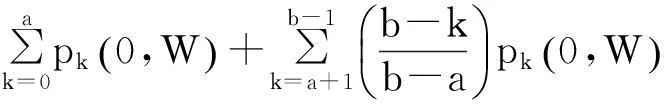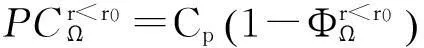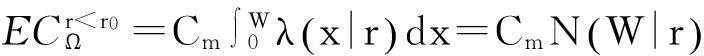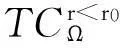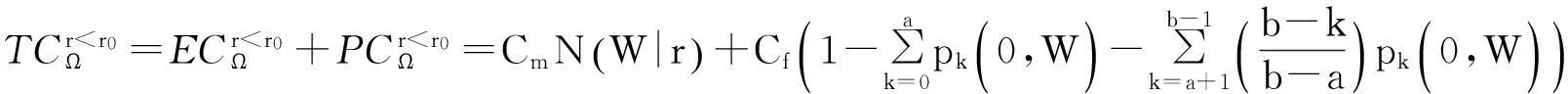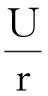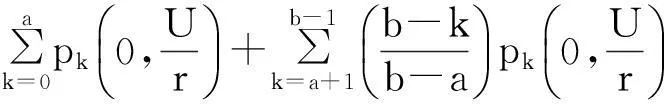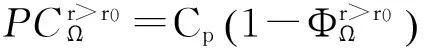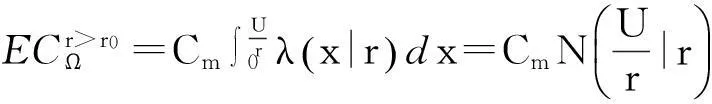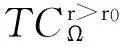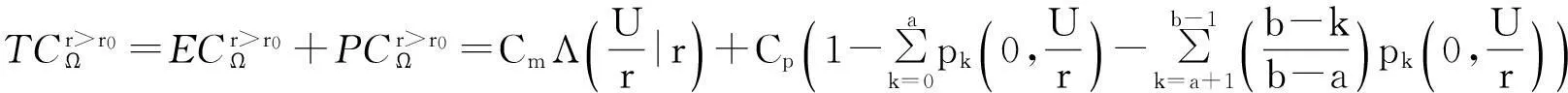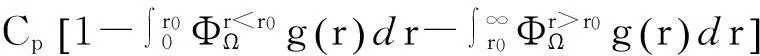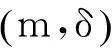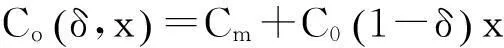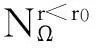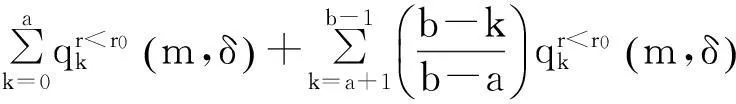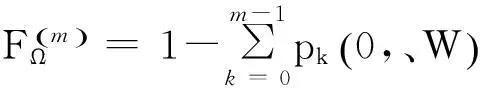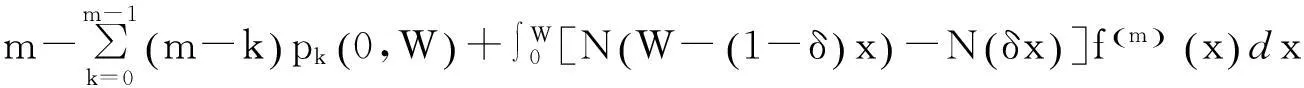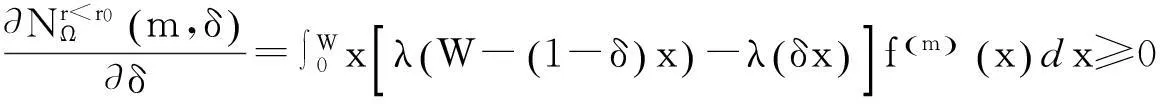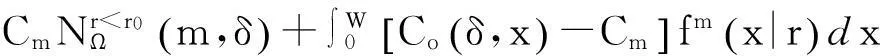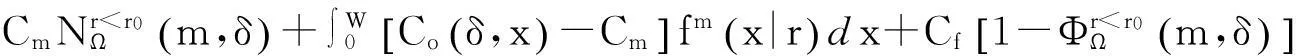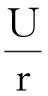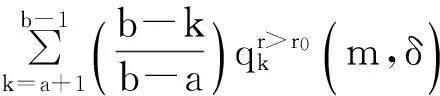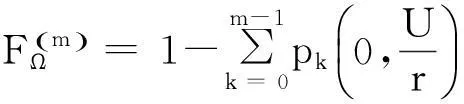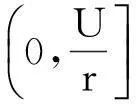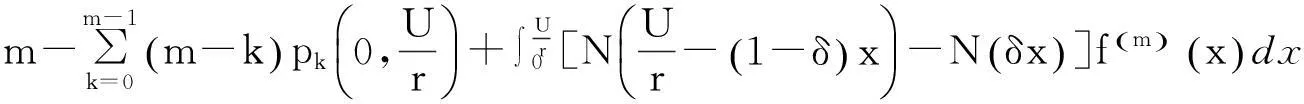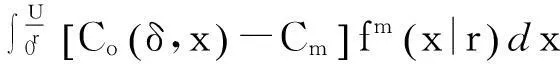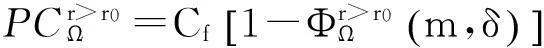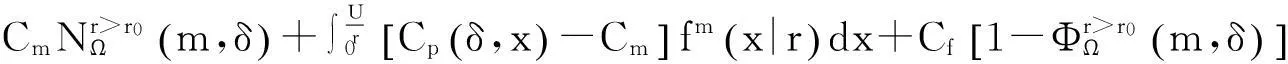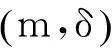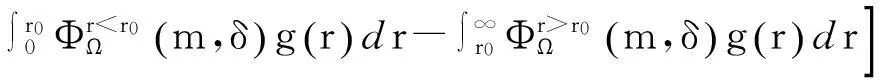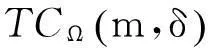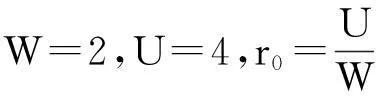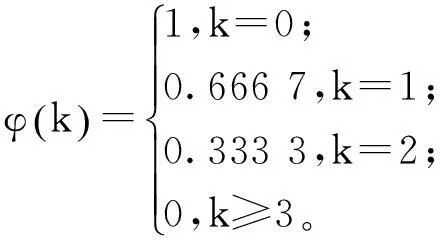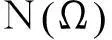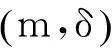面向二维保证的产品大修策略制定
王玉堃, 刘子先
(天津大学 管理与经济学部,天津 300072)
面向二维保证的产品大修策略制定
王玉堃, 刘子先
(天津大学 管理与经济学部,天津 300072)
摘要:为更有效地制定制造商在二维保证政策下的维修策略,针对以往面向产品保证的维修策略研究中,忽略顾客满意度对制造商成本产生的影响这一缺点,将顾客满意度下降对制造商造成的隐性损失考虑在内,分别构建最小维修策略和大修策略下的制造商期望总成本分析模型。以汽车产品安全气囊系统中的传感器部件为例,利用两阶段过程方法,求解获得使制造商在二维保证政策下期望总成本最小的大修策略。研究结果表明,与最小维修策略相比,大修策略使制造商的期望总成本降低了22%,顾客满意度上升到61%,为制造商制定二维保证政策下的维修策略提供了有效的决策支持。
关键词:二维保证; 顾客满意度; 最小维修; 大修
产品保证是制造商向消费者提供的契约性协议,用以规范制造商对其所销售产品的权利和义务[1]。在正常使用条件下,若产品在保证范围内发生失效,顾客有权向制造商提出保证索赔,制造商需对失效产品进行维修、更换或赔偿。产品在保证范围内的性能对顾客的满意度有重要影响,可以认为,顾客满意度为顾客继续购买制造商产品的可能性[2]。若产品失效过于频繁,顾客的满意度将迅速下降,最终可能导致顾客转向购买其他竞争厂商的产品。
上述文献着重于寻求如何使制造商保证服务成本最小化的保证服务策略,并无考虑产品失效带来的顾客的满意度下降对制造商造成的隐性损失。已有的保证分析模型多数面向一维保证政策,尚缺乏同时考虑顾客满意度和二维保证的维修策略研究。本文针对二维保证政策,将顾客满意度对制造商在保证范围内的期望总成本影响考虑在内,分别构建制造商在最小维修策略和大修策略下的期望总成本分析模型,其中,制造商的期望总成本分为保证服务成本和顾客满意度下降所产生的惩罚成本两部分。通过两阶段过程分析获得使制造商期望总成本最小的大修策略。最后将最优大修策略与最小维修策略进行对比,验证大修策略的优越性。
1二维保证政策
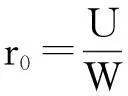

图1 二维保证范围
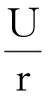
2制造商期望总成本分析模型
2.1模型假设与数学符号
在构建成本分析模型之前,模型的若干假设列举如下。
•制造商为顾客所购买的产品提供二维免费维修保证政策,从产品售出之日起,到保证政策终止前,制造商为失效产品提供免费维修;
•与产品的平均失效间隔相比,制造商对失效产品的修复时间忽略不计;
•在正常使用产品的情况下,用户向制造商所提出的保证索赔均合理;
•在保证范围内,用户接受制造商提供的维修策略,并在产品失效后立即要求保证服务。
模型中所涉及的数学符号及含义如表1所示。

表1 数学符号及含义
2.2模型构建
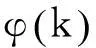
(1)
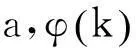
本文分别考虑2种类型的维修策略。
•最小维修策略。在这种策略下,制造商对失效产品采取最小维修,维修后的产品失效率与失效前相同。
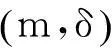
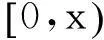
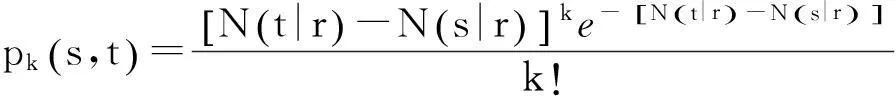
(2)
将顾客的满意度对制造商在产品保证范围内总成本的影响考虑在内,制造商的期望总成本TCΩ等于制造商的期望保证服务成本ECΩ和制造商失去顾客的期望惩罚成本PCΩ之和。
TCΩ=ECΩ+PCΩ。
(3)
2.2.1最小维修策略
在最小维修策略下,为获得TCΩ,需根据产品的实际使用率考虑2种情况:r
情况1:r (4) 制造商在产品保证范围内的期望惩罚成本为 (5) 制造商在产品保证范围内的期望保证服务成本表示为 (6) (7) (8) 则制造商承担的期望惩罚成本为 (9) 制造商在产品保证范围内的期望保证服务成本表示为 (10) (11) 综合r (12) 2.2.2(m,δ)维修策略 (13) (14) 则顾客继续购买制造商产品的概率为 (15) 制造商对产品实行大修的概率为 (16) 产品在保证范围内的期望失效次数为 (17) 当m保持不变,对δ取导,有 (18) (19) (20) 综合式(19)和式(20),当r (21) (22) 顾客继续购买制造商产品的概率为 (23) 制造商在保证范围内对产品实行大修的概率为 (24) (25) (26) (27) 综合式(26)和式(27),制造商在保证范围内的期望总成本为 (28) (29) 3算例分析 (30) 这表示当产品在保证范围内的失效次数超过两次,顾客将不再继续购买制造商的产品。制造商失去一个顾客的惩罚成本为Cf=1 000。 表2 最优的(m, δ)大修策略 4结论 参考文献: [1]MURTHY D N P, DJAMALUDIN I. Product warranty and reliability[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2006, 143(1): 133-146. [2]MURTHY D N P, JACK N. Warranty servicing strategies to improve customer satisfaction[J]. IMA Journal of Management Mathematics, 2004, 15(2): 111-124. [3]BLISCHKE W R, MURTHY D N P. Product warranty management - I: A taxonomy for warranty policies[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1992, 62(2): 127-148. [4]PHAM H, WANG H Z. Imperfect maintenance[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1996, 94(4): 425-438. [5]NGUYEN D G. Studies in warranty policies and product reliability[D]. Australia: The University of Queensland, 1984. [6]JACK N, VAN DER DUYN SCHOUTEN F. Optimal repair-replace strategies for a warranted product[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2000, 67(1): 95-100. [7]YEH R H. Optimal age-replacement policy for nonrepairable products under renewing free-replacement warranty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2005, 54(1): 92-97. [8]PASCUAL R, ORTEGA J H. Optimal replacement and overhaul decisions with imperfect maintenance and warranty contracts[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2006, 91(2): 241-248. [9]CHIEN Yuhung. Optimal age for preventive replacement under a combined fully renewable free replacement with a pro-rata warranty[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2010, 124(2): 198-205. [10]ISKANDAR B P, MURTHY D N P. Repair-Replace strategies for Two-Dimensional Warranty Policies[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2003, 38(9): 1233-1241. [11]ISKANDAR B P. A new repair-replace strategy for items sold with a two-dimensional warranty[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2005, 32(6): 669-682. [12]VARNOSAFADERANI S, CHUKOVA S. A two-dimensional warranty servicing strategy based on reduction in product failure intensity[J]. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 2012, 63(2): 201-213. [13]SHAHANAGHI K, NOOROSSANA R, JALAIL-NAINI S G, et al. Failure modeling and optimizing preventive maintenance strategy during two-dimensional extended warranty contracts[J]. Engineering failure analysis, 2013, 28(1): 90-102. [14]MANNA D K, PAL S, SINHA S. A use-rate based failure model for two-dimensional warranty[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineeing, 2007, 52(3): 229-240. Product Overhaul Strategy Formulation under Two-dimensional Warranty WANG Yukun, LIU Zixian (College of Management and Economics, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China) Abstract:In the previous research on maintenance strategy under warranty, the effect of customer satisfaction on the cost to the manufacturer has been ignored. According to this shortcoming, the hidden loss due to the drop of customer satisfaction is considered in order to develop an effective maintenance strategy under two-dimensional warranty for the manufacturer. The expected total cost analysis models under the minimal repair strategy and the overhaul strategy are respectively developed. Taking the sensor of the airbag system in the automobile product for example, the optimal overhaul strategy is obtained through two-stage process. The results show that compared with the minimal repair strategy, implementing the overhaul strategy can effectively reduce by 22% the total expected cost to the manufacturer, and increase to 61% the probability of repurchase of the customer. This provides effective decision-making support for the manufacturer to formulate the maintenance strategy under two-dimensional warranty. Key words:two-dimensional warranty; customer satisfaction; minimal repair; overhaul 中图分类号:F272 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1007-7375(2016)01- 0031- 07 doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007- 7375.2016.01.005 作者简介:王玉堃(1989-),河南省人,博士研究生,主要研究方向为工业工程和产品保证. 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(71171142) 收稿日期:2014- 09- 29