应力梯度下晶内微裂纹演化的有限元模拟
程 强, 黄佩珍
(南京航空航天大学 机械结构力学及控制国家重点实验室,南京 210016)
应力梯度下晶内微裂纹演化的有限元模拟
程 强, 黄佩珍
(南京航空航天大学 机械结构力学及控制国家重点实验室,南京 210016)
基于表面扩散和蒸发—凝结机制的经典理论,对应力梯度下金属材料内部晶内微裂纹演化进行了有限元模拟。数值分析结果表明:在应力梯度下,椭圆形晶内微裂纹演化存在临界应力梯度、临界形态比以及临界线宽。当应力梯度和形态比均小于临界值或线宽大于临界值时,微裂纹以稳定的形态向高应变能密度区移动,不发生分节现象;反之,微裂纹在移动的同时分节成左右两个裂腔,且应力梯度和形态比的增大和线宽的减小能加速微裂纹分节。
表面扩散; 应力梯度; 晶内微裂纹; 有限元模拟; 微裂纹分节
1 引 言
在内连导线的制造和使用过程中会不可避免的出现裂纹性缺陷。当电流通过内连导线时,驱动原子沿电子流方向迁移。物质原子在微裂纹表面的迁移导致微裂纹的变形和漂移;而当物质原子从内连导线负极流出,流入导线正极会在正极产生压应力,而在负极产生拉应力,因而沿导线产生一个线性应力梯度。该应力梯度会驱动原子在微裂纹表面迁移,改变微裂纹的形状和位置,严重影响内连导线的可靠性[1,2]。因此研究在应力梯度下微裂纹的规律具有重要的理论意义和工程应用价值[3-5]。
到目前为止,已有应力梯度和电势梯度驱动孔洞迁移速度的解析解[6-8]。但以往的工作侧重于孔洞的漂移速度,至今未见文献详细报道应力梯度下微裂纹的演化规律。
本文应用有限单元法数值模拟应力梯度下晶内微裂纹的演化,且采用如图1所示的模型。
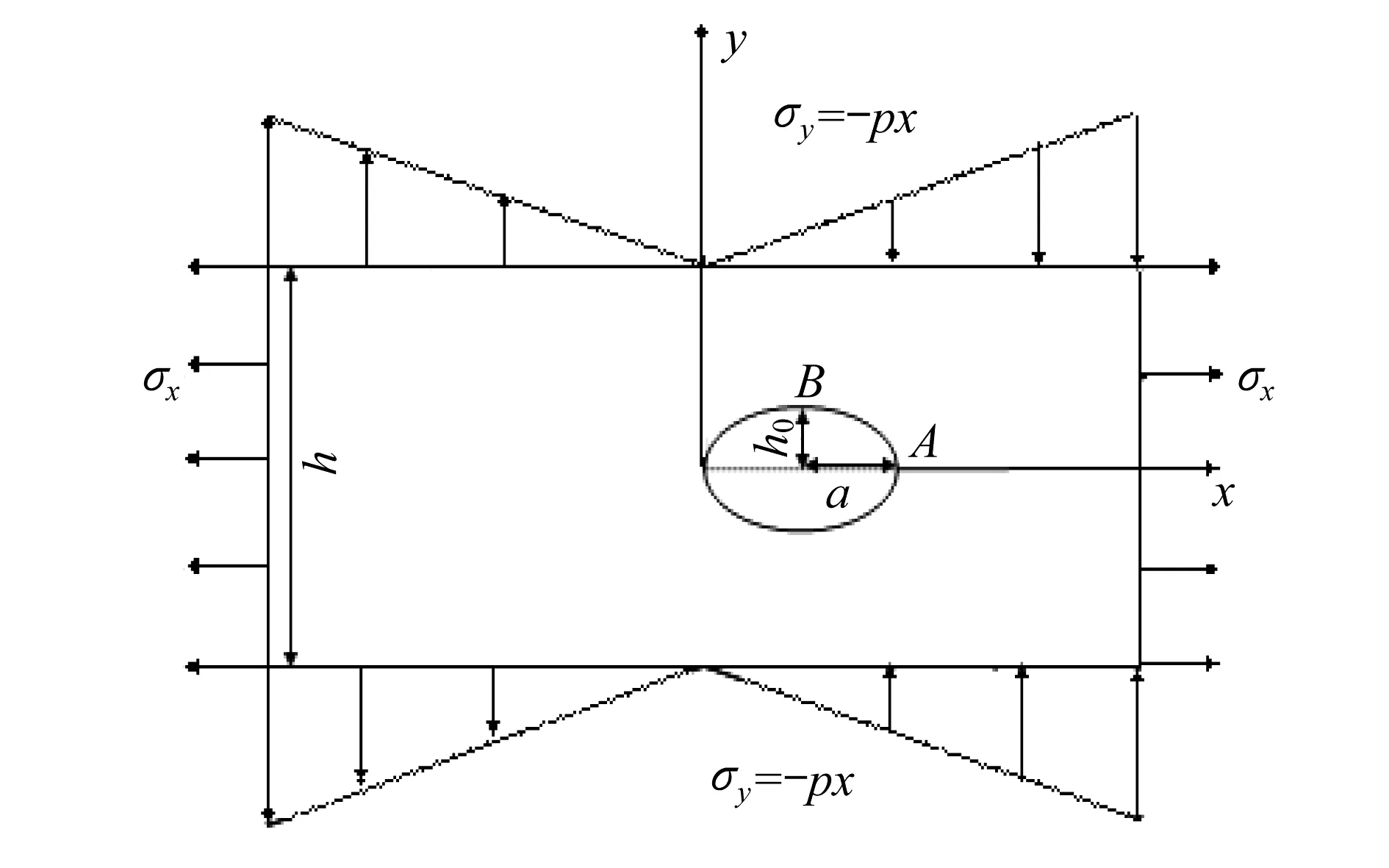
图1 应力梯度下晶内微裂纹模型Fig.1 A model of an intragranular microcrack under the stress gradient field
图1中,a与h0分别表示微裂纹在x、y轴方向上的半轴长,h为内连导线的宽度,x,y为微裂纹在水平方向和竖直放置的位移,p为应力在竖直方向的梯度,σx,σy分别为水平方向和竖直方向的应力。
假设微裂纹所在的弹性体相对微裂纹为无限大,且第三维尺寸认为无限大,则可以视为平面应变问题,且采用形态比β=a/h0表示微裂纹的形状。
2 基本理论
2.1 表面扩散
表面扩散的动力学定律:

(1)
式中J为原子沿表面扩散的流量,M为表面原子迁移率,F为驱动力。
表面法向速度vns和表面法向虚位移δrns由物质守恒定律有:
(2)
(3)
其中,δI为表面物质虚位移。
2.2 蒸发—凝结
晶粒表面每一点动力学定律为
(4)
其中,vnv为表面法向速度,p为驱动力,m为蒸发—凝结过程的界面迁移率。
2.3 包含蒸发—凝结和表面扩散的弱解描述
当两种机制共同作用时,表面法向速度vn和表面法向虚位移δrn分别为
(5)
(6)
根据广义虚位移原理,有
(7)
其中,S为微裂纹表面积,δG为系统自由能增量,将式(1)-(6)代入式(7),可得弱解描述:
(8)
2.4 有限元方法

(9)
(10)
其中,xi,yi,Ii,Ji,i=1,2,分别为第i个单元格的水平位移、竖直位移、表面等顶虚位移以及原子沿表面扩散的流量,Im和Jm为中间节点的物质虚位移和相应的流量。
对式(8)积分,可得有限元控制方程:
(11)
式中,He为方度矩阵,fe为作用在物体上的载合向量。
3 数值计算
3.1 应力梯度对微裂纹演化的影响
3.2 形态比对微裂纹演化的影响
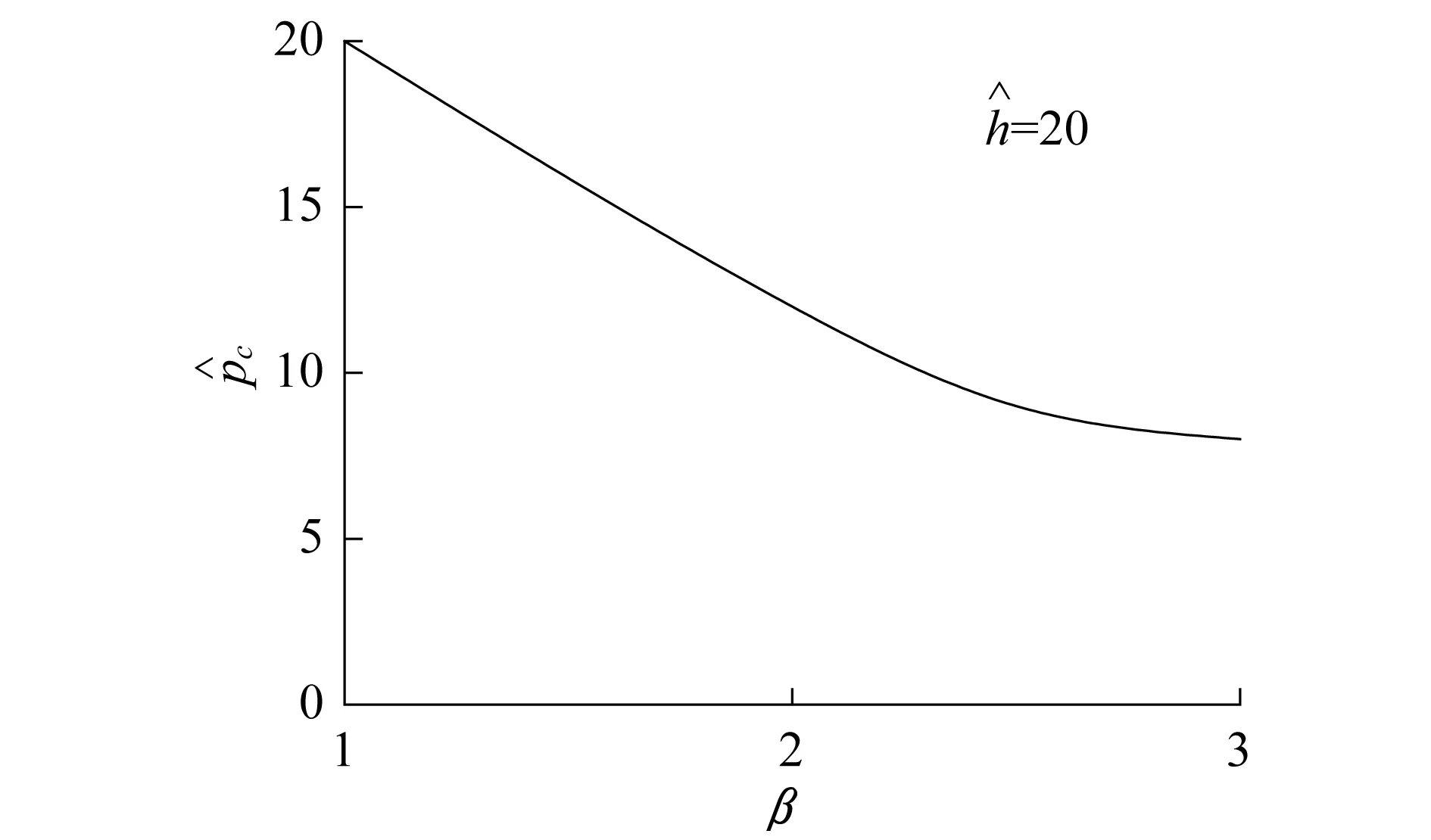
由图5可知,微裂纹在表面能作用下两端向中心收缩,在靠近中心的位置形成尖端。随着形态比的继续增大,微裂纹在靠近中心的位置形成尖端的同时发生了位置漂移,并且在漂移的过程中伴随着裂腔分节的现象。图6给出了形态比对裂腔分节时间的影响规律。由图可知,当应力梯度为一定值时,微裂纹分节时间随着形态比的增大而减小,且减小的速率随着形态比的增大而减小。
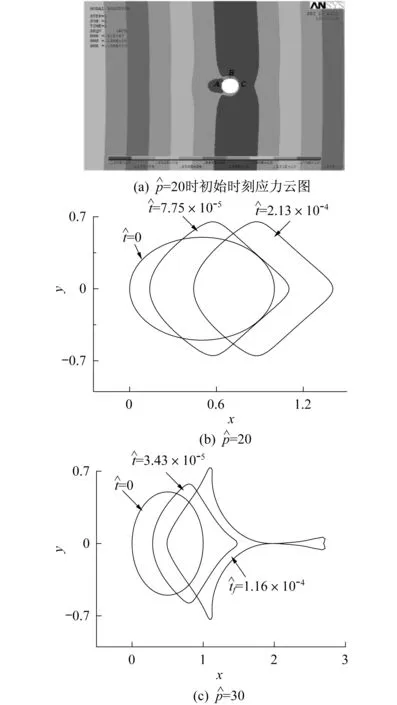
图时晶内微裂纹演化Fig.2 The evolution of the intragranular microcrack

图3 分节时间f随应力梯度变化Fig.3 The splitting time f as a function of
图随β变化Fig.

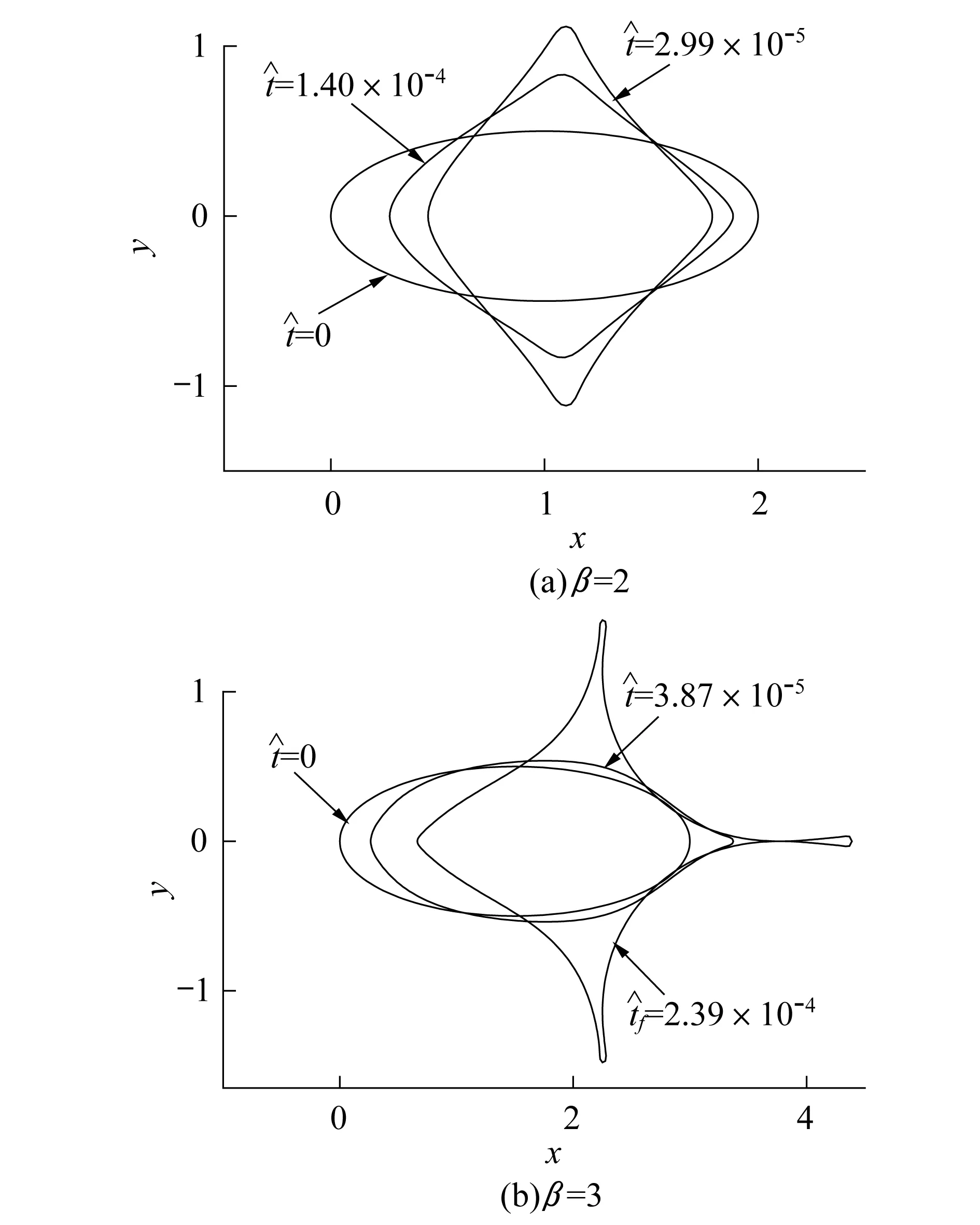
图时晶内微裂纹的演化Fig.5 The evolution of the intragranular microcrack
3.3 线宽对微裂纹演化的影响

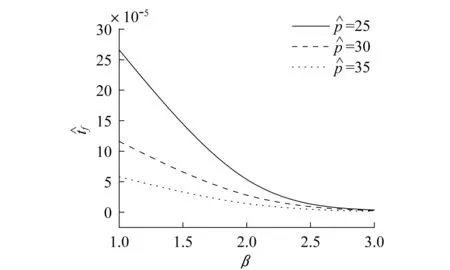
图6 分节时间f随β变化Fig.6 The splitting time f as a function of β
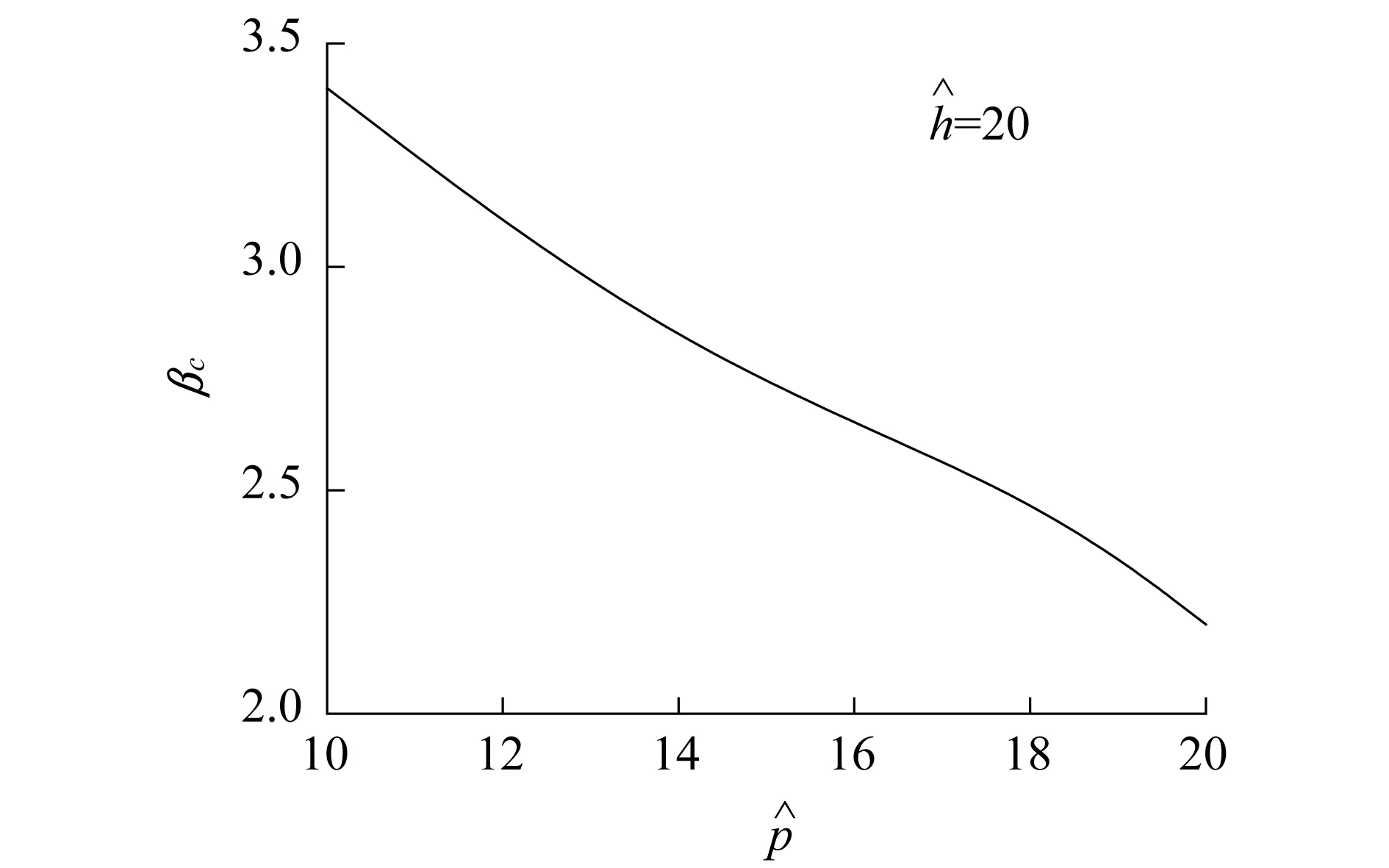
图7 βc随变化Fig.
4 结 论
本文数值模拟了应力梯度下晶内微裂纹的演化,得出以下结论:
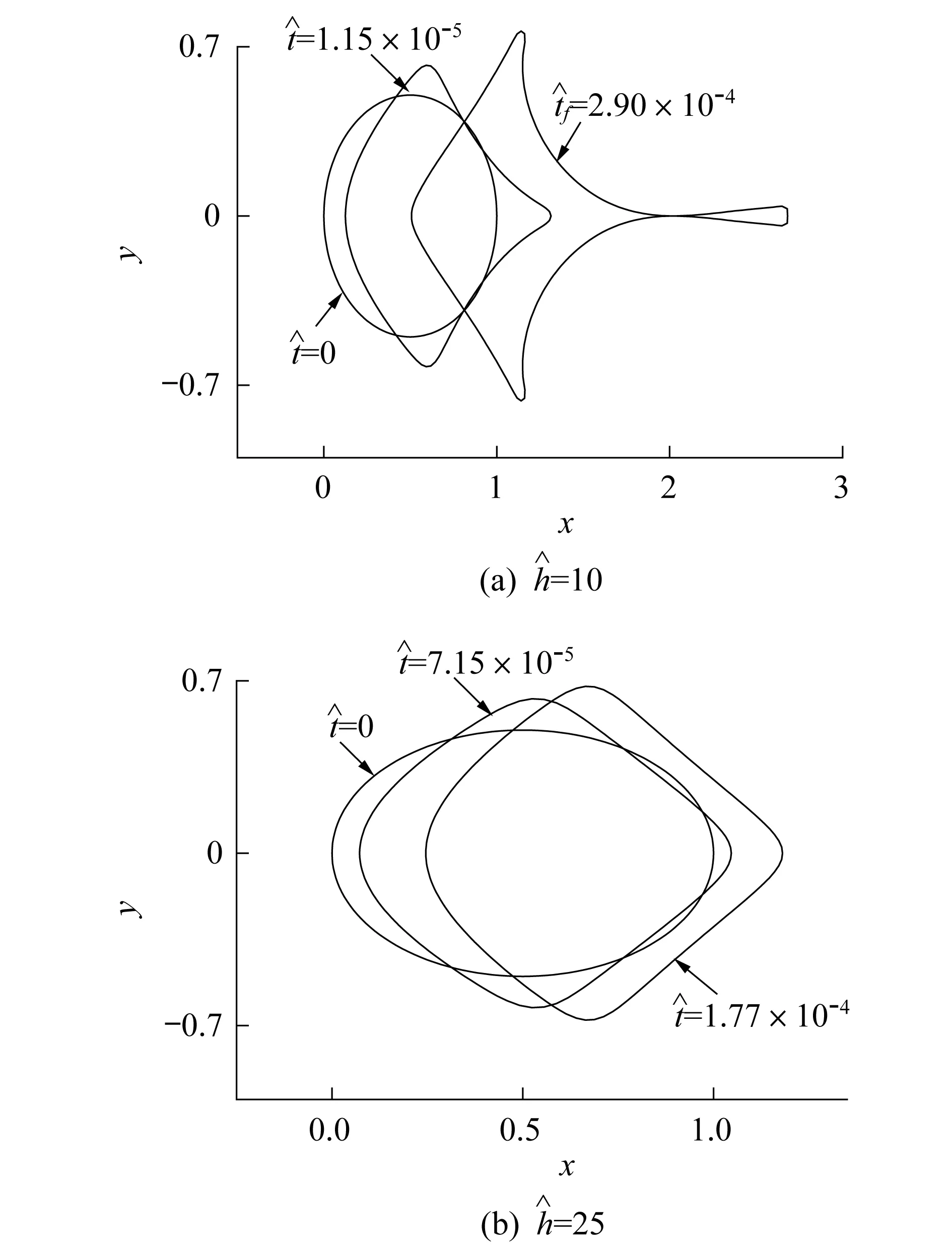
图时晶内微裂纹的演化Fig.8 The evolution of the intragranular microcrack

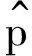
[1] Bower A F,Shankar S.A finite element model of electromigration induced void nucleation,growth and evolution in interconnects[J].Modelling & Simulation in Materials Science & Engineering,2007,15(8):923-940(18).
[2] Bhate D N,Bower A F,Kumar A.A phase field model for failure in interconnect lines due to coupled diffusion mechanisms[J].Journal of the Mechanics & Physics of Solids,2002,50(10):2057-2083.
[3] Krug J,Dobbs H T.Current-induced faceting of crystal surfaces[J].Physical Review Letters,1994,73(14):1947-1950.
[4] Schimschak M,Krug J.Surface Electromigration as a Moving Boundary Value Problem[J].Physical Review Letters,1997,78(78):278-281.
[5] Li Z,Chen N.Electromigration-driven motion of an elliptical inclusion[J].Applied Physics Letters,2008,93(5):051908-051908-3.
[6] Dong X,Li Z.An analytical solution for motion of an elliptical void under gradient stress field[J].Applied Physics Letters,2009,94(7):071909-07 1909-3.
[7] Cho J,Gungor M R,Maroudas D.Electromigrat-ion-driven motion of morphologically stable voids in metallic thin films:Universal scaling of migration speed with void size[J].Applied Physics Letters,2004,85(12):2214-2216.
[8] Wang H,Li Z,Sun J.Effects of stress and tem-perature gradients on the evolution of void in metal interconnects driven by electric current and mechanical stress[J].Modelling & Simulation in Materials Science & Engineering,2006,14(4):607-615.

程 强 男(1991-),安徽安庆人,硕士,主要研究微结构演化。

黄佩珍 女(1972-),浙江浦江人,教授,博导,主要研究方向为工程问题的力学建模与数值仿真。
Finite Element Simulation of the Intragranular MicrocracksEvolution in a Stress Gradient Field
CHENGQiang,HUANGPeizhen
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures,Nanjing University ofAeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 210016,China)
Based on the classical theory of surface diffusion and evaporation-condensation,a finite element program is developed for simulating the evolution of intragranular microcracks in metallic material in a stress gradient field.Numerical analysis results show that there exists critical values of the stress gradient,the aspect ratio and line width for the ellipse intragranular microcracks under the stress gradient field.When the stress fradient and the aspect ratio are both less than their critical values,or the line width is more than its critical value,the microcrack will move to the higher stress zone by a stable form.Otherwise,it will split into two microcracks.And the increase of the stress gradient and the aspect ratio are beneficial to the microcrack splitting.The decrease of the line width will accelerate the splitting process.
surface diffusion; stress gradient; intragranular microcrack; finite element simulation; microcrack splitting
江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK20141407);江苏高校优势学科建设工程资助项目
TG 113
A

