基于时域响应灵敏度分析的板结构损伤识别
第一作者 傅奕臻 男,博士生, 1988年生
通信作者 吕中荣 男,副教授, 1975年生
邮箱:lvzhr@mail.sysu.edu.cn
基于时域响应灵敏度分析的板结构损伤识别
傅奕臻,魏子天,吕中荣,刘济科
(中山大学 力学系,广州510006)
摘要:提出了一种基于响应灵敏度分析的有限元模型修正法,对平板结构的局部损伤进行识别。在正问题研究中,将结构的局部损伤模拟为板结构单元杨氏模量的减少,建立了板结构的有限元动力学方程,利用直接积分法获得了结构强迫振动响应。在损伤识别反问题中,基于响应灵敏度分析,直接利用结构的动态响应进行有限元模型修正和损伤识别。算例表明,本文方法能有效识别板类结构的局部损伤,具有需要测点数目少,损伤识别精度高,对模拟的测量噪声不大敏感的优点。
关键词:损伤识别;板;响应灵敏度;模型修正
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(11172333, 11272361);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(13lgzd06);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(20130171110039);广东省科技计划项目(2012A030200011);博士后基金(2013M531893)资助
收稿日期:2013-09-23修改稿收到日期:2014-01-27
中图分类号:O32文献标志码: A
Damage identification of a plate based on response sensitivity analysis in time domain
FUYe-zhen,WIEZi-tian,LÜZhong-rong,JIUJi-ke(Department of Applied Mechanics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract:A response sensitivity-based approach was presented to identify local damages in an isotropic plate structure using the finite element model updating. The local damage was considered as a reduction of elemental Young’s modulus of the plate, the FE dynamic equations of the plate were built. The forced vibration responses of the plate under external excitations were obtained with Newmark direct integration. For its damage identification, a response sensitivity-based finite element model updating approach was used to identify local damages of the plate in time domain. Numerical examples showed that the proposed method is effective to identify local damages of plates; good identified results can be obtained with short time histories of a few measurement points, and it is insensitive to the simulated measurement noise.
Key words: damage identification; plate; response sensitivity; model updating
板作为一种重要的结构构件类型,在工程中广泛地应用于航空航天、汽车、机械和土木工程等领域。开发一种早期的损伤检测方法对保持板整体结构的完整性和安全性是非常重要的。人们在板类结构的损伤识别方面进行了大量的研究。Cawley 等[1]研究了一种利用频率改变来检测板类结构损伤的算法。Cornwell 等[2]将最初应用于一维结构的模态能量法推广到板类结构的损伤检测之中。Li 等[3]提出了一种应变模态法对板类结构的损伤进行识别。Yam 等[4]通过对板类结构进行静态和动态响应灵敏度分析来识别损伤。Wu 等[5]根据均布载荷板的表面曲率变化情况来识别损伤。Yoon 等[6]将最初用于一维结构损伤检测的 gapped-smoothing 法进一步推广应用于二维板类结构中。Bayissa等[7]提出了一种新的基于弯矩响应功率谱密度的损伤敏感参数,应用于两维板类结构的损伤识别中。Qiao 等[8]研究了一种新的静态/动态响应组合技术来提高复合材料层合板的损伤检测。该技术表明在保持静载荷作用下,损伤处的动态响应其异常可能会更加明显且容易检测。Fan等[9]提出了一种二维(2D)连续小波变换的损伤检测算法。该方法利用 Dergauss2D小波检测平板式结构的损伤,提出了2-D小波系数等值面的概念,这种等值面能生成损伤的具体位置和近似形状或面积。Kazem等[10]提出了一种两步程序法来确定薄板结构的各种损伤及受损程度。徐峰等[11]利用损伤因子进行了板架结构的损伤识别。最近,Zhang等[12]利用频率偏移面曲率法(frequency shift surface curvature)进行板结构损伤识别。
提出一种基于响应灵敏度分析的有限元模型修正法,通过测量的结构动态响应来识别各向同性中厚板的局部损伤。首先使用Reissner-Mindlin板单元建立板结构的有限元模型,考虑其横向剪切变形。然后利用板单元的杨氏模量减少来模拟结构的局部损伤,并采用罚函数法和Tikhonov正则化方法进行求解。以悬臂板为例,说明所提方法的正确性和有效性。算例表明,利用测量的若干结构动态响应能够有效地识别板类结构的单一损伤和多个损伤。同时研究了噪声的大小,研究表明测量噪声对损伤识别的结果有影响。
1理论方法
1.1板的受迫振动
外激励下各向同性板的运动方程用有限元法表示如下:
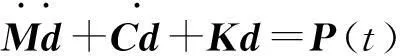
(1)

1.2刚度参数的动态响应灵敏度
一般来说,当局部损伤发生在结构的某单元处,它会导致单元刚度特性的降低(如杨氏模量)。对式(1)的两端同时对杨氏模量求导,可以得到:
(2)

(3)
1.3模型修正问题的目标函数
在反问题中,采用一种基于灵敏度的动态响应有限元模型修正法[13]来识别系统的局部损伤。模型修正的目标函数就是使测量和计算的结构动力响应的残差最小,见式(4):
(4)
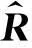
1.4损伤参数识别
利用罚函数法[14],识别方程可写为:
(5)
其中
(6)
St=ti=
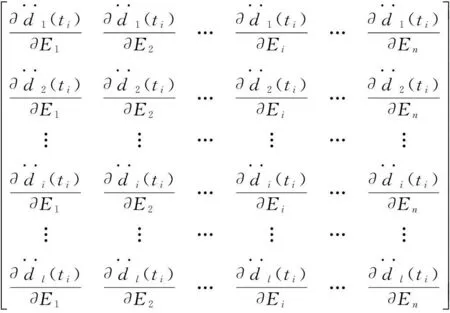
方程(5)可以通过阻尼最小二乘法(DLS)[15]求解,表达式为:
(8)
其中,λ是非负阻尼正则化参数。式(8)的解等同于如下函数求解其最小值问题
Tikhonov正则化方法[16]用来求解最优正则化参数,其使用L-曲线[17]作为优化函数。当λ≈0的时候,ΔEj就接近由最小二乘法计算的结果。L-曲线法的计算方法可以查找文献[18]。第j次迭代的修正杨氏模量矢量Ej+1表达式如下:
Ej+1=Ej+ΔEj
(10)
当满足如下条件时,可以认为迭代结束,跳出循环:

(11)
这里容许值Tol =1×10-8。
1.5迭代算法步骤
首先,给定一组单元杨氏模量初始值E0,E0每一项可为完好板的各项数值,迭代步骤为:
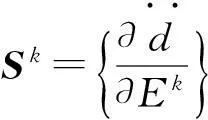
步骤3:由式(10)计算Ek+1。
步骤4:让k=k+1,然后重复“步骤1”至“步骤3”步直到满足容许条件。
2数值模拟
2.1悬臂板单损伤识别
在本算例中,悬臂钢板的尺寸为500 mm×500 mm×50 mm(见图1)。板的各物理量表示如下:杨氏模量E=210 GPa,密度ρ=7.8×103kg/m3,泊松比υ=0.3。MATLAB软件包用于建立板单元模型,有限元模型中,板被划分成25个4节点Reissner-Mindlin板单元。由有限元法计算得到前6阶固有频率为172.5,406.9,1 091.5,1 348.4,1 506.1和2 522.7 Hz。为了得到板的受迫响应,在第36号节点沿z轴负方向施加某一冲击荷载,荷载表达式为

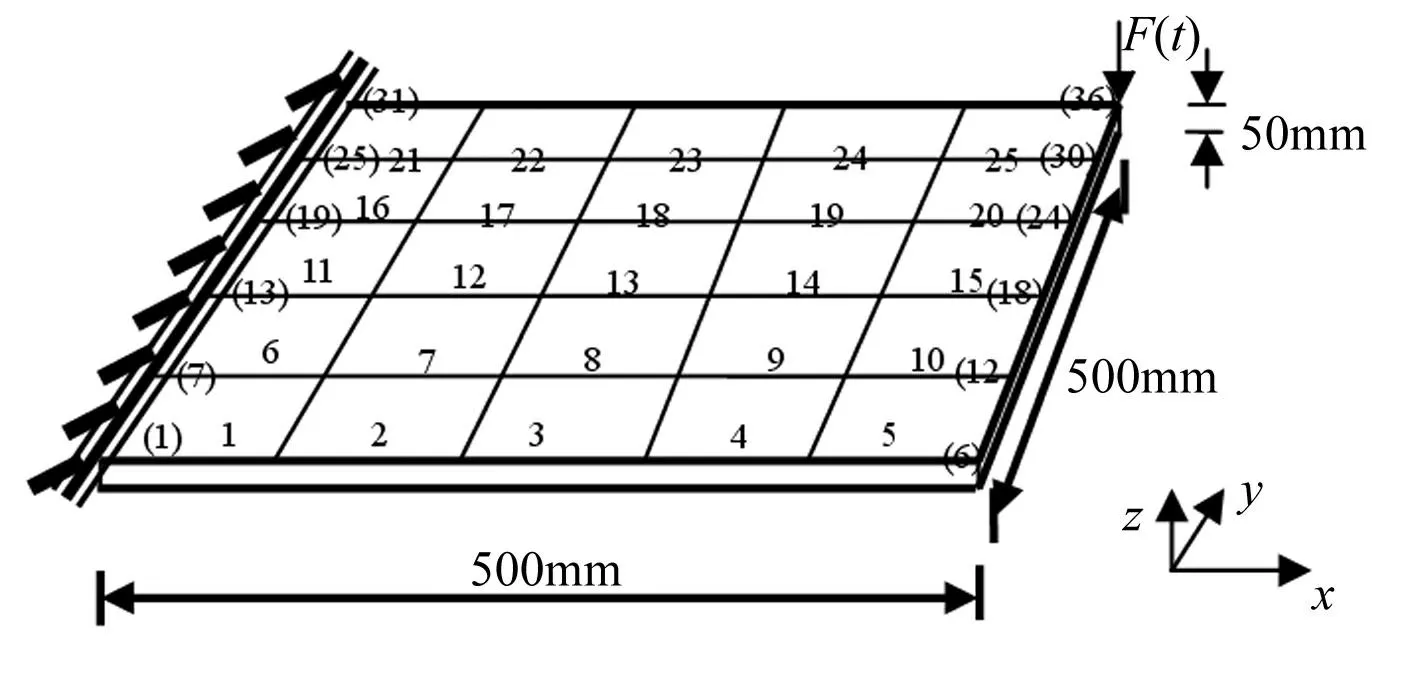
图1 一边固支钢板 ((1), (2), …, (36) 为节点编号;1, 2,…, 25 为单元编号) Fig.1 A cantilever steel plate ((1), (2),…, (36) denote node number of FEM; 1, 2,…, 25 denote element number)
假设局部损伤位于第1个单元,其杨氏模量降低5%。前6阶固有频率为172.0, 406.0, 1 089.4, 1 348.1, 1 503.2以及2 519.3 Hz。这也表明,局部损伤对固有频率的改变是非常小的。选取第4号、18号、34号节点作为加速度测点。模型修正的参数个数等于板的单元数。由于损伤较小,将损伤参数的下限取为板无损时杨氏模量的60%。权矩阵取单元阵。14次迭代后,识别数据开始收敛,结果(见图2)。最优化正则参数λopt=4.15×10-11。这可以看出单损伤精确识别出来了。最大识别误差出现在第6号板单元, 仅为0.04%。这个算例也表明了所用方法的有效性和准确性。
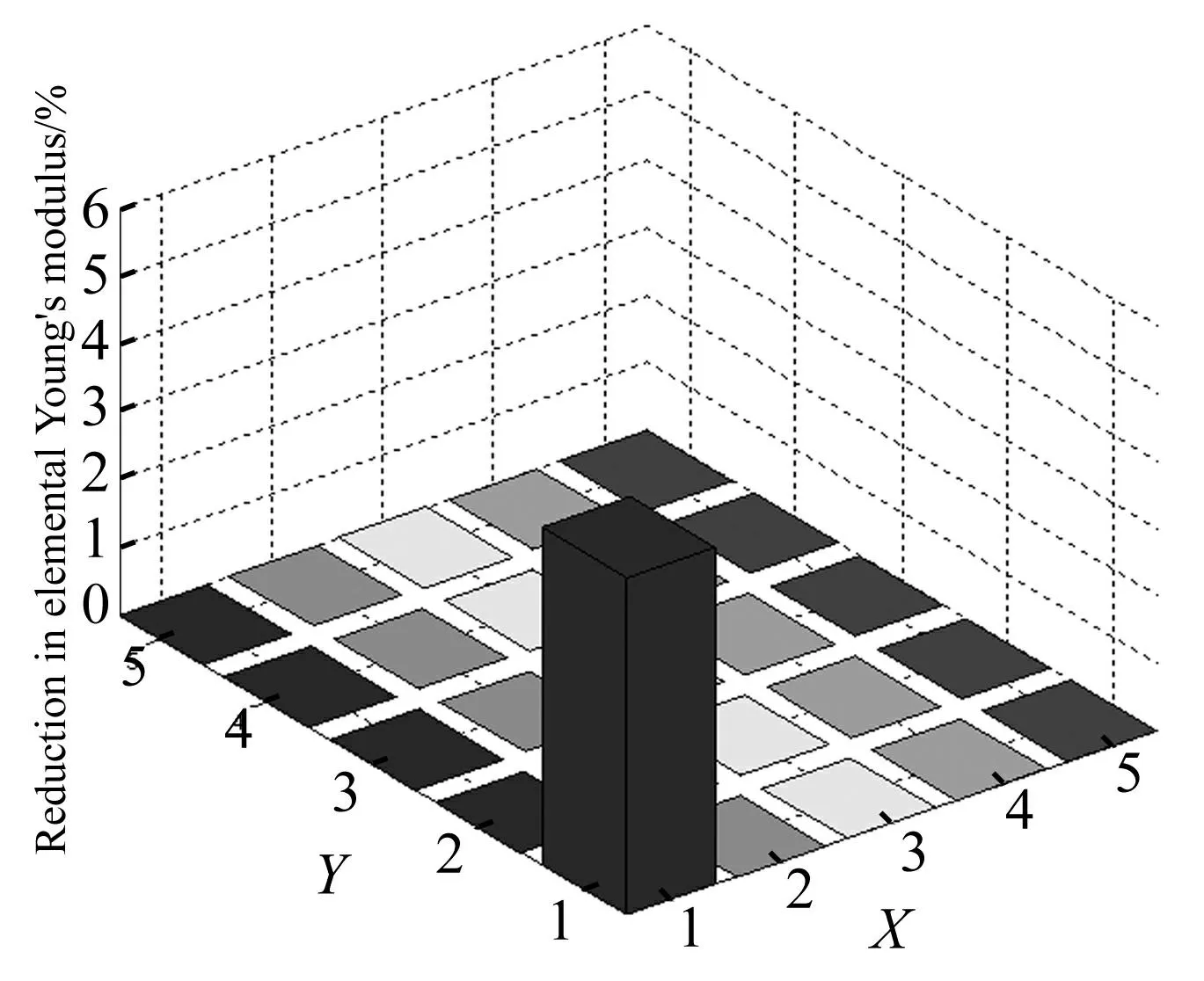
图2 单损伤的识别(不含噪声) Fig.2 Identification of a single local damage (noise free)
为研究测量噪声对识别精度的影响,在模拟的测量加速度中加入5%的噪声,16次迭代后识别结果收敛,最大误差为0.99%, 位于第2号板单元。最优正则化参数λopt=2.5×10-11。识别结果(见图3), 即使有5%的噪声,识别结果仍有较好的精度。

图3 单损伤的识别(5%噪声) Fig.3 Identification of a single local damage (5% noise)
2.2两跨连续板多损伤识别
两跨连续板边界条件为左右两边简支,尺寸5 000 mm×2 500 mm×60 mm(见图4)。杨氏模量E=25 GPa,密度ρ=2.8×103kg·m-3,泊松比υ=0.2。有限元建模中,将板划分50个4节点Reissner-Mindlin板单元。模型修正中的参数个数等于有限元单元数。板先后受到两次冲击荷载,第一次作用在第25号节点,方向为Z轴负方向,荷载为
第二次作用在第42号节点,方向为Z轴负方向,荷载为

此板有8处损伤,定位于第1、第10、第16、第18、第23、第34、第41、第50号单元。杨氏模量分别减少15%, 10%, 15%, 8%, 10% , 10%, 6% 和15%。选择10个测点:第3、第9、第14、第19、第26、第31、第41、第43、第49、第52号节点做加速度测点。若加入5%的噪声,21次迭代后识别结果收敛,最大误差为3.83%位于、第21号板单元。最优正则化参数λopt=4.40×10-9。识别结果(见图5), 即使有5%的噪声,识别结果仍然较准确。
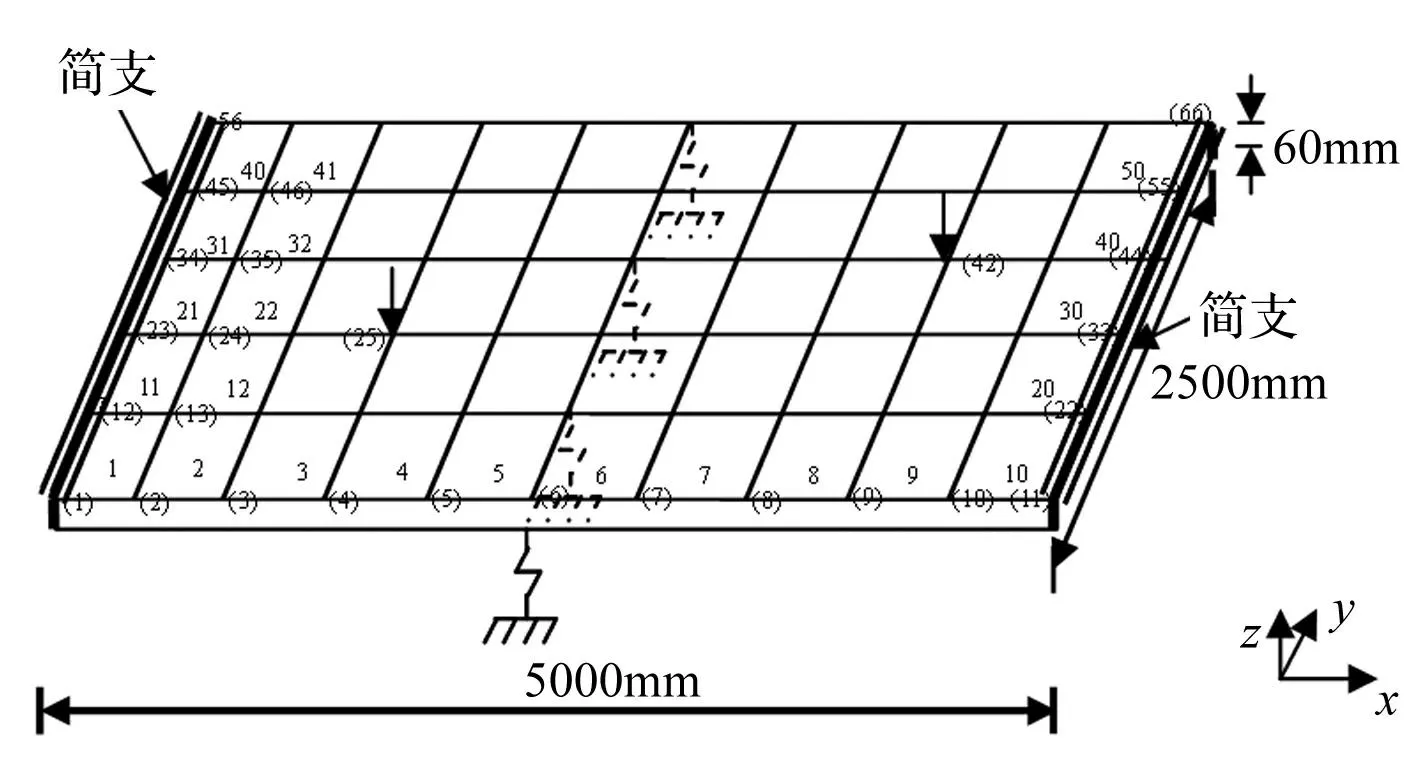
图4 两跨对边简支板 ((1), (2), …, (66)为节点编号,1,2,…,50为单元编号) Fig.4 Sketch of a two-span plate ((1), (2), …, (66) denote node number of the FEM; 1,2,…,50 denote element number) (Dimensions not scaled)
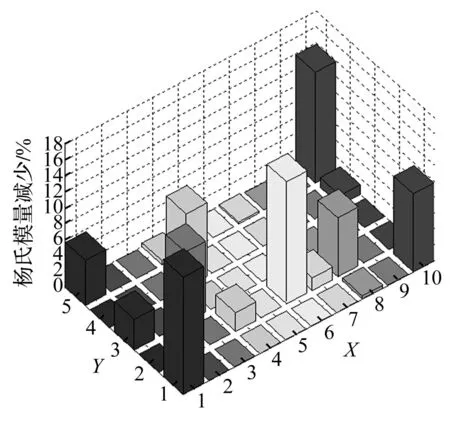
图5 两跨板多损伤识别(5%噪声) Fig.5 Multiple damage identification in a two-span plate (5% noise)
3结论
采用基于灵敏度的有限元模型修正法对板结构的局部损伤进行识别。通过罚函数法和Tikhonov正则化对识别方程进行迭代求解得到识别结果。两个数值算例表明所提的方法能有效识别板类结构的局部损伤,具有需要测点数目少,损伤识别精度高,对模拟的测量噪声不大敏感的优点,具有较好的工程应用潜力。
参 考 文 献
[1] Cawley P, Adams R D. The location of defects in structures from measurements of natural frequencies[J]. Journal of Strain Analysis, 14: 49-57.
[2] Cornwell P, Doebling S W, Farrar C R. Application of the strain energy damage detection method to plate-like structures[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1999, 224: 359-374.
[3] Li Y Y, Cheng L, Yam L H, et al. Identification of damage locations for plate-like structures using damage sensitive indices: strain modal approach[J]. Computers and Structures. 2002, 80: 1881-94.
[4] Yam L H, Li Y Y, Wong W O. Sensitivity studies of parameters for damage detection of plate-like structures using static and dynamic approaches[J]. Engineering Structures, 2002, 24: 1465-1475.
[5] Wu D, Law S S. Sensitivity of uniform load surface curvature for damage identification in plate structure[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics-ASME, 2005, 127: 84-92.
[6] Yoon M K, Heider D, Gillespie Jr J W,et al. Local damage detection using the two-dimensional gapped smoothing method[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 279: 119-139.
[7] Bayissa W L, Haritos N. Damage identification in plate-like structures using bending moment response power spectral density[J]. Structural Health Monitoringan International Journal, 2007, 6: 5-24.
[8] Qiao P Z, Lu K,Lestari W. A combined static/dynamic technique for damage detection of laminated composite plates[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2008, 48: 17-35.
[9] Wei F, Pizhong Q. A 2-D continuous wavelet transform of mode shape data for damage detection of plate structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46: 4379-4395.
[10] Kazemi S, Fooladi A, Rahai A R. Implementation of the modal flexibility variation to fault identification in thin plates[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2010, 66: 414-426.
[11] 徐峰, 彭海阔, 孟光. 基于损伤因子的板架结构损伤识别方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2010, 29(12): 22-25.
XU Feng, PENG Hai-kuo, MENG Guang. Damage detection for plate-like structure based on damage index[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,, 2010, 29(12): 22-25.
[12] Zhang, et al.Damage detection in plates structures based on frequency shift surface curvature[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2013, 332(25): 6665-6684.
[13] Lu Z R, Law S S, Identification of system parameters and input force from output only[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,2007,21:2099-2111.
[14] Friswell M I, Mottershead J E. Finite element model updating in structural dynamics[J]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publisher, 1995.
[15] Hansen P C. Rank-deficient and discrete ill-posed problems: numerical aspects of linear inversion[M]. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA; 1998.
[16] Tikhonov A M. On the solution of ill-posed problems and the method of regularization[J]. Soviet Mathematics,1963,4:1035-1038.
[17] Hansen P C. Regularization tools-a matlab package for analysis and solution of discrete Ⅲ-Posed Problem[J]. Numerical Algorithms,1992,6(1):1-35.
[18] Hansen P C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve[J]. Siam Rev,1992; 34: 561-80.


