拟加工误差或使用磨损所造成的失谐,在失谐叶盘动态特性分析中得到广泛的应用[30-32]。
另一种实现失谐的方法是改变叶片的几何形状,这种方式同时改变了系统的质量和刚度矩阵。在这种情况下,不仅模态频率变化较大,而且模态振型也会发生较大的变化,因此被称为“非比例失谐(nonproportional mistuning)[29]”。非比例失谐与实际情况更为接近,可用来模拟加工误差、裂纹、掉角、外物打伤等所造成的失谐。Lim等[33]采用改变叶片单元位置和形状的方法模拟了外物打伤造成的单个叶片大几何失谐的情况(图3[33]);Capiez-Lernout等[34-35]则通过改变叶片截面前缘和尾缘的扭转角的方法模拟了加工误差造成的几何失谐;张辉有和王红建[36]则通过改变叶片厚度来模拟叶盘的几何失谐。
4 几何失谐叶盘结构的建模
在前面介绍的各种模型中,失谐多是通过假设的形式引入到叶盘中的。研究表明,叶盘中实际存在的几何失谐同时改变了名义模型的刚度和质量的分布,某些情况下其振动特性与比例失谐叶盘有显著差别[37],因此需在分析模型中准确体现几何失谐的影响。随着测量和建模技术的进步,近年来提出了通过叶片表面坐标测量获取精确几何失谐的方法,主要有接触式测量和非接触式测量两种方法。
在接触式测量方面,Sinha等[38]与普惠公司合作,采用坐标测量机获取叶片表面坐标。通过对测量数据的恰当正交分解(Proper Orthogonal Decomposition,POD)获取几何失谐的数据特征,结合CAD和CAE软件建立有限元模型。
非接触式的光学测量是获取叶片表面几何失谐的另一种主要手段。与接触式测量方法相比,该方法更为快捷方便,适应性更广,但精度要比接触式稍低。Kaszynski等[39]实现了利用光学扫描高精度测量整体叶盘几何坐标的自动化过程,利用测量数据重建了几何失谐叶盘的三维模型,进而通过有限元分析获取其动态特性(图4[39])。在其后续研究中,还提出一种直接关联名义有限元模型和几何测量数据的网格变形法[40-41]以快速精确地建立几何失谐叶盘的有限元模型。
5 多级叶盘结构的建模
在多级叶盘的动态分析中,有限元模型占有主导地位。Bladh等[42]建立了简化的两级失谐叶盘的有限元模型,研究了盘的柔性以及盘间耦合对失谐动态特性的影响。葛长闯等[43-44]以某型发动机两级压气机叶盘为研究对象,建立有限元模型并对其自由振动特性进行分析,并基于应变能定义了新的模态局部化因子。D’Souza等[45-46]研究了两级叶盘的概率动态特性,并首次考虑了气动作用对多级叶盘失谐动态特性的影响。需要指出的是,多级叶盘的有限元模型规模一般都很大,需要对其进行减缩处理以提高分析效率。
叶盘结构模型减缩技术
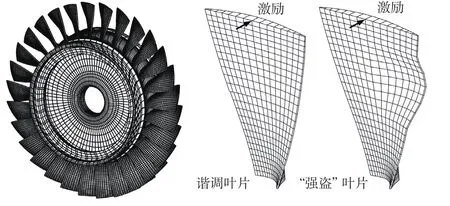
图3 失谐叶盘的有限元模型Fig.3 Finite element model for bladed disk
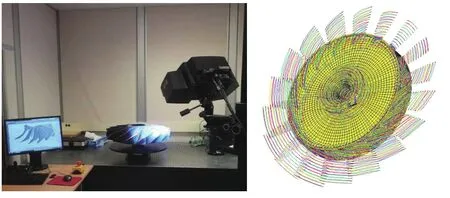
图4 非接触式几何失谐测量系统Fig.4 Optical 3D canning system for geometrical mistuning
由于失谐破坏了叶盘结构的周期对称性,通常情况下须采用完整模型进行分析,加之实际工程中的叶盘几何形状复杂、模型规模大,给计算带来很大困难。特别是对于多级叶盘,即使是在谐调的情况下,由于两级叶片数一般不存在公约数,因此在分析中往往需要采用整体模型,这导致多级叶盘有限元模型的规模会更大。并且,失谐具有很强的随机性,很多情况下需要通过蒙特卡洛模拟对多个样本的分析以获取其统计特征,进一步增加了计算负荷。
为此,国内外学者研究了各种模型减缩技术和高效的求解方法,以实现高效、高保真的模拟和分析叶盘结构动态特性的目的。目前,广泛应用的模型减缩方法主要有基于部件的减缩、基于模态族的减缩和基于周期对称性的减缩等3大类。
1 基于部件的减缩技术
基于系统部件的模态综合法(Component Mode Synthesis,CMS)[47-48]是结构动力学中常用的子结构模态综合法,是将复杂的整体结构分成较小、较易于处理的动态子结构的一种方法。对于叶盘结构,常见的是将叶片和轮盘分别处理为子结构,两个子结构之间用固定界面、自由界面或混合界面连接。这类方法在单级叶盘的失谐分析中已得到广泛的应用,具体可参考相关文献[6]和专著[49],这里重点介绍该方法在几何失谐叶盘中的扩展应用。
Lim等[33,50]针对外物打伤造成的单个叶片大几何失谐的情况进行研究,提出了基于系统部件的杂交模态综合法,将失谐叶盘分为谐调叶盘(谐调子结构)和相应的叶片失谐部分(失谐子结构),进而进行子结构的模态减缩。
Beck等[51-53]提出了适用于失谐叶盘动态特性分析的Craig-Bampton部件模态综合法(C-B CMS),该方法可将叶片与轮盘分别作为子结构(共n+1个)或者将每个扇区作为子结构(共n个)。对于比例失谐的情况,各叶片采用与谐调叶片相同的减缩基;而对于存在几何偏差的非比例失谐的情况,各叶片则需采用不同的减缩基。在其后续的研究中,该模型减缩方法还被应用至双流道[54-56]叶盘的动态特性分析中(图5[55])。
2 基于模态族的减缩技术
叶盘结构是一种典型的周期结构,即使在失谐状态下,其模态仍具有成族出现的特征。利用这一特征,Yang和Griffin[57]提出了使用部分谐调模态(subset of nominal system modes,SNM)作为基向量进行模型减缩;Feiner和Griffin[58]进一步对基向量进行减缩,仅使用一族模态对叶盘进行减缩,称为基础失谐模型(Fundamental Model of Mistuning,FMM),除稳态频响分析外,该模型可用于失谐叶盘瞬态响应分析[59]和失谐识别[60-62]等。在Martel等[63-64]提出的渐近失谐模型(Asymptotic Mistuning Model,AMM)中,使用的则是能够反映系统动态特性的最小模态子集,提高了这种基于模态族的减缩方法的适用性(图6[63])。
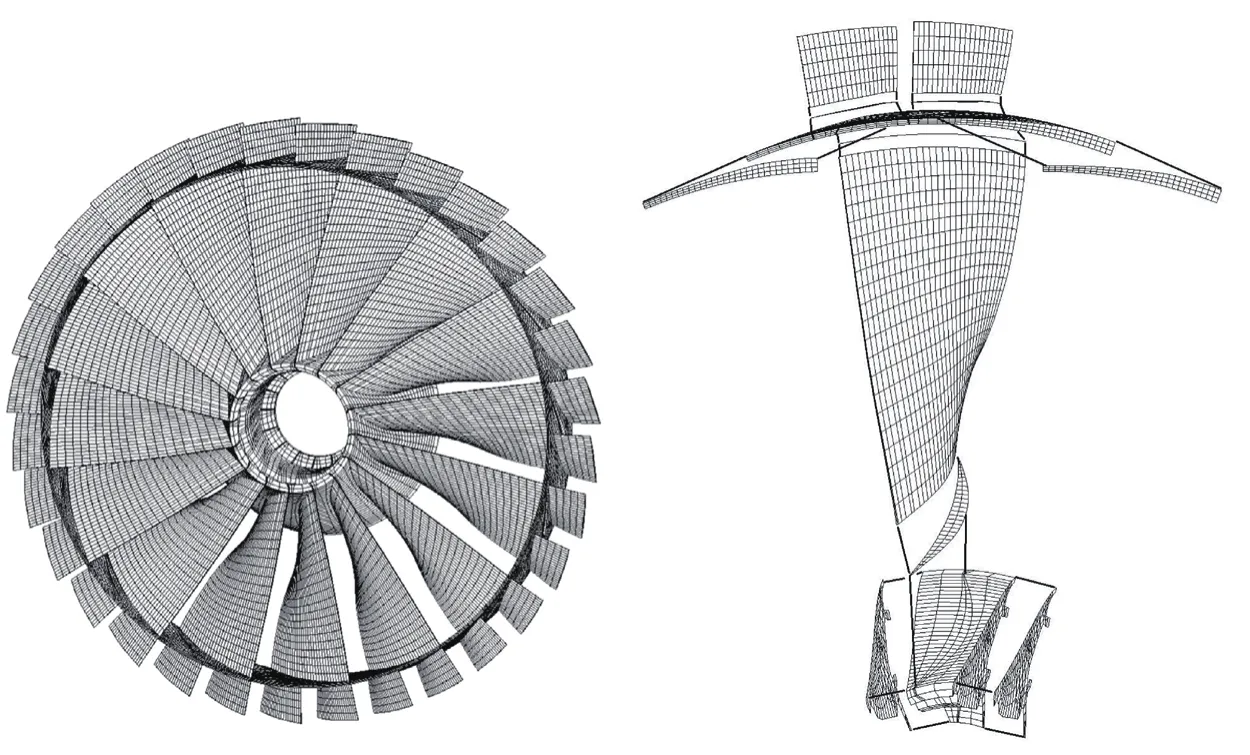
图5 双通道整体叶盘及其子结构划分Fig.5 Dual flow-path integrally bladed rotor and its cyclic sector C-B CMS partitionment
前面已经说明,几何失谐属于非比例失谐,使得叶片的振型发生较为显著的变化,这就使得前面介绍的模态减缩方法的精度受到一定的影响。Ganine等[65-66]针对几何失谐叶盘,通过静模态补偿(static mode compensation,SMC)对模态减缩方法进行改进,将大的几何失谐和小的随机失谐采用不同的减缩基分别处理,而后再将两者叠加。该方法可准确高效地预测几何失谐叶盘的模态和响应等动态特性。
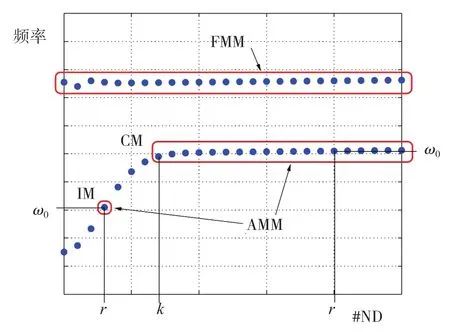
图6 FMM和AMM失谐降阶模型的模态选取Fig.6 Choices of basic vectors of FMM and AMM
为了解决模态减缩方法在几何失谐叶盘动态特性分析中的精度问题,Sinha[67-68]提出一种改进的模态域分析(modified modal domain analysis,MMDA)方法。该方法首先对叶片几何失谐数据进行[67]POD分析,以获取失谐特征(图7);进而将具有这些几何失谐特征的叶盘进行谐调情况下的模态分析,与名义设计谐调叶盘的模态共同组成模态减缩基。在后续的研究中,该方法也应用到多级几何失谐叶盘[69]、工业叶盘[70]、失谐识别[71]、受迫响应统计特性分析[72]等。
3 基于周期对称性的减缩技术
叶盘结构是一种典型的循环周期对称结构,在单级叶盘的谐调分析中,仅可采用一个扇区进行分析。失谐和多级叶盘虽然破坏了严格意义上的周期对称性,但仍可认为是广义的周期对称结构,可利用该性质对分析模型进行减缩。
姚建尧等[73-74]提出了一种利用周期对称性求解失谐叶盘瞬态响应的计算方法。该方法将失谐部分作为非线性激励移到运动方程右端,左端仍保持谐调的形式,仍可仅用单扇区进行求解分析。失谐非线性激励可与结构本身的非线性(摩擦、间隙、大变形等)和非线性气动载荷等一并处理,提高了分析效率。王培屹和李琳[75]基于周期对称的谐波平衡法,提出了利用单扇区模型计算失谐叶盘稳态频率响应的方法,该方法的关键仍在于对失谐激励的处理方式。
周期对称性在多级叶盘的建模中有着更为广泛的应用。多级叶盘周期对称建模中最大的挑战在于每级叶盘的叶片数量不同,需要对级间连接部分进行特殊处理。Song等[76]提出了多级叶盘的逐级模态综合法,将每一级作为一个部件,在每一级中都可仅用一个扇区进行建模分析;在级间边界处理上,利用级间鼓筒的轴对称性,通过傅里叶基向量来实现级间的坐标转换,以满足不同级间的边界条件(图8[76])。在后续研究中,该方法被应用至多级叶盘的系统参数识别中[77]。Laxalde等[78]采用类似的方法处理级间连接鼓筒,但级间使用的是连续的网格。需要说明的是,上述两个研究都是针对多级谐调叶盘进行的。
Bhartiya和Sinha[69]同样将谐调多级叶盘的每一级作为子结构分别进行分析,在边界处理时,分别选取连接鼓筒处的约束模态和自由模态作为减缩基,并利用之前研究的MMDA方法对几何失谐多级叶盘进行动态特性分析。
失谐叶盘结构动态特性分析评价
叶盘结构中的失谐对其动态特性产生非常显著的影响,为定量衡量失谐的影响,国内外学者定义了一系列无量纲参数,如模态局部化因子、幅值放大因子、模态参与因子等。此外,人为失谐、科氏力、非线性等因素也会对失谐叶盘的动态特性产生更为复杂的影响。
1 失谐叶盘动态特性的评价
失谐对叶盘结构动态特性最为明显的影响表现为模态局部化和振动传递局部化,为定量描述这些现象,分别定义了模态局部化因子和幅值放大因子。王建军等[79]基于实际叶盘结构失谐振动局部化的基本特征和物理含义,分别定义了基于模态位移、模态应力和模态应变能的模态局部化因子,得到评价失谐叶盘结构模态局部化程度的定量方法。在这些定义中,都需要将失谐模态与相应的谐调模态进行比较,为了使两者的对应更具有物理意义,姚建尧等[80-81]提出振型的节径谱的概念,通过失谐振型的主节径成分确定与之对应的谐调振型。
在失谐对叶盘响应的定量评价方面,广泛采用的是幅值放大因子,其定义为失谐最大响应(位移或应力)与谐调最大响应之比。这种定义物理意义明确,计算简便,在工程和学术界得到广泛应用[18,32,72,82-84]。
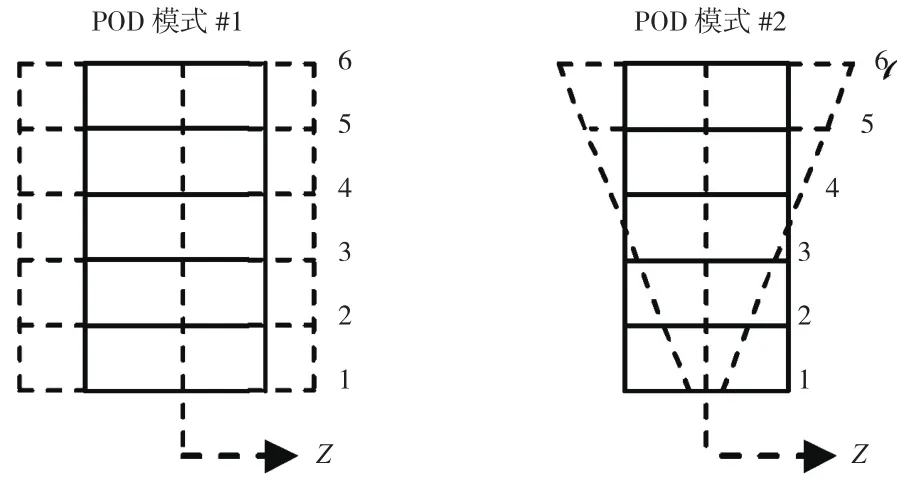
图7 叶片几何失谐的POD特征Fig.7 Blade thickness for each POD feature
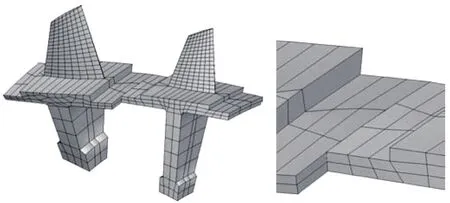
图8 多级叶盘的周期对称模型Fig.8 Cyclic model for multistage bladed disk
与单级叶盘相比,多级叶盘模态局部化特性的评价要更为复杂,主要需考虑级间耦合的问题。Sternchuss和Balmes[85]通过应变能定义了各级的模态参与因子(relative participation factor),以衡量各阶模态是以单级振动为主导还是以耦合振动为主导。D’Souza和Epureanu[86]则分别利用应变能比(strain energy ratio)和模态置信因子对多级叶盘的模态进行分类评价。多级叶盘响应评价相对简洁,一般仍采用与单级叶盘的相同的幅值放大因子[69]。
此外,Rotea和D’Amato[11]和姚建尧等[16-17]也试图从系统鲁棒性的角度评价失谐叶盘的动态特性,但目前只能应用于简单的集中参数模型。Nikolic等[87]提出了通过增加失谐范围来提高叶盘结构鲁棒性的设计理念;Mbaye等[88]提出利用错频手段提高叶盘结构的鲁棒性。
2 人为失谐的影响
Kaza和Kielb[89-90]的研究表明,适当程度的人为失谐可以有效提高压气机的颤振裕度。目前,引入人为失谐或错频以抑制颤振已成为发动机设计的常用技术手段[91-93]。同时,某些人为失谐也能有效地抑制随机失谐对叶盘响应的不利影响。Choi等[94]研究了AB两种叶片类型人为失谐排列方式对随机失谐响应放大的抑制效果,并应用至离心叶盘的设计中。Kenyon和Griffin[82]研究了更为复杂的谐波形式的人为失谐对随机失谐叶盘响应的影响。Murthy和Mignolet[95]研究了干摩擦阻尼器人为失谐对叶盘的影响。姚建尧等[80-81]则利用节径谱和模态激励因子的概念,很好地解释了随机失谐的阈值效应和人为失谐的作用机理。袁惠群[96]、李岩[97]和赵天宇等[98]分别采用蚁群算法、离散遗传粒子群算法和模拟退火算法对人为失谐排列方式进行优化。
3 科氏力的影响
叶盘在高速旋转的工作状态下,科氏力会对其动态特性产生较为显著的影响。李永强等[99]基于薄壳理论考虑了科氏力对旋转叶片动频的影响,但并未考虑对轮盘的影响。Huang和Kuang[24]采用连续参数模型研究了考虑科氏力效应下的失谐叶盘的模态局部化,结果表明,科氏力可能会加剧失谐叶盘的模态局部化现象。Nikolic等[100]研究了科氏力和失谐共同作用下叶盘的响应特性,并进行了相应的试验验证,结果表明,某些情况下科氏力使得失谐响应显著增大。辛健强等[101]采用有限元法对考虑科氏力的工业叶盘进行分析,结果同样表明,科氏力对失谐叶盘的模态和响应特性会产生显著的影响。
4 非线性的影响
在失谐叶盘动态特性分析中,也考虑了摩擦、裂纹、大变形等非线性因素的影响。
干摩擦阻尼器是航空发动机中最常见的阻尼器之一,其对失谐叶盘动态特性,特别是响应水平有着显著的影响。Poudou和Pierre[102]提出了带干摩擦阻尼器的叶盘结构响应计算的频域-时域混合方法。Cha和Sinha[103]研究了白噪声和窄带激励下带摩擦阻尼器的失谐叶盘响应的统计特性。王红建[104]和贺尔铭等[105]研究了干摩擦阻尼失谐对叶盘受迫响应的影响,结果表明,干摩擦散乱失谐会导致阻尼件减振性能的降低。Petrov等[106-111]系统研究了考虑摩擦和间隙等非线性因素情况下的失谐叶盘的建模和分析技术。
裂纹是叶片中常见的缺陷形式,同样是引起失谐的主要因素之一。Kuang和Huang[25]以及Hou[27]通过连续参数模型考虑了叶片裂纹位置以及大小对失谐叶盘模态局部化的影响,但并未考虑裂纹的非线性性质。Saito等[112]建立了裂纹叶片的有限元模型,并考虑了裂纹开合造成的非线性,基于模态综合法建立了裂纹失谐叶盘的降阶模型;在其后续研究中,还将其扩展至多级叶盘[113]和裂纹检测中[114]。Wang等[115]利用类似的方法对失谐离心叶盘进行了分析。
大变形和大位移所引起的几何非线性对失谐叶盘有一定的影响。Capiez-lernout等[116-119]研究了考虑几何非线性的高负荷离心压气机叶盘的建模、降阶和响应分析技术。
结论和展望
本文重点回顾了失谐叶盘的建模、降阶以及动态特性分析评价等方面的相关研究进展,着重对多级叶盘和几何失谐叶盘的最新研究进行了介绍。需要指出的是,由于论文篇幅有限,这里并未涉及叶盘结构流固耦合、失谐识别、试验技术等重要领域。
从前述的研究进展可以看出,随着计算机软硬件和建模技术的不断提高,失谐叶盘高保真模型已得到广泛的应用,特别是基于坐标测量的精细建模技术也已于近年来开始应用。但由于失谐叶盘的随机性,更为关注其动态特性的统计特征,因此高效精确的降阶技术仍是研究的重要方向之一。为了更加准确地预测失谐响应及其概率分布特征,进行失谐叶盘流固耦合的概率特性分析也是未来重要的研究方向之一。
除理论研究外,如何将失谐分析和设计的理念在工程中加以应用,指导航空发动机的设计、评估和使用是未来需要重点关注的问题。
[1]李其汉,王延荣.航空发动机结构强度设计问题[M].上海: 上海交通大学出版社,2014.
LI Qihan,WANG Yanrong.The design problem of aero-engine structure strength[M].Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press,2014.
[2]李其汉,王延荣,王建军.航空发动机叶片高循环疲劳失效研究[J].航空发动机,2003,29(4): 16-18.
LI Qihan,WANG Yanrong,WANG Jianjun.Investigation of high cycle fatigue failures for the aero engine blades[J].Aeroengine,2003,29(4):16-18.
[3]王建军,李其汉,朱梓根.失谐叶片-轮盘结构系统振动局部化问题的研究进展[J].力学进展,2000,30(4): 517-528.
WANG JianJun,LI Qihan,ZHU ZiGen.Vibratory localization of mistuned bladed disk assemblies—a review[J].Advances in Mechanics,2000,30(4): 517-528.
[4]SRINIVASAN A V.Flutter and resonant vibration characteristics of engine blades[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1997,119(10): 742-775.
[5]SLATER J C,MINKIEWICZ G R,BLAIR A J.Forced response of bladed disk assemblies-a survey[J].Shock and Vibration Digest,1999,31(1): 17-24.
[6]CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.Modeling and analysis of mistuned bladed disk vibration: status and emerging directions[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2006,22(2):384-396.
[7]臧朝平,兰海强.失谐叶盘结构振动问题研究新进展[J].航空工程进展, 2011,2(2): 133-142.
ZANG Chaoping,LAN Haiqiang.Advances in research vibration problem of mistuned blisk assemblies[J].Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2011,2(2): 133-142.
[8]白斌,白广忱,童晓晨,等.整体叶盘结构失谐振动的国内外研究状况[J].航空动力学报,2014,29(1): 91-103.
BAI Bin,BAI Guangchen,TONG Xiaochen,et al.Research on vibration problem of integral mistuned bladed disk assemblies at home and abroad[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2014,29(1): 91-103.
[9]王建军,许建东,李其汉.失谐叶片-轮盘结构振动局部化的分析模型[J].汽轮机技术, 2004,46(4): 256-259.
WANG Jianjun,XU Jiandong,LI Qihan.Analytical models of mistuned bladed disk assembles—a review[J].Turbine Technology,2004,46(4): 256-259.
[10]CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.Using Intentional mistuning in the design of turbomachinery rotors[J].AIAA Journal,2002,40(10): 2077-2086.
[11]ROTEA M,D’AMATO F.New tools for analysis and optimization of mistuned bladed disks[C]//38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit,2002.
[12]王建军,姚建尧,李其汉.刚度随机失谐叶盘结构概率模态特性分析[J].航空动力学报,2008,23(2): 256-262.
WANG Jianjun,YAO Jianyao,LI Qihan.Probability characteristics of vibratory mode of bladed disk assemblies with random stiffness mistuning[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2008,23(2): 256-262.
[13]MIGNOLET M P,LIN C.Identification of structural parameters in mistuned bladed disks[J].Journal of Vibration and Acoustics,1997,119(3): 428-438.
[14]MIGNOLET M P,RIVAS-GUERRA A J,DELOR J P.Identification of mistuning characteristics of bladed disks from free response data—part I[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2001,123(2): 395-403.
[15]RIVAS-GUERRA A J,MIGNOLET M P,DELOR J P,et al.Identification of mistuning characteristics of bladed disks from free response data—part II[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2001,123(2): 404-411.
[16]姚建尧,王建军,李其汉.失谐周期结构的鲁棒分析模型[J].应用力学学报,2009,26(3): 426-431.
YAO Jianyao,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Robustness analysis model for mistuned periodic structures[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics,2009,26(3): 426-431.
[17]姚建尧,王建军,李其汉.失谐叶盘结构鲁棒性能分析[J].航空动力学报,2010,25(7): 1634-1639.
YAO Jianyao,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Robust performance analysis of mistuned bladed disks[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2010,25(7):1634-1639.
[18]廖海涛,王建军,李其汉.多级叶盘结构随机失谐响应特性分析[J].振动与冲击,2011,30(3): 22-29.
LIAO Haitao,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Mistuned forced response characteristics analysis of mistuned multi-stages bladed disks[J].Journal of Vibration And Shock,2011,30(3): 22-29.
[19]SINHA A.Reduced-order model of a mistuned multi-stage bladed rotor[C]//Proceedings of GT2007,ASME Turbo Expo 2007:Power for Land,Sea and Air,2007.
[20]TURCOTTE J S,HOLLKAMP J J,GORDON R W.Vibration of a mistuned bladed-disk assembly using structurally damped beams[J].AIAA Journal,1998,36(12): 2225-2228.
[21]TOMIOKA T,KOBAYASHI Y,YAMADA G.Analysis of free vibration of rotating disk–blade coupled systems by using artificial springs and orthogonal polynomials[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1996,191(1): 53-73.
[22]RZADKOWSKI R.The general model of free vibrations of mistuned bladed discs,part i:Theory[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1994,173(3): 377-393.
[23]RZADKOWSKI R.The general model of free vibrations of mistuned bladed discs,part ii: Numerical results[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1994,173(3): 395-413.
[24]HUANG B W,KUANG J H.Mode locallization in a rotating mistuned turbo disk with Coriolis effects[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2001,43: 1643-1660.
[25]KUANG J H,HUANG B W.The effect of blade crack on mode localization in rotating bladed disks[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1999,227(1): 85-103.
[26]HUANG B W,KUNG H K,KUANG J H.Stability in a twisted periodic blade system with cracks[J].AIAA Journal,2006,44(7): 1436-1444.
[27]HOU J.Cracking-induced mistuning in bladed disks[J].AIAA Journal,2006,44(11):2542-2546.
[28]叶先磊,王建军,朱梓根,等.大小叶片结构连续参数模型和振动模态[J].航空动力学报,2005,20(1): 66-72.
YE Xianlei,WANG Jianjun,ZHU Zigen,et al.Continuous parameter model and vibration modal of splitter vane rotor[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2005,20(1): 66-72.
[29]LIM S H,BLADH R,CASTANIER M P,et al.A compact,generalized component mode mistuning representation for mode bladed disk vibration[C]//44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures,Structural Dynamics,and Materials Conference.2003.
[30]BLADH R,PIERRE C,CASTANIER M P.Dynamic response predictions for a mistuned industrial turbomachinery rotor using reducedorder modeling[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2002,124(4): 311-324.
[31]于长波,王建军,李其汉.错频叶盘结构的概率模态局部化特性分析[J].航空动力学报,2009,24(9): 2040-2045.
YU Changbo,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Probability characteristics for vibratory mode of detuned bladed disk assemblies[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2009,24(9): 2040-2045.
[32]于长波,王建军,李其汉.失谐叶盘结构的概率响应局部化特性[J].航空动力学报,2010,25(9): 2006-2012.
YU Changbo,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Probability characteristics for response localization of mistuned bladed disk assemblies[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2009,25(9): 2006-2012.
[33]LIM S H,BLADH R,CASTANIER M P,et al.Compact,generalized component mode mistuning representation for modeling bladed disk vibration[J].AIAA Journal,2007,45(9): 2285-2298.
[34]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E,SOIZE C.Nonparametric modeling of random uncertainties for dynamic response of mistuned balded disks[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2004,126(7): 610-618.
[35]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E,SOIZE C,LOMBARD J P,et al.Blade manufacturing tolerances definition for a mistuned industrial bladed disk[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2005,127(7): 621-628.
[36]张辉有,王红建.一种基于叶盘结构几何失谐的降阶分析方法[J].航空工程进展,2014,5(4): 481-486.
ZHANG Huiyou,WANG Hongjian.A reduced order model of bladed disks with geometric mistuning[J].Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2014,5(4): 481-486.
[37]BECK J A,BROWN J M,SLATER J C,et al.Probabilistic mistuning assessment using nominal and geometry based mistuning methods[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2013,135(5): 51004.
[38]SINHA A,HALL B,CASSENTI B,et al.Vibratory parameters of blades from coordinate measurement machine data[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2008,130(1): 523-531.
[39]KASZYNSKI A A,BECK J A,BROWN J M.Uncertainties of an automated optical 3d geometry measurement,modeling,and analysis process for mistuned integrally bladed rotor reverse engineering[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2013,135(10): 1025-1034.
[40]KASZYNSKI A A,BECK J A,BROWN J M.Automated finite element model mesh updating scheme applicable to mistuning analysis[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition.American Society of Mechanical Engineers,2014.
[41]KASZYNSKI A A,BECK J A,BROWN J M.Experimental validation of a mesh quality optimized morphed geometric mistuning model[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition.2015.
[42]BLADH R,CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.Effects of multi-stage coupling and disk flexibility on mistuned bladed disk dynamics[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines & Power,2001,125(1): V004T033A040.
[43]葛长闯,王建军,刘永泉.2级叶片-轮盘系统模态特性研究[J].航空发动机,2009,35(5): 19-23.
GE Changchuang,WANG Jianjun,LIU Yongquan.Investigation of characteristics of twostage blade-disk system modal[J].Aeroengine,2009,35(5): 19-23.
[44]葛长闯,王建军,刘永泉.失谐多级整体叶盘振动模态特性定量评价方法研究[J].航空发动机,2012,38(1): 25-28.
GE Changchuang,WANG Jianjun,LIU Yongquan.Quantitative assessment method of vibration mode characteristics for mistuned multistage blisk[J].Aeroengine,2012,38(1): 25-28.
[45]D’SOUZA K X,EPUREANU B I.A statistical characterization of the effects of mistuning in multistage bladed disks[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2012,134(1): n37-n47.
[46]D’SOUZA K X,JUNG C,EPUREANU B I.Analyzing mistuned multistage turbomachinery rotors with aerodynamic effects[J].Journal of Fluids and Structures,2013,42: 388-400.
[47]CRAIG R,CHANG C.Free-interface methods of substructure coupling for dynamic analysis[J].AIAA Journal,1976,14(11): 1633-1635.
[48]CRAIG R R.Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses: an overview[C]// Proceedings of AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures,Structural Dynamics,and Materials Conference and Exhibit.2000.
[49]王建军,李其汉.航空发动机失谐叶盘振动减缩模型与应用[M].北京: 国防工业出版社,2009.
WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Methods and applications of reduction modeling for mistuned bladed disk vibration in aero-engine[M].Beijing:National Defend Industry Press ,2009.
[50]LIM S,CASTANIER M,PIERRE C.Vibration modeling of bladed disks subject to geometric mistuning and design changes[C]//45th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures,Structural Dynamics and Material Comference.2004.
[51]BECK J A,BROWN J M,SLATER J C,et al.Probabilistic mistuning assessment using nominal and geometry based mistuning methods[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2012,135(5): 1085-1097.
[52]BECK J A,BROWN J M,CROSS C J,et al.Component-mode reduced-order models for geometric mistuning of integrally bladed rotors[J].AIAA Journal,2014,52(7): 1345-1356.
[53]BECK J A,BROWN J M,KASZYNSKI A A,et al.Geometric mistuning reduced-order models for integrally bladed rotors with mistuned disk–blade boundaries[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2015,137(7): 71001.
[54]BECK J A,BROWN J M,KASZYNSKI A A,et al.Mistuned response prediction of dual flow-path integrally bladed rotors with geometric mistuning[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2015,137(6): 62501.
[55]BECK J A,BROWN J M,SCOTTEMUAKPOR O E,et al.Dynamic response characteristics of dual flow-path integrally bladed rotors[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2015,336: 150-163.
[56]BECK J A,SCOTT-EMUAKPOR O E,BROWN J M,et al.Validation of geometric mistuning reduced-order models for single and dual flow-path integrally bladed rotors[C]//17th AIAA Non-Deterministic Approaches Conference.2015.
[57]YANG M T,GRIFFIN J H.A reduced-order model of mistuning using a subset of nominal system modes[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2001,123(10): 893-900.
[58]FEINER D M,GRIFFIN J H.A fundamental model of mistuning for a single family of modes[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2002,124(10): 597-605.
[59]AYERS J P,FEINER D M,GRIFFIN J H.A reduced-order model for transient analysis of bladed disk forced response[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2006,128(7): 466-473.
[60]FEINER D M,GRIFFIN J H.Mistunign identification of bladed disks using a fundamental mistuning model—part ii:application[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(1): 159-165.
[61]FEINER D M,GRIFFIN J H.Mistuning identification of bladed disks using a fundamental mistuning model—part i: theory[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(1): 150-158.
[62]王帅,王建军,李其汉.一种基于模态减缩技术的整体叶盘结构失谐识别方法[J].航空动力学报,2009,24(3): 662-669.
WANG Shuai,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Mistuning identification of integrally bladed disk based on the modal reduced technique[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2009,24(3): 662-669.
[63]MARTEL C,CORRAL R.Asymptotic description of maximum mistuning amplification of bladed disk forced response[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2009,131(2): 435-446.
[64]KHEMIRI O,MARTEL C,CORRAL R.Quantitative validation of the asymptotic mistuning model using a high fidelity bladed disk model[C]// ASME Turbo Expo 2010: Power for Land,Sea,and Air.2010.
[65]GANINE V,LEGRAND M,PIERRE C,et al.A reduction technique for mistuned bladed disks with superposition of large geometric mistuning and small model uncertainties[C]//Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery.2008.
[66]GANINE V,LEGRAND M,MICHALSKA H,et al.A sparse preconditioned iterative method for vibration analysis of geometrically mistuned bladed disks[J].Computers & Structures,2009,87(5): 342-354.
[67]SINHA A.Reduced-order model of a bladed rotor with geometric mistuning[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land,Sea and Air.2007.
[68]SINHA A.Reduced-order model of a bladed rotor with geometric mistuning[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2009,131(3): 310-314.
[69]BHARTIYA Y,SINHA A.Reduced order model of a multistage bladed rotor with geometric mistuning via modal analyses of finite element sectors[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2012,134(4): 410-411.
[70]VISHWAKARMA V,SINHA A,BHARTIYA Y,et al.Modified modal domain analysis of a bladed rotor using coordinate measurement machine data on geometric mistuning[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2015,137(4): 110-121.
[71]BHARTIYA Y,SINHA A.Geometric mistuning identification of integrally bladed rotors using modified modal domain analysis[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2014,136(12): 205-215.
[72]VISHWAKARMA V,SINHA A.Forced response statistics of a bladed rotor with geometric mistuning[J].AIAA Journal,2015,53(9): 2776-2781.
[73]姚建尧,王建军.周期对称性在叶盘结构瞬态响应求解中的应用[J].航空动力学报,2011,26(2): 385-391.
YAO Jianyao,WANG Jianjun.Application of cyclic symmetry property in transient forced vibration of bladed disks[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2011,26(2): 385-391.
[74]YAO J Y,ZHU W X,HU N,et al.Application of symmetry property for transient response analysis of mistuned bladed disks[C]//52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference.2016.
[75]王培屹,李琳.用于失谐叶盘动力学特性分析的减缩计算方法[J].航空动力学报,2014,29(6): 1395-1402.
WANG Peiyi,LI Lin.Reduced order computational method for analysis of mistuning bladed disk dynamics characteristic[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2014,29(6): 1395-1402.
[76]SONG S H,CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.Multi-stage modeling of turbine engine rotor vibration[C]// ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference.2005.
[77]SONG S H,CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.System identification of multistage turbine engine rotors[C]// Proceedings of GT2007,ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land,Sea and Air.2007.
[78]LAXALDE D,LOMBARD J P,THOUVEREZ F.Dynamics of multistage bladed disks systems[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2007,129(5): 1058-1064.
[79]王建军,于长波,姚建尧,等.失谐叶盘振动模态局部化定量描述方法[J].推进技术,2009,30(4): 457-461.
WANG Jianjun,YU Changbo,YAO Jianyao,et al.Vibratory mode localization factors of mistuned bladed disk assemblies[J].Journal of Propulsion Technology,2009,30(4): 457-461.
[80]姚建尧,王建军,李其汉.基于振型节径谱的失谐叶盘结构动态特性评价[J].推进技术,2011,32(5): 645-653.
YAO Jianyao,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Dynamic characteristics assessment of mistuned bladed disk using nodal diameter spectrum of mode shapes[J].Journal of Propulsion Technology,2011,32(5): 645-653.
[81]YAO J Y,WANG J J,Li Q H.Improved modal localization and excitation factors for understanding mistuned bladed disk response[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2011,27(1): 50-60.
[82]KENYON J A,GRIFFIN J H.Forced response of turbine engine bladed disks and sensitivity to harmonic mistuning[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2003,125(1): 113-120.
[83]LIAO H T,WANG J J,YAO J Y,et al.Mistuning forced response characteristics analysis of mistuned bladed disks[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2010,132(12): 1113-1122.
[84]KHEMIRI O,MARTEL C,CORRAL R.Forced response of mistuned bladed disks:quantitative validation of the asymptotic description[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2014,30(2): 397-406.
[85]STERNCHUSS A,BALMES E.Reduction of multistage rotor models using cyclic modeshapes[C]// Proceedings of GT2007,ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land,Sea and Air.2007.
[86]D’SOUZA K X,EPUREANU B I.A statistical characterization of the effects of mistuning in multistage bladed disks[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2012,134(1): 1137-1147.
[87]NIKOLIC M,PETROV E P,EWINS D J.Robust strategies for forced response reduction of bladed discs on large mistuning concept[C]// Proceedings of GT2007,ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land,Sea and Air.2007.
[88]MBAYE M,SOIZE C,OUSTY J,et al.Robust analysis of design in vibration of turbomachines[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2013,135(2): 210-218.
[89]KAZA K R V,KIELB R E.Flutter and response of a mistuned cascade in incompressible flow[J].AIAA Journal,1982,20(8): 1120-1127.
[90]KAZA K R V,KIELB R E.Flutter of turbofan rotors with mistuned blades[J].AIAA Journal,1984,22(11): 1618-1625.
[91]徐建民,宋兆泓.错频叶片转子的稳定性分析[J].北京航空航天大学学报,1986(4): 21-32.
XU Jianmin,SONG Zhaohong.The stability analysis of the rotor of the fault frequency[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,1986(4): 21-32.
[92]郑赟,王静.错频对叶片的气动弹性稳定性影响[J].航空动力学报,2013,28(5):1029-1036.
ZHENG Yun,WANG Jing.Influence of frequency mistuning on aeroelastic stability of blade[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2013,28(5):1029-1036.
[93]徐可宁,王延荣,刘金龙.压气机转子错频叶盘结构振动响应分析[J].燃气涡轮试验与研究,2013,26(3): 6-12.
XU Kening,WANG Yanrong,LIU Jinlong.Vibration response analysis on mistuned bladed disk assembly of compressor rotors[J].Gas Turbine Experiment and Research,2013,26(3): 6-12.
[94]CHOI B K,LENTZ J,MIGNOLET M P.Optimization of intentional mistuning patterns for the reduction of the forced response effects of unintentional mistuning: formulation and assessment[J].Antipode,2002,16(3): 47-59.
[95]MURTHY R,MIGNOLET M P.On the benefits of intentional mistuning of friction dampers to reduce the response of tuned and mistuned bladed disks[C]// ASME Turbo Expo 2013: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition.2013.
[96]袁惠群,张亮,韩清凯,等.基于蚁群算法的航空发动机失谐叶片减振排布优化分析[J].振动与冲击,2012,31(11): 169-172.
YUAN Huiqun,ZHANG Liang,HAN Qingkai,et al.Optimization of mistuning blades arrangement for vibration absorption in an aeroengine based on artificial ant colony algorithm[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2012,31(11):169-172.
[97]李岩,袁惠群,梁明轩.基于改进DPSO算法的航空发动机失谐叶片排序[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2013,33(4): 569-572.
LI Yan,YUAN Huiqun,LIANG Mingxuan.Mistuned blade sorting based on improved dpso algorithm for aero-engine[J].Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science),2013,33(4): 569-572.
[98]赵天宇,袁惠群,杨文军,等.非线性摩擦失谐叶片排序并行退火算法[J].航空动力学报,2016,31(5): 1053-1064.
ZHAO Tianyu,YUAN Huiqun,YANG Wenjun.Mistuned blade arrangement with non-linear friction based on parallel annealing algorithm[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2016,31(5): 1053-1064.
[99]李永强,李健,郭星辉.科氏力对旋转叶片动频的影响[J].振动与冲击,2006,25(1): 79-83.
LI Yongqiang,LI Jian,GUO Xinghui.Effect of coriolis force on dynamic frequency of high speed spinning blade[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2006,25(1): 79-83.
[100]NIKOLIC M,PETROV E P,EWINS D J.Coriolis forces in forced response analysis of mistuned bladed disks[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2007,129(10): 730-739.
[101]辛健强,王建军,李其汉.科氏力对失谐叶盘振动特性的影响分析[J].推进技术,2011,32(5): 637-644.
XIN Jianqiang,WANG Jianjun,LI Qihan.Analysis on vibration characteristics of mistuned bladed disk assemblies with Coriolis force[J].Journal of Propulsion Technology,2011,32(5):637-644.
[102]POUDOU O,PIERRE C.Hybrid frequency-time domain methods forthe analysis of complex structural systems with dry friction damping[C]//44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS Structures,Structural Dynamics,and Materials Conference.2003.
[103]CHA D,SINHA A.Statistics of responses of a mistuned and frictionally damped bladed disk assembly subjected to white noise narrow band excitations[J].Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics,2006,21: 384-396.
[104]王红建,贺尔铭,余仕侠.具有干摩擦散乱失谐的叶盘受迫响应特性[J].航空动力学报,2006,21(4): 711-715.
WANG Hongjian,HE Erming,YU Shixia.Forced response characteristics of bladed disks with disordered dry friction[J].Journal of Aerospace Power,2006,21(4): 711-715.
[105]贺尔铭,王红建,余仕侠.含有非线性摩擦阻尼的失谐叶盘系统受迫响应研[J].机械强度,2007,29(4): 532-535.
HE Erming,WANG Hongjian,YU Shixia.Investigation of forced response of mistuned bladed disks with non-linear friction damping[J].Journal of Mechanical Strength,2007,29(4):532-535.
[106]PETROV E P.A method for use of cyclic symmetry properties in analysis of nonlinear multiharmonic vibrations of bladed disks[J].Journal of Turbomach,2004,126(1):175-183.
[107]PETROV E P,EWINS D J.Generic friction models for time-domain vibration analysis of bladed disks[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(1): 184-192.
[108]PETROV E P,EWINS D J.Methods for analysis of nonlinear multiharmonic vibrations of mistuned bladed disks with scatter of contact interface characteristics[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2005,127(1): 128-136.
[109]PETROV E P,ZACHARIADIS Z I,BERETTA A,et al.A study of nonlinear vibrations in a frictionally damped turbine bladed disk with comprehensive modeling of aerodynamic effects[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines& Power,2013,135(3): 1239-1251.
[110]PETROV E P,DEPARTMENT M E,FRICTION,et al.Analysis of flutter-induced limit cycle oscillations in gas-turbine structures with[J].Journal of Turbomachinery,2014,134:61011-61018.
[111]SEVER I A,PETROV E E,EWINS D J.Experimental and numerical investigation of rotating bladed disk forced response using under-platform friction dampers[C]// Proceedings of GT2007,ASME Turbo Expo 2007: Power for Land,Sea and Air.2007.
[112]SAITO A,CASTANIER M P,PIERRE C.Effects of a cracked blade on mistuned turbine engine rotor vibration[J].Journal of Vibration and Acoustics,2009,131(6): 49-62.
[113]D’SOUZA K,SAITO A,EPUREANU B I.Reduced-order modeling for nonlinear analysis of cracked mistuned multistage bladed-disk systems[J].AIAA Journal,2012,50(2): 304-312.
[114]JUNG C,SAITO A,EPUREANU B I.Detection of cracks in mistuned bladed disks using reduced-order models and vibration data[J].Journal of Vibration and Acoustics.2012,134(6): 1-10.
[115]WANG S,ZI Y,LI B,et al.Reduced-order modeling for mistuned centrifugal impellers with crack damages[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2014,333(25): 6979-6995.
[116]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E,SOIZE C,MBAYE M.Geometric nonlinear dynamic analysis of uncertain structures with cyclic symmetry-Application to a mistuned industrial bladed disk[C]// International Conference on Uncertainty in Structural Dynamics.2014.
[117]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E E L,SOIZE C,MBAYE M.Mistuning analysis and uncertainty quantification of an industrial bladed disk with geometrical nonlinearity[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2015,356: 124-143.
[118]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E E L,SOIZE C,MBAYE M.Uncertainty quantification for an industrial mistuned bladed disk with geometrical nonlinearities[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2015: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition.2015.
[119]CAPIEZ-LERNOUT E E L,SOIZE C,MBAYE M.Uncertainty quantification in nonlinear structural dynamics for mistuned bladed disks[C]//UNCECOMP 2015,1st ECCOMAS Thematic International Conference on Uncertainty Quantification in Computational Sciences and Engineering.2015.

