气道上皮细胞紧密连接在小鼠哮喘中的病理学改变
李凡,吴琦,孙昕,李宽,张颖超,李雪,李玉,张秋阳,徐龙,陈怀永
气道上皮细胞紧密连接在小鼠哮喘中的病理学改变
李凡1,吴琦2△,孙昕2,李宽2,张颖超3,李雪2,李玉2,张秋阳2,徐龙2,陈怀永2
摘要:目的探讨小鼠支气管哮喘(哮喘)中气道上皮紧密连接的病理学改变。方法10只小鼠随机分为对照组和哮喘组,每组5只。哮喘组于第0、7天腹腔注射鸡卵清蛋白(OVA)溶液,在第14、15、16天以雾化的OVA熏诱小鼠,1h/次、1次/d;对照组用PBS溶液替代OVA;2组小鼠在第18天回收肺组织,采用免疫荧光染色法评价小鼠哮喘模型的有效性,荧光定量PCR检测紧密连接相关蛋白基因Claudin 1、Claudin 3、Claudin 4、Claudin 5、Claudin 7、Clau⁃din 10在肺组织中的表达。结果哮喘组Claudin 3、Claudin 4、Claudin 10mRNA水平较对照组低(P<0.05),而Clau⁃din 1、Claudin 5、Claudin 7mRNA水平与对照组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论哮喘病理过程中气道上皮细胞紧密连接松散,提示气道上皮屏障破坏。
关键词:哮喘;连接蛋白类;气道上皮黏膜;钙激活氯离子通道蛋白3;紧密连接蛋白;Claudin 3
支气管哮喘(哮喘)是一种反复发作的慢性气道炎症性疾病,是各个年龄段均可发病的一种综合征,受多种因素的影响[1]。包括儿童在内,全球至少有3.34亿人患有哮喘[2]。支气管哮喘的早期主要是分泌物增多、气道内炎性细胞浸润等一些可逆性的病理改变。抗炎(氟替卡松等)或联合支气管扩张(沙美特罗等)等治疗可有效控制哮喘的严重程度,但无法根治[3]。气道上皮黏膜损伤是哮喘气道炎症反应的初始源头,损伤后得不到修复是炎症持续存在的主要因素[4]。紧密连接(tight junction,TJ)能选择性地调节离子和其他溶质细胞间的运输[5],与气道上皮的完整性密切相关,但TJ是否与哮喘的病理学改变有关,尚少见报道。本研究通过建立小鼠哮喘模型,检测紧密连接相关蛋白(Claudins)在哮喘小鼠中的表达,以期揭示哮喘与气道上皮改变的关系,为哮喘的治疗提供病理学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料健康8~12周龄SPF级C57BL/6小鼠10只,体质量20~30 g,购自北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司。哮喘造模用熏箱为自制玻璃箱(27 cm×20 cm×10 cm)。荧光定量PCR仪(Light Cycler 96,Roche),酶标仪(Multiskan Go,Ther⁃mo)。Trizol(Invitrogen),逆转录试剂盒购(TIANGEN生物),SYBR®Green(Roche)。兔源CLCA3一抗抗体(Abcam),驴源抗兔二抗(Alexa Fluor®594 DonkeyAnti-Rabbit,Invitrogen),DAPI荧光封片剂(DAPI Fluoromout- G,Southern Biotech,0100-20)。
1.2方法
1.2.1小鼠哮喘模型的建立采用随机数字表法将10只小鼠分为2组,每组5只。哮喘组于第0、7天腹腔注射鸡卵清蛋白(OVA)溶液[10 μg/g,以氢氧化铝为佐剂,以磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)为溶剂,配制成质量浓度为100 g/L溶液]。在第14、15、16天以雾化的1% OVA(PBS为溶剂)熏诱小鼠,1h/次,1 次/d。对照组以PBS替代OVA,其他条件相同。2组小鼠在第18天处死,取肺组织。
1.2.2免疫荧光染色用7.5%的水合氯醛溶液麻醉小鼠后取出肺组织,10%福尔马林溶液固定、脱水、石蜡包埋、切片。5 μm石蜡切片于55℃~60℃烘烤溶解脱蜡,放入煮沸的柠檬酸抗原修复液中修复2min;冷却至室温,PBS缓冲液泡洗后滴加5%牛血清蛋白(BSA)室温封闭30min;PBS缓冲液泡洗后加一抗于4℃孵育过夜;PBS缓冲液泡洗,5% BSA稀释抗体(免疫荧光二抗为1∶500稀释),加二抗室温孵育1.5h。PBS缓冲液泡洗后用DAPI荧光封片剂避光封片10min;荧光显微镜观察。
1.2.3荧光定量PCR Trizol法提取肺组织RNA,用50 μL 无RNA酶水(RNase-free water)溶解RNA。检测RNA质量,吸光度(A)260/280值需在1.8~2.0之间;以RNA为模板逆转录后,以cDNA为模板进行RT-PCR扩增。分别检测Claudin 1、3、4、5、7和10基因的表达情况,引物由华大基因合成,引物序列见表1。qPCR总反应体系10 μL,循环参数:50℃2min,95℃预变性3min,然后95℃10 s,60℃30 s,72℃20 s,40个循环。待测样本特定基因相对表达量的计算方法为2-△Ct,样本特定基因△Ct=该基因循环阈值(Ct)-内参基因(β-actin)Ct值。

Tab.1 Primer sequences表1 引物序列
1.3统计学方法采用Excel分析数据,定量指标采用均数±标准差(±s)表示,2组间比较采用t检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1哮喘模型建立与对照组比较,哮喘组小鼠普遍兴奋度降低,食欲减退,体质量下降。小鼠肺组织石蜡切片中红色荧光标记钙激活氯离子通道蛋白3 (Chloride channel, calcium activated, familymember 3,Clca 3),蓝色荧光为DAPI标记的细胞核。倒置荧光显微镜下对照组中肺间质与肺上皮细胞核蓝色着色明显,大气道上皮细胞无明显红色着色,即无Clca3阳性细胞。哮喘组肺间质与肺上皮细胞核蓝色着色明显,大气道上皮细胞中出现Clca3阳性细胞,明显多于对照组,证实哮喘造模成功,见图1。
2.2肺组织紧密连接相关基因的表达哮喘组肺组织中,Claudin 3、4和10mRNA表达水平较对照组低(均P<0.05)。其中,Claudin 3的表达水平较其他基因高,且在哮喘组中下降最为明显。在哮喘组肺组织和对照组肺组织中Claudin 1、Claudin 5和Claudin 7mRNA水平变化差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见图2。
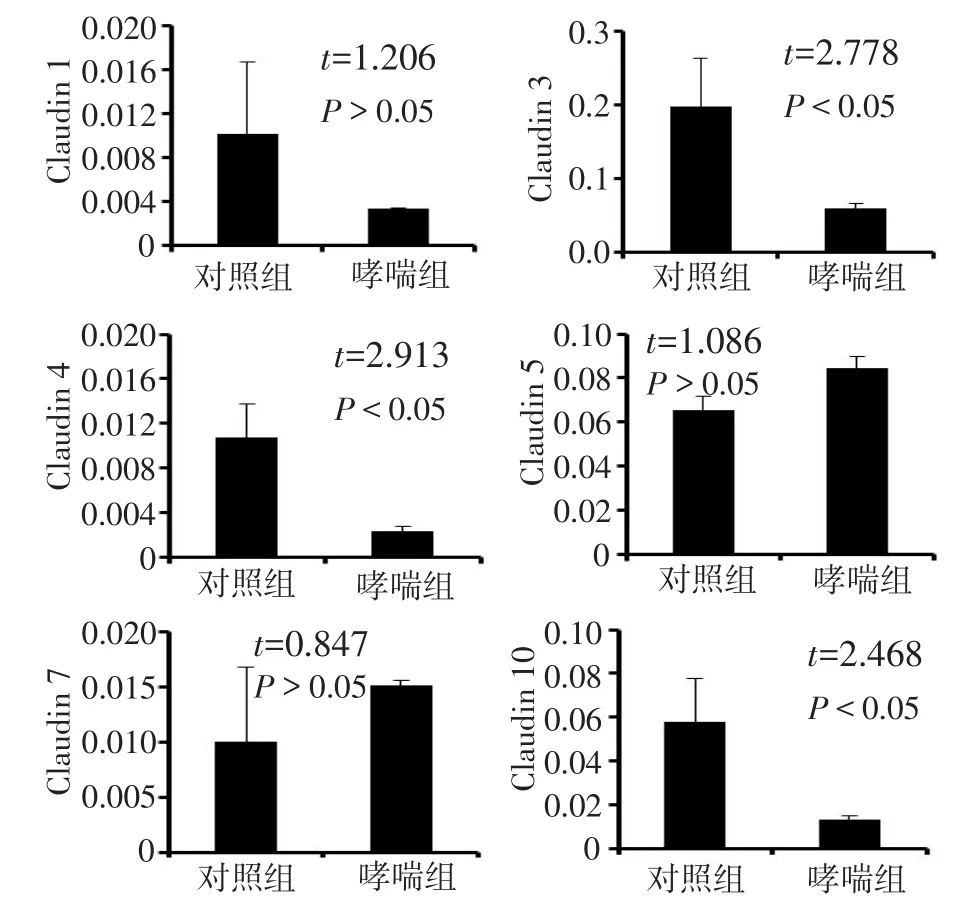
Fig.2 Gene expression of Claudins in lung tissues during asthma development图2 哮喘中Claudins基因在肺组织中的表达变化情况
3 讨论
哮喘是一种环境和遗传因素相互作用引起的复杂的异质性慢性炎症失调[6-7]。哮喘的主要病理学特征包括气道变应性炎症、分泌物增多、气道内炎性细胞浸润,并释放出多种细胞因子[8]。TJ是上皮细胞间屏障重要组成部分,控制电解质和生物分子跨上皮运输,与肺气道上皮黏膜的完整性密切相关,Claudins是紧密连接的主要成分。在Claudins家族中,Claudin 3主要在Ⅱ型肺泡细胞中表达,Claudin 4在肺泡上皮细胞中也有表达,急性肺损伤后,Clau⁃din 4的表达会上调。Claudin 4表达的增加会增强肺泡上皮的跨膜电阻,Claudin 4基因敲除后,小鼠肺上皮易损性显著增强[9]。蛋白激酶D(PKD)又能通过下调Claudin 1来负向调节人气道上皮屏障的形成和完整性[10]。丙烯醛诱发急性肺损伤后,Clau⁃din 5表达水平也随之增加[11]。以上说明在病理环境下,Claudins的调节机制很复杂。
Clca3是一种可靠的哮喘特异性蛋白[6]。本研究结果表明,哮喘组中Clca3阳性的细胞明显多于对照组,证实哮喘造模成功。Claudins与哮喘的发生具有一定的相关性,哮喘病理过程中气道上皮细胞紧密连接松散,全肺组织中Claudin 3、4、10的下调能增加上皮对生物分子的通透性,加快炎性因子的跨上皮运输,加重气道变应性炎症,从而引发哮喘。同时本研究发现,Claudin 1、Claudin 5和Claudin 7的基因表达水平在哮喘中没有发生明显变化。这些Claudin基因表达的变化是否也体现在蛋白质水平上需要进一步的研究考证。
此外,哮喘中还发现气道上皮破损的情况,上皮屏障的完整性与哮喘密切相关[12]。屋尘螨(HDM)过敏原是哮喘患病率增加的原因之一,尘螨Ⅰ类抗原(Der p1)能剪切TJ相关蛋白ZO1、Occludin和Clau⁃din 1,使气道上皮细胞紧密连接松散,进而破坏气道上皮屏障[13-14]。气道上皮损伤后能激活Hippo/Yap途径,肺部损伤修复的过程中Hippo/Yap途径可通过调节Ajuba,调控肺上皮干/祖细胞的增殖和分化[15]。因此,Claudins有可能通过调节气道上皮紧密连接间接参与调控肺上皮损伤修复的Hippo/Yap途径,但其中的机制还需要进一步研究。恢复气道上皮正常的结构,从而有效终止哮喘气道炎症反应可作为未来治疗哮喘的新方向。
(图1见插页)
参考文献
[1] Wenzel SE.Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical tomo⁃lecular approaches[J].Natmed, 2012, 18(5): 716-725.doi: 10.1038/nm.2678.
[2] Asher I, Pearce N.Global burden of asthma among children[J].Int J Tuberc Lung Dis, 2014, 18(11):1269- 1278.doi: 10.5588/ijtld.14.0170.
[3] Kandeelm, Balaham, Inagaki N, et al.Current and future asthma therapies[J].Drugs Today (Barc), 2013, 49(5):325-339.doi: 10.1358/dot.2013.49.5.1950149.
[4] Royce SG, Li X, Tortorella S, et al.Mechanistic insights into the contribution of epithelial damage to airway remodeling.Novel thera⁃peutic targets for asthma[J].Am J Respir Cellmol Biol, 2014, 50(1): 180-192.doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0008OC.
[5] Aijaz S, BaldamS,matter K.Tight junctions:molecular architecture and function[J].Int Rev Cytol, 2006, 248:261-298.doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(06)48005-0.
[6] Todam, TulicmK, Levitt RC, et al.A calcium-activated chloride channel (HCLCA1) is strongly related to IL-9 expression andmu⁃cus production in bronchial epithelium of patients with asthma[J].J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2002, 109(2):246-250.
[7] Royce SG, Cheng V, Samuel CS, et al.The regulation of fibrosis in airway remodeling in asthma[J].Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2012, 351(2): 167-175.doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.01.007.
[8] Wong CK,ho CY, Ko FW, et al.Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-17, IL-6, IL-18 and IL-12) and Th cytokines (IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13) in patients with allergic asthma[J].Clin Exp Immu⁃nol, 2001, 125(2):177-183.
[9] Kageh, Flodby P, Gao D, et al.Claudin 4 knockoutmice: normal physiological phenotype with increased susceptibility to lung injury [J].Am J Physiol Lung Cellmol Physiol, 2014, 307(7):L524-L536.doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00077.2014.
[10] Ganh, Wang G,hao Q, et al.Protein kinase D promotes airway epi⁃thelial barrier dysfunction and permeability through down-regula⁃tion of claudin- 1[J].J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(52):37343- 37354.doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511527.
[11] Jang AS, Concel VJ, Bein K, et al.Endothelial dysfunction and claudin 5 regulation during acrolein-induced lung injury[J].Am J Respir Cellmol Biol, 2011, 44(4):483-490.doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0391OC.
[12]holgate ST.The airway epithelium is central to the pathogenesis of asthma[J].Allergol Int, 2008, 57(1):1-10.doi: 10.2332/allergolint.R-07-154.
[13] Wanh, WintonhL, Soeller C, et al.Der p1 facilitates transepitheli⁃al allergen delivery by disruption of tight junctions[J].J Clin Invest, 1999, 104(1):123-133.doi: 10.1172/JCI5844.
[14] Wanh, WintonhL, Soeller C, et al.The transmembrane protein oc⁃cludin of epithelial tight junctions is a functional target for serine peptidases from faecal pellets of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus [J].Clin Exp Allergy, 2001, 31(2):279-294.
[15] Lange AW, Sridharan A, Xu Y, et al.Hippo/Yap signaling controls epithelial progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the em⁃bryonic and adult lung[J].Jmol Cell Biol, 2015, 7(1):35-47.doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mju046.
(2015-10-10收稿2015-10-28修回)
(本文编辑魏杰)
The pathological changes in airway epitheilal tight junctions inmousemodel with asthma
LI Fan1, WU Qi2△, SUN Xin2, LI Kuan2, ZHANG Yingchao3, LI Xue2, LI Yu2, ZHANG Qiuyang2, XU Long2, CHENhuaiyong2
1 Tianjinmedical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2 Department of Basicmedical Research,Tianjinhaihehospital; 3 Department of Respiratory, Tianjin Baodihospital△Corresponding Author E-mail:wq572004@163.com
Abstract:Objective To investigate the pathological changes of airway epitheliummucosa in asthmaticmice.Meth⁃ods Tenmice were divided into two groups: control group and asthma group, fivemice in each group.Asthma group was sensitized with chicken ovalbumin (OVA) by intraperitoneal injection on day 0 and 7.Mice were then challenged with OVA on day 14, 15, and 16, 1hour each time, once a day.Control group was given PBS solution instead of OVA.Lungs were col⁃lected at day 18 in two groups.Immunofluorescence staining was used to evaluate asthmaticmousemodel.Quantitative PCR was applied to detect the expression of Claudin 1, Claudin 3, Claudin 4, Claudin 5, Claudin 7 and Claudin 10 in lung tissues.Results The expressions of Claudin 3, Claudin 4 and Claudin 10 were significantly lower in asthma group than those in control group (P < 0.05).There were no significant differences in Claudin 1, Claudin 5 and Claudin 7mRNA levels between control group and asthma group (P > 0.05).ConclusionTight junctions of airway epithelium are loosed in asthma, suggest⁃ing that epithelial permeability is increased.
Key words:asthma; connexins; airway epithelium; chloride channel, calcium activated, familymember 3; tight junc⁃tion protein; Claudin 3
通讯作者△E-mail:wq572004@163.com
作者简介:李凡(1990),女,硕士在读,主要从事呼吸病学研究
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(31471121);天津市科委基础项目(14JCYBJC25700,13JCYBJC40000)
中图分类号:R562.2+5
文献标志码:A
DOI:10.11958/20150210
作者单位:1天津医科大学(邮编300070);2天津市海河医院基础医学实验部;3天津市宝坻区人民医院呼吸科

