高速电机发展与设计综述
张凤阁 杜光辉 王天煜 刘光伟
(1.沈阳工业大学电气工程学院 沈阳 110870
2.沈阳工程学院机械工程学院 沈阳 110136)
高速电机发展与设计综述
张凤阁1杜光辉1王天煜2刘光伟1
(1.沈阳工业大学电气工程学院沈阳110870
2.沈阳工程学院机械工程学院沈阳110136)
摘要对高速电机的发展现状进行了分析,总结了现有不同类型高速电机的极限指标,详细论述了高速电机的结构与设计特点,包括定子设计、不同类型转子结构设计、转子系统动力学分析以及轴承选型和冷却系统设计等,最后论述了高速电机发展所面临的问题,展望了高速电机的发展趋势。
关键词:高速电机转子强度冷却系统高速轴承电机设计
0引言
高速电机具有体积小、功率密度大、可与高速负载直接相连、省去传统的机械增速装置、减小系统噪音和提高系统传动效率等特点[1-3],在高速磨床、空气循环制冷系统、储能飞轮、燃料电池、天然气输送高速离心压缩机以及作为飞机或舰载供电设备的分布式发电系统等领域具有广阔的应用前景[4-6],目前已成为国际电工领域的研究热点之一。
高速电机的主要特点是转子速度高、定子绕组电流和铁心中磁通频率高、功率密度和损耗密度大[1]。这些特点决定了高速电机具有不同于常速电机特有的关键技术与设计方法。
高速电机的转子速度通常高于10 000 r/min,在高速旋转时,常规叠片转子难以承受巨大的离心力,需要采用特殊的高强度叠片或实心转子结构[7,8];对于永磁电机来说,转子强度问题更为突出,因为烧结而成的永磁材料不能承受转子高速旋转产生的拉应力[9],必须对永磁体采取保护措施;转子与气隙高速摩擦,在转子表面造成的摩擦损耗远大于常速电机,给转子散热带来很大困难;为了保证转子有足够的强度,高速电机转子多为细长型,因此与常速电机相比,高速电机转子系统接近临界转速的可能性大大增加,为了避免发生弯曲共振,必须准确预测转子系统的临界转速;普通电机轴承无法在高速下可靠运行,必须采用高速轴承系统。
高速电机绕组电流和铁心中磁通交变频率很高,会在电机绕组、定子铁心以及转子中产生较大的高频附加损耗。定子电流频率较低时,通常可以忽略趋肤效应和邻近效应对绕组损耗的影响,但在高频情况下,定子绕组会产生明显的趋肤效应和邻近效应,增大绕组附加损耗;高速电机定子铁心中磁通频率高,趋肤效应的影响不能忽略[10,11],常规的计算方法会带来较大误差,为了准确计算高速电机的定子铁心损耗,需要探索高频工况下的铁耗计算模型;定子开槽与绕组非正弦分布引起的空间谐波以及PWM供电产生的电流时间谐波均会在转子中产生较大的涡流损耗,由于转子体积小、散热条件差,会给转子散热带来极大困难,因此转子涡流损耗的准确计算以及探索有效降低转子涡流损耗的措施,对高速电机可靠运行具有重要意义;同时,高频电压或电流也给大功率高速电机的控制器设计带来了挑战[12,13]。
高速电机的体积远小于同等功率的常速电机,不仅功率密度和损耗密度大,而且散热困难,如果不采用特殊散热措施,会使电机温升过高,从而缩短绕组寿命,特别对于永磁电机,在转子温升过高的情况下,永磁体易发生不可逆退磁[14-16]。设计良好的冷却系统,能有效降低定转子温升,是大功率高速电机长期稳定运行的关键。
综上所述,高速电机在转子强度、转子系统动力学、电磁设计、冷却系统设计与温升计算、高速轴承以及控制器的研制等方面存在许多常规电机所不具有的特殊关键问题,因此高速电机的设计是一个集电磁场-转子强度-转子动力学-流体场与温度场等多物理场多次迭代的综合设计过程。目前应用于高速领域的电机类型主要有感应电机、永磁电机、开关磁阻电机以及爪极电机,每种电机类型又有不同的拓扑结构。
本文对国内外不同类型高速电机的发展现状进行了分析,总结了现有不同类型高速电机的极限指标;详细分析了高速电机结构与设计特点,包括定子设计、不同类型转子结构设计、转子系统动力学分析与轴承选取以及冷却系统的设计等,最后分析了高速电机发展所面临的主要问题,展望了高速电机的发展趋势与前景。
1高速电机的发展现状
高速电机通常指转速超过10 000 r/min或难度值(转速和功率平方根的乘积)超过1×105的电机[17],现有的各类电机中,成功实现高速化的主要有感应电机、内转子永磁电机、开关磁阻电机以及少数外转子永磁电机和爪极电机等[11]。为了分析各类型高速电机的特点,在文献[17]的基础上,本文对国内外各类型高速电机的发展现状进行了进一步的总结和扩展,并按照难度值进行了排列。
1.1高速感应电机
感应电机转子结构简单、转动惯量低,并能在高温和高速的条件下长时间运行,因此感应电机在高速领域应用比较广泛[11]。表1给出了国内外高速感应电机的发展现状。国内外最大功率的高速感应电机为15 MW,转速为20 000 r/min,为ABB公司2002年研制,采用实心转子结构;高速感应电机最大速度为180 000 r/min,功率为10 kW,采用磁悬浮轴承,实心转子结构,线速度为219 m/s,电机的效率约为85%。国内对高速感应电机的研究相对滞后,其中重庆德马电机[27]研制了一系列高速感应电机,海军工程大学[1]、沈阳工业大学[37]、哈尔滨工业大学[44]以及浙江大学等针对高速感应电机开展了许多研究工作,海军工程大学对2.5 MW高速感应电机开展了研究[1],重庆德马电机研制了100 kW、25 000 r/min高速感应电机[33],国内高速感应电机的发展水平远低于国外。
从表1可看出,采用实心转子结构的高速感应电机最大难度值高达24.49×105,转子表面线速度可达367 m/s,而采用常规叠片转子结构的高速感应电机最大难度值仅为3×105,转子表面线速度最高为185 m/s;在难度值大于3×105或转子表面线速度大于185 m/s的高速感应电机多采用实心转子结构或高强度叠片转子结构。文献[24]介绍的一台2 000 kW、15 000 r/min、转子表面线速度为290 m/s的高速感应电机转子采用了AISI4130合金钢铸成的高强度叠片结构,文献[36]介绍的一台5 kW、92 500 r/min、转子表面线速度为240 m/s的高速感应电机转子也采用了高强度合金铸成的叠片转子结构。
1.2内转子高速永磁电机
永磁电机具有效率和功率因数高及转速范围大等优点,因此其在高速应用领域倍受青睐。相对于外永磁转子电机,内转子永磁电机具有转子半径小及可靠性强的优点,成为高速电机的首选。
内转子高速永磁电机的发展现状如表2所示。可以看出,内转子高速永磁电机的最大功率已达8 MW,转速15 000 r/min,为面贴式永磁转子,采用碳纤维保护套捆扎;最高转速的永磁电机为500 000 r/min,功率为1 kW,转子表面线速度为261 m/s,采用合金保护套。国内对高速永磁电机的研究主要集中在浙江大学、沈阳工业大学、哈尔滨理工大学、哈尔滨工业大学、西安交通大学、南京航空航天电机、东南大学、北京航空航天大学、江苏大学、北京交通大学、广东工业大学、南车株洲电机有限公司等,他们对高速永磁电机有面贴式(SPM)和内置式(IPM)两种转子结构。从表2可看出,除少数采用内置式转子结构外,其余多采用面贴式永磁转子结构。文献[89]对一台11 kW、50 000 r/min的高速永磁电机设计了内置式转子结构,该电机转子表面线速度为233 m/s,转子采用高强度叠片材料。采用常规叠片材料的高速内置式永磁电机,最大难度值为1.13×105,最大转子表面线速度为135 m/s。
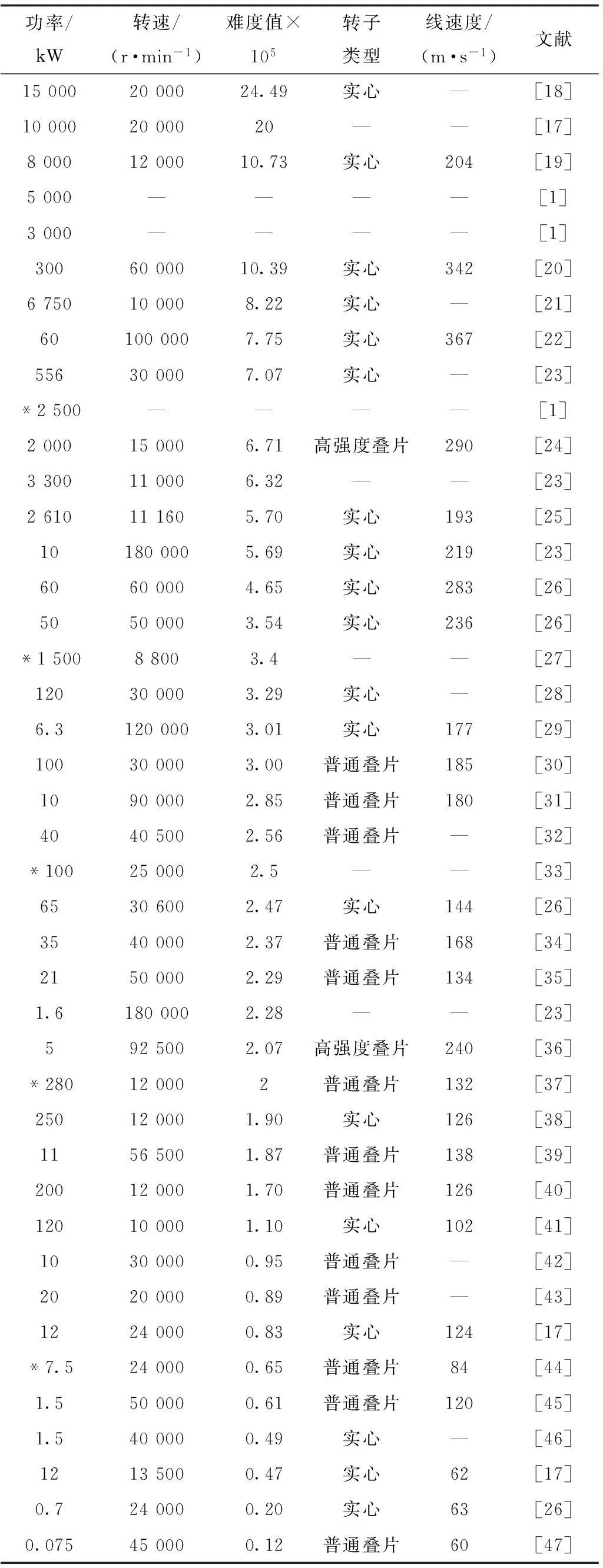
表1 高速感应电机的发展
注:*表示国内高速电机的发展状况。
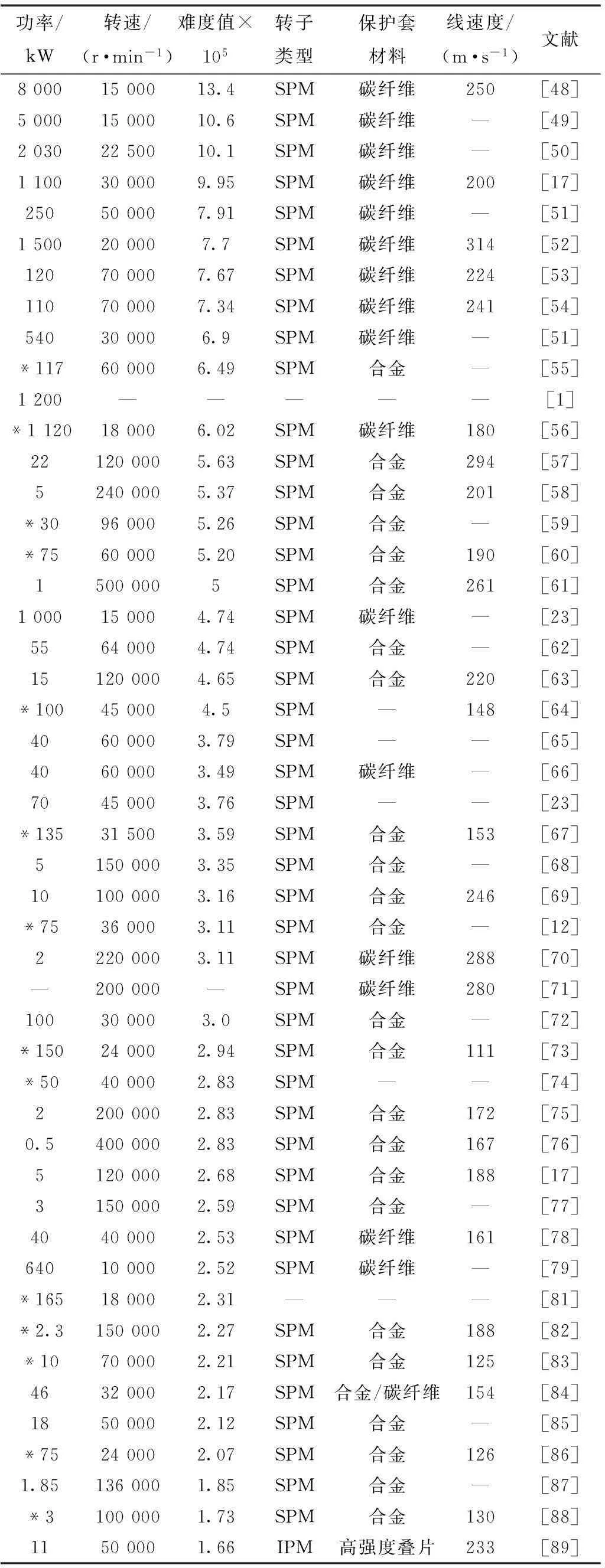
表2 内转子高速永磁电机的发展

续表2
注:*表示国内高速电机的发展状况。

图1 沈阳工业大学研制的1 120 kW、18 000 r/min高速永磁电机Fig.1 1 120 kW、18 000 r/min high speed permanent magnet machine designed by shenyang university of technology
表贴式永磁转子主要有两种保护措施,一种是采用碳纤维捆扎,一种是采用合金护套。从表2可看出,采用合金护套时,高速电机的最大难度值为6.49×105,最大功率为135 kW,最大转子表面线速度为294 m/s。而采用碳纤维捆扎的高速电机最大功率高达8 000 kW,最大表面线速度为314 m/s。
1.3高速开关磁阻电机
开关磁阻电机以结构简单、坚固耐用、成本低廉以及耐高温等优点而备受瞩目,在高速领域的应用日益广泛,国内外高速开关磁阻电机的发展现状如表3所示。高速开关磁阻电机目前可达的最大难度值为3.51×105,最大功率为250 kW(转速22 000 r/min),最高转速为200 000 r/min(功率1 kW)。南京航空航天大学[112]、北京交通大学[113]、湖南工业大学[122]、华中科技大学[123]等对高速开关磁阻电机开展了相关研究工作,其中南京航空航天大学研制了1 kW、130 000 r/min的开关磁阻电机[112]。

表3 高速开关磁阻电机的发展
注:*表示国内高速电机的发展状况。
1.4其他类型高速电机
高速电机除上述3种类型的电机外,还有少数外转子永磁电机与爪极电机。本文对国内外其他类型的高速电机进行的不完全统计如表4所示。外转子高速永磁电机最高难度值为3.17×105(28 kW、60 000 r/min),最大功率为100 kW,最高转速为60 000 r/min。哈尔滨工业大学[125]、山东大学[130]、浙江大学[133]针对外转子高速永磁电机开展了相关的研究工作,沈阳工业大学对双定子单转子轴向磁通电机[93]和外转子爪极高速电机[129]进行了一定研究。
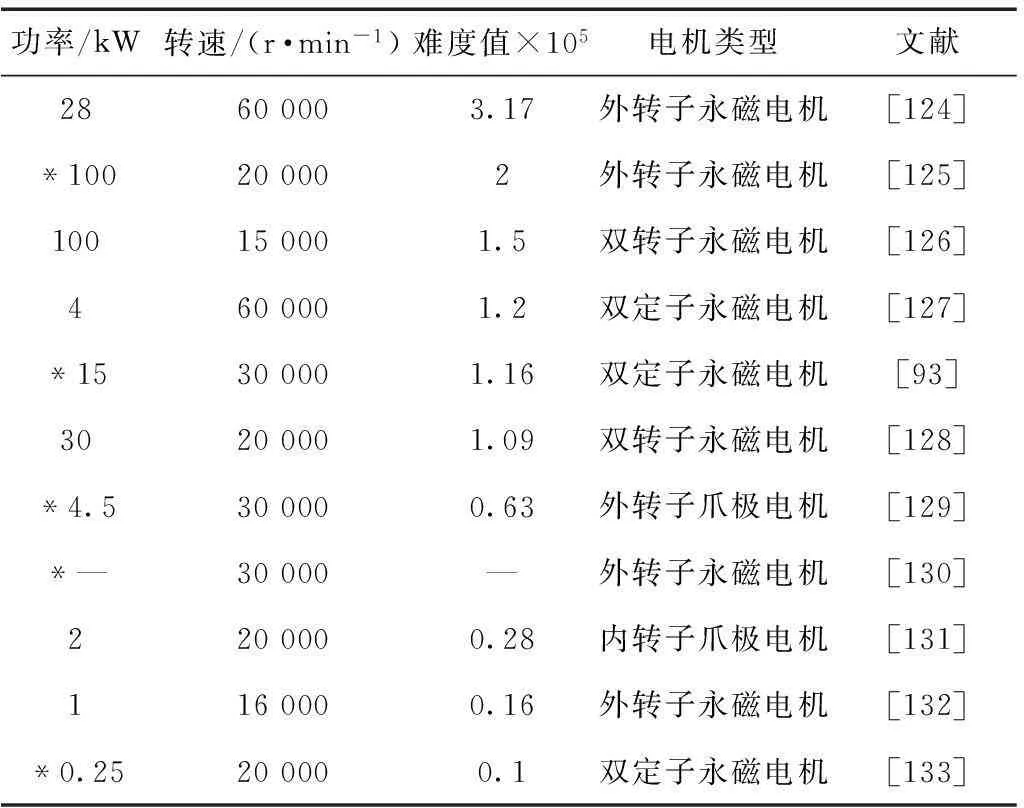
表4 其他类型高速电机的发展
注:*表示国内高速电机的发展状况。
1.5不同类型高速电机的比较分析
基于国内外高速电机的发展现状和相关文献,本文在文献[17]的基础上,对现有不同类型和结构高速电机的极限指标进行了统计,如表5所示。实心转子感应电机可达到的难度值和转子表面线速度最大,采用碳纤维保护措施的内转子永磁电机次之。这两种结构高速电机的难度值均超过了10×105、转子表面线速度超过了300 m/s。兆瓦级以上的高速电机类型多为实心转子感应电机和碳纤维保护措施的内转子永磁电机,也有少数高强度叠片感应电机。高强度叠片感应电机的最大难度值和转子表面线速度与采用合金护套的内转子永磁电机接近,分别为6.5×105和290 m/s,但采用合金护套的内转子高速永磁电机目前达到的最大功率仅为135 kW,因为合金护套中会产生大量的涡流损耗,不宜用于较大功率的高速永磁电机。高速开关磁阻电机、常规叠片高速感应电机、外转子高速永磁电机的最大难度值相近,约为3×105~3.5×105,目前阶段的最大功率均在300 kW以下,最大转子表面线速度在185~210 m/s之间。内置式高速永磁电机的最大难度值低于1.2×105,高强度叠片内置式永磁电机的最大表面线速度可达233 m/s,但采用常规叠片时仅为135 m/s。爪极电机所能承受的难度值最低,小于1×105。

表5 现有不同类型高速电机的极限指标
从以上分析可知,感应电机、永磁电机、开关磁阻电机是高速电机最常用的3种类型。文献[134]基于20 kW、26 000 r/min的高速电机,对采用3种不同类型转子的电机性能进行了对比,得到永磁电机的效率和功率密度最高,开关磁阻电机的效率居中、功率密度最低。表6对3种转子类型高速电机的优缺点进行了比较。虽然永磁电机具有较高的效率与功率密度,但永磁体抗拉强度低、抗高温特性较差,需要特殊的保护措施和良好的散热条件,加工较复杂。
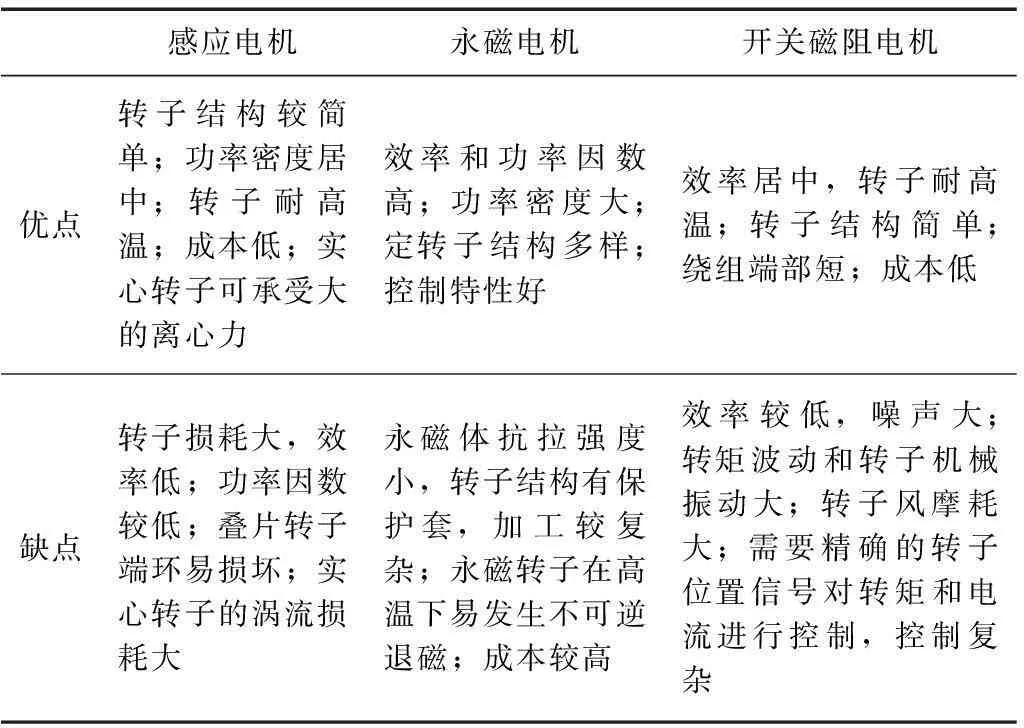
表6 不同类型高速电机的对比
2定子结构的设计
2.1极数
高速电机一般设计为2极或4极。对于2极电机,永磁体可采用整体结构,定子电流和铁心中磁场的交变频率较低,有利于降低高频附加损耗,但2极电机的定子绕组端部较长、铁心轭部较厚[1]。4极电机与2极电机相反,定子绕组端部较短,铁心轭部较薄,但定子绕组电流和铁心中磁场的交变频率较高[1]。
2.2槽数
槽数有多槽、少槽和无槽3种方案可选择。无槽方案不产生高频齿谐波磁场,对减小转子涡流损耗十分有利,但气隙较大,永磁体产生的气隙磁通密度小,永磁材料利用率低[1]。少槽方案气隙磁通密度谐波幅值大,转子涡流损耗大,这对于高速电机来说是不可取的。多槽方案既可获得较高的气隙磁通密度,提高材料利用率,又不会产生过大的转子涡流损耗。
2.3铁心材料
高速电机频率高,高频下的定子铁心将产生较大的铁耗,通过合理选取定子铁心材料,可有效降低定子损耗,提高电机的电磁性能。图2为不同定子材料单位重量铁耗随频率的变化曲线。其中,B20AT1500、B27AH1500、B35AH300分别为0.2 mm、0.27 mm和0.35 mm的硅钢片材料,Vacoflux50为0.2 mm的钴钢片,Somaloy700为软磁复合(SMC)材料,Metglas2605SA1为非晶合金材料。从图2可看出,非晶合金材料的单位铁耗远小于其他材料,但该种材料的饱和磁感应强度较低(为1.2~1.3 T),适用于铁心磁通密度较低的高速电机。当电机的工作频率低于1 000 Hz时,SMC材料单位铁耗值高于普通硅钢片,当工作频率高于2 000 Hz时,SMC材料才能有效减小高速电机的铁心损耗[131]。单位钴钢片的损耗值小于硅钢片,但钴钢片的抗拉强度较小,约为硅钢片的一半。
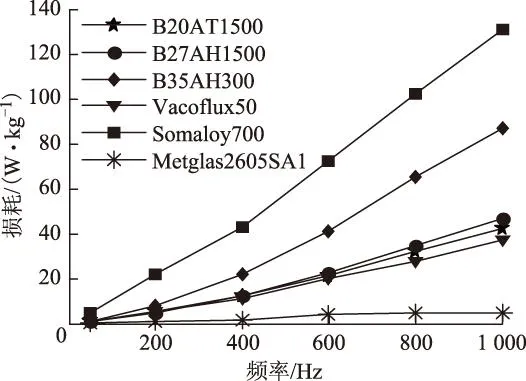
图2 不同定子铁心材料的损耗曲线Fig.2 Losses of different core materials
2.4定子绕组
传统定子绕组端部较长,增加了转子的轴向长度,从而降低了转子系统的刚度。环型绕组结构可有效缩短定子绕组端部长度,其不利之处是线圈嵌线工艺较复杂[1]。
高速电机频率较高,会在定子绕组的导体中产生较大的趋肤效应和邻近效应,从而造成附加损耗,为了降低定子绕组中的损耗,定子绕组须采用许多根较小直径的细导线并联绕制,绕组的导体半径r一般要小于磁场在导体中的透入深度,即为
式中,μ为导体的磁导率;σ为导体的电导率;ω为交变磁场角频率。
文献[11]对圆铜线绕组的交直流损耗进行了分析,当电机频率在1 kHz以下时,定子绕组的交、直流损耗比约为1,可忽略趋肤效应和邻近效应的影响;文献[49]对一台5 MW、6.3 kV的高速永磁电机采用了扁铜线绕组结构,并对定子绕组损耗进行了分析,分析结果显示,当频率为400 Hz时,定子绕组的交流损耗约为直流损耗的3倍,因此扁铜线绕组的交、直流损耗比受频率影响非常明显,在进行高频铜耗计算时,必须考虑趋肤效应和邻近效应的影响。
3转子结构的设计
3.1笼型转子
3.1.1转子槽型
高速叠片式笼型转子通常采用闭口槽,闭口槽类型主要有圆形槽、水滴槽、平行槽3种,如图3所示。圆形槽的优势为对转子铁心上应力的分布影响较小,可保证转子具有较高的机械强度,工艺简单、成本低,而缺点为转子齿磁通密度易产生局部过大,导条电流密度过高,转子铜耗较大。水滴槽和平行槽是在圆形槽之上改良的,可有效减小转子齿磁通密度,同时增大了导条面积,减小了导条上的电流密度,具有较小的转子铜耗,但机械强度低于圆形槽[15,37]。
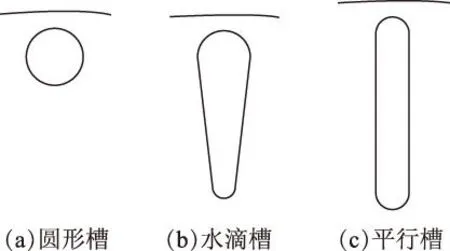
图3 转子槽型Fig.3 Rotor slot structures
3.1.2转子铜条材料
纯铜在温度较高的情况下会发生软化现象,因此在高速感应电机的设计中,主要采用铜合金作为转子导条材料。表7列出了几种常用的铜合金材料属性[135],在选择导条材料时,要综合考虑机械强度和转子铜耗,在保证机械强度的情况下,应选择电导率较大的铜合金。
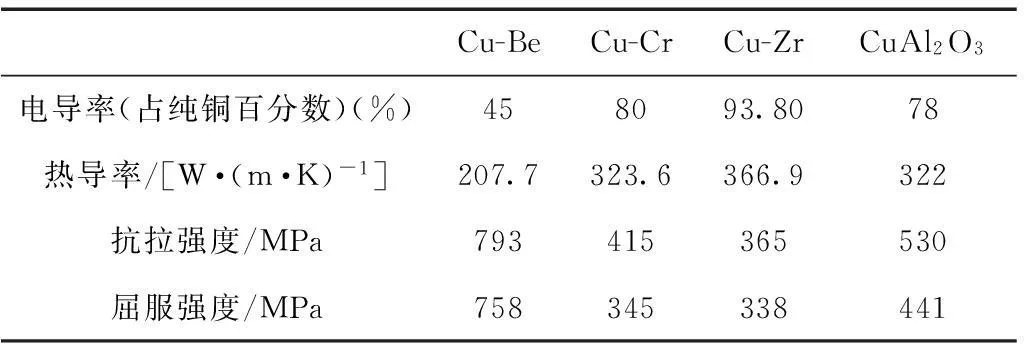
表7 不同导体材料属性
3.1.3端环的保护
感应电机的端环与铜条是焊接而成的,当高速旋转时,焊接处易发生损坏,因此必须对端环进行保护,目前最常用的保护措施是用铆钉将端环与转子铁心固定在一起以增加转子整体的机械强度,如图4所示[136]。

图4 转子端环保护Fig.4 Rotor end ring protection
3.2实心转子
实心转子高速感应电机有如图5所示的4种转子结构[17]。文献[137]基于一台75 kW、60 000 r/min的高速感应电机,对4种转子结构的应力和损耗进行了比较分析,如图6所示。可以看出,实心钢转子结构和铜屏蔽转子结构的转子强度较好,开槽实心转子的转子应力远大于其他3种转子结构,但实心钢转子结构的转子涡流损耗最大,开槽实心转子次之;铜屏蔽转子和笼型实心转子因为在转子材料中有铜导体,这些铜导体为电流提供了通路,能够减小一部分涡流,所以这两种转子的损耗比另外两种转子损耗低。
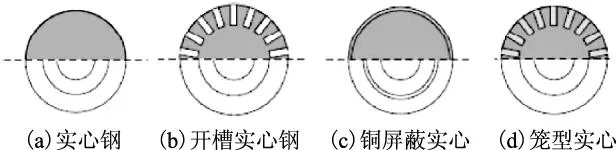
图5 实心转子结构Fig.5 Solid rotor structures

图6 不同实心转子结构的应力和转子涡流损耗比较Fig.6 Comparisons of stress and rotor eddy current loss with different solid rotor structures
3.3永磁转子
3.3.1永磁材料
常用的永磁体材料主要有NdFeB和SmCo。NdFeB材料的剩磁密度和矫顽力较大,但易受温度影响,最大可承受温度约为220 ℃,抗拉强度约为80~140 MPa,SmCo材料的剩磁密度较小,受温度影响较小,可承受的温度高达350 ℃,但抗拉强度小,约为25~35 MPa,使用SmCo永磁材料时会增加保护套厚度和等效气隙长度。
3.3.2内置式永磁转子
为了改善传统内置式永磁转子结构在高速运行时易在隔磁桥处应力过大的问题,内置式高速永磁转子多采用永磁体分段,并在永磁体段间设置加强筋的结构。图7列举了几种常用的内置式高速永磁转子结构。图7a为一字形永磁体分段结构,该种分段结构也可采用V形和W形等结构型式。文献[95]在8 kW、40 000 r/min的高速永磁电机中采用了2极结构,分析了永磁体层数及每层加强筋数量等对电磁特性和转子应力的影响,永磁体层数对转子应力的影响很小,可忽略不计,最终样机采用了图7d所示的转子结构,该种结构具有较小的漏磁系数。文献[5]介绍了一种新型切向式高速永磁电机转子结构,如图7e所示,C形硅钢片挂在高强度的不导磁轴上,永磁体为不等厚结构,靠近转轴处较厚,沿半径方向逐渐减小,这种结构即可降低硅钢片应力,又拥有较小的漏磁系数。
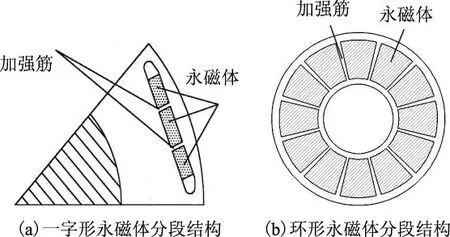

图7 内置式永磁转子结构Fig.7 Interior permanent magnet rotor structures
3.3.3表贴式永磁转子结构及其保护措施
表贴式高速永磁电机的转子结构如图8所示。图8a为实心永磁体结构,该转子结构为2极,永磁体采用平行充磁的方式。查阅到的相关文献中介绍的75 kW、60 000 r/min[60],150 kW、24 000 r/min[73],0.5 kW、400 000 r/min[76]和0.1 kW、500 000 r/min[90]的高速永磁电机均采用了该种转子结构。图8b为2极环形永磁体结构,采用了平行充磁方式和永磁体不分块技术,该种转子结构即为2极Halbach结构,加工较简单,多用于转子外径较小的高速永磁电机,2.3 kW、150 000 r/min[82]和10 kW、70 000 r/min[83]等高速电机均采用了该种结构。图8c为面包式永磁转子结构,该结构的气隙磁通密度更接近正弦波,谐波较小,但所需永磁体较厚,文献[52,53]分别介绍的1.5 MW、20 000 r/min和120 kW、70 000 r/min的高速永磁电机均采用该种转子结构。图8d为永磁体分段转子结构,极间间隙可由高温塑料、环氧树脂、碳纤维、合金等材料填充,从而降低保护套在极间间隙处的弯曲应力,提高转子可靠性,该种转子结构为高速永磁电机最常用的转子结构。为了降低转子涡流损耗,Halbach充磁转子结构越来越多的在高速电机中应用,图8e给出了3种Halbach充磁结构,30 kW、20 000 r/min[128]和640 kW、10 000 r/min[79]的高速永磁电机均采用了该种转子结构。
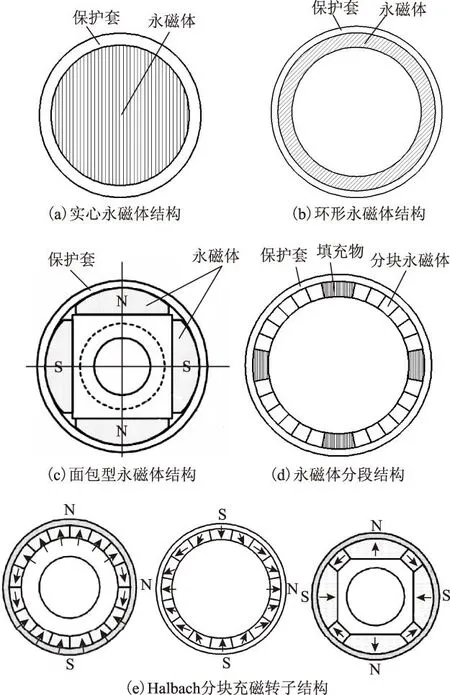
图8 表贴式永磁转子结构Fig.8 Surface permanent magnet rotor structures
对于表贴式永磁转子,必须对永磁体采取保护措施:一种保护方法是在永磁体外面用高强度非导磁护套(如Inconel718、钛合金等[5]),另一种保护方法是采用碳纤维等高强度纤维捆扎。两种材料的特性如表8所示。考虑温度和弯曲应力时碳纤维护套的最大可承受应力约为1 400~1 700 MPa[71],大于合金钢护套最大抗拉强度,但合金护套可承受的最大温度(290 ℃)远高于碳纤维护套(180 ℃)。合金钢材料的电导率较高,电机空间谐波和时间谐波会在合金保护套中产生较大的涡流损耗。采用碳纤维捆扎时保护套厚度和高频涡流损耗较小,但碳纤维是热的不良导体,不利于永磁转子的散热。文献[138]介绍的在合金保护套内层加入铜屏蔽层可有效抑制转子涡流损耗,但对碳纤维保护措施抑制效果并不明显。文献[82]在合金保护套上开设轴向和周向浅槽来降低转子涡流损耗,周向浅槽结构如图9所示。

表8 不同保护套材料属性
图9 合金护套周向开槽结构Fig.9 Circumferential grooves on alloy retaining sleeve
针对高速永磁电机,文献[139]提出了一种半导磁的合金保护套,相对磁导率为7.2,与非导磁合金保护套相比,采用半导磁保护套可明显改善电机的空载反电动势波形。文献[140]介绍了一台75 kW、60 000 r/min的高速永磁电机,该文从电磁特性、转子应力、转子温度等方面综合比较了碳纤维保护套、非导磁合金护套以及半导磁合金护套的性能。采用碳纤维护套所需保护套厚度、转子损耗、转子温度均最小,采用半导磁合金护套所需永磁体厚度最小,保护套厚度小于非导磁合金护套,但转子涡流损耗远大于非导磁合金护套和碳纤维保护套。
文献[141]对一台1 120 kW、18 000 r/min的高速永磁电机设计了两种保护措施:一种采用纯碳纤维保护措施,一种采用合金钢和碳纤维共同组成的混合保护措施,如图10所示。其中纯碳纤维保护套与永磁体采用过盈配合,混合保护措施与永磁体采用间隙配合,间隙处填充高强度粘合剂,混合保护措施可降低纯碳纤维保护套的弯曲应力。实验表明采用上述保护措施的两种转子样机均能在22 000 r/min安全运行。

图10 1 120 kW、18 000 r/min高速永磁电机转子结构Fig.10 Rotors of 1 120 kW、18 000 r/min high speed permanent magnet machine
文献[71,142]中介绍的转速分别为200 000 r/min和60 000 r/min的两台高速永磁电机,在碳纤维保护套内层均缠绕了一层较薄的玻璃丝纤维,目的在于有效抑制在永磁体弯曲处和永磁体分块对碳纤维护套造成的弯曲应力,提高保护套可靠性。
4转子系统的动力学设计与轴承设计
4.1转子系统动力学设计
转子动力学设计是高速旋转机械设计的重要内容,转子旋转时,转子的质量中心和回转中心总会有一定的偏差,使转子产生周期性的离心干扰力,使得转子的偏心进一步增加,转子振动的幅度进一步增大,当转子的转速与转子的临界转速接近时,转子将会发生剧烈的弯曲振动,引起整个机组振动,严重时甚至使得转子遭到破坏。对于刚性转子,工作转速n应低于一阶临界转速nc1,即n<0.7nc1;对于挠性转子,应使工作转速在一阶临界转速nc1和二阶临界转速nc 2之间,即1.4nc1 4.2轴承设计 高速电机的安全稳定运行与轴承可靠性密不可分。目前在高速电机中应用的轴承主要有滚珠轴承、充油轴承、空气轴承和磁悬浮轴承。文献[1,5]对上述轴承的特点进行了对比分析。文献[135]对目前高速电机所采用的轴承类型进行了统计,如图11所示。可以看出,高速电机多采用磁悬浮轴承和滚球轴承,其中磁悬浮轴承可实现主动控制,可在整个转速范围内调节轴系的动态性能,完全无接触,不需要润滑,使用寿命长,这些优点使磁悬浮轴承在高速电机领域具有广阔的应用前景[5]。国内对高速电机轴承也开展了许多研究工作。西安交通大学、南京航空航天电机、沈阳工业大学、江苏大学等对所研制的高速电机采用了磁悬浮轴承[74,112,60],浙江大学、沈阳工业大学等对陶瓷球轴承在高速电机中的应用也进行了一定的研究[83,129],北京航空航天大学对高速电机的空气轴承进行了研究[144],沈阳工业大学在兆瓦级高速永磁电机样机中采用了充油轴承[56]和磁悬浮轴承,其中充油轴承在额定运行时发生漏油问题,而磁悬浮轴承能安全稳定运行。 图11 高速电机轴承分布Fig.11 Bearing distributions of high speed machine 5冷却系统设计 高速电机的功率密度和损耗密度较大,设计良好的冷却系统、降低电机温升是高速电机设计的又一关键技术。文献[60]对一台150 kW、16 000 r/min的高速永磁电机的转子自散冷技术进行了设计与分析;文献[42,54]分别在10 kW、30 000 r/min和110 kW、70 000 r/min的高速永磁电机中采用了机壳水冷的冷却结构。文献[145]对制冷机用高速永磁电机设计了内外风冷的冷却结构,如图12所示,其中外风道开设在机壳上,内风道开设在定子槽内,该种冷却结构借助制冷机产生的冷却介质,从机壳一侧的入口进入外风道,带走定子热量后,进入内风道,从机壳另一侧的出口流出。 图12 制冷机用高速电机冷却结构Fig.12 Cooling structure of high speed machine for refrigerator 文献[59]对一台30 kW、96 000 r/min的高速永磁电机设计了如图13所示的冷却结构,该冷却结构采用空气冷却,在定子槽内开设内风道,在电机机壳外侧设置有外风道,冷却空气从电机一端进入,从另一端流出。 图13 30 kW、96 000 r/min高速电机冷却结构Fig.13 Cooling structure of 30 kW、96 000 r/min high speed machine 对于环形绕组结构,可在环形绕组的内外槽中开设冷却通道,如图14所示,冷却通道内可通入空气或油,带走定转子热量,查阅到的相关文献中介绍的75 kW、36 000 r/min[12],75 kW、60 000 r/min[60],117 kW、60 000 r/min[55]的高速永磁电机均采用了该种冷却结构。 图14 环形绕组高速电机冷却结构Fig.14 Cooling structure of high speed machine with toroidal windings 高速永磁电机也可采用径向和轴向混合冷却结构[146],如图15所示。定子铁心分为两段,机壳上开设有冷却通道,冷却空气从定子铁心中间、定子绕组端部以及机壳外冷却通道等多路流入,带走电机热量,后从电机机壳上开设的出口处流出,为了更好地降低电机温升,机壳冷却通道内可通入水等冷却介质。 图15 轴向与径向混合冷却结构Fig.15 Axial and radial mixing cooling structure 大功率高速电机多采用槽内风冷与机壳水冷相结合的冷却结构。沈阳工业大学对一台1 120 kW、18 000 r/min的高速永磁电机,分析了槽内风冷与机壳水冷相结合的3种冷却结构:混合通风与螺旋水路、轴向通风与螺旋水路以及轴向通风与直槽水路[56,147,148],其中轴向通风与螺旋水路结构如图16所示,混合通风是将定子分为两段,从定子中间进风,经过槽内的轴向风道,从机壳两侧出风。混合通风的冷却效果好于单一轴向通风,螺旋水路和直槽水路的冷却效果相近。文献[50,80]分别为2 030 kW、22 500 r/min和640 kW、10 000 r/min的高速永磁电机设计了风冷和水冷相结合的冷却结构,在定子槽内开设轴向通风道,在定子机壳开设了中间进水和两端出水的两条并联支路螺旋水路。 图16 风冷和水冷相结合冷却结构Fig.16 Cooling structure combined air with water 6高速电机面临的问题及发展趋势 经过近年来的发展,国外对高速电机的研究已具备了相当的基础,产业化势头良好。相比于国外,国内对高速电机的研究基础还较薄弱,产业化水平较低,国内对高速电机的研制多集中在中小功率和较低转速的范围内,与国外尚有较大差距。综合国内外的发展和研究现状,针对兆瓦级以上的大功率高速电机和超高速高速电机的研究与应用还较少,在高速电机的设计与分析方面仍有一些问题亟需解决,主要包括: 1)高速电机的设计是一个多物理场和多学科交叉的综合设计过程,基于电磁场、应力场、转子动力学、流体场与温度场等多物理场耦合方法来分析高速电机的技术尚不成熟。 2)高速轴承仍有很多问题亟需解决:滚球轴承不能承受过高的转速,充油轴承系统庞大且在高速旋转时易发生漏油问题,空气轴承承载负载能力有限,磁悬浮轴承控制复杂、价格昂贵。 3)大功率高速电机功率变换系统、控制系统与控制策略、实时监测系统的研发还很薄弱;大功率高速电机的转子动力学设计技术有待完善;高速电机的加工工艺复杂,距离产业化的要求还很远。 4)定转子损耗的理论分析、计算方法以及实验验证等方面有待进一步研究;大功率高速永磁电机多采用风冷和水冷相结合的冷却方式,冷却结构复杂,冷却效果有限。 5)永磁体抗拉强度低、耐温能力差制约着高速永磁电机向超高速和大功率方向发展,研发更高抗拉强度和更高耐温水平的永磁材料对高速电机的发展具有重要意义。 6)对于面贴式永磁电机,合金保护套存在较大的涡流损耗,碳纤维保护套的导热系数较差,给高速永磁电机的转子散热带来了较大困难,因此开发高导热特性的纤维材料对于高速转子的设计有重要价值。 7)常规叠片转子不能承受较大的离心力,实心转子存在较大的涡流损耗,需要对新型高强度转子叠片材料和结构进行深入研究。 综上所述,高速电机发展和研究方向主要有:大功率高速电机和超高速高速电机的关键问题研究;基于多物理场和多学科的耦合设计;定转子损耗的理论研究与实验验证;高强度与高耐温能力的永磁材料、高导热系数的纤维材料等新材料的开发及应用;高强度转子叠片材料和结构的研究;不同功率和转速等级下高速轴承的应用;良好散热系统的设计;高速电机控制系统的研制;满足产业化要求的转子加工及装配新工艺等。 参考文献 [1]王凤翔.高速电机的设计特点及相关技术研究[J].沈阳工业大学学报,2006,28(3):258-263. Wang Fengxiang.Study on design feature and related technology of high speed electrical machines[J].Journal of Shenyang University of Technology,2006,28(3):258-263. [2]Gieras J F.Design of permanent magnet brushless motors for high speed applications[C]//17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS),Hangzhou,2014:1-16. [3]Moghaddam R R.High speed operation of electrical machines,a review on technology,benefits and challenges[C]//IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE),Pittsburgh,PA,2014:5539-5546. [4]Bianchi N,Bolognani S,Luise F.Potentials and limits of high-speed PM motors[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2004,40(6):1570-1578. [5]董剑宁,黄允凯,金龙,等.高速永磁电机设计与分析技术综述[J].中国电机工程学报,2014,34(27):4640-4653. Dong Jianning,Huang Yunkai,Jin Long,et al.Review on high speed permanent magnet machines including design and analysis technologies[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2014,34(27):4640-4653. [6]Tenconi A,Vaschetto S,Vigliani A.Electrical machines for high-speed applications:design considerations and tradeoffs[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2014,61(6):3022-3029. [7]Boglietti A,Cavagnino A,Tenconi A,et al.Key design aspects of electrical machines for high-speed spindle applications[C]//36th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society,Glendale,AZ,2010:1735-1740. [8]Kolondzovski Z,Arkkio A,Larjola J,et al.Power limits of high-speed permanent-magnet electrical machines for compressor applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion,2011,26(1):73-82. [9]沈建新,李鹏,郝鹤,等.高速永磁无刷电机电磁损耗的研究概况[J].中国电机工程学报,2012,33(3):62-74. Shen Jianxin,Li Peng,Hao He,et al.Study on electromagnetic losses in high-speed permanent magnet brushless machines-the state of the art[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,33(3):62-74. [10]Borisavljevic A,Polinder H,Ferreira J A.On the speed limits of permanent-magnet machines[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2010,57(1):220-227. [11]江善林.高速永磁同步电机的损耗分析与温度场计算[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2010. [12]Dong Jianning,Huang Yunkai,Jin Long,et al.Thermal optimization of a high-speed permanent magnet motor[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2014,50(2):749-752. [13]Danilevich J B,Kruchinina I Y,Antipov V N,et al.Some problems of the high-speed permanent magnet miniturbogenerators development[C]//18th International Conference on Electrical Machines,Vilamoura,2008:1-4. [14]Ede J D,Zhu Z Q,Howe D.Rotor resonances of high-speed permanent magnet brushless machines[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2002,38(6):1542-1548. [15]Gerada D,Mebarki A,Brown N L,et al.Design aspects of high-speed high-power-density laminated-rotor induction machines[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2011,58(9):4039-4047. [16]Cho H W,Ko K J,Choi J Y,et al.Rotor natural frequency in high-speed permanent-magnet synchronous motor for turbo-compressor application[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetic,2011,47(10):4258-4261. [17]Gerada D,Mebarki A,Brown N L,et al.High-speed electrical machines:technologies,trends,and developments[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2014,61(6):2946-2959. [18]Ahrens M,Bikle U,Gottkehaskamp R,et al.Electrical design of high-speed induction motors of up to 15 MW and 20 000 RPM[C]//International Conference on Power Electronics,Machines and Drives,Bath,United Kingdom,2002:381-386. [19]Pyrhonen J,Nerg J,Kurronen P,et al.High-speed,high output,solid-rotor induction motor technology for gas compression[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2010,57(1):272-280. [20]Gieras J F,Saari J.Performance calculation for a high-speed solid-rotor induction motor[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2012,59(6):2689-2700. [21]James O,Samotyj M,Ferrier R.Applications of high speed horsepower ASD controlled induction motors to gas pipeline[C]//Fifth European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications,Brighton,1993,5:430-435. [22]Saari J,Arkkio A.Losses in high speed asynchronous motors[C]//Proceedings of ICEM,1994,3:704-708. [23]Rahman M A,Chiba A,Fukao T.Super high speed electrical machines-summary[C]//IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting,Denver,CO,2004,2:272-1275. [24]Caprio M,Lelos V,Herbst J,et al.Advanced induction motor endring design features for high speed applications[C]//IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives,San Antonio,TX,2005,1:993-998. [25]Wood B M,Olsen C L,Hartzo G D,et al.Development of an 11 000 r/min 3 500 HP induction motor and adjustable speed drive for refinery service[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,1997,33(3):815-825. [26]Lahteenmaki J.Design and voltage supply of high-speed induction machines[D].Espoo,Finland,Helsinki University of Technology,2002. [27]重庆德马电机有限公司.上海鼓风机厂大功率压缩机高速电机[EB/OL].http://www.dmbp.com/news.asp?id=1777,2014-8-8. [28]Papini L,Gerada C,Gerada D,et al.High speed solid rotor induction machine:analysis and performances[C]//17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Hangzhou,2014:2759-2765. [29]Bumby J R,Spooner E,Jagiela M.Equivalent circuit analysis of solid-rotor induction machines with reference to turbocharger accelerator applications[J]//IEE Proceedings:Electric Power Applications,2006,153(1):31-39. [30]Viggiano F,Schweitzer G.Active magnetic support and design of high speed rotors for powerful electric drives[C]//International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings,1992,1:549-558. [31]Gerada D,Mebarki A,Brown N L,et al.Design,modelling and testing of a high speed induction machine drive[C]//IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition,Raleigh,NC,2012:4649-4655. [32]Popa D C,Fodorean D.Design and performances evaluation of a high speed induction motor used for the propulsion of an electric vehicle[C]//2014 International Symposium on Power Electronics,Electrical Drives,Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM),Ischia,2014:88-93. [33]重庆德马电机有限公司.重庆通用公司制冷压缩机高速电机[EB/OL].http://www.dmbp.com/news. asp?id=1772,2014-8-8. [34]Siegwart R,Larsonneur R,Traxler A.Design and performance of high speed milling spindle in digitally controlled AMB’s[C]//International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings,1990,1:197-204. [35]Soong W L,Kliman G B,Johnson R N,et al.Novel high-speed induction motor for a commercial centrifugal compressor[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2000,36(3):706-713. [36]Mekhiche M,Kirtley J L,Tolikas M,et al.High speed motor drive development for industrial applications[C]//International Conference IEMD ′99 Electric Machines and Drives,Seattle,WA,1999,1:244-248. [37]李玉超.280kW高速感应电动机的设计与分析[D].沈阳:沈阳工业大学,2015. [38]Huppunen J.High-speed solid-rotor induction machine-electromagnetic calculation and design[D].Finland,Lappeenranta:Lappeenranta University of Technology, 2004. [39]Kim Y K,Choi M C,Suh K H,et al.High-speed induction motor development for small centrifugal compressor[C]//5th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Shenyang,2001,2:891-894. [40]Ikeda M,Sakabe S,Higashi K.Experimental study of high speed induction motor varying rotor core construction[J].IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion,1990,5(1):98-103. [41]Aho T.Electromagnetic design of a solid steel rotor motor for demanding operation environments[D].Finland,Lappeenranta:Lappeenranta University of Technology, 2007. [42]Hong D K,Choi J H,Han P W,et al.Analysis of high speed induction motor for spindle made by copper die casting process[J].Internationl Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,2012,13(12):2251-2257. [43]Centner M,Hanitsch R,Schafer U.Comparison of high-speed induction motors employing cobalt-iron and silicon electrical steel[C]//18th International Conference on Electrical Machines,Vilamoura,2008:1-6. [44]江虹.高速感应电动机电磁设计方法的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2006. [45]Larsson M,Johansson M,Naslund L,et al.Design and evalution of high-speed induction machine[C]//IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference,2003,1:77-82. [46]Klma J,Vitek O.Analysis of high-speed induction motor[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Mechatronics-Mechatronika,Brno,2014:85-91. [47]Anbarasu R,Gupta R K,Sharma N D,et al.Design and experimental investigation of high speed squirrel cage induction motor[C]//Proceedings of the 1996 International Conference on Power Electronics,Drives and Energy Systems for Industrial Growth (PEDES),New Delhi,1996,2:920-926. [48]Bailey C,Saban D M,Guedes Pinto P.Design of high-speed direct-connected permanent-magnet motors and generators for the petrochemical industry[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2009,45(3):1159-1165. [49]Gonzalez D A,Saban D M.Study of the copper losses in a high-speed permanent-magnet machine with form-wound windings[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2014,61(6):3038-3045. [50]Huynh C,Hawkins L,Farahani A,et al.Design and development of a two-megawatt,high speed permanent magnet alternator for shipboard application[J].Naval Engineers Journal,2005,17(4):23-29. [51]Shelley T.Direct coupled turbines power the future[J].Eureka,1995,15(9):35-36. [52]Paulides J J H,Jewell G W,Howe D.An evaluation of alternative stator lamination materials for a high-speed,1.5 MW permanent-magnet generator[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2004,40(4):2041-2043. [53]Huynh C,Zheng L P,Acharya D.Losses in high speed permanent magnet machines used in microturbine applications[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2009,131(2):1-6. [54]Aglen O,Andersson A.Thermal analysis of a high-speed generator[C]//38th IAS Annual Meeting: Conference Record of the Industry Applications Conference,Salt Lake,United States,2003,1:547-554. [55]邱洪波.高速永磁发电机转子涡流损耗优化及对温度分布影响的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨理工大学,2014. [56]张凤阁,杜光辉,王天煜,等.1.12 MW 高速永磁电机不同冷却方案的温度场分析[J].电工技术学报,2014,29(S):66-72. Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Temperature field analysis of 1.12 MW high speed permanent magnet machine with different cooling schemes[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2014,29(S):66-72. [57]Wang K,Jin M J,Shen J X,et al.Study on rotor structure with different magnet assembly in high-speed sensorless brushless DC motors[J].IET Electric Power Applications,2010,4(4):241-248. [58]Shigematsu K,Oyama J,Higuchi T,et al.The study of eddy current in rotor and circuit coupling analysis for small size and ulta high speed motor[C]//The 4th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference,Xi’an,2004,1:275-279. [59]Zhang Xiaochen,Li Weili,Kou Baoquan,et al.Electrothermal combined optimization on notch in air-cooled high-speed permanent-magnet generator[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2015,51(1):1-10. [60]邢军强.高速永磁电机转子涡流损耗及通风散热研究[D].沈阳:沈阳工业大学,2011. [61]Zwyssig C,Duerr M,Hassler D,et al.An ultra-high speed,500 000 r/min,1 kW electrical drive system[C]//Power Conversion Conference,Nagoya,2007:1577-1583. [62]Cho H,Jang S.The influence of operating mode on rotor losses in high speed permanent magnet synchronous motor/generator for micro-gas turbine[C]//IEEE International Magnetics Conference,San Diego,CA,2006:983-986. [63]Hong D K,Woo B C,Koo D H.Rotordynamics of 120 000 r/min 15 kW ultra high speed motor[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetic,2009,45(6):2831-2834. [64]田野,孙岩桦,杨利花,等.带弹性支撑和挤压油膜阻尼器的高速电机支撑系统实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2012,32 (27):79-86. Tian Ye,Sun Yanhua,Yang Lihua,et al.Experimental studies on support systems of high speed motors with flexible squirrel-cage support and squeeze film dampers[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,32(27):79-86. [65]Xu Longya,Wang Changjiang.Implementation and experimental investigation of sensorless control schemes for PMSM in super-high variable speed operation[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd IAS Annual Meeting,St.Louis,MO,USA,1998,1:483-489. [66]鲍海静.飞轮储能用高速永磁同步电机设计及关键技术研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2014. [67]高义冬.飞轮储能用高速永磁同步电机的设计与分析[D].镇江:江苏科技大学,2014. [68]Takahashi I,Koganezawa T,Su G,et al.A super high speed PM motor drive system by a quasi-current source inverter[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,1994,30(3):683-690. [69]Riemer B,Lessmann M,Hameyer K.Rotor design of a high-speed permanent magnet synchronous machine rating 100 000 rpm at 10 kW[C]//IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE),Atlanta,GA,2010:3978-3985. [70]Noguchi T,Takata Y,Yamashita Y,et al.220 000 r/min 2 kW PM motor drive for turbocharger[J].Electrical Engineering in Japan,2007,161(3):31-40. [71]Borisavljevic A,Polinder H,Ferreira J A.Enclosure design for a high-speed permanent magnet rotor[C]//5th IET Conference on Power Electronics,Machines and Drives,Brighton,UK,2010:1-6. [72]Smith D J B,Mecrow B C,Atkinson G J,et al.Shear stress concentrations in permanent magnet rotor sleeves[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM),Rome,2010:1-6. [73]Dong Jianning,Huang Yunkai,Jin Long,et al.Development of an air-cooled 150kW high speed permanent magnet motor with gramme ring windings for turbo blowers[C]//17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Hangzhou,2014:3534-3538. [74]田拥胜,孙岩桦,虞烈.高速永磁电机电磁轴承转子系统的动力学及实验研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2012,32(9):116-123. Tian Yongsheng,Sun Yanhua,Yu Lie.Dynamical and experimental researches of active magnetic bearing rotor systems for high-speed pm machines[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,32(9):116-123. [75]Pfitser P D,Perriard Y.Very high speed slotless PM motors:analytical modelling,optimization,design and torque measurement methods[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2010,57(1):296-303. [76]Hong D K,Joo D,Woo B C,et al.Performance verification of a high speed motor-generator for a microturbine generator[J].Internationl Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,2013,14(7):1237-1244. [77]Hu Y,Wu T,Chow L,et al.Design of a 3 kW 150k RPM super high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines,Berlin,2014:2543-2548. [78]Binder A,Schneider T,Klohr M.Fixation of buried and surface-mounted magnets in high-speed permanent-magnet synchronous machines[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2006,42(4):1031-1037. [79]Luise F,Tessarolo A,Agnolet F,et al.A high-performance 640 kW 10 000 r/min halbach-array PM slotless motor with active magnetic bearings,part II:manufacturing and testing[C]//International Symposium on Power Electronics,Electrical Drives,Automation and Motion,Ischia,2014:1245-1250. [80]Luise F,Tessarolo A,Agnolet F,et al.A high-performance 640 kW 10 000 r/min halbach-array PM slotless motor with active magnetic bearings,part I:preliminary and detailed design[C]//International Symposium on Power Electronics,Electrical Drives,Automation and Motion,Ischia,2014:1237-1244. [81]南车电机公司成功研制高速永磁变频电机系统[EB/OL].新华网.http://www.hn.xinhuanet.com/2015-04/29/c_1115134170.htm,2015-4-29. [82]沈建新,郝鹤,袁承.高速永磁无刷电机转子护套周向开槽的有限元分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2012,32(36):53-60. Shen Jianxin,Hao He,Yuan Cheng.FEA study on circumferential grooves on rotor retaining sleeve of high-speed PM brushless motors[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,32(36):53-60. [83]郝鹤.高速永磁无刷电机多场综合分析及无位置传感器控制[D].杭州:浙江大学,2014. [84]Fernando W U N,Gerada C.High speed permanent magnet machine design with minimized stack-length under electromagnetic and mechanical constraints[J].International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics,2014,46(1):95-109. [85]El-Hasan T.Rotor eddy current determination using finite element analysis for high-speed permanent magnet machines[C]//IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics,Istanbul,2014:885-889. [86]陈亮亮,祝长生,王萌.碳纤维护套高速永磁电机热态转子强度[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2015,49(1):162-172. Chen Liangliang,Zhu Changsheng,Wang Meng.Strength analysis for thermal carbon-fiber retaining rotor in high-speed permanent magnet machine[J].Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science,2015,49(1):162-172. [87]Lin S,Wu T X,Zhou L,et al.Modeling and design of super high speed permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM)[C]//IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference,Dayton,OH,2008:41-44. [88]沈建新,陈利根.永磁无刷电机中平行充磁2极气隙磁场的解析计算[J].电机与控制应用,2006,33(1):7-10. Shen Jianxin,Chen Ligen.Analytical calculation of air gap field in 2-pole permanent magnet brushless motor with parallel-magnetisation[J].Machines and Control Application,2006,33(1):7-10. [89]Honda Y,Yokote S,Higaki T,et al.Using the halbach magnet array to develop an ultrahigh-speed spindle motor for machine tools[C]//Conference Record of the 1997 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, New Orleans,LA,1997,1:56-60. [90]Zwyssig C,Kolar J W,Thaler W.Design of a 100 W,500 000 rpm permanent-magnet generator for mesoscale as turbines[C]//Conference Record of the 2005 Industry Applications Conference,2005,1:253-260. [91]陈小军.高速永磁无刷直流电机磁热耦合分析与效率优化研究[D].广州:广东工业大学,2013. [92]Nagorny A S,Dravid N V,Jansen R H,et al.Design aspects of a high speed permanent magnet synchronous motor/generator for flywheel applications[C]//IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives,San Antonio,TX,2005:635-641. [93]次元平.高速电主轴永磁电机结构的研究[D].沈阳:沈阳工业大学,2015. [94]Hsu J S,Burress A,Lee S T,et al.16 000 rpm Interior permanent magnet reluctance machine with brushless field excitation[C]//IEEE Industry Application Society Annual Meeting,Edmonton,Alta,2008:l-6. [95]Kim S I,Kim Y K,Lee G H,et al.A novel rotor configuration and experimental verification of interior PM synchronous motor for high-speed applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2012,48(2):843-846. [96]Luca P,Tsarafidy R,David G,et al.A high-speed permanent-magnet machine for fault-tolerant drivetrains[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2014,61(6):3071-3080. [97]Jang S M,Cho H W,Lee S H,et al.Analysis of cogging torque for high speed motor/generator[C]//Sixth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Beijing,China,2003,1:205-207. [98]薛劭申.高速永磁无刷电机设计与控制系统研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2011. [99]Boubaker N,Matt D,Enrici P,et al.Study of banding techniques with a view to reduce the rotor eddy-current loss in a high-speed actuator dedicated to an aeronautical application[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines,Berlin,2014:2583-2587. [100]Hwang C C,Hung S S,Liu C T,et al.Optimal design of a high speed SPM motor for machine tool applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2014,50(1):2276092. [101]Xu Jianchun,Liu Chuang.Research on high-speed permanent magnet generator for a miniature turbojet[C]//Proceedings of 6th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications,Beijing,2011:2783-2786. [102]Schneider T,Petersen J,Binder A.Influence of pole pair combinations on high-speed bearingless permanent magnet motor performance[C]//4th IET Conference on Power Electronics,Machines and Drives,York,2008:707-711. [103]Upadhyay P,Mohan N.Design and FE analysis of surface mounted permanent magnet motor/generator for high-speed modular flywheel energy storage systems[C]//IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition,San Jose,CA,2009:3630-3633. [104]Cho H W,Jang S M,Choi S K.A design approach to reduce rotor losses in high-speed permanent magnet machine for turbo-compressor[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2006,42(10):3521-3523. [105]Zhu Z Q,Ng K,Howe D.Design and analysis of high-speed brushless permanent magnet motors[C]//Eighth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives,Cambridge,UK,1997:381-385. [106]余莉,胡虔生,崔杨,等.高速永磁无刷直流电动机铁耗的分析计算及实验[J].微特电机,2008(3):11-13.Yu Li,Hu Qiansheng,Cui Yang,et al.Analysis and calculation of the iron losses of high speed permanet motor[J].Micro Motor,2008(3):11-13. [107]Richter E,Ferreira C.Performance evaluation of a 250 kW switched reluctance starter generator[C]//Conference Record of the 1995 IEEE Industry Applications Conference,Orlando,FL,1997,1:434-440. [108]Ferreira C A,Jones S R,Heglund W S,et al.Detailed design of a 30 kW switched reluctance S/G system for a gas turbine application[J]//IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,1995,31(3):553-561. [109]Bartolo J B,Geradal C.The electromagnetic design of a high speed 45 kW switched reluctance machine having a novel rotor geometry for aerospace application[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS),Berlin,2014:2513-2519. [110]Ikaheimo J,Kolehmainen J,Kansakangas T,et al.Synchronous high-speed reluctance machine with novel rotor construction[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2014,61(6):2969-2975. [111]Morel L,Fayard H,Fos R V,et al.Study of ultra high speed switched reluctance motor drive[C]//Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference,Rome,2000,1:87-92. [112]周强,刘闯,朱学忠,等.超高速开关磁阻电动机设计[J].中国电机工程学报,2009,29(9):87-92.Zhou Qiang,Liu Chuang,Zhu Xuezhong,et al.Design of super high speed switched reluctance motor[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2009,29(9):87-92. [113]裴丽娜.超高速开关磁阻电机电磁分析与设计[D].北京:北京交通大学,2010. [114]金坚.6/4结构高速开关磁阻电机的研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2009. [115]周强.高速开关磁阻电机的关键技术研究与实践[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2008. [116]Brauer H J,De Doncker R W.Thermal modeling of a high speed SRM for vacuum cleaners[J].European Power Electronics and Drives Journal,2012,22(2):22-29. [117]范冬,杨艳,邓智泉,等.无轴承高速开关磁阻电机设计中的关键问题[J].电机与控制学报,2006,10(6):547-552. Fan Dong,Yang Yan,Deng Zhiquan,et al.The key technology on designing a high-speed bearingless switched reluctance motor[J].Electric Machines and Control,2006,10(6):547-552. [118]孙健.6/2结构高速开关磁阻电机的研究与实现[D].南京,南京航空航天大学,2007. [119]Kim J,Krishnan R.High efficiency single-pulse controlled switched reluctance motor drive for high speed (48 krpm) application:analysis,design,and experimental verification[C]//IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting,Edmonton,Alta,2008,1:1-8. [120]Kunz J,Cheng S,Duan Y,et al.Design of a 750 000 r/min switched reluctance motor for micro machining[C]//IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE),Atlanta,GA,2010:3986-3992. [121]Lee D H,Pham T H,Ahn J W.Design and operation characteristics of four-two pole high speed SRM for torque ripple reduction[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial,2013,60(9):3637-3643. [122]朱宏基.电动工具用高速开关磁阻电机的设计与实现[D].株洲:湖南工业大学,2014. [123]张珍.小功率高速开关磁阻电机驱动系统的设计与应用[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012. [124]Howe D,Mason P,Mellor P H,et al.Flywheel peak power buffer for electric hybrid vehicles[C]//International Conference IEMD ′99 Electric Machines and Drives,Seattle,WA,1999:508-510. [125]李杏.飞轮储能用外转子高速永磁同步电机研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2013. [126]Kohari Z.Test results of a compact superconducting flywheel energy storage with disk-type,permanent magnet motor/generator unit[J].IEEE Transactions on Application Superconductivity,2009,3(19):2095-2098. [127]Nguyen T D,Tseng K J,Zhang S,et al.A flywheel cell for energy storage system[C]//IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies,Singapore,2008:214-219. [128]Seok M J,Dae J Y,Kyoung J K,et al.Design and experimental evaluation of synchronous machine without iron loss using double-sided halbach magnetized PM rotor in high power FESS[J].IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2008,44(11):4337-4340. [129]刘光伟,赵新刚,张凤阁,等.高速永磁爪极电机铁耗与空气摩擦损耗计算[J].电工技术学报,2015,30(2):148-154. Liu Guangwei,Zhao Xingang,Zhang Fengge,et al.Iron loss and air friction loss for high speed permanent magnet claw pole machines[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2015,30(2):148-154. [130]徐衍亮,赵建辉,房建成.高速储能飞轮用无铁心永磁无刷直流电动机的分析与设计[J].电工技术学报,2004,19(12):24-28. Xu Yanliang,Zhao Jianhui,Fang Jiancheng.Analysis and design of coreless permanent magnet brushless DC machine in high-speed energy storage flywheel application[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2004,19(12):24-28. [131]黄允凯,胡虔生,朱建国.顾及旋转铁耗的高速爪极电机三维磁热耦合分析[J].电工技术学报,2010,25(5):54-60. Huang Yunkai,Hu Qiansheng,Zhu Jianguo.Magneto-thermal analysis of a high-speed claw pole motor considering rotational core loss[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2010,25(5):54-60. [132]Ignat M,Haraguta I C.The asyncronous high speed motor for an axial compressor application[C]//International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics and 2011 Electromotion Joint Conference ,Istanbul,2013:211-215. [133]Zhang C,Tseng K J,Nguyen T D,et al.Design and loss analysis of a high speed flywheel energy storage system based on axial-flux flywheel-rotor electric machines[C]//9th International Power and Energy Conference,Singapore,2010:886-891. [134]Fodorean D,Popa D C,Minciunescu P,et al.Study of a high-speed motorization for electric vehicle based on PMSM,IM and VRSM[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM),Berlin,2014:2577-2582. [135]Bartolo J B,Zhang H,Gerada D,et al.High speed electrical generators,application,materials and design[C]//IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design Control and Diagnosis,Paris,2013:47-59. [136]Lateb R,Enon J,Durantay L.High speed,high power electrical induction motor technologies for integrated compressors[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Tokyo,2009:1-5. [137]Zhou Hao,Wang Fengxiang.Comparative study on high speed induction machine with different rotor structures[C]//International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Seoul,2007:1009-1012. [138]周凤争.高速永磁无刷直流电机转子涡流损耗的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2008. [139]Yon J M,Mellor P H,Wrobel R,et al.Analysis of semipermeable containment sleeve technology for high-speed permanent magnet machines[J].IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion,2012,27(3):646-653. [140]张凤阁,杜光辉,王天煜,等.基于多物理场的高速永磁电机转子护套研究[J].电机与控制学报,2014,18(6):15-21. Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Rotor containment sleeve study of high-speed PM machine based on multi-physics fields[J].Electric Machines and Control,2014,18(6):15-21. [141]Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Rotor retaining sleeve design of a 1.12 MW high-speed PM machine[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2015,51(5):3675-2685. [142]张凤阁,杜光辉,王天煜,等.高速永磁电机转子不同保护措施的强度分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2013,33(增):195-202. Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Rotor strength analysis of high-speed permanent magnet under different protection measures[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2013,33(S):195-202. [143]王天煜.高速永磁电机转子综合设计方法及动力学特性的研究[D].沈阳:沈阳工业大学,2010. [144]李艳明,郭宏,谢清明,等.充磁导致的超高速永磁同步电机不平衡磁拉力[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2013,39(6):771-775. Li Yanming,Guo Hong,Xie Qingming,et al.Unbalanced magnetic pull due to the magnetizing in super high speed permanent magnet synchronous machine[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2013,39(6):771-775. [145]张治平,钟瑞兴,谢蓉,等.空调器及其制冷机的电机的冷却结构[P].201110282627.7,2011-09-21. [146]Arkkio A,Jokinen T,Lantto E.Induction and permanent-magnet synchronous machines for high-speed applications[C]//8th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems,Nanjing,2005:871-876. [147]张凤阁,杜光辉,王天煜,等.1.12 MW高速永磁电机多物理场综合设计[J].电工技术学报,2015,30(12):171-180. Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Integrated design of 1.12 MW high speed PM machine based on multi-physics fields[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2015,30(12):171-180. [148]Zhang Fengge,Du Guanghui,Wang Tianyu,et al.Electromagnetic design and loss calculations of a 1.12 MW high-speed permanent-magnet motor for compressor applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion,2016,31(1):132-140. 张凤阁男,1963年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为特种电机及其控制和新能源技术。 E-mail:zhangfg@sut.edu.cn 杜光辉男,1987年生,博士研究生,研究方向为高速电机设计。 E-mail:duguanghui1104@163.com(通信作者) Review on Development and Design of High Speed Machines ZhangFengge1DuGuanghui1WangTianyu2LiuGuangwei1 (1.School of Electrical EngineeringShenyang University of TechnologyShenyang110870China 2.School of Mechanical EngineeringShenyang Institute of EngineeringShenyang110136China) AbstractThis paper analyzes the development state of high speed motors, and sums up the limit affordable values of different high speed machines.The structures and design feathers of high speed machines are analyzed in detail, including stator design, different rotor structure designs, rotor dynamics analysis, bearings selection, as well as cooling system design.At last, the problems faced by high speed machines development are summarized and development trends are prospected. Keywords:High speed machine, rotor strength, cooling system, high speed bearing, machine design 作者简介 中图分类号:TM355 收稿日期2015-09-10改稿日期2015-11-03 教育部长江学者和创新团队发展计划(IRT1072)、国家自然科学基金(51207094)和辽宁省特聘教授资助项目。