An Empirical Study on How to Intensively Use Land and Tap Land Potential in Ma’anshan City
, ,2*
1. College of Economics and Management, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei 230036, China; 2. Institute of Land and Resources, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei 230036, China
1 Introduction
Ma’anshan City (31°17’-32°03’N, 117°53’-118°52’E) is on the south bank of the lower and middle reaches of the Yangtze River. It is an industrial city stretching across the Yangtze River, and borders Hefei to the west, Wuhu to the southwest, and Nanjing to the east. It is also at the conjunction of the coastal and the Yangtze River economic regions, an east door of Anhui opening to the outside world. It is an important port city along the Yangtze River, and also the core city of the Yangtze River Delta economic circle within Anhui Province. It is located in the subtropical zone, with distinct seasons and abundant rainfall. The city has many lakes and rivers, with a total area of reservoirs at about 22.37 km2. The terrain is relatively flat, slightly higher in the northeast and lower in the southwest. Plains and hills show ribbon-like parallel distribution. It has jurisdiction over three districts, three counties, one national economic and technological development zone, one state-level high-tech industrial development zone, one provincial-level high-tech industrial development zone, and six provincial-level economic development zones, a total area of 4049 km2(urban area of 704 km2and built area of 86 km2). The urbanization rate reaches 61%. In 2014, the city achieved 135.741 billion yuan of GDP, 20.27 billion yuan of fiscal revenue, industrial added value of 62.5 billion yuan, fixed assets investment of 167 billion yuan, total social consumer goods retail sales of 34 billion yuan, 30950 yuan of urban residents’ per capita disposable income and rural residents’ per capita disposable income of 13920 yuan.
2 Current situation of land use in Ma’anshan City
2.1GeneraloverviewIn 2014, the city’s total area of construction land was 67605.99 ha, accounting for 16.7% of total land area. The area of land for city, town and village as well as mining and industry was 55062.36 ha, accounting for 81.45% of total construction land area; the area of land for transportation and water conservation was 11094 ha, accounting for 16.41%; the area of other land types was 1449.63 ha, accounting for 2.14%. The urban construction land has the following characteristics: (i) total area of construction land is large, occupying 57% of the total land; (ii) residential land and the land for mining and industry has a large share, 60% of construction land area; (iii) the proportion of transportation land is small, only 5% of the construction land.
2.2DynamicanalysisofconstructionlanduseDuring 2005-2014, the construction land area in Ma’anshan City increased from 49802.68 ha to 67605.99 ha, with an average annual growth of 1780.33 ha. The urban and rural construction land area increased from 39845.55 ha to 55062.36 ha; the area of land for transportation and water conservation increased from 8859.84 ha to 11094 ha; the area of other construction land types increased from 1097.3 ha to 1449.63 ha (Fig. 1).
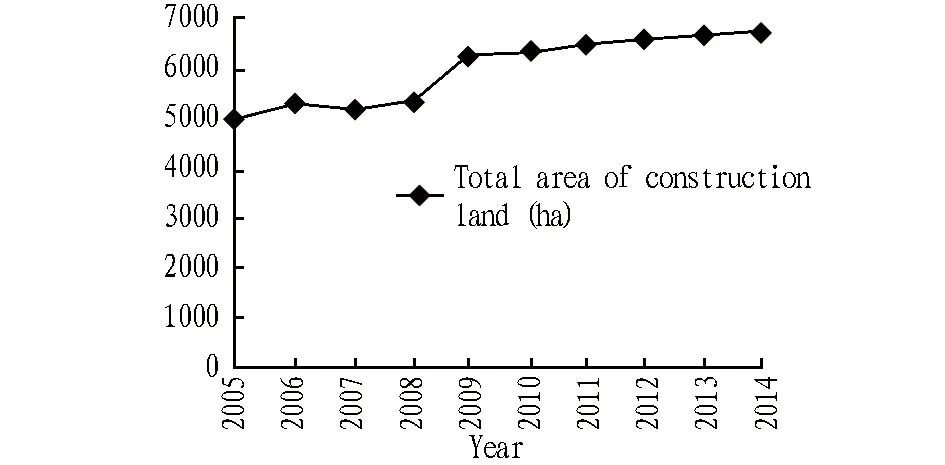
Fig.1 Dynamic construction land use in Ma’anshan City (2005-2014)
3 Problems in construction land use
3.1ObviouscontradictionbetweensupplyanddemandMa’anshan City is at the rapid development stage of urbanization and industrialization, and there is a huge demand for construction land. With advance in the strategy of development toward East Anhui and the strategy of industry transfer demonstration zone construction in Wanjiang City Belt, land demand will remain at a high level for quite a long time, and it is predicted that the level of urbanization will increase to 80% in 2020. The demand for various types of land, especially construction land, will be large for quite a long time. With the development of the tourism industry, it will increase the land for traffic, post and telecommunications, and communications, as well as the land for trade, food processing and other supporting industries, so the demand for construction land is large[1]. Thus, as the state implements the supply-side economic structural adjustment and reforms, the supply of new construction land will be strictly controlled, and if there is no way to arrest the growth trend of construction land, the contradiction between supply and demand of land will become more prominent.
3.2IrrationalstructureoflandsupplyAccording to the state-owned construction land supply plan of Ma’anshan City in 2011, the city’s land quota for industrial projects was 476.76 ha; the land quota for housing was 671.75 ha; the land quota for transportation was 769.51 ha; the land quota for public management and public service was 212.23 ha. In the construction land supply plan, the quota is mostly concentrated in transportation land, housing land and industrial land, accounting for 33.94%, 29.63% and 21.03% of national construction land supply plan, respectively, while the land for public management and public services occupies only 9.36%. The supply structure is irrational, and especially old housing renovation, low-rent housing and public rental housing occupy a small share of housing land[2].
3.3LoweconomicalandintensiveuseleveloflandIn 2014, the total land supply of Ma’anshan City was 1475.51 ha, the new construction land accounted for 72%, and the stock of land was only 424.05 ha, accounting for only 28% of the total land supply. The low level of economical and intensive land use is mainly due to urban land idling and abandoning, serious illegal urban land use, low urban land use efficiency, scattered layout of township enterprises, and too large land use scale.
4 Practice of intensively using land and tapping land potential in Ma’anshan City
4.1FullytappinglandpotentialandrevitalizingidlelandCurrently, the total arable land area of Ma’anshan City is 124440 ha, but the per capita arable land area is only 0.0541 ha, suggesting that the contradiction between land supply and demand is very prominent. It is neither realistic nor possible to achieve sound and rapid socio-economic development by relying solely on existing land resources. On the one hand, it develops and introduces a number of policies and measures, and establishes a long-term mechanism to revitalize the stock of land. The government utilizes administrative law and economic means to "wake up" each plot of "sleeping" land. On the other hand, it develops the measures to encourage enterprises to use the stock land.
4.2PromotingoldcitytransformationandimprovingtheeconomicalandintensivelanduseIn accordance with the overall land use plan and regulatory plan, the old city transformation fully takes into account all aspects of the development, and the transformation scope is not limited to the old city itself. It fully considers the specific surrounding circumstances of the land to be transformed, changes the traditional ways of increasing construction land by extension and expansion, and releases the old city’s land space to meet the needs of urban economic development. Ma’anshan’s old city transformation methods mainly include transformation of village in the city and rebuilding of dilapidated houses. Currently, there are still 43 villages in the city and dilapidated houses in the urban area, with a total area of 640 ha. The national land area is about 166.7 ha while the collective land area is about 31.6 ha, involving about 30000 households relocated due to building demolition.
4.3Expandingthespacefordevelopmentandpromotingtransformationandupgradingofdevelopmentzones(i) In terms of the supply of land for development zones, it strictly controls the new land area, construction scope of development zones, and the new land quantity. The land supply is in strict accordance with the national industrial policy and land supply policy, and the prohibited projects must not be assigned to the development park. At the same time, it strictly controls the scale of land for the project, and strictly manages the land quota. (ii) It implements differentiated management of development and construction and strictly controls the land supply conditions of new industrial projects. The project investment in national development zone is not less than 100 million yuan, and the expected revenue per mu is not less than 0.3 million yuan per year; the project investment in provincial development zone is not less than 60 million yuan, and the expected revenue per mu is not less than 0.2 million yuan per year; the project investment in county development zone is not less than 50 million yuan, and the expected revenue per mu is not less than 0.15 million yuan per year. (iii) It conducts standardized factory construction under the guidance of the government’s plan, utilizes market economy means to construct multi-storey factory in the planned zones and industrial parks in line with the industrial layout form, builds supporting complete infrastructure, and uses the methods of market-oriented operation, attracting investors and businesses to invest and operate after the construction of factory.
4.4TransferringtheindustrialenterprisesfromdowntowntothesuburbsandrationallyutilizingtheprimelocationThe industrial enterprises transfer from downtown to the suburbs, and the industries in the original plant change from secondary industry to tertiary industry[8]. With economic development and the accelerated pace of urbanization, the areas where many factory sites are located have all become the prime areas for urban development and construction. In this context, the prime location is not suited to the development of industrial land, so the secondary industry retreats from the downtown, and the tertiary industry is introduced, which is not only in line with the needs of economic development, but also consistent with development trends of industry and commerce.
4.5Adoptingthree-dimensionalmodelofdevelopmentandrationallyusingtheurbanspaceThe three-dimensional model of development is to combine the development over the city, development on the surface and development under ground for unified planning and utilization of urban space, in order to maximize the capacity of the environment and improve environmental quality in limited urban space. The development and utilization of space over the city is generally restricted by economic and technical conditions, and the development of urban functions is limited to housing and office, coupled with some tourism space. The most common form is the development and utilization of high-rise buildings, which reduces the area of land occupied and increases the efficiency of land use. Underground space development is generally based on transportation facilities and shopping malls.
4.6ReclaimingtheabandonedlandforindustryandminingandpromotinglandresourcesrecyclingThe abandoned land types for industry and mining in Ma’anshan City include tailing ponds, quarries, dressing works, and abandoned kilns. Dangtu County has the largest distribution area, followed by Yushan District, Hanshan County, Hexian County, and Huashan District. The scale of abandoned land for industry and mining is large in Dangtu County, mainly in western and southern parts of Dangtu, with a total area of 525.6 ha; the scale of abandoned land for industry and mining is also large in Hexian County, with small single plots, and the abandoned land is scattered in the central and northern part of Hexian County, with a total area of 161.99 ha; the scale is large and the abandoned land is scattered in Hanshan County, and the main type of land for mining and industry is abandoned kiln, with a total area of 292.36 ha; Yushan District now has 353.17 ha of abandoned land for industry and mining; the scale is small in Huashan District, with a total area of 59.49 ha. On the one hand, the reclamation of abandoned land for industry and mining helps to save construction land and increase effective use area of construction land, to some extent alleviating the contradiction between supply and demand of land for construction; on the other hand, the reclamation will turn the abandoned land for industry and mining with zero benefit into arable land, which improves the intensive use and output efficiency of land, promotes the recycling of land resources, and improves ecological environment in the reclamation area and the surrounding areas.
4.7StrengtheninglandconsolidationandimprovingsharedresponsibilitymechanismforillegallanduseIn recent years, Ma’anshan Land and Resources Bureau highlights land consolidation and land supply, and improves the project land approval mechanism and shared responsibility mechanism for illegal land use. It improves the law enforcement supervision mechanism of land and resources, gives play to the forefront role of townships, towns and villages, strictly implements dynamic inspection responsibility, and improves city-county-town-village inspection supervision network system; strengthens cadre team building, strictly implements honest and clean government accountability system, establishes administrative power early warning mechanism, further implements special control over some outstanding issues in construction, and strictly supervises violations of construction land development and utilization and use of major project funds; strictly implements project tracking and management and construction land development and utilization reporting system, and prevents idle land and waste to ensure economical and intensive land use.
5 Recommendations
5.1MakingaplantoguidetheworkofintensivelyusinglandandtappinglandpotentialLand is non-renewable resource, and if it is misused and destroyed, it will be difficult to be restored or it will take a long time to recover its value, so in the development and utilization of land resources, we must follow the principle of seeking truth from facts, strengthen overall planning and rational use, consider the relationship between social needs and sustainable development, and make a good long-term land use plan.
5.2EstablishingsustainablelandusemechanismIt is necessary to constantly increase municipal financial expenditure on urban infrastructure building purposefully, and increase environmental protection and environmental governance efforts, to create a favorable external environment for the economic development of the city. We can take part of land use right transfer fees as special funds for the city construction to make up for the current deficiencies. Through government’s guidance and support, it is necessary to attract funds from foreign companies, private enterprises and local enterprises, to jointly strengthen urban construction.
5.3EstablishingevaluationmechanismforeconomicalandintensivelanduseIrrational structure of urban land, a hidden factor that hampers the economical and intensive land use in the city, is often easily overlooked. The measuring standards should not be solely based on GDP and yield. There is a need to shift from the pursuit of maximal use efficiency of single plot to the pursuit of optimal overall urban structure and function. When Ma’anshan City continues to promote land replacement, it is necessary to improve the plot ratio in the central city, make unified plan and rational layout based on functional zoning, and improve the supporting environment facilities.
5.4Improvingmarket-basedlandallocationMarket mechanism is the inherent power for economical and intensive land use, and to make the land market play a good role, we must not blindly introduce or retain those large companies with overcapacity, and must not randomly adjust the land plans. The municipal government should reduce administrative intervention in industrial development, respect the law of industrial development, respect the choice made by enterprises in the market, supply land to enterprises according to the laws, scientifically guide enterprises’ land use, and use marketization to truly reflect the actual price of land factor.
[1] WANG WM, HAN TK. Land utilization planning[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2002. (in Chinese).
[2] Maanshan Statistics Bureau. Maanshan statistical yearbook, 2014[M].Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2014. (in Chinese).
 Asian Agricultural Research2016年5期
Asian Agricultural Research2016年5期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Is It Worthwhile for Farmers to Grow Grain?—A Study of Farmers’ Behavior of Growing Grain
- Establishment of Chinese Agricultural Brand Value Scale and Study of Its Reliability and Validity Based on Customer Value
- How to Develop Chinese Rural Tourism in the Context of New Urbanization?
- Chinese Customers’ WTP for Legal Digital Music Downloading
- High Standard Capital Farmland Construction Based on Grain Security
- Research on the Brand Construction of Agritourism Enterprise in Chongqing
