BP神经网络模型预测肝肿瘤运动趋势可行性研究
姚晔 戈伟强 周云 张立波
200040 上海,复旦大学附属华东医院放疗科
BP神经网络模型预测肝肿瘤运动趋势可行性研究
姚晔 戈伟强 周云 张立波
200040 上海,复旦大学附属华东医院放疗科
目的 利用BP(back propagation)神经网络模型对1例肝癌碘油介入术后患者的肝肿瘤运动趋势进行预测。方法 使用X射线容积成像系统对某肝癌患者进行扫描,采集各时相呼吸运动图像。利用碘油标记方法,对肝癌病灶进行定位,并通过图像检测技术,获取病灶标记点的运动轨迹。对标记点的运动轨迹数据进行分析,建立BP神经网络模型,并用其预测下一时间段的运动曲线,将预测结果与肿瘤标记点实际的运动轨迹进行比较分析。结果 利用BP神经网络可以有效预测肝肿瘤的运动趋势,在一定时间段内可保持良好的精准度,误差在1个像素距离内,但在呼吸运动峰值处预测精准度尚不理想,误差接近2个像素距离。结论 BP神经网络模型是预测肝肿瘤运动的一种新方法,可能对肝癌的体部立体定向放疗以及实时跟踪放疗精准度的提升有一定帮助,且具有一定的临床价值。
肝肿瘤;BP神经网络;呼吸预测;图像跟踪
随着肿瘤放射治疗(简称:放疗)进入“精确定位、精确计划、精确治疗”时代,对肿瘤的实时跟踪定位提出了更高要求。放疗过程中,胸腹部肿瘤的位移主要是受呼吸运动的影响。肿瘤病灶在呼吸周期内随着时间表现出与呼吸运动相关性的运动,这使得定位扫描、靶区勾画、计划设计、实际照射之间存在着偏差,影响了放疗的精度。为了减少呼吸运动带来的影响,放疗工作者采取了各种方法,比如:呼吸训练、门控技术等。利用电子射野影像装置或者锥形束计算机断层成像装置的图像引导技术为肿瘤病灶的实时跟踪提供了可能,但图像获取及分析速度、系统延迟、患者额外照射的剂量等,仍然是有待解决的问题。本研究针对动态实时跟踪肿瘤的前沿问题,提出一种呼吸信号预测模型,利用已获取的呼吸信号数据对患者的呼吸运动状态进行预测,并对预测数据进行验证和评价。
1 资料与方法
选取1例肝癌碘油介入术后患者,在透视模式下,使用Elekta公司Synergy-S直线加速器机载的X射线容积成像系统进行锥形束CT扫描,记录其自由呼吸状态下碘油显影的运动时序。
考虑到呼吸运动在头脚方向的幅度最为明显,而且与胸腹部肿瘤运动具有良好的相关性,本研究仅计算肿瘤在头脚方向上的运动轨迹。采用小波变换方法对图像进行增强,对增强后的图像进行边缘检测,使用Canny算子实现膈肌边缘提取,通过Matlab编程跟踪碘油标记点的运动轨迹。
利用Matlab软件建立一套BP(back propagation)网络,反馈步进为26,将前160个呼吸运动的数据作为输入数据。由于BP神经网络的隐含层节点数对BP神经网络预测精准度有较大的影响,所以经过调试,创建BP网络。
使用训练好的BP模型进行预测,并将预测数据与实测的后40个呼吸运动的采样数据进行分析和比较。
2 结果
根据扫描的肝癌患者自由呼吸状态下碘油显影的运动时序图,采得30个呼吸周期,共243幅图像(图1)。
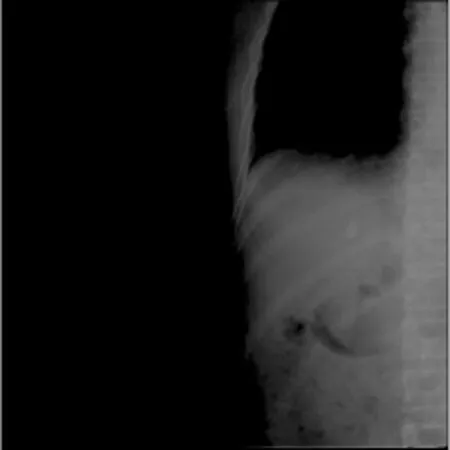
图1 肝癌碘油介入术后患者在透视模式下X射线容积成像系统锥形束CT扫描图Fig.1 A liver cancer patient with iodised oil interventional operation in 2 dimensional mode of Cone Beam CT
建立患者肿瘤运动的碘油运动曲线,去除首尾若干杂散点,本次研究共采用226个有效采样点。将碘油运动曲线映射为患者的呼吸运动曲线(图2)。

图2 肝癌患者的呼吸运动曲线Fig.2 Breath motion curve of the liver cancer patient
网络创建成功后,对该BP网络模型进行训练(图3),待系统达到收敛条件时,系统自动停止迭代(图4~5)。

图3 BP网络训练Fig.3 BP network training

图4 系统训练收敛图Fig.4 Convergence of network training
该BP网络模型较好地预测了呼吸运动的状态,在40个测试点中,除了个别几点外,90%的预测数据偏差在2%以内,精准度良好,在呼吸运动的峰值处偏差较为明显(图6)。总体来说达到了临床的需要。

图5 系统训练回归分析Fig.5 Regression of network training

图6 BP网络模型预测结果及分析 图中,A:BP网络预测输出;B:BP网络预测误差。Fig.6 Prediction and analysis of the BP network model
3 讨论
作为训练使用的历史数据量过少无疑会影响预测精度,尤其对于一个处理非线性数据的网络,如果缺乏足够多的网络训练数据,网络预测值可能存在较大的误差。另外,过多训练数据也会增加计算量,增加了训练时间,对减少系统延迟无益。因此,历史数据量选择要合理。
合适的参数、权重有利于预测精准度及提高效率。同时BP神经网络构建时应注意隐含层节点数的选择,如果隐含层节点数太少,BP网络不能很好地学习,即不能建立复杂的映射关系,需要增加训练次数,训练的精准度也受影响;节点数太多,训练时间增加,网络容易过拟合,即仅训练样本预测准确,但其他样本预测误差较大。究竟如何选择还需针对不同病例数据进行大量实验后总结规律。
本研究发现,对于本例肝肿瘤运动曲线峰值处的预测误差较大,可能是由于呼吸运动没有严格的周期性所导致。在今后进一步研究中,将本研究病例中的神经网络预测与呼吸门控技术相结合,或许能够达到比较理想的效果。
与目前大多数研究方法一样,本研究所做工作仅为对历史数据做回顾性分析,并验证其准确率,如若投入临床,真正实现实时跟踪放疗,还需与测量装置相连接(例如包括与X射线容积成像系统系统的软硬件接口等),其有效性和实时性还有待检验。
利益冲突 本研究由署名作者按以下贡献声明独立开展,不涉及任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明 戈伟强、周云负责方法建立和命题设计;姚晔、张立波负责试验、数据获取与分析;姚晔负责论文起草;戈伟强负责审阅。
[1]Ruan D,Fessler JA,Balter JM.Real-time prediction of respiratory motion based on local regression methods[J].Phys Med Biol,2007, 52(23):7137-7152.DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/52/23/024.
[2]Keall PJ,Mageras GS,Balter JM,et al.The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76 [J].Med Phys,2006,33(10):3874-3900.DOI:http://dx.doi. org/10.1118/1.2349696.
[3]Zhao B,Yang Y,Li T,et al.Statistical analysis of target motion in gated lung stereotactic body radiation therapy[J].Phys Med Biol, 2011,56(5):1385-1395.DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/56/5/011.
[4]Murphy MJ.Tracking moving organs in real time[J].Semin Radiat Oncol,2004,14(1):91-100.DOI:10.1053/j.semradonc.2003. 10.005.
[5]欧阳斌,卢文婷,窦建洪,等.基于非参数回归的呼吸运动预测方法在实时跟踪放疗中的应用[J].南方医科大学学报,2011,31(10):1682-1686.DOI:CNKI:44-1627/R.20111004.1152. 009.Ouyang B,Lu WT,Dou JH.Prediction of respiratory motion based on nonparametric regression for real-time tumor-tracing radiotherapy[J].J South Med Univ,2011,31(10):1682-1686.
[6]Hoisak JD,Sixel KE,Tirona R,et al.Correlation of lung tumor motion with external surrogate indicators of respiration[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2004,60(4):1298-1306.DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.07.68.1.
[7]Ahn S,Yi B,Suh Y,et al.A feasibility study on the prediction of tumour location in the lung from skin motion[J].Br J Radiol,2004, 77(919):588-596.DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1259/bjr/ 64800801.
[8]Ozhasoglu C,Murphy MJ.Issues in respiratory motion compensation during external-beam radiotherapy[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2002,52(5):1389-1399.DOI:10.1016/S0360-3016(01)02789-4.
[9]Ruan D.Kernel density estimation-based real-time prediction for respiratory motion[J].Phys Med Biol,2010,55(5):1311-1326. DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/55/5/004.
[10]Krauss A,Nill S,Oelfke U.The comparative performance of four respiratory motion predictors for real-time tumour tracking[J].Phys Med Biol,2011,56(16):5303-5317.DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/56/16/015.
[11]Murphy MJ,Pokhrel D.Optimization of an adaptive neural network to predict breathing[J].Med Phys,2009,36(1):40-47.DOI:10. 1118/1.3026608.
[12]Ramrath L,Schlaefer F,Ernst A,et al.Prediction of respiratory motion with a multi-frequency based Extended Kalman Filter[J].Int J CARS,2007,2(Suppl 1):S56-60.DOI:10.1007/s11548-007-0083-7.
[13]Kakar M,Nyström H,Aarup LR,et al.Respiratory motion prediction by using the adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system(ANFIS)[J].Phys Med Biol,2005,50(19):4721-4728.DOI:http://dx. doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/50/19/020.
Feasibility study on liver tumor motion prediction based on back propagation neural network
Yao Ye,Ge Weiqiang,Zhou Yun,Zhang Libo
Departmentof RadiationOncology,HuadongHospitalAffliatedtoFudanUniversity,Shanghai200040,China
Ge Weiqiang,Email:gortonge@sina.com
Objective This study was performed to determine the feasibility of liver tumor motion prediction based on back propagation(BP)neural network.MethodsA liver cancer patient was scanned using X-ray volume imaging, and all breath motion figures were recorded.The tumor was located using an iodized oil mark.The mark motion track was gathered through image processing.A BP model was established based on the marked track.This model was used for tumor prediction.The results were compared with the true mark track.ResultsAccurate prediction of liver tumor was achieved via BP neural network, with a deviation of less than 1 pixel.However,the predicted value was less accurate at the peak of the breath motion curve,with a deviation of less than 2 pixels.ConclusionsBP neural network is proposed as a new approach for liver tumor motion prediction.This network is beneficial to enhance the accuracy of liver stereotactic body radiation therapy and real-time adaptive radiation therapy.The proposed approach could be applied clinically.
Liver neoplasms;BP neural network;Breath prediction;Image track
戈伟强,Email:gortonge@sina.com
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4114.2016.01.005
2015-07-19)

