热休克蛋白72在低氧环境下大鼠肾脏间质纤维化中的表达及意义*
王妍君,杨佳佳
(1.青海大学附属医院肾病内科;2.青海大学医学院)
热休克蛋白72在低氧环境下大鼠肾脏间质纤维化中的表达及意义*
王妍君1,杨佳佳2
(1.青海大学附属医院肾病内科;2.青海大学医学院)
目的 探讨低氧环境下大鼠肾脏间质纤维化中热休克蛋白72(heat shock protein,HSP72)的表达及意义。方法 将雄性SD大鼠随机分为四组:常氧组(4只)、低氧组、低氧+溶剂对照组、低氧+槲皮素干预组(各12只)。于低压氧舱建立低氧动物模型,分别于第3、7、14 d处死各组大鼠。取肾脏组织,应用免疫印迹法(western blot)检测HSP72表达;采用免疫组化染色法比较各组HSP72蛋白在肾脏小管间质表达水平,了解各组肾小管间质病变程度与HSP72的关系。结果 与常氧组比较,低氧环境下各组HSP72在大鼠肾小管间质中表达增加,并且随着缺氧时间延长而增加,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.001)。给予槲皮素干预后,HSP72表达抑制,与低氧组及低氧+溶剂对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。常氧组与各组比较,肾小管间质病变程度最轻(肾小管形态基本正常、间质无水肿)。在低氧环境下的各组比较中,槲皮素干预组的肾小管间质病变程度为轻,低氧组与低氧+溶剂对照组病变均较重。结论 低氧环境可引起肾小管间质中HSP72表达增加,并且随着缺氧时间延长而增加。低氧组、低氧+溶剂对照组中HSP72呈现高表达,与人工(槲皮素)抑制HSP72比较,肾小管间质病变程度反而更重。提示,虽然HSP72升高是保护性应激反应,但并不能充分缓解缺氧引起的脏器损伤,其原因可能为HSP72保护作用时效较短或具有一定的滞后性。
低氧 肾脏 热休克蛋白72
正常肾脏组织由于其结构和功能特点,对氧的需求量很大,耐受缺氧的能力较低,容易出现缺氧性肾损害。有实验证明,大鼠在海拔5600 m缺氧6 h左右就能够导致微血管内皮细胞、肾小管间质的损伤,导致肾脏炎症反应和纤维化的发生[1]。而肾小管间质低氧又是促进肾脏疾病进展和间质纤维化的重要原因[2-4]。因此低氧条件下机体的各种敏感性指标变化成为近些年来国内外研究的热点。热休克蛋白(heat shockproteins,HSP)是一组结构上高度保守的多肽,参与机体正常生长、发育和分化。当机体受到缺氧刺激时,HSP迅速产生而启动内源性保护机制,因此它是细胞应激反应最主要的效应蛋白。其中HSP72是最保守且最易诱导表达的HSP家族成员之一,在包括肾脏的多个组织和器官中均有少量表达,而在热应激、低氧、缺血再灌注等多种应激刺激下表达明显增加,能促进受损细胞修复,具有抗炎、抗细胞凋亡作用[5,6]。以往国内外关于HSP72的研究主要集中在短时、急性损伤等应激反应中的表达变化,而对于低氧环境下HSP72表达变化与肾小管间质病变关系的研究较少。因此本研究通过低氧大鼠模型观察HSP72在肾小管间质中表达的变化,来探讨低氧状况下HSP72在肾小管间质病变的作用及意义。
1 对象与方法
1.1 实验对象和分组情况
3月龄健康雄性SD大鼠40只,体重(280~320)g,在青海大学医学院动物房中适应性喂养1 w。随机分为四组:常氧组(4只)、低氧组、低氧+溶剂对照组、低氧+槲皮素干预组(各12只)。常氧组于常规动物房饲养。余各组置低压氧舱(模拟海拔5000m低氧环境,氧浓度11.3%),于第3、7、14 d处死各组大鼠,每次4只。取肾脏组织,应用免疫印迹法(western blot)检测HSP72表达。然后采用免疫组化染色法观察比较四组HSP72蛋白在肾脏小管间质表达,同时通过苏木素复染观察比较四组肾小管受损、肾间质纤维化程度。
1.2 主要试剂及仪器
小鼠抗HSP72单克隆抗体(abcom,美国)、兔抗GAPDH(abcom,美国)、辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记的山羊抗小鼠IgG(博士德生物)、辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)标记的山羊抗兔IgG(博士德生物)、PI细胞裂解液(Keygen)、槲皮素(Sigma,美国)、蛋白标准分子量marker(Thermo,美国)、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Pierce公司,美国)、ECL发光试剂盒(Pierce公司,美国)、PVDF膜(Millipore,美国)、5×上样缓冲液(康为世纪,北京)、1×PBS(Solarbio,北京)、20×TBS(Solarbio,北京)、Tris-Hcl PH6.8/PH8.8(Solarbio,北京)、30%丙烯酰胺(Solarbio,北京)、Ttween 20(Biotopped,北京)、TEMED(Biotopped,北京)、10×SDS电泳缓冲液(Beyotime,江苏)。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 标本采集及处理
低氧+溶剂对照组:大鼠腹腔注入2 mL的0.1 M磷酸盐缓冲溶液(PBS)后建立低氧模型。
低氧+槲皮素干预组:大鼠腹腔注入槲皮素(按50mg/kg剂量溶于2mL的0.1M PBS中)后建立低氧模型。
肾脏标本:大鼠用10%水合氯醛(0.3mL/100mg)行腹腔注射麻醉后,沿腹正中线分层剪开大鼠腹壁,取肾脏髓质,用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定。
1.3.2 HSP72表达检测
制质量分数为12%的SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶,80 V电压电泳1 h,然后增加电压至130 V,电泳完成后,取出凝胶,用湿转法将蛋白质转到PVDF膜上(0.45nm),用TBST洗膜后,放入用TBST稀释的质量分数为5%的脱脂奶粉中,摇床室温孵育2 h,封闭非特异性蛋白结合位点。一抗孵育:将PVDF膜置1抗中4 ℃过夜孵育(HSP72 1:1000,GAPDH 1:5000);用TBST充分洗膜5次,TBS洗膜1次,10 min/次;二抗孵育:分别加入HRP标记的山羊抗小鼠、HRP标记的山羊抗兔的二抗孵育(1:1000),常温孵育1.5 h;用TBST充分洗膜9次,TBS洗膜1次,6 min/次;洗膜后用ECL发光,上机曝光。
1.3.3 免疫组化实验
选取HSP72表达量最高的时间点上的肾脏组织,按照免疫组化试剂盒说明具体操作,观察比较各组肾小管间质中HSP72的表达。结果判断标准:胞质染色呈棕黄色、深褐色颗粒为阳性反应。用Image-J图像分析软件分析HSP72蛋白的表达状况。
1.3.4 肾小管、间质病变程度比较
用苏木素复染切片观察肾小管间质结构,肾小管间质损伤程度依据肾小管上皮细胞刷状缘的脱落、间质炎细胞的浸润、间质纤维化程度判断[7]。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS22.0统计软件进行分析, 计量资料用均数±标准差表示,各组间比较采用方差分析,组间两两比较采用q检验。检验水准α=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 HSP72蛋白表达(图1,表1)

Figure 1 HSP72 expression in each group after giving different kinds of intervention
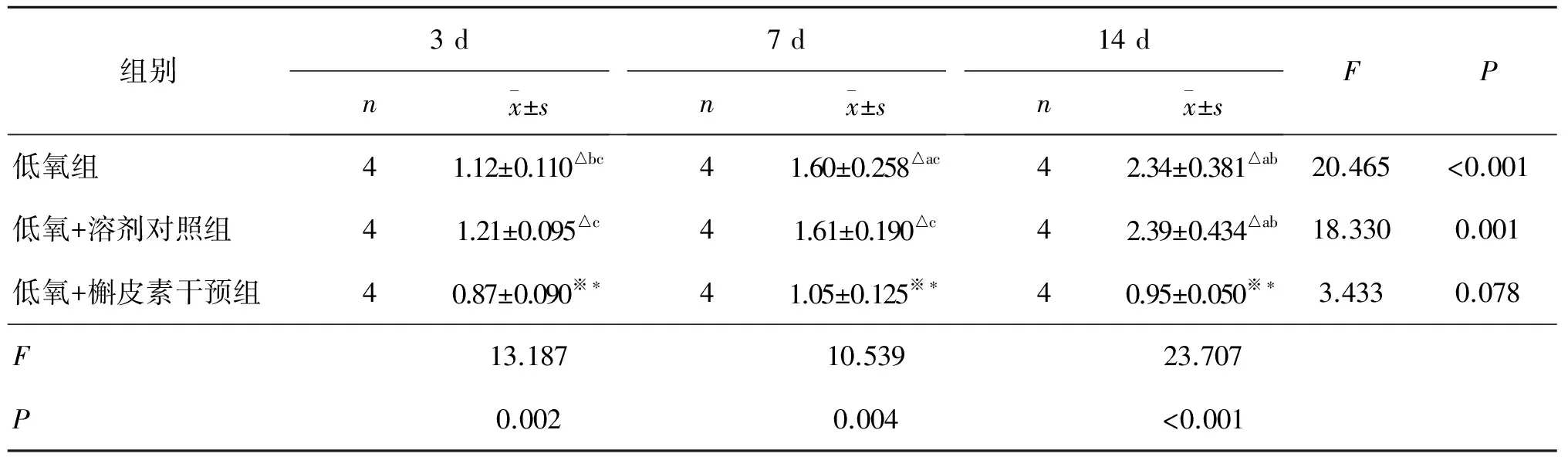
Table 1 HSP72 expression after hypoxia and hypoxia+Quercetin intervention
※:与低氧组比较,P<0.05;*:与低氧+溶剂组比较,P<0.05;△:与低氧+槲皮素比较,P<0.05;a:与处理3 d组比较,P<0.05;b:与处理7 d组比较,P<0.05;c:与处理14 d组比较,P<0.05.
(1)与常氧组(0.36±0.096)比较,各时间点上低氧组、低氧+溶剂对照组、低氧+槲皮素干预组的HSP72表达值均明显高于常氧组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。(2)低氧环境下各组随缺氧时间的延长HSP72表达值有逐渐增多趋势,低氧组及低氧+溶剂对照组中HSP72表达值均在14 d时达高峰(2.34±0.38,2.39±0.43);两两比较结果显示,低氧+溶剂对照组与低氧组的HSP72表达值差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而低氧+槲皮素干预组的HSP72表达值明显受到抑制,与低氧+溶剂对照组和低氧组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.2 免疫组化实验(表2,图2)

Table 2 HSP72 expressions in pathological section on 14th day
*:与常氧组比较,P<0.05;△:与低氧组14 d比较,P<0.05;※:与低氧+溶剂对照组14 d比较,P<0.05.
根据WB结果选取HSP72表达量最高的时间点(14d)上的各组肾脏组织比较。(1)常氧组HSP72在肾脏组织中表达最少。(2)低氧组、低氧+溶剂对照组HSP72在肾脏组织中表达最多,但两组间无显著性差异。(3)低氧+槲皮素干预组中的HSP72在肾脏组织中表达与其他3组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
Figure 2 Pathological section of each group on 14 days
(1)与低氧环境下其余各组比较,常氧组肾小管间质病变程度最轻:肾小管上皮细胞刷状缘无明显脱落,无炎性细胞浸润。(2)低氧组与低氧+溶剂对照组之间病变程度无明显差别,但与低氧+槲皮素干预组比较,上述两组肾小管间质病变程度较重:肾小管上皮细胞脱落明显,细胞核浓染,排列紊乱。
3 讨论
HSP72是一种高度保守的内源性细胞保护性蛋白[8,9],在应激时发挥细胞保护作用。机制可能包括:(1)提高细胞对应激原的耐受性[10];(2)帮助蛋白正确折叠等[11];(3)减轻过氧化及炎症反应[12-14];(4)抗细胞凋亡作用[15,16]。已有研究表明肾脏缺血后HSP72表达会明显增高[17]。
本研究的大鼠低氧模型实验显示,HSP72在常氧组几乎很少表达,但在低氧环境下,肾脏间质中HSP72表达量增加,并且随着缺氧时间延长而增加,与常氧组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。说明低氧也是诱导肾脏间质中HSP72表达增加的重要原因,其表达量与缺氧时间呈正相关。
HSP72在缺氧和/或缺血再灌注中的保护作用已有大量的研究肯定。多项研究表明,预先诱导HSP72高表达,在心、脑、肝、肾等器官的缺血/再灌注损伤中发挥出细胞保护作用[18-22]。但是HSP72表达与肾小管间质损伤的相关研究国内外报道较少。参考相关文献,因槲皮素具有抑制HSP72转录与翻译的特点[23-25],因此本研究通过槲皮素干预HSP72表达模型发现,较长时间(2w)的低氧环境下通过给予槲皮素干预HSP72表达后,肾小管上皮细胞刷状缘脱落较轻、肾间质无明显水肿,显示肾间质纤维化程度未进一步加重(肾小管上皮细胞脱落导致肾小管萎缩是肾间质纤维化进展的一个标志[26])。相反,低氧组和低氧+溶剂对照组中HSP72呈现高表达,肾小管间质病变程度却更重。这一结果提示,HSP72可能并不能充分缓解缺氧引起的病变,其保护作用可能时效较短、存在功能老化现象。与Todryk SM及石丽研究结果一致[27,28]。此外这一结果与一些研究中发现HSP72过度表达有促进细胞凋亡作用[29,30],以及某研究中发现[31]HSP72可以促进动脉粥样硬化的发生,是否均提示HSP72在组织细胞中的高表达有可能为双向作用,有待进一步研究阐明。
[1]Manotham K,Tanaka T,Matsumoto M,et al.Transdifferentiation of cultured tubular cells induced by hypoxia[J].Kidney Int,2004,65(3):871-80.
[2]陈晓农,陈楠.肾小管间质病变与慢性肾脏疾病进展关系的研究[J].上海医学,2001,24(2):75-7.
[3]Bascands JL,Schanstra JP.Obstructive nephropathy:insights from genetically engineered animals[J].Kidney Int,2005,68(3):925-37.
[4]Rodriguez-Iturbe B,Johnson RJ.Tubulointerstitial damage and progression of renal failure[J].Kidney Int Suppl,2005,99:S82-6.
[5]Mazzali M,Jefferson JA,Ni Z,et al.Microvascular and tubulointerstitial injury associated with chronic hypoxia-induced hypertension[J].Kidney Int,2003,63(6):2088-93.
[6]Dai CL,Xia ZL,Kume M,et a1.Heat shock protein 72 normothermic ischemia,and the impact of congested portal blood reperfusion on rat liver[J].World J Gastroenterol,2001,7(3):415-18.
[7]邹万忠主编.肾活检病理学[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2009:51-4.
[8]Samali A,Orrenius S.Heat shock proteins:regulations for stress response and apoptosis[J].Cell Stress Chaperons,1998,3(4):228-36.
[9]Macario AJ,Conway de Macario E.Sick chaperones,cellular stress,and disease[J].N Engl J Med,2005,353(14):1489-501.
[10]Caccam o AE,Desenzani S,Bettuzzi S,et al.Nuclear clusterin ccumulation during heat shock response:implications for cell survival and thermo-tolerance induction in immortalized and prostate cancer cells[J].J Cell Physiol,2006,207(1):208-19.
[11]Hartl FU,Hayer-Hartl M.Molecular chaperones in the cytosol:from nascent chain to folded protein[J].Science,2002,295(5561):1852-8.
[12]Menezes JM,Hierholzer C,Harbrecht BG,et a1.The modulation of hepatic injury and heat shock expression by inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase after hemorrhagic shock[J].Shock,2002,17(1):13-8.
[13]Singleton KD,Wischmeyer PE. Effects of HSP70.1/3 gene knockout on acute respiratory distress syndrome and the inflammatory response following sepsis[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2006,290(5):L956-61.
[14]Nakada J,Matsura T,Ishibe Y,et al.Oral administration of geranylgeranylacetone improves survival rate in a rat endotoxin shock model:administration timing and heat shock protein 70 induction[J].Shock,2005,24(5):482-7.
[15]Sreedhar AS,Csermely P.Heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis:New strategies in tumor therapy:a comprehensive review[J].Pharmacol Ther,2004,101(3): 227-57.
[16]Didelot C,Schmitt E,Garrido C,et a1.Heat shock proteins:endogenous modulators of apoptotic cell death[J].Handb Exp Pharmacol,2006,172:171-98.
[17]Vicencio A,Bidmon B,Ryu J,et al.Developmental expression of HSP-72 and ischemic tolerance of the immature kidney[J].Pediatr Nephrol,2003,18(2):85-91.
[18]Suzuki K,Murtuza B,Sammut IA,et a1.Heat shock protein 72 enhances manganese superoxide dismutase activity during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury,associated with mitochondrial protection and apoptosis reduction[J].Circulation,2002 Sep 24,106(12 Suppl 1):1270-6.
[19]Uchida S,Fujiki M,Kobayashi H,et a1.Geranylgeranylacetone,a noninvasive heat shock protein inducer,induces protein kinase C and leads to neuroprotection against cerebral infarction in rats[J].Neurosci Lett,2006,396(3):220-4.
[20]Yamagami K,Yamamoto Y,Yamaoka Y,et a1.Effects of geranylgeranylacetone administration before heat shock preconditioning for conferring tolerance against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat livers[J].J Lab Clin Med,2000,135(6):465-75.
[21]Basile DP,Donohoe D,Van Why SK,et a1.Resistance to ischemic acute renal failure in the Brown Norway rat:a new model to study cytoprotection[J].Kidney Int,2004,65(6):2201-11.
[22]Park KM,Kramers C,Bonventre JV,et al.Prevention of kidney ischemia/reperfusion-induced functional injury,MAPK and MAPK kinase activation and inflammation by remote transient ureteral obstruction[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(3):2040-9.
[23]Nakanoma T,Ueno M,Iida M,et al.Effects of quercetin on the heat-induced cytotoxicity of prostate cancer cells[J].Int J Urol,2001,8(11):623-30.
[24]Nagai N,Nakai A,Nagata K.Quercetin suppresses heat shock response by down regulation of HSF1[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1995,208(3):1099-105.
[25]Fujita M,Nagai M,Takahara J,et al.Synegistic cytotoxic effect of querecetin and heat treatment in a lymphoid cell line(OZ)with low HSP70 expression[J].Leuk Res,1997,21(2):139-45.
[26]Yang J,Liu Y.Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis[J].Am J Pathol,2001,159(4):1465-75.
[27]Todryk SM,Gough MJ,Pockley AG.Facets of heat shock protein 70 show immunotherapeutic potential[J].Immunology,2003,110(1):1-9.
[28]石丽,罗朋立.急性低氧环境下热休克蛋白72在大鼠肾脏中的表达及意义[J].青海医学院学报,2014,35(1):36-40.
[29]Quindry JC,Hamilton KL,French JP,et a1.Exercise-induced HSP-72 elevation and cardioprotection against infarct and apoptosis[J].J Appl Physiol,2007,103(3):1056-62.
[30]Marsh SA,Pat BK,Gobe GC,et a1.Evidence for a non-antioxidant,dose-dependent role of alpha-lipoic acid in caspase-3 and ERK2 activation in endothelial cells[J].Apoptosis,2005,10(3):657-65.
[31]刘兴晖,祝成亮,宋惠,等.热休克蛋白72的克隆表达及其对人脐静脉内皮细ECV304凋亡的影响[J].郧阳医学院学报,2009,28 (3):222-5.
HSP72 protein Expression and the significance in rats′ renal interstitial fibrosis under hypoxic environment*
Wang Yanjun1,Yang Jiajia2
(1.Renal Department of Qinghai University Affiliated Hospital;2.Qinghai University Medical College)
Objective To explore the heat shock protein 72(HSP72)expression and the significance in rats′ renal interstitial fibrosis under hypoxia environment.Methods 40 male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups:4,12,12 and 12 rats,respectively,were included in the normoxia group,hypoxia group,hypoxia+solvent control group,hypoxia+Quercetin intervened group.In the hypobaric chamber,Rats were killed at third,7th,14th day,respectively.Renal tissues were removed and HSP72 expression were detected by Western blot.By using Immunohistochemical staining method,the expressions of HSP72 protein in the renal tubular interstitial in the four groups were compared,the relationship between the tubulointerstitial lesions and the level of HSP72 were understood.Results Compared with the normoxia group,each group under hypoxia increased expression of HSP72 in rats′ renal tubular interstitial,with a consistent increasing over the prolonged time of hypoxia.The difference was statistically significant(P<0.001).After Quercetin intervened,The expression of HSP72 was inhibited and comparing with the hypoxia group and the hypoxia+solvent control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Renal tubulointerstitial lesion of the normoxia group was the mildest when compared with other groups(tubular morphology was normal and there was no edema).Under the hypoxia environment,the lesion of the hypoxia+quercetin intervened group was the milder.The lesion of the hypoxia group and the hypoxia+solvent control group were more severe.Conclusions Hypoxia can increase the expression of HSP72 in tubulointerstitial,which have a consistent increasing as the hypoxia time is prolonged.Hypoxia group,hypoxia+solvent control group show high expression of HSP72,and the tubulointerstitial lesion are more severe compared with the hypoxia+quercetin intervened group.It is suggested that although the elevation of HSP72 expression is a protective stress response,but it cannot adequately alleviate the organ damage caused by hypoxia,possibly the protective effect is short-lived or have a certain lag.
Hypoxia Kidney Heat shock protein 72
*:青海大学中青年科研基金项目(2013-QYY-9) 王妍君(1980~),女,汉族,江苏籍,主治医师
R364.4
A
10.13452/j.cnki.jqmc.2016.02.003
2016-02-03

